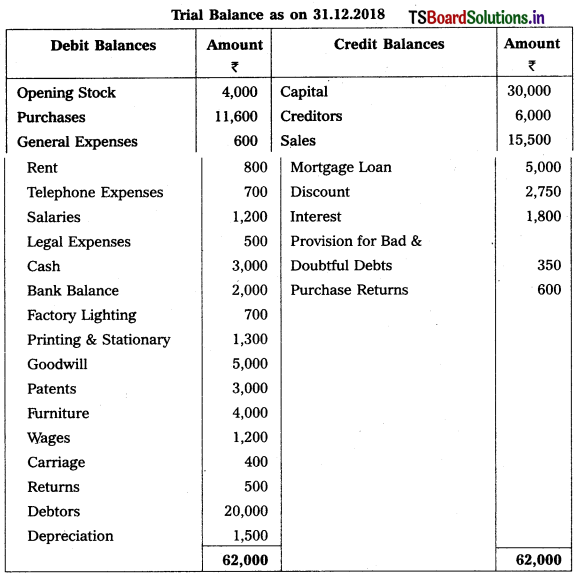
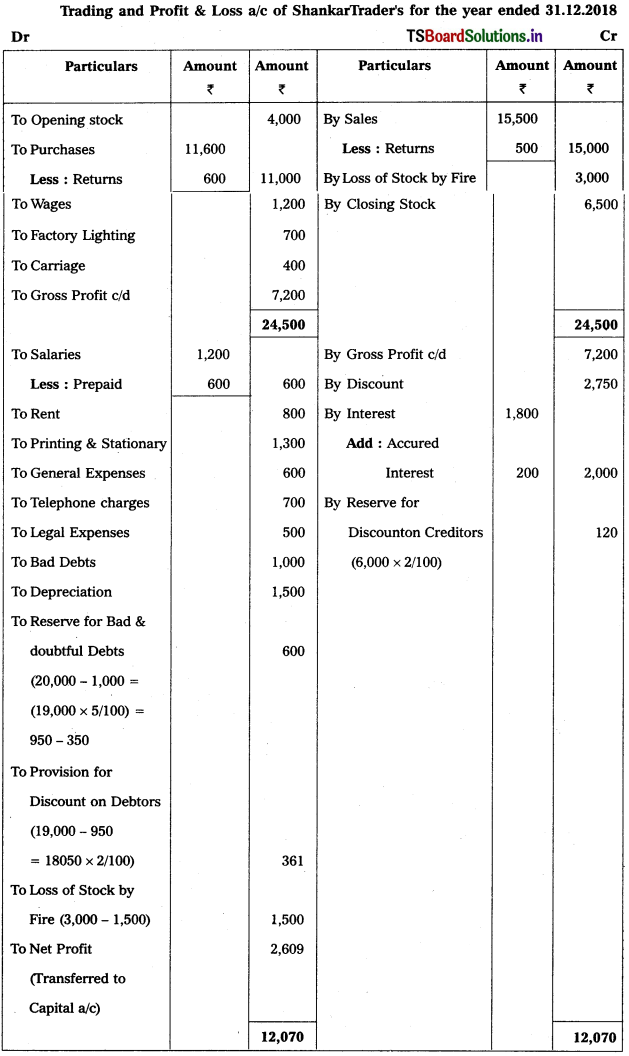
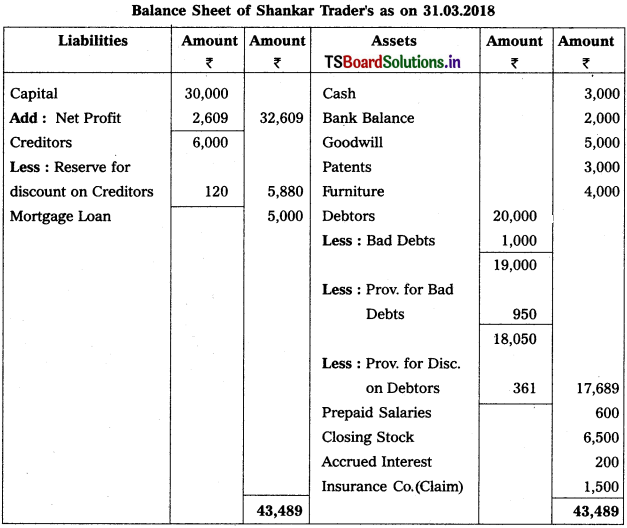
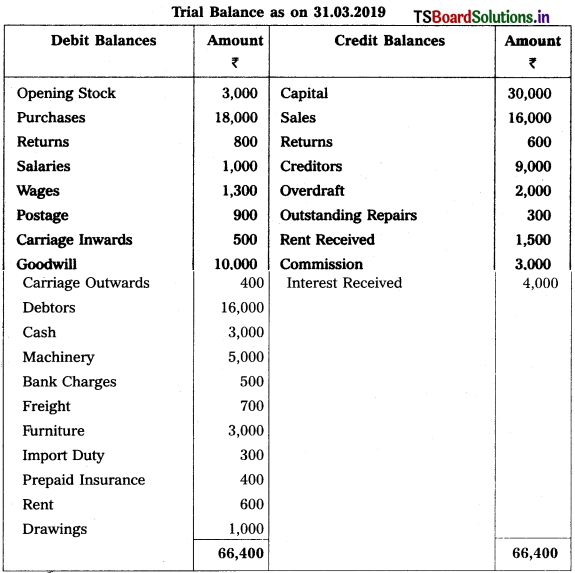
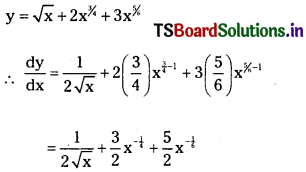
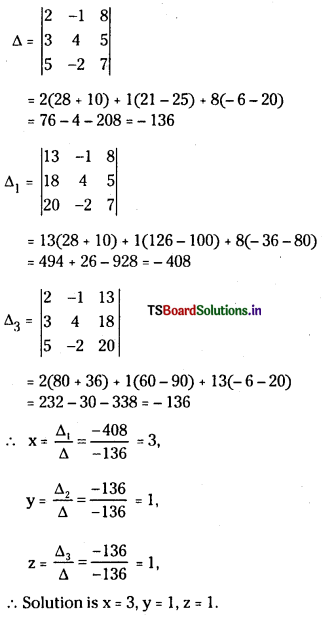
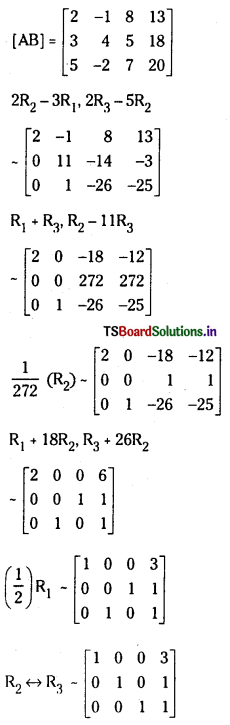
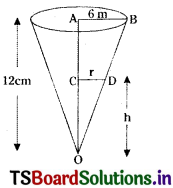
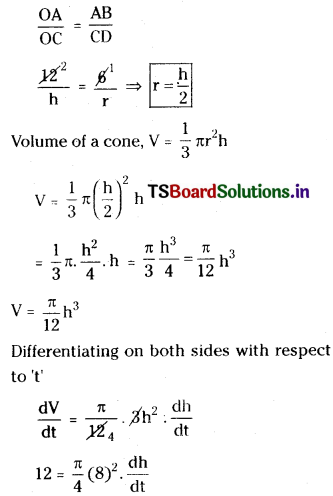
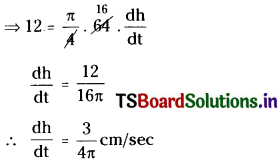
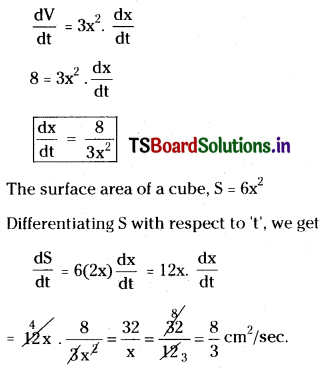
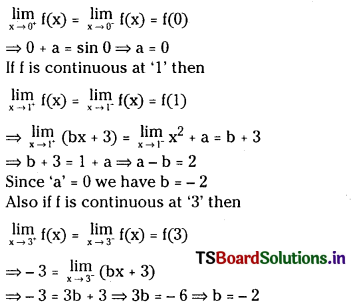
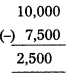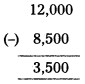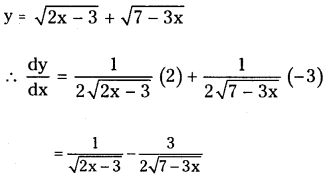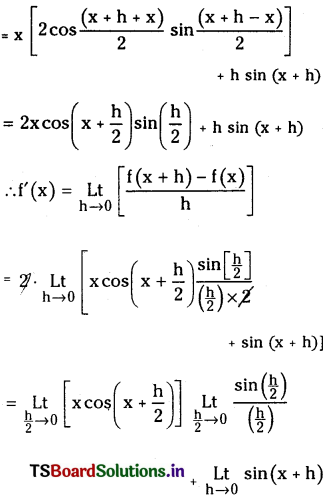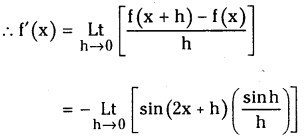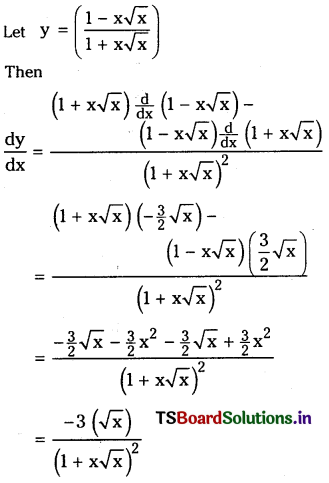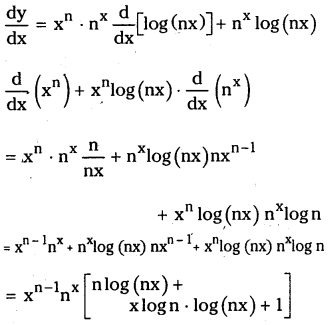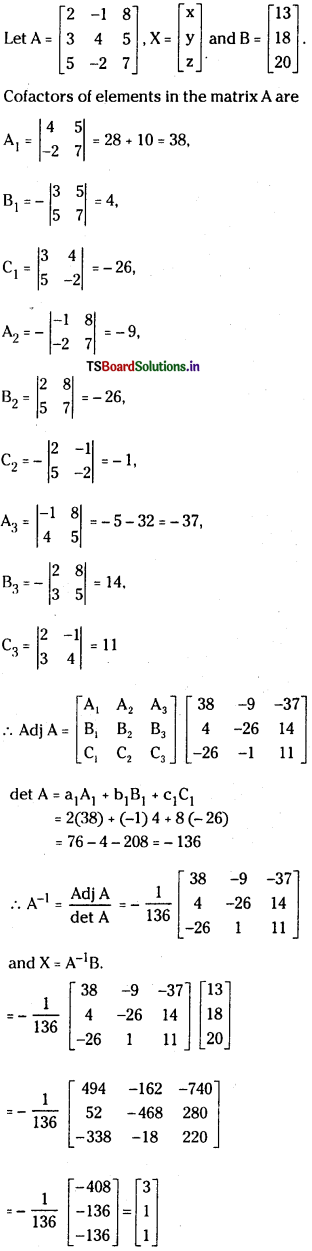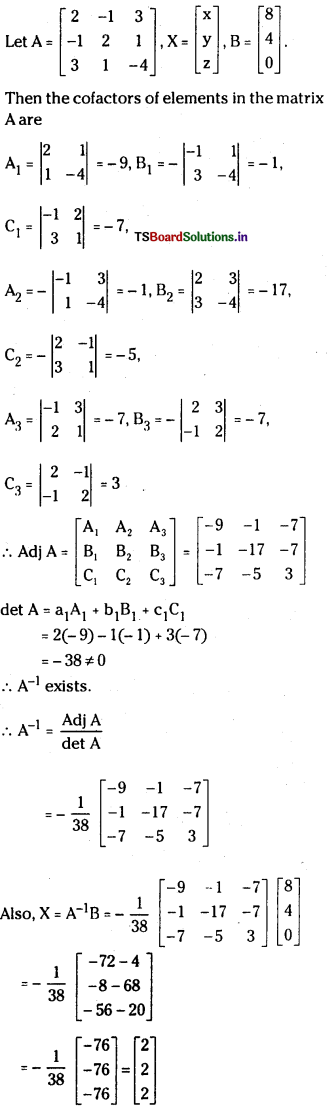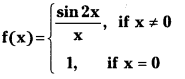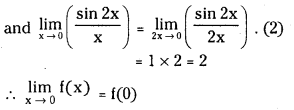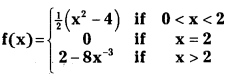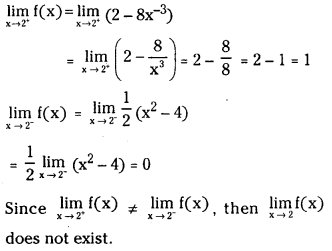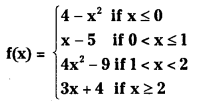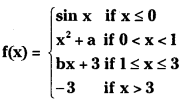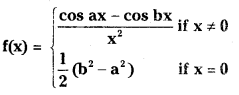Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 9th Lesson Final Accounts of Sole Trading Concerns Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 9th Lesson Final Accounts of Sole Trading Concerns
Essay Questions:
Question 1.
Define final accounts and explain various stages in their preparation.
Answer:
Final Accounts :
- To know the business results and financial position at the end of the period, the business prepares various statement which are called as “Final Accounts”.
- These final accounts of a sole trader are prepared based on the nature of the business establishments.
- If the business organization is trading concern it has to prepare Trading Account, profit & loss account and Balance sheet, if the concern is manufacturing entities they prepare manufacturing account, trading account, profit and loss account and Balance sheet.
Various stages in Financial Accounts :
1. Trading account:
- Preparation of Trading Account is the first stage in final accounts. It is prepared to find the “Gross Profit” or “Gross Loss”, which is transferred to profit and loss account.
- Trading account is a “nominal account” in nature. All the trading expenses should be debited and trading incomes should be credited to this trading account.
2. Profit & Loss account:
- The second stage of the preparation of final account is the preparation of profit & loss account. Profit & loss account is prepared to find out the Net Profit or Net Loss of the business. This is a nominal account.
- The balance of profit and loss account is transfered to capital account in Balance sheet.
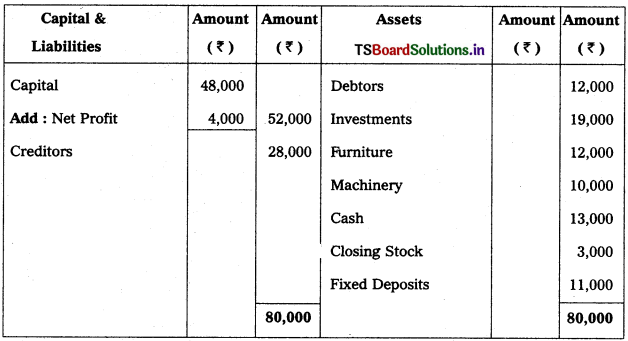
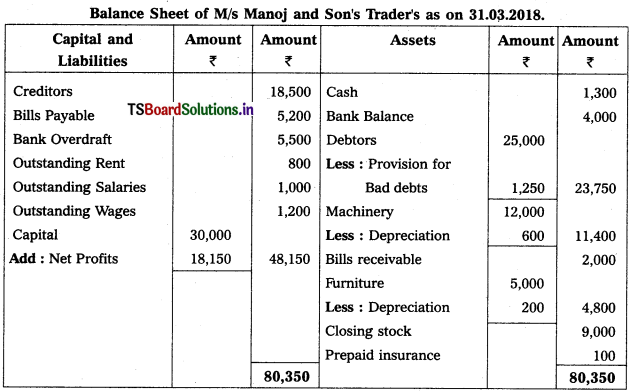
3. Balance Sheet:
Balance sheet is the statement prepared to find out financial position i.e., assets and liabilities of a concern on a given date. In preparing Balance Sheet, liabilities and capital are shown on the left hand side and the assets are shown on the right hand side.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe various types of expenses and incomes with suitable examples.
Answer:
In the preparation of final accounts, clear distinction is made between capital and revenue items. The allocation of expenditure and incomes between capital and revenue plays a vital role in the preparation of correct and true financial statements of the business concerns.
Business expenditure of a concern can be broadly classified into :
- Capital expenditure,
- Revenue expenditure,
- Deferred revenue expenditure.
1. Capital Expenditure :
Capital expenditure is the expenditure which is normally incurred for acquiring fixed assets which increases the earning capacity of the business. Benefits of capital expenditure extends over number of years. Examples of capital expenditure are purchase of fixed assets like plant, building, installation of machinery and their improvement. These are shown as assets in Balance Sheet.
2. Revenue Expenditure :
Revenue expenditure is the expenditure which is incurred in normal course of the business activities. The benefit of revenue expenditure is limited to only one accounting year. Examples of revenue expenditure are payment of salaries, rent, carriage, advertisement etc. These are debited to profit and loss account.
3. Deferred Revenue Expenditure :
Any amount of revenue expenditure spent in huge sums and its benefits spread over more than one year is called deferred revenue expen-diture. It includes the expenses like preliminary expenses, discount on issue of shares and debentures, heavy amount spent of advertisement, shifting of business premises etc.
Incomes are divided into capital receipts and revenue receipts :
1. Capital Receipts / Capital Income :
Amount received as investment by the owners, raised by way of loans and sale proceeds of fixed assets is called capital receipts (or) capital income. Ex. Capital, sale of machinery. All the capital receipts are recorded as liability in the Balance Sheet.
2. Revenue Receipts / Revenue Income :
Amount received in the normal course of business is called revenue receipts and includes sale of goods, interest, discount, commission etc. These incomes are credited to profit and loss a/c.
3. Deferred Income :
This consists of income which spreads over several years is called deferred income. Ex. Rent or interest received for more than one year.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the differences between trading account and profit & loss account.
Solution:
| Basis | Trading account | Profit & Loss account |
| 1. Meaning & object | Trading account is prepared to findout the Gross profit / Gross loss of the business. | Profit & loss account is prepared to find out the Net profit / Net loss of the business. |
| 2. Timing | Trading account is prepared before the profit and loss a/c. | Profit & loss account is prepared after the trading account. |
| 3. Accounts | In the trading account, the direct expenses and direct incomes are posted. | In profit and loss account, the accounts related to the indirect expenses and indirect incomes are posted. |
| 4. Trasfer of Balance | The balance of trading account is transferred to profit & loss a/c. | The balance of profit & loss account is transferred to capital account in balance sheet. |
| 5. Stage | Trading account is the first stage of the final accounts. | Profit & loss account is the second stage of the final accounts. |
Question 4.
Present the main features, advantages and limitations of final accounts.
Answer:
Features :
- Final accounts consider monetary transactions only.
- Final accounts considers only those transactions which are of historical nature, i.e., the transactions which are already taken place.
- Preparation of final accounts is a legal requirement.
- Final accounts are used by internal and external users for their decision making.
Advantages :
- Business profit or loss can be known to the trader through the trading account and profit and loss account (Income statements).
- Financial position can be revealed by the preparation of Balance Sheet.
- Final accounts are important source of finance information and this help the trader or management to plan the financial activities of the business concern for any period or time.
- Financial statement help the trader to take business decisions by comparing current year results with the results of the previous year statements.
- As the profit & loss account discloses either profit or loss, based on which a trader prepares himself to pay the taxes correctly.
- Tax authorities also needs financial statements to determine the account of tax exactly.
- As financial statements reveals the solvency position of the organization, the banks and other lending organizations may con v r for extending the loan facility.
Limitations :
- Do not reflect the current prices as they are based on the historical costs. *
- Do not consider qualitative data, such as, qualLy, efficiency of workforce, employee and employer relationship, motivation level of employees, value of human resources etc.
- Do not reveal the accurate picture of the business, as certain values of assets and some expenses and income items are based on the judgement of the management, who may have prejudice.
![]()
Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Give the objectives of final accounts.
Answer:
The main objectives of preparation of final accounts are :
- To ascertain the profit or loss of the business for a particular period. (By preparing Trading and Profit & Loss Account.)
- To find out the financial position of the business concern on a specified date or period. (By preparing the Balance Sheet).
Question 2.
Write the features of Trading Account.
Answer:
Features :
- It is the first stage of final accounts.
- Trading account is a Nominal account.
- It helps to find the Gross Profit or Gross Loss.
- It records only the net sales and direct cost of goods sold.
- The balance of trading account is transferred to profit and loss account.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the meaning and main characteristics of profit & loss account
Answer:
After preparing the trading account, profit and loss account is prepared to find out the net profit or net loss of the business. This is also a nominal account. So, all the expenses and losses should be debited and all the incomes and gains to be credited to profit and loss account.
The balance of profit and loss account is either net profit or net loss and the same is added or deducted from the capital account in the balance sheet.
Characteristics of Profit and Loss Account :
- Profit & Loss account is a Nominal account.
- It is prepared at end of the financial year.
- It records all current year indirect expenses and incomes.
- It reveals net profit or net loss.
- Net profit ratio can be calculated.
- Current year administration expenses and other expenses can be compared with the previous years expenses.
- It facilitates for the preparation of Balance Sheet.
Question 4.
Briefly explain various types of assets.
Answer:
Assets :
Property of any description belonging to a person or business organization can be named as an asset. Assets are the ‘ownings’ of a business and they may be classified as follows :
1. Fixed Assets :
The assets permanent in nature and not intended for the re-sale, but are used to carry the business continuously are called fixed assets. They earn profit or gain to the business.
Ex : Land and buildings, machinery, furniture etc. These assets are recorded in the balance sheet after deducting depreciation if any.
Fixed Assets can be further classified as :
a) Tangible Assets – which can be seen and touched, e.g., Furniture, Machinery etc.
b) Intangible assets – which can neither be seen nor touched, e.g., Patents, Goodwill etc.
2. Current Assets :
These assets are held for resale or can be converted into cash on a later date. These are also known as floating or circulating assets. Cash, Stock, Debtors, Bank balance etc., are the examples of these assets.
![]()
Question 5.
Define Manufacturing Account and give it contents.
Answer:
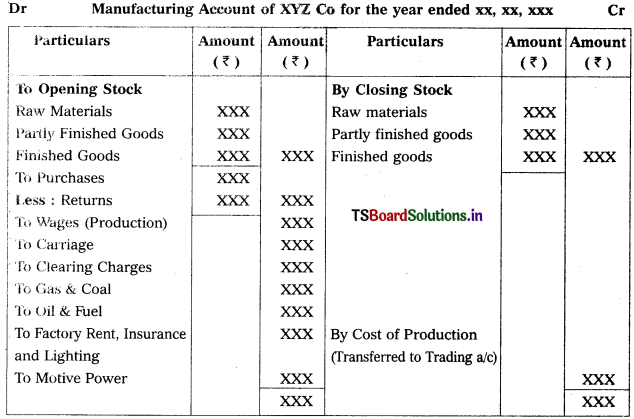
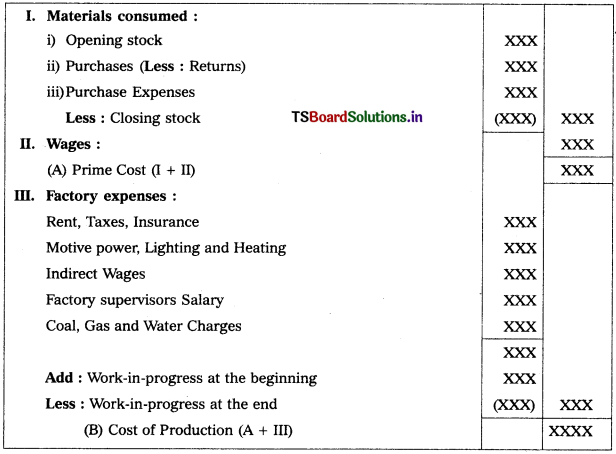
Manufacturing Account:
A trader or a business concern who undertakes the job of manufacturing or production of goods will prepare this account.
As trading account it is also a nominal account. Hence, all the expenses incurred on goods and factory will be considered and rec orded at debit side of it and in progress and sale of scrap etc., are recorded at creuit side and the difference debit and credit will be termed as ‘Cost of Production’, wnieh will be transferred to the debit side of the trading account.
This accovnt may be prepared either on horizontal form or on vertical form.
Horizontal form Proforma:
Vertical form Proforma:
Manufacturing Account of XYZ Co., for the year ending XX, XX, XXX
![]()
Very Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Define deferred expenditure.
Answer:
The Deferred Expenditure consists of revenue and capital items. Benefits from these expenses are spread over several years. In other words, the expenses which are incurred in one accounting year but benefits of the same accrue in the future years are called as Deferred Expenses.
Ex : amount of expenditure on advertisement in the initial years, expenditure incurred on research and development, innovation etc.
Question 2.
Define current assets & current liabilities.
Answer:
a. Current Assets:
Current assets are those assets which are for resale or can be converted into in short period, usually within one year. These are also known as floating or circulating assets.
Ex.: Cash in hand, Cash at bank, Sundry debtors, Stock-in-trade etc.
b. Current Liabilities :
These liabilities are payable by the business organisation within one accounting period. These are short term liabilities as they are repayable in not more than 12 months from the date of acquiring them.
Ex.: Bills payable, Sundry creditors, Bank overdraft etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Give examples of intangible assets.
Answer:
Intangible assets are those which cannot be seen and touched.
Ex.: Patents, Goodwill etc.
Question 4.
Write accounting equation.
Answer:
- The relationship of assets with liabilities and owners equity in the equation form is known as “Accounting Equation”.
- Accounting Equation: Assets = Liabilities + Capital
- The complete picture of the balance sheet in manner of accounting equation.
Question 5.
Write a short note on Opening Stock & Closing stock.
Answer:
a) Opening Stock :
The opening stock is the first item to be shown on the debit side of trading account. The closing stock of the preceeding year is the opening stock of the current year.
b) Closing Stock :
It is the unsold stock left with the organization on the last day of the accounting year. The closing stock of the current year becomes the opening stock of the next year.
If the closing stock is given in the adjustments, record it in the trading account on credit side and also in Balance Sheet on assets side.
![]()
Additional Questions:
Question 1.
Capital expenditure.
Answer:
- Capital expenditure is the expenditure which is normally incurred for acquiring fixed assets or assets which increase the earning capacity of the business. Benefits of capital expenditure are extended over a number of years.
- Ex. : Purchase of fixed assets like machinery, building, furniture etc.
Question 2.
Revenue expenditure
Answer:
- Revenue expenditure is the expenditure incurred in the normal course of the business activities. The benefit of revenue expenditure is restricted to only one accounting year.
- Ex: Office expenses such as rent, salaries, selling expenses like carriage outwards, advertisement expenses.
Question 3.
Capital income.
Answer:
- Any amount received as investment by the owners, raised by way of loans and income received on sale of fixed assets is called capital income.
- Ex.: Capital, sale of machinery.
![]()
Problems:
Question 1.
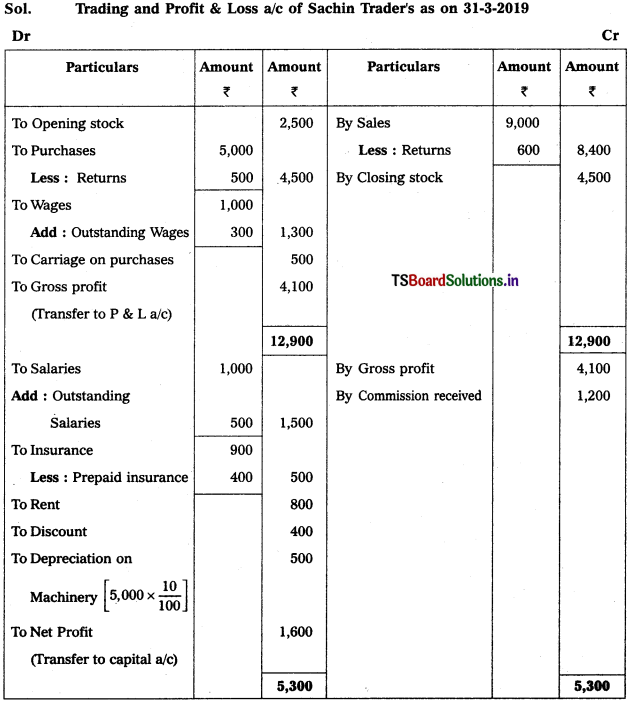
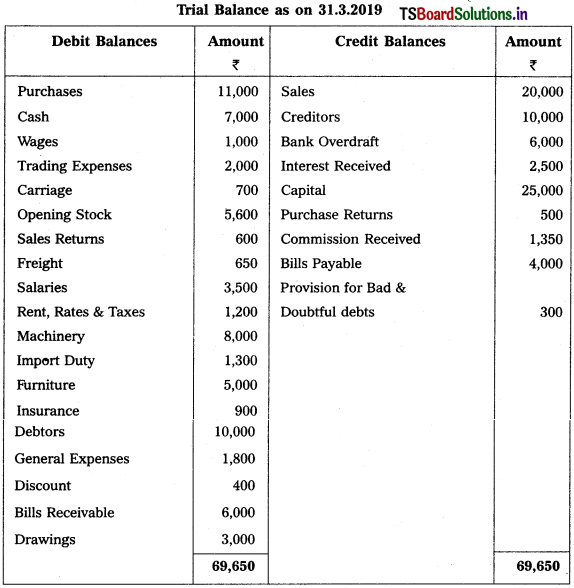
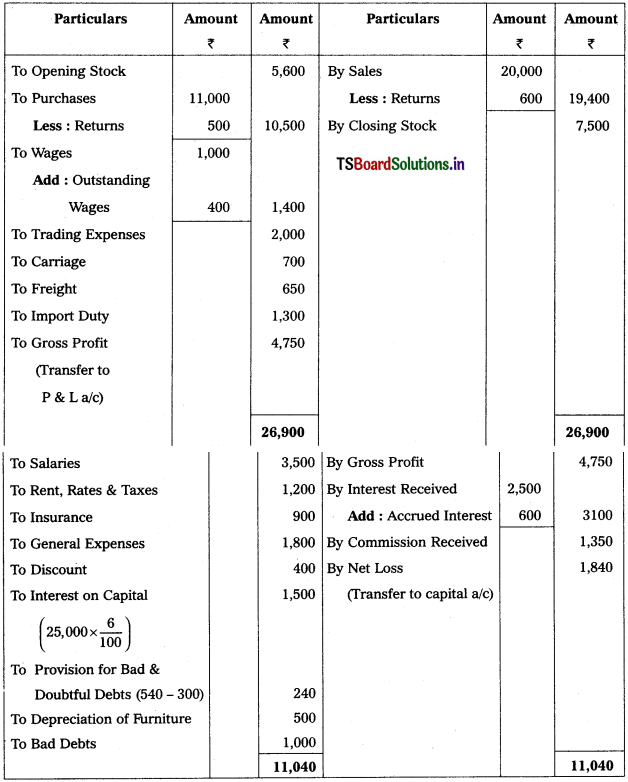
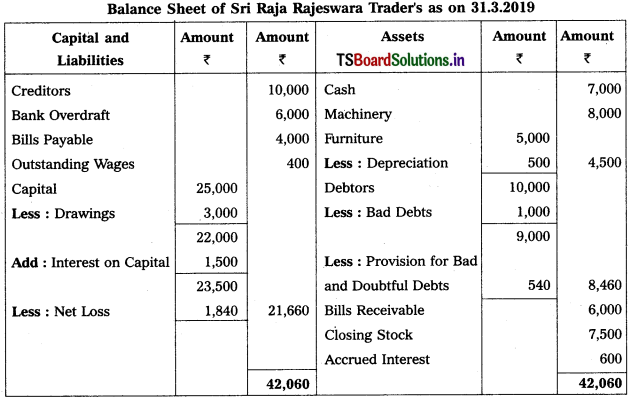
Prepare Trading Account of Srikanth Traders for the year ended 31.12.2015.
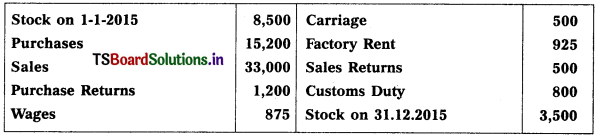
Solution:
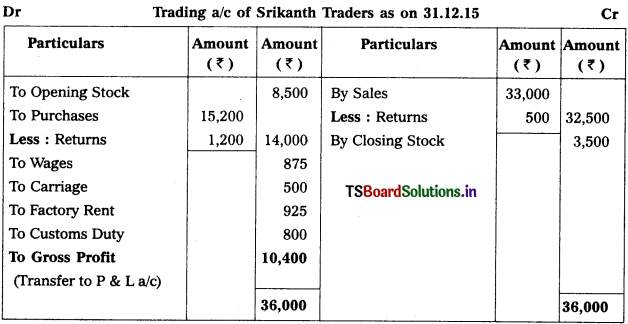
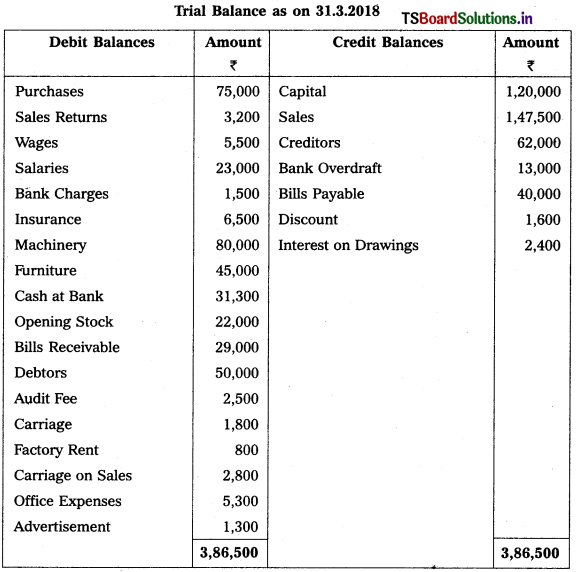
Question 2.
Prepare Trading Account from the following particulars for the year ended 31.03.2017 :
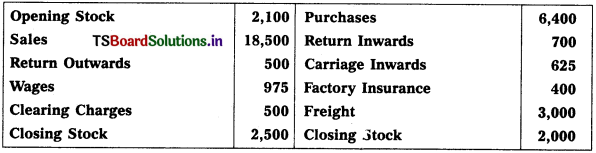
Solution:
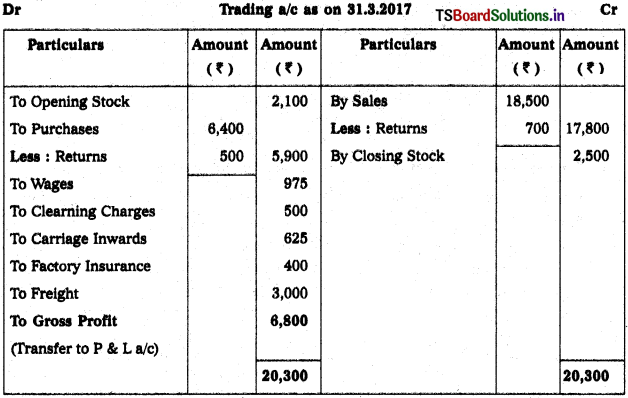
![]()
Question 3.
Prepare Trading Account:
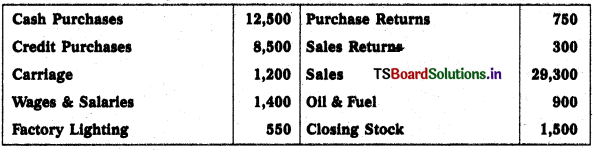
Solution:
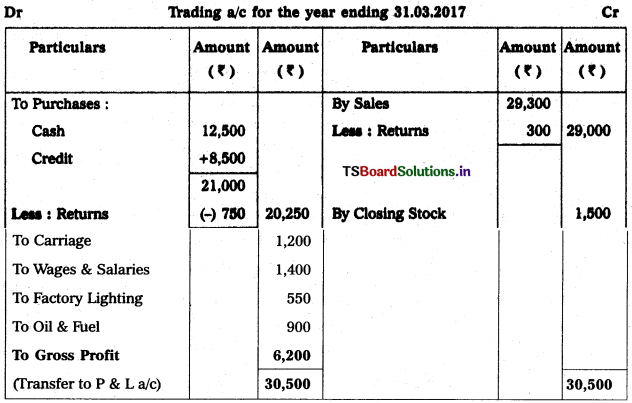
Question 4.
Prepare Trading Account of Hyderabad Traders as on 31,12.2017 :
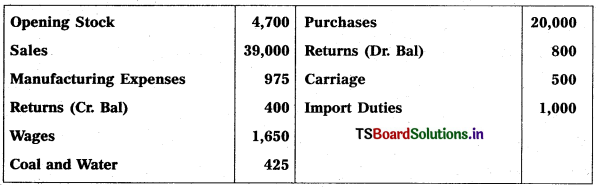
Solution:
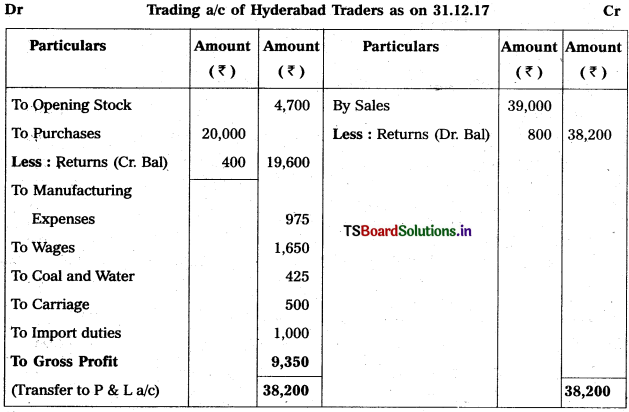
Note :
Manufacturing expenses given twice so, 2nd one is not taken into problem.
![]()
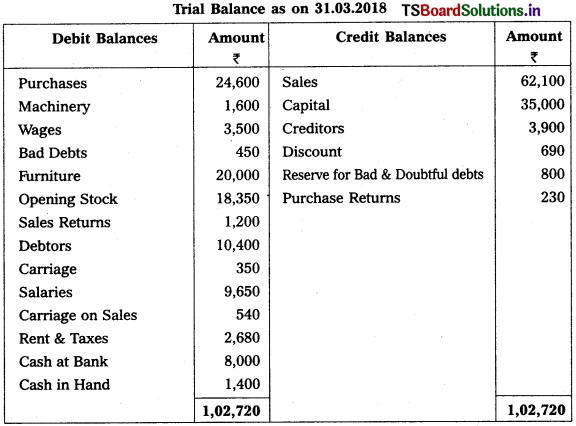
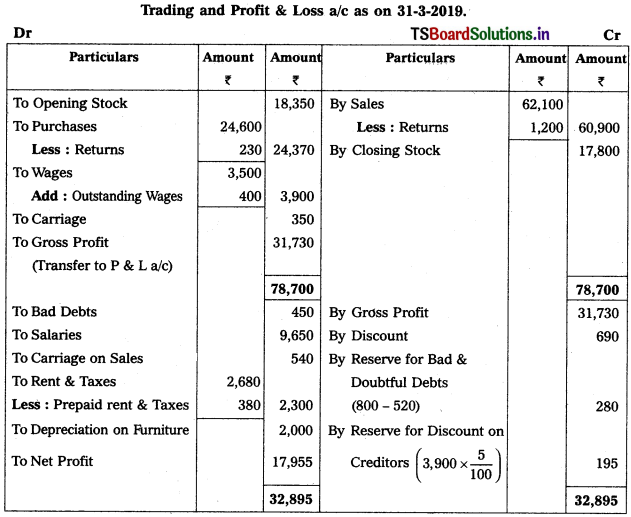
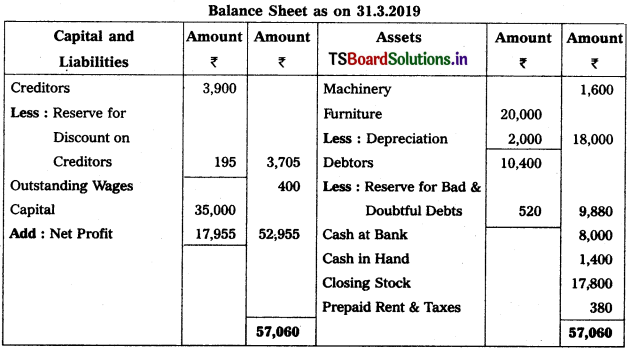
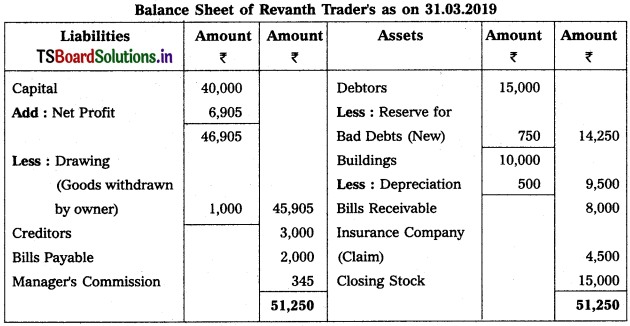
Question 5.
From the following particulars, prepare Profit & Loss a/c as on 31.03.2019 :
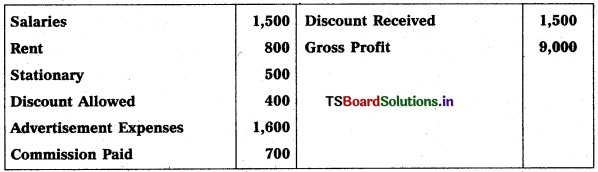
Solution:
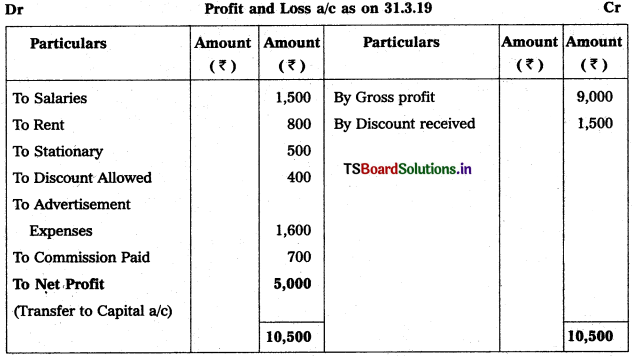
Note :
Stationary is given twice so we take 1st one and ignore 2nd one.
Question 6.
Prepare Profit & Loss a/c from the following particulars :
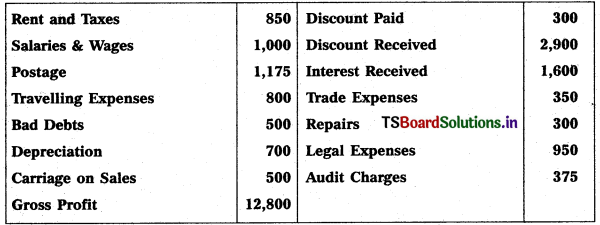
Solution:
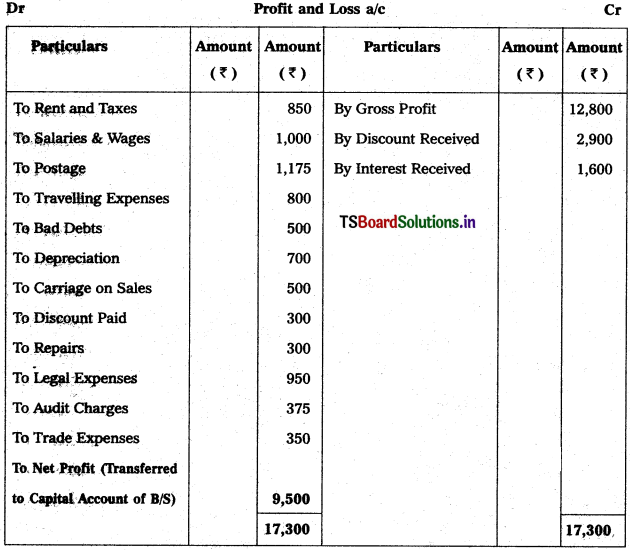
![]()
Question 7.
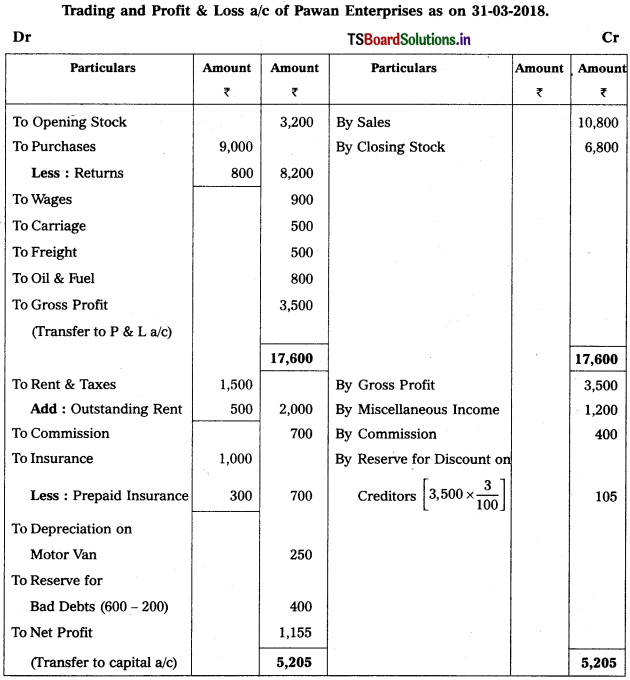
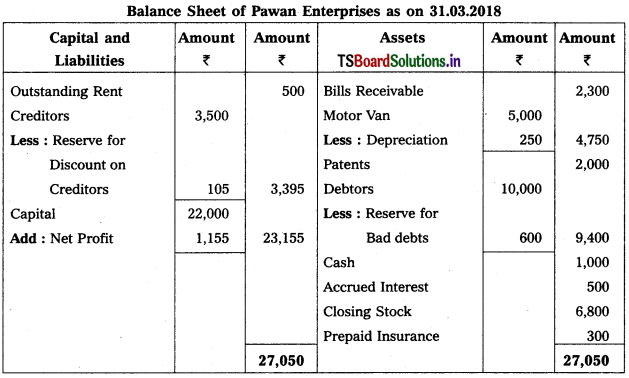
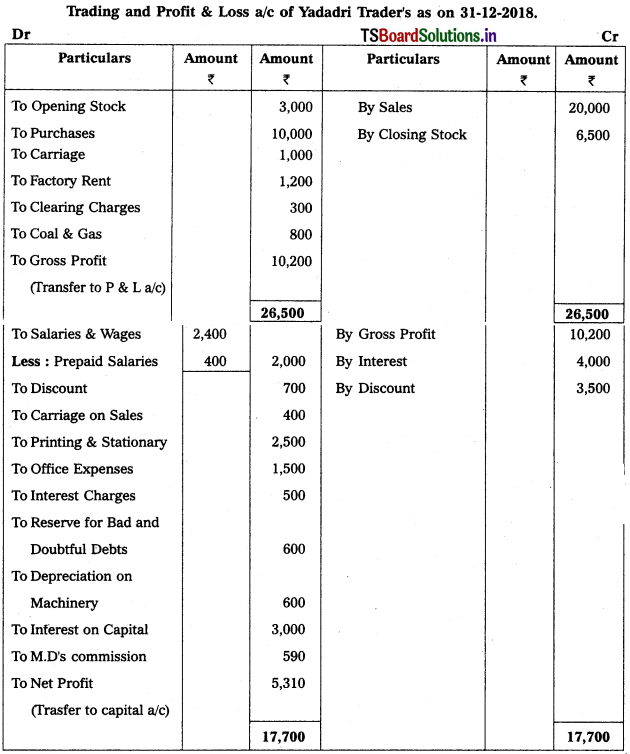
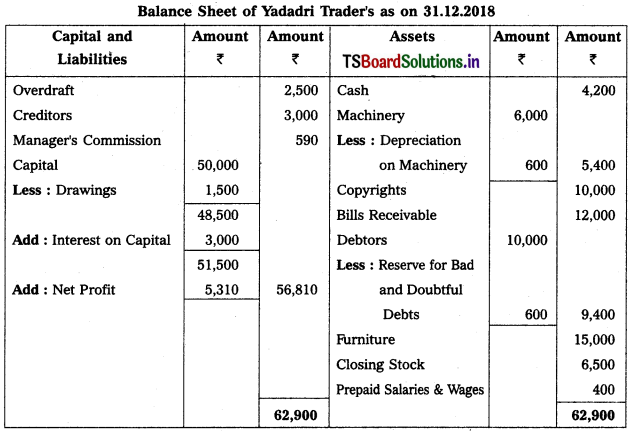
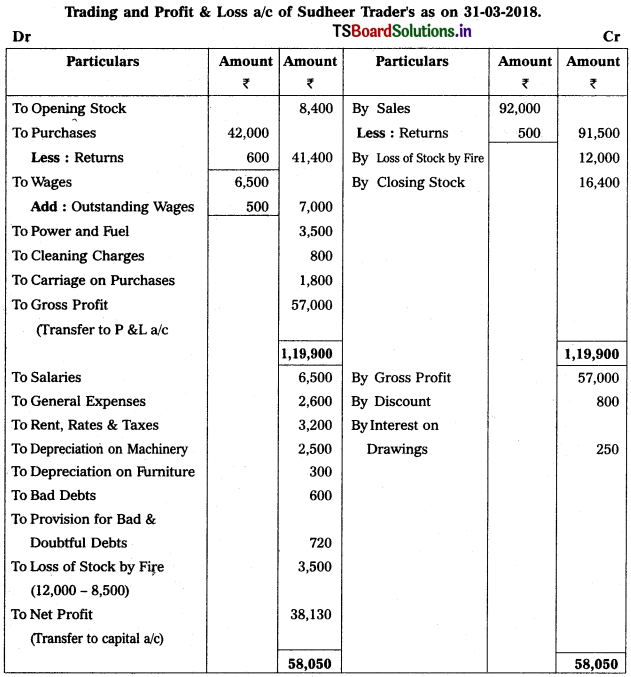
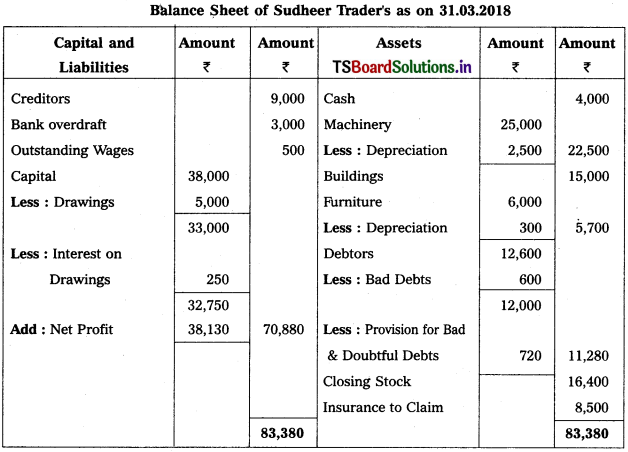
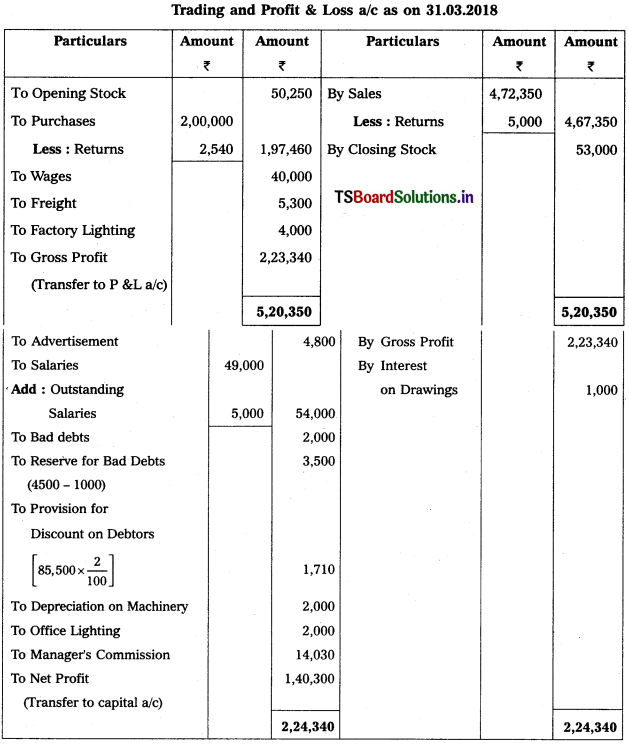
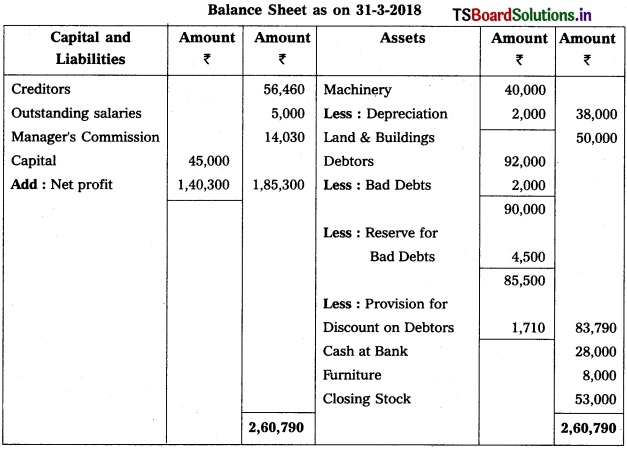
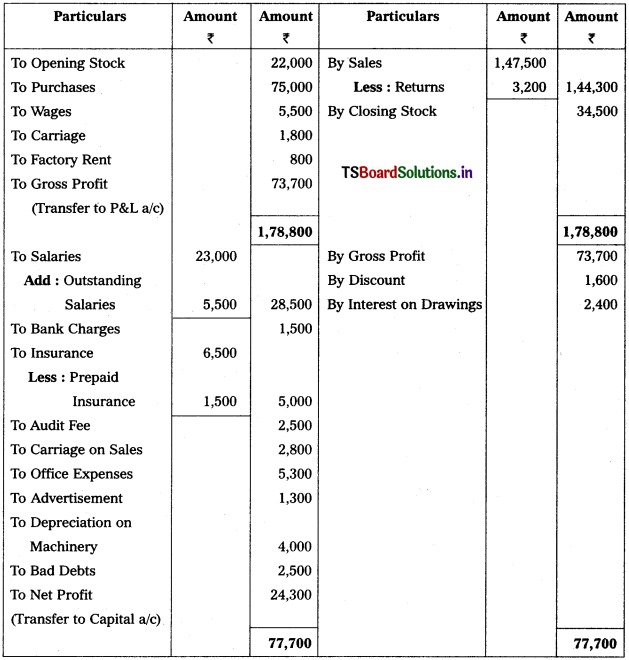
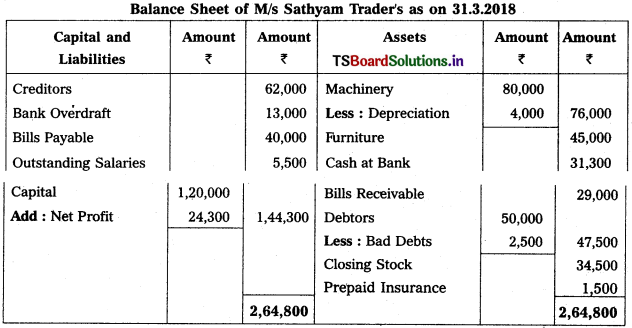
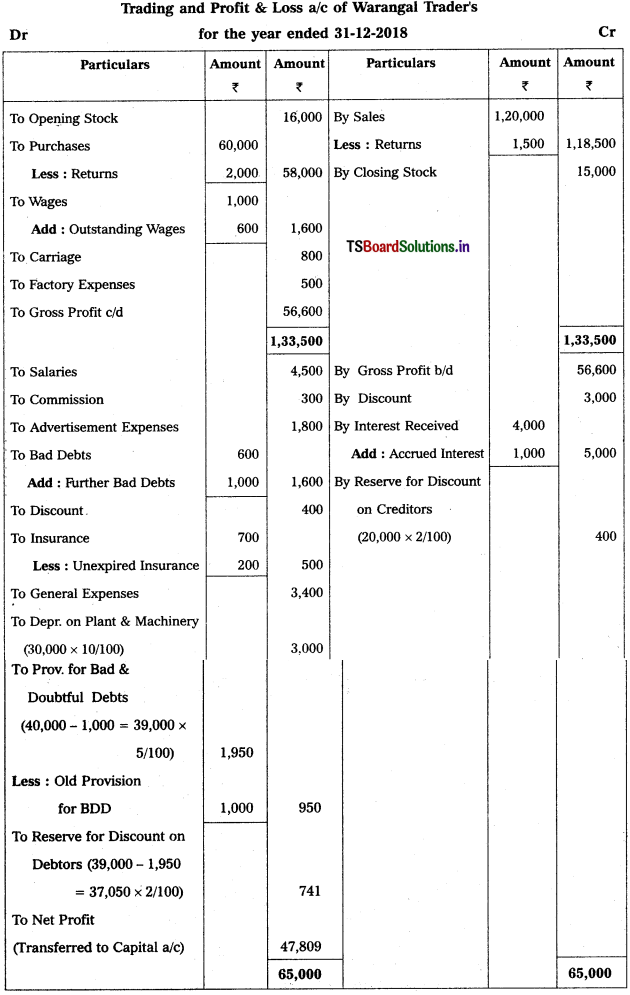
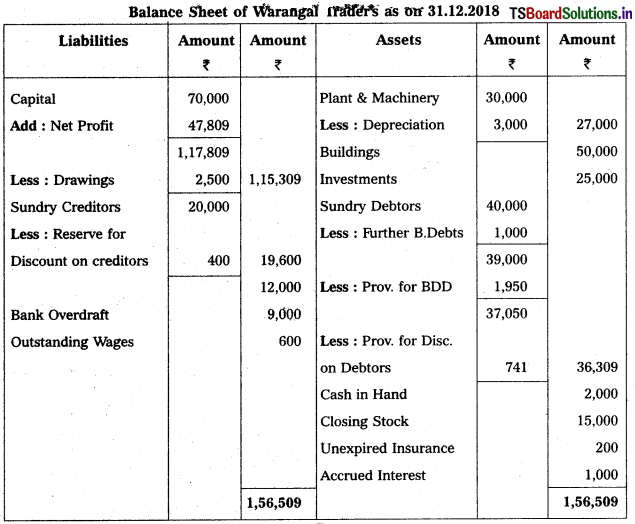
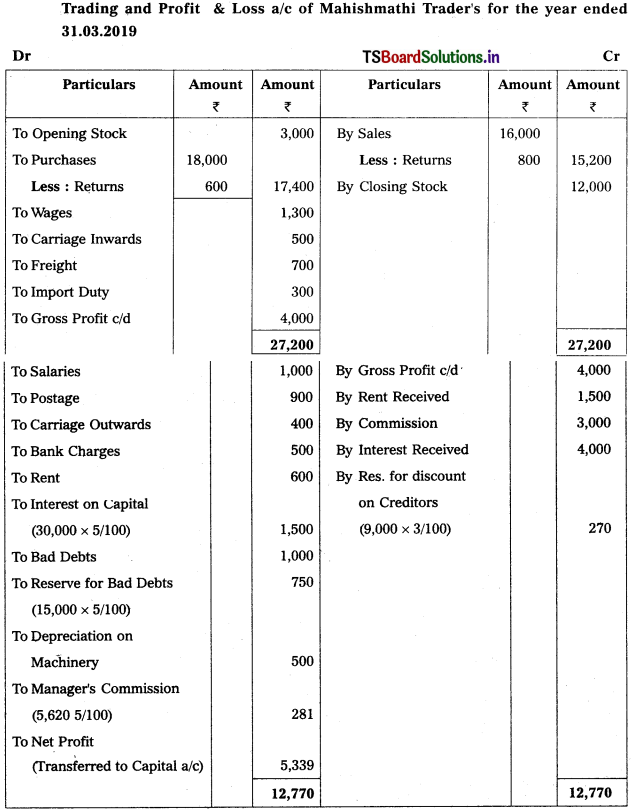
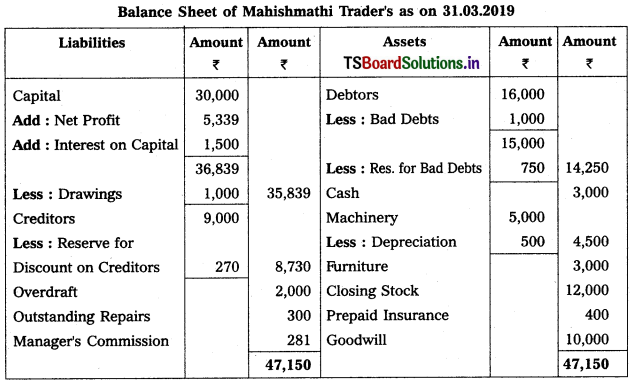
From the following particulars, prepare Trading and Profit & Loss a/c as on 31.12.2018.
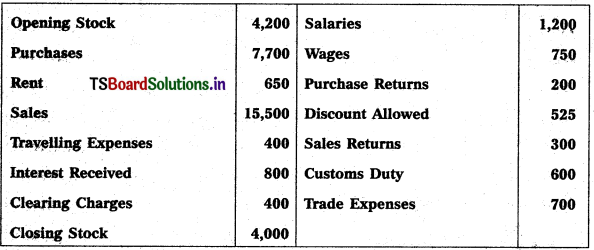
Solution:
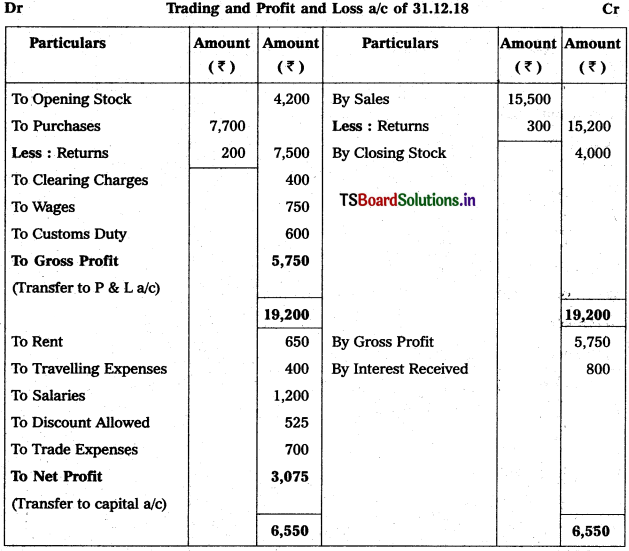
Question 8.
Prepare Trading a/c & Profit & Loss a/c of Suresh Traders for the year ending 31.12.2017.
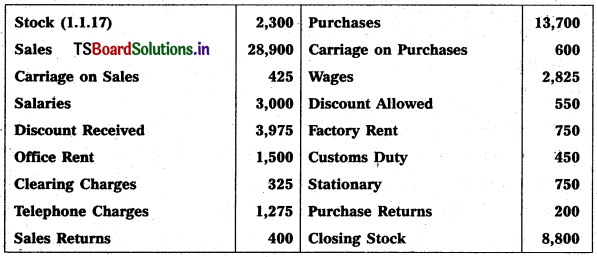
Solution:
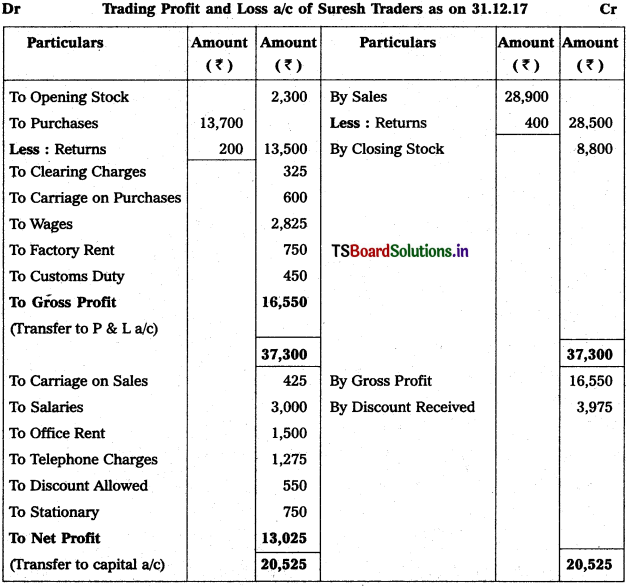
![]()
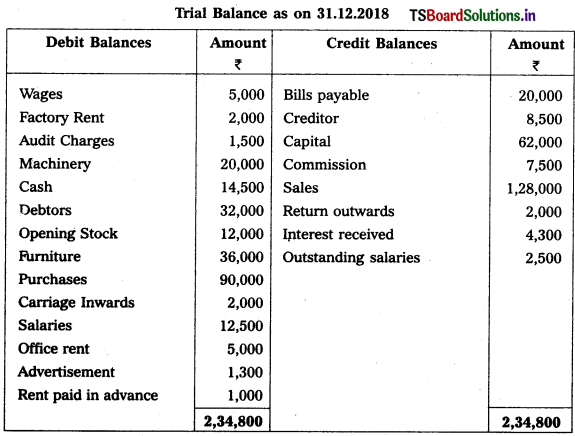
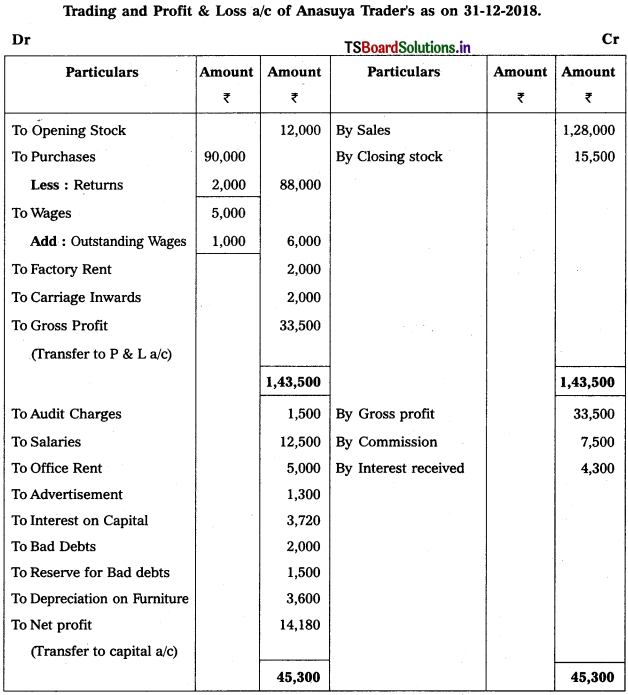
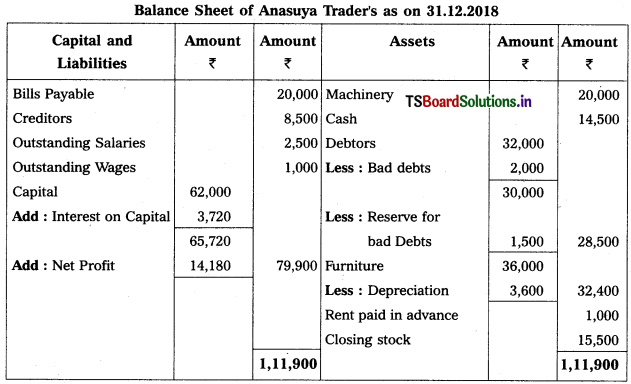
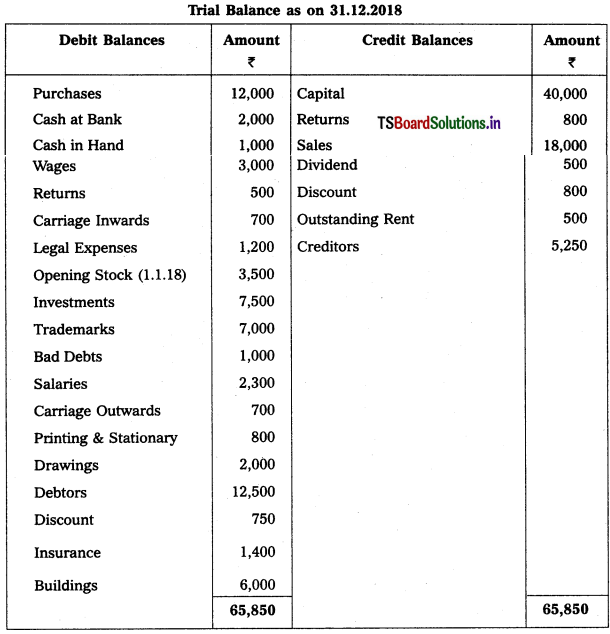
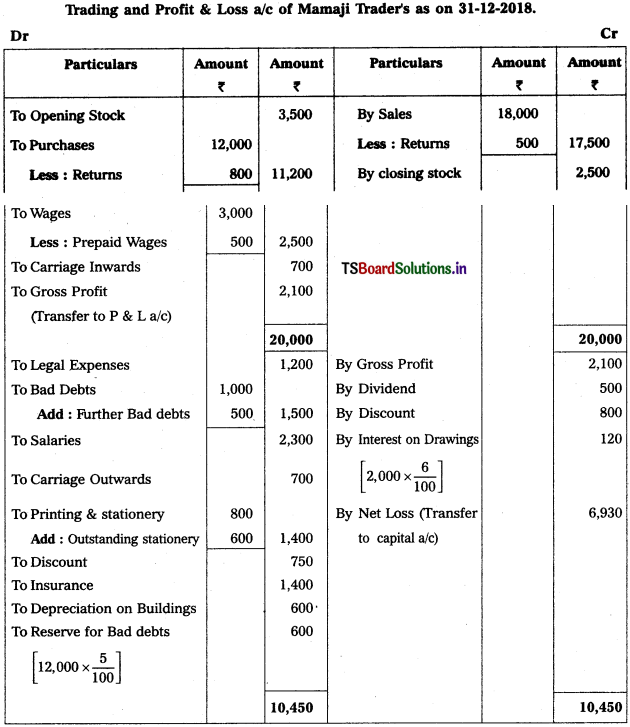
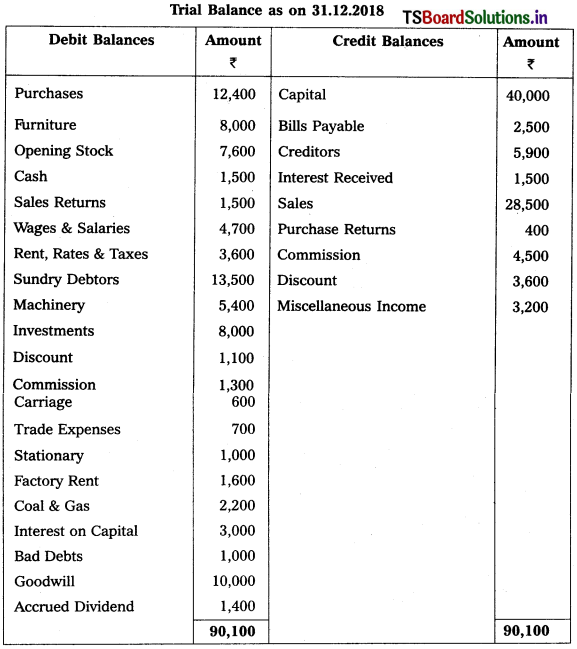
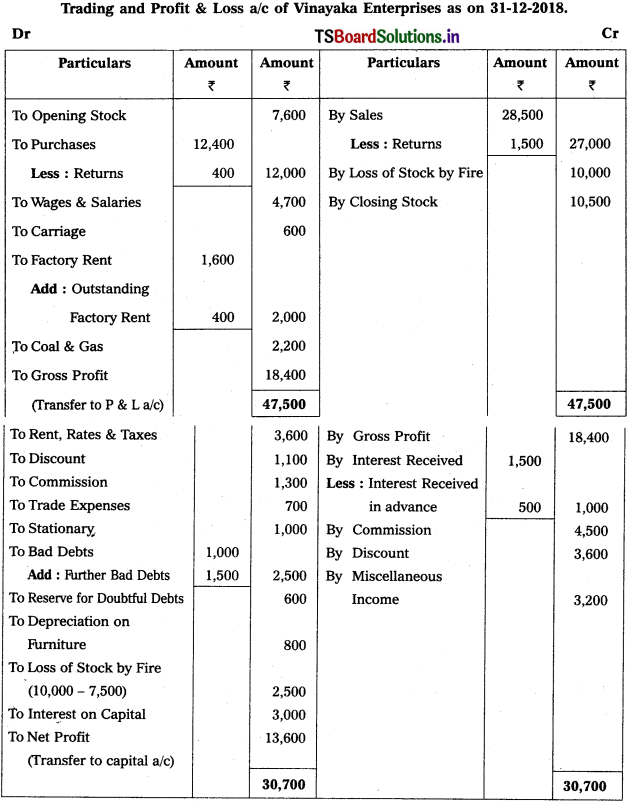
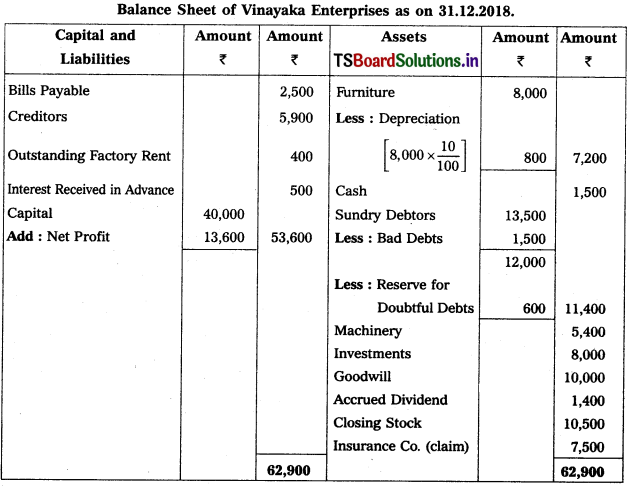
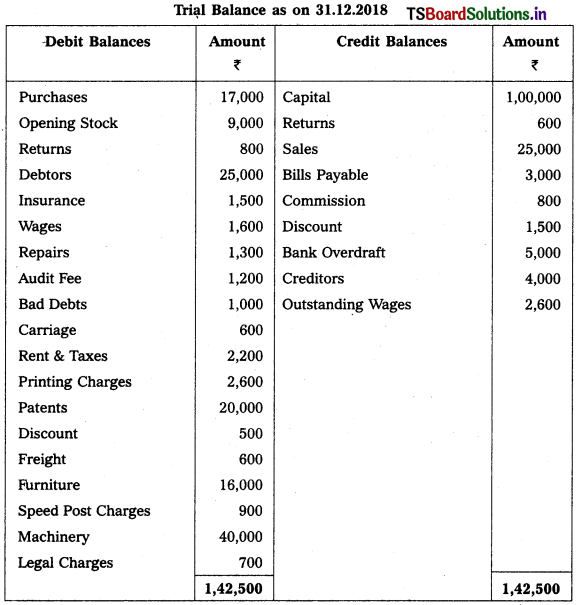
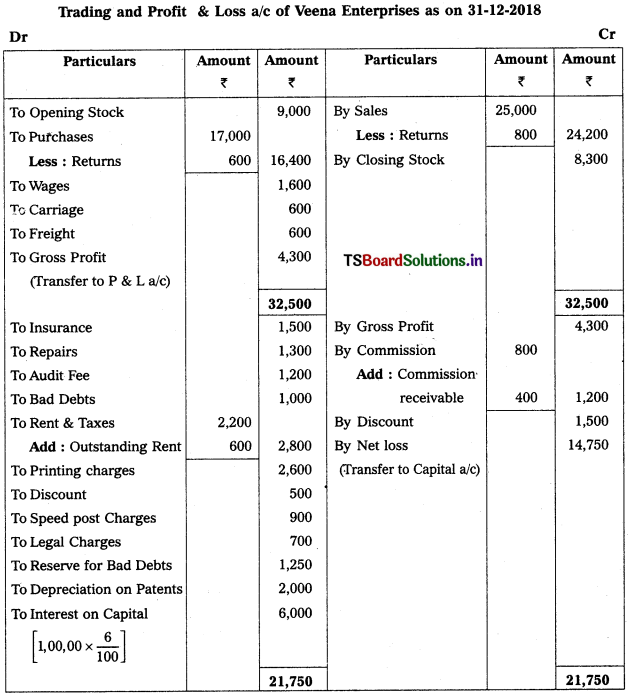
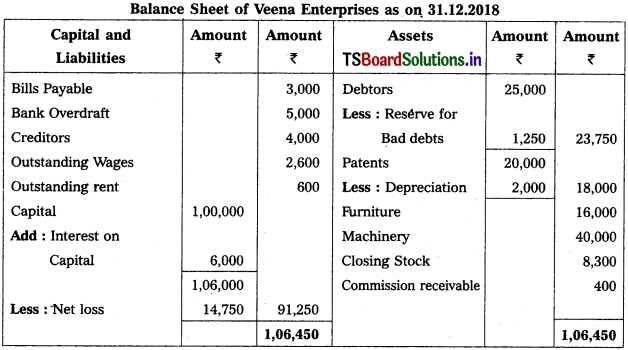
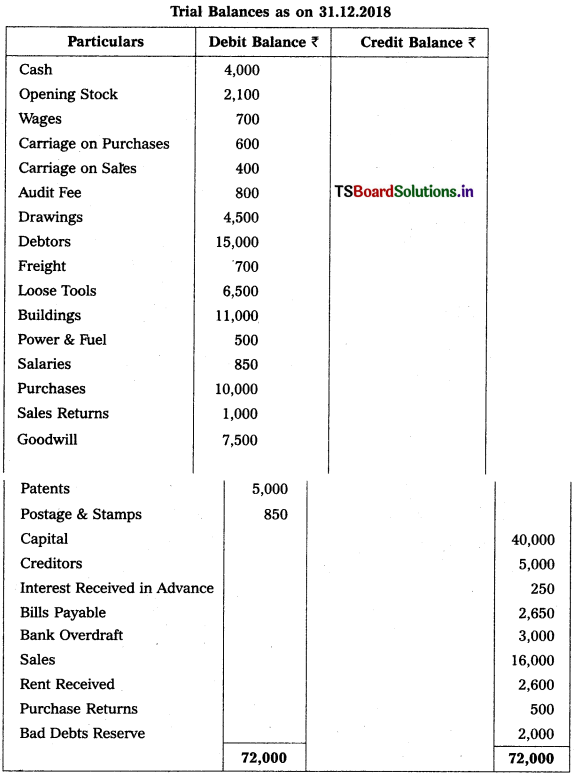
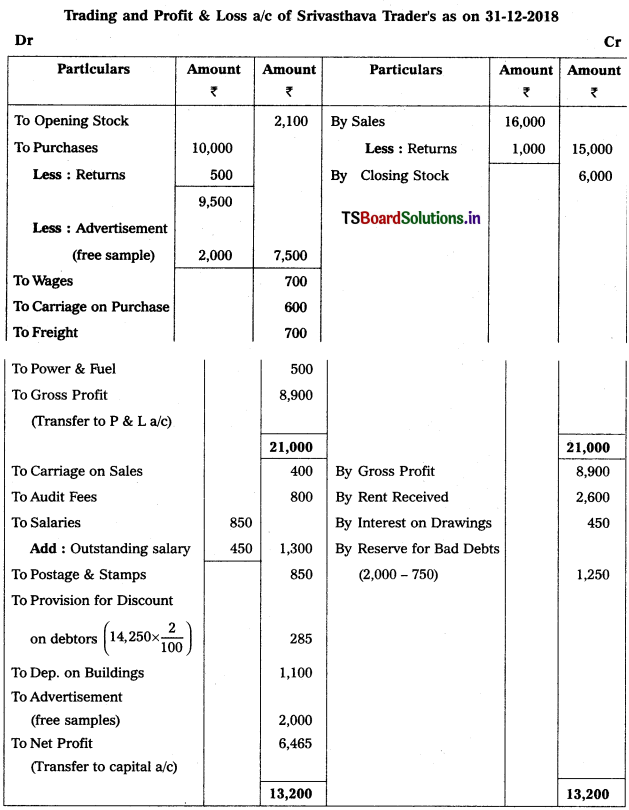
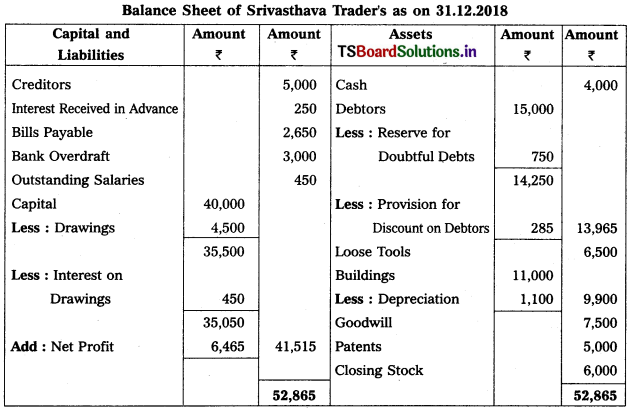
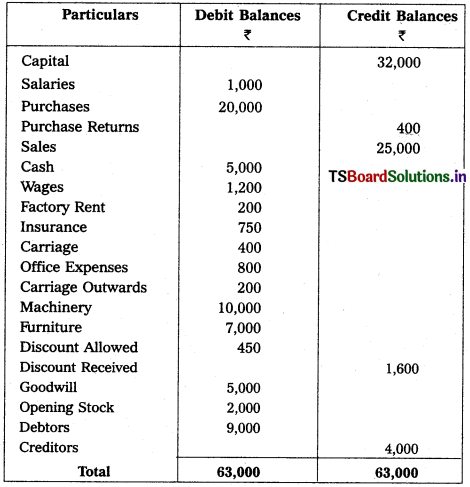
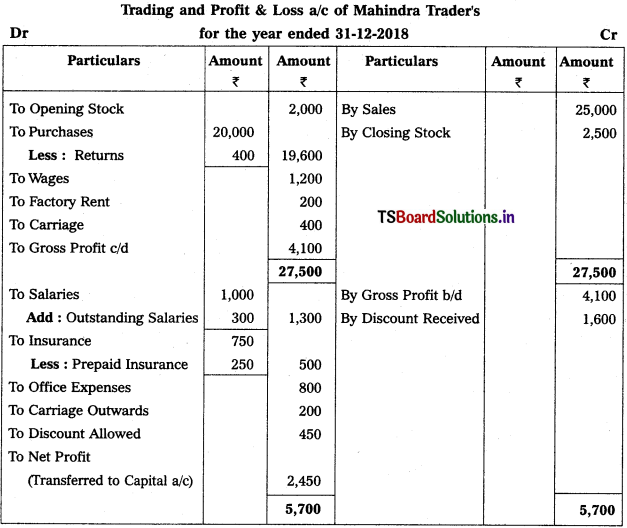
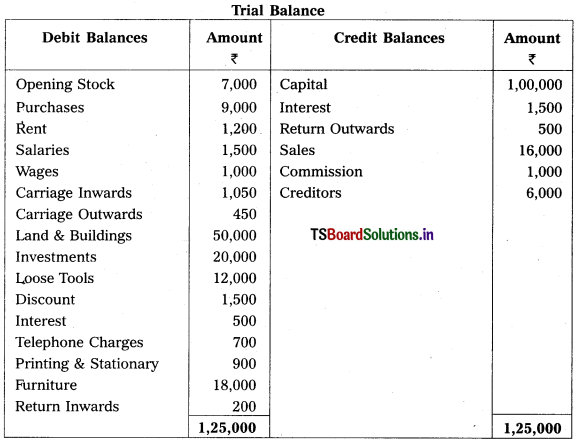
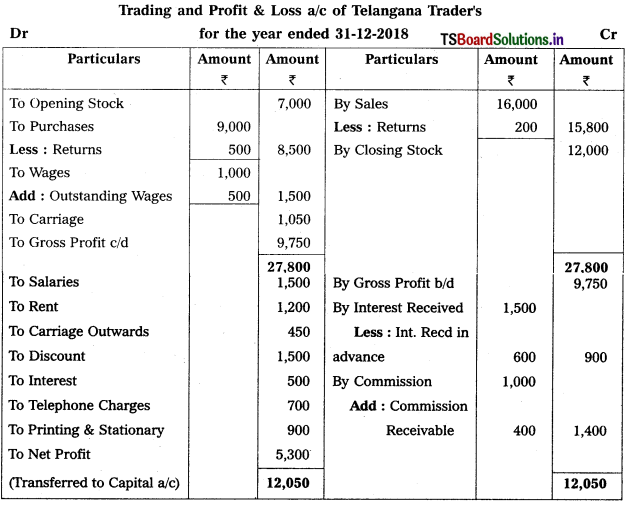
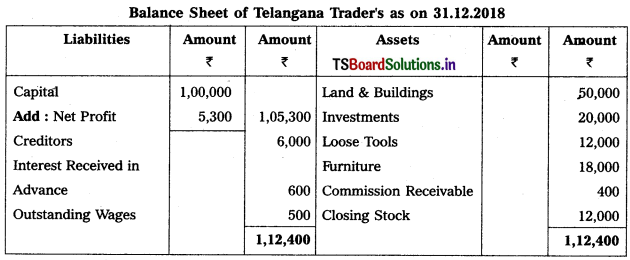
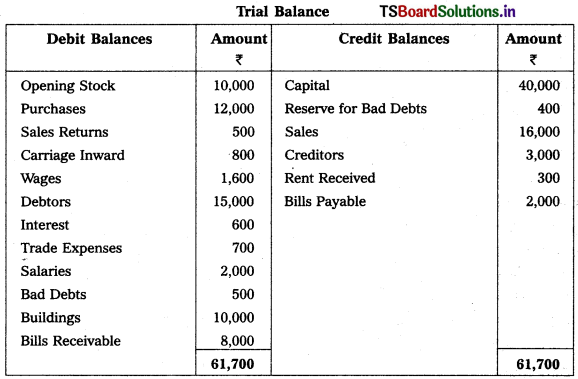
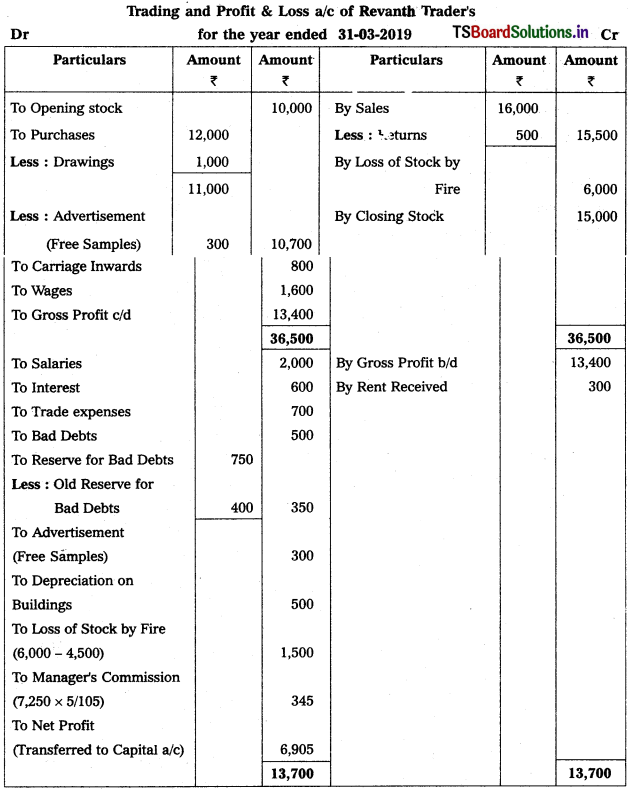
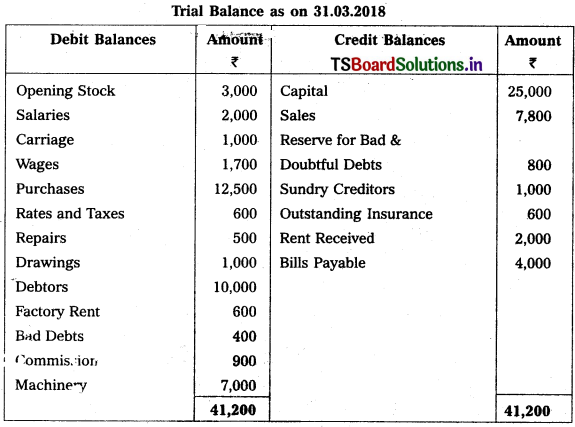
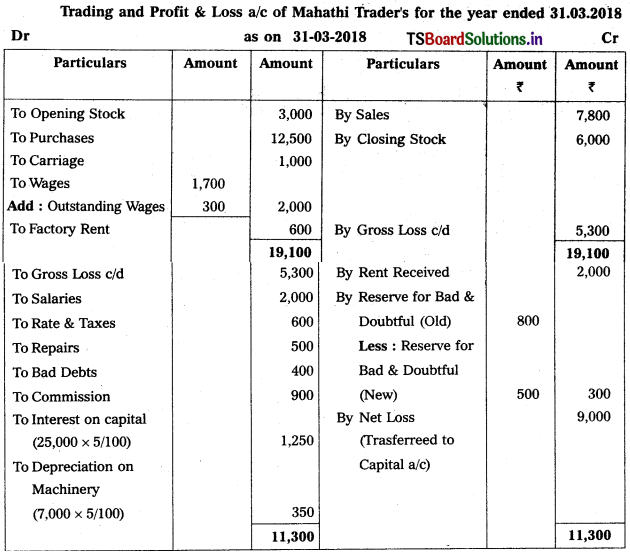
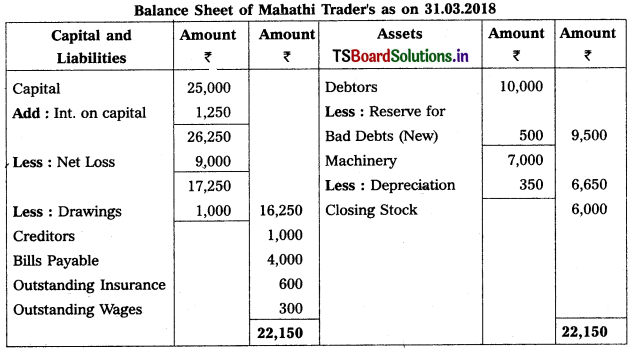
Question 9.
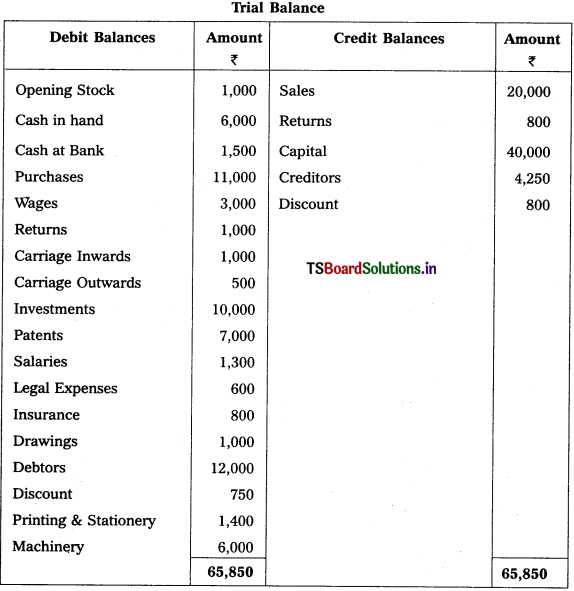
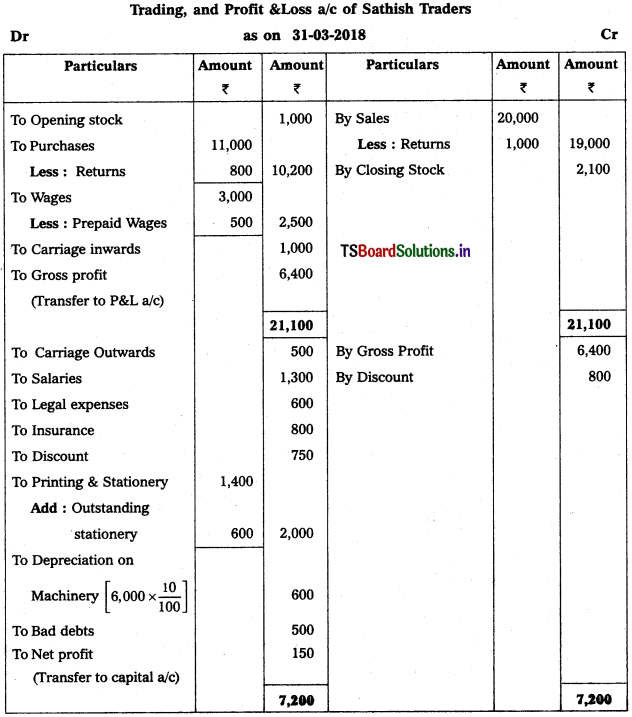
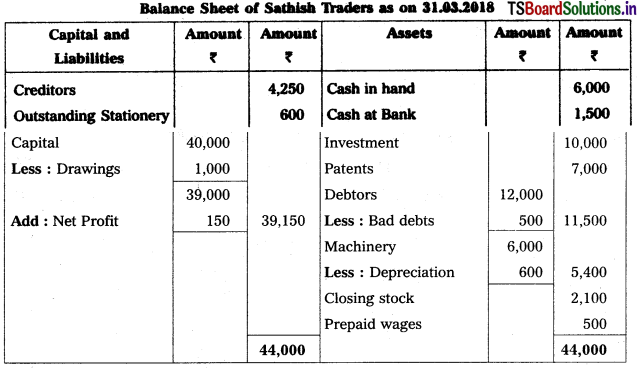
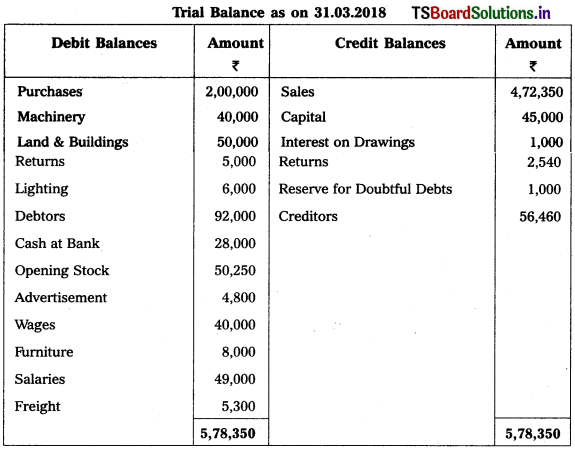
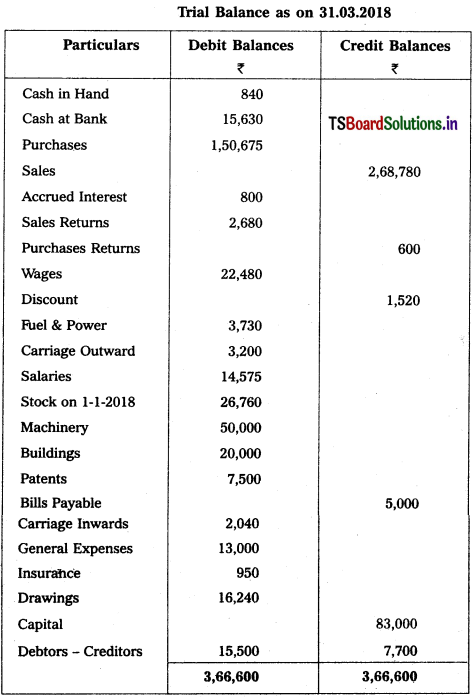
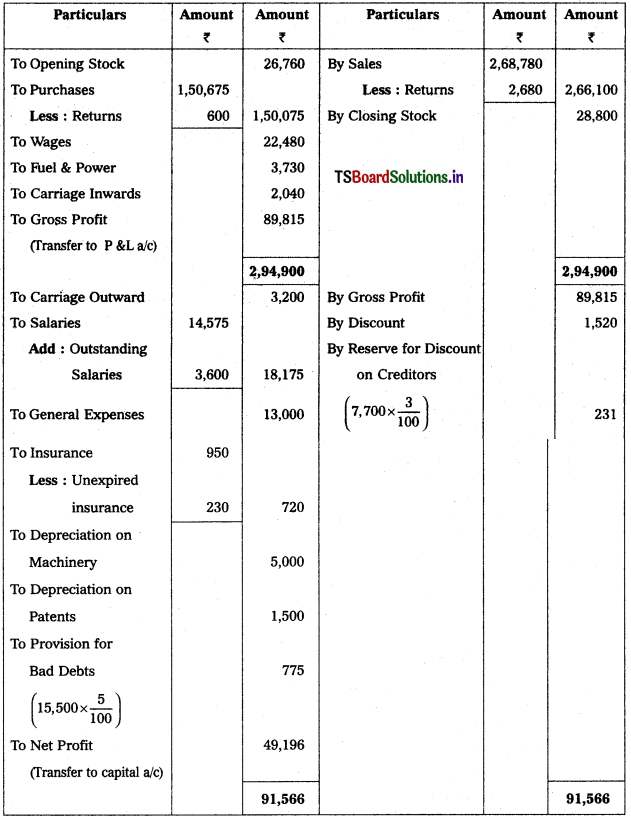
From the following Trial Balance, prepare Trading a/c, and Profit & Loss a/c of Ms. Veena Reddy for the year ended 31.12.2018.
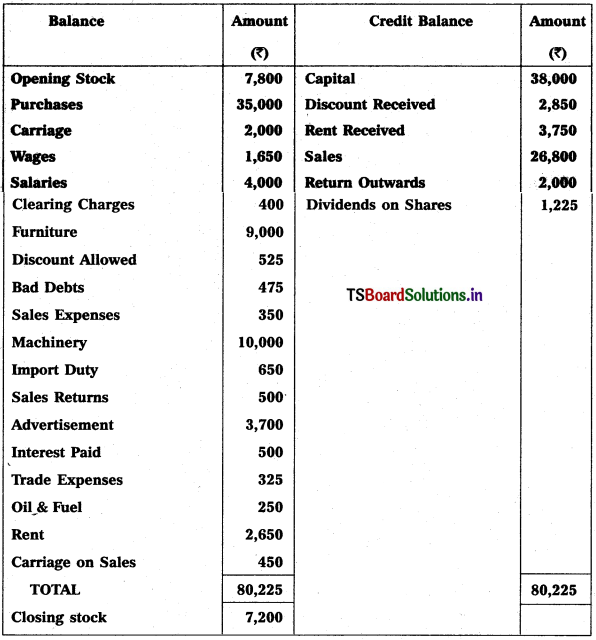
Solution:
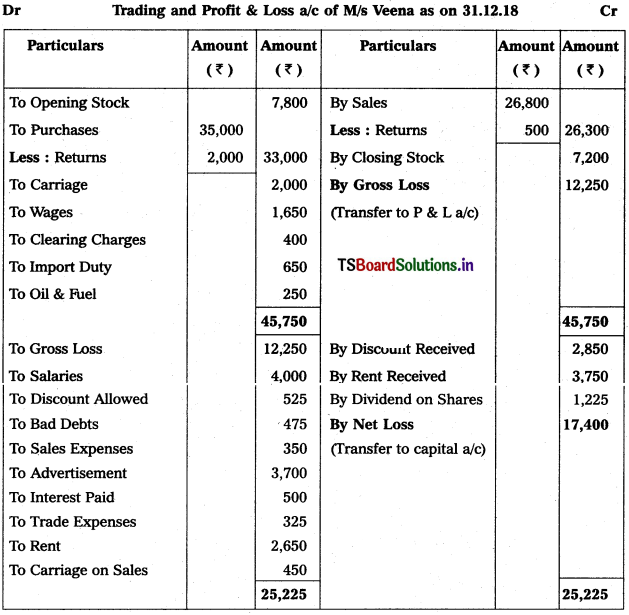
Question 10.
Prepare Trading Account and Profit & Loss a/c (amounts in rupees).
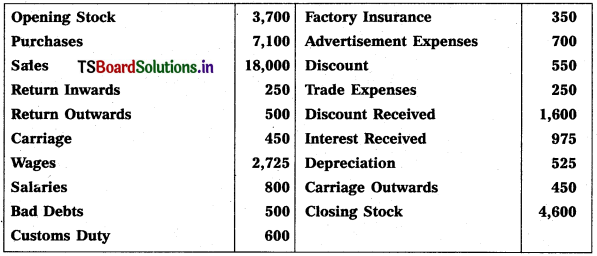
Solution:
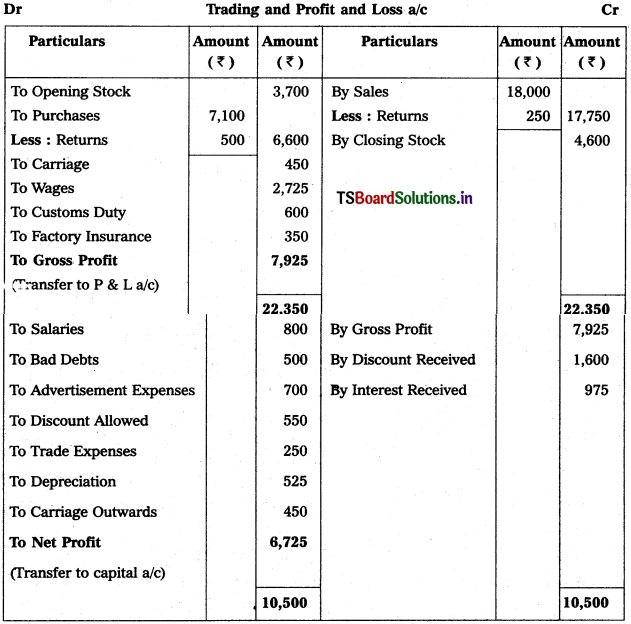
![]()
Question 11.
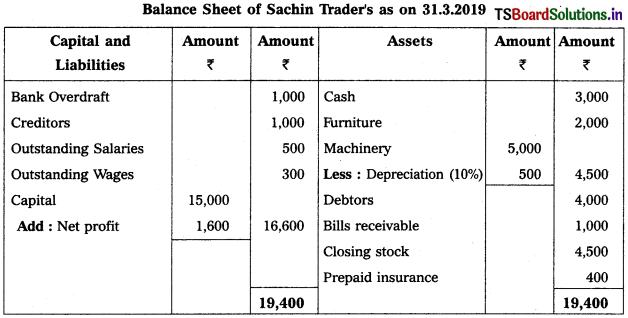
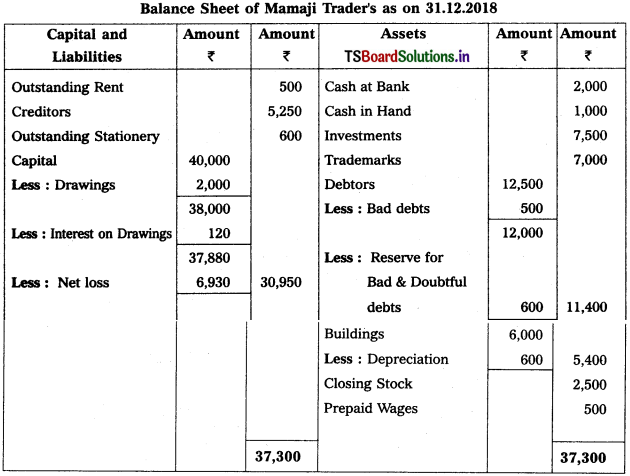
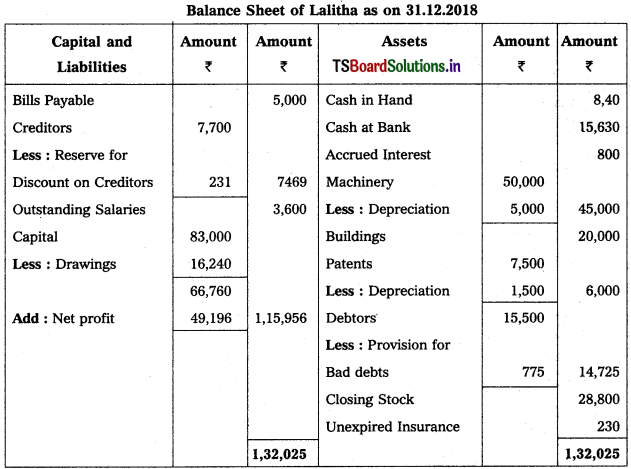
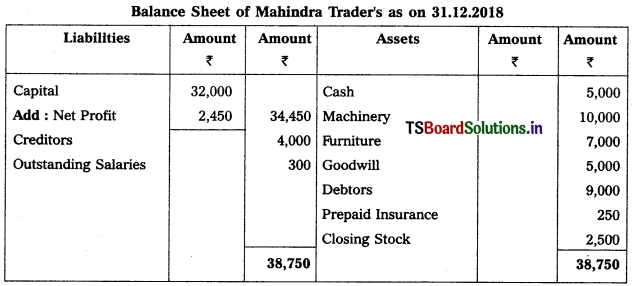
Prepare Balance Sheet from the following details of Yadagiri as on 31.12.2016.
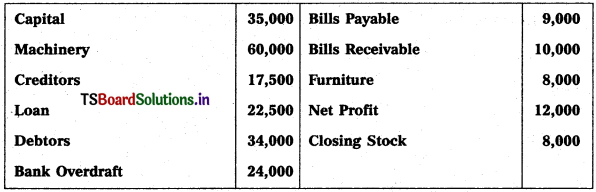
Solution:
Balance Sheet of Yadagiri as on 31.12.16
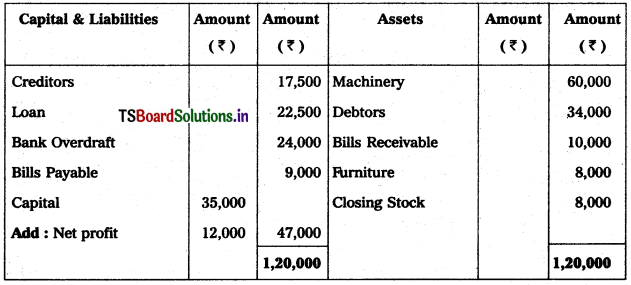
Question 12.
Prepare Balance Sheet of Karnakar Reddy Traders from the following as on 31.12.2017.
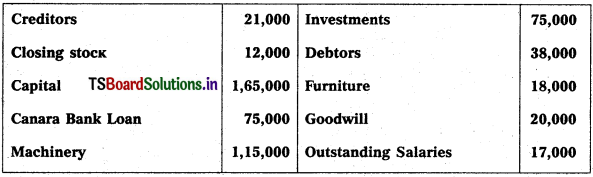
Solution:
Balance Sheet of Karnakar Reddy as on 31.12.2017
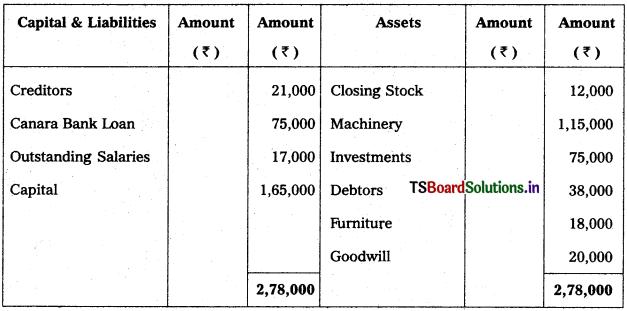
![]()
Question 13.
Prepare Balance Sheet of Madhavi Traders for the year ended on 31.12.2016.
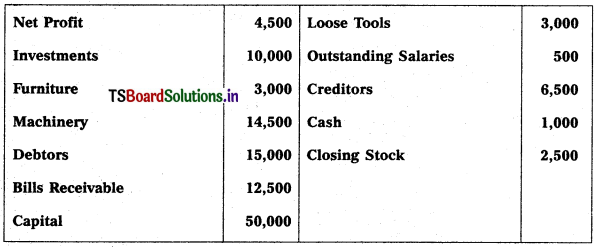
Solution:
Balance Sheet of Madhavi Traders as on 31.12.16
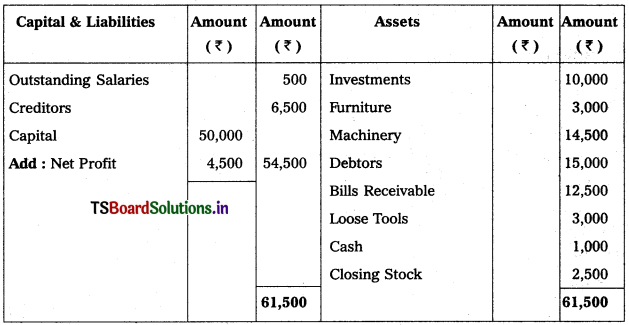
Question 14.
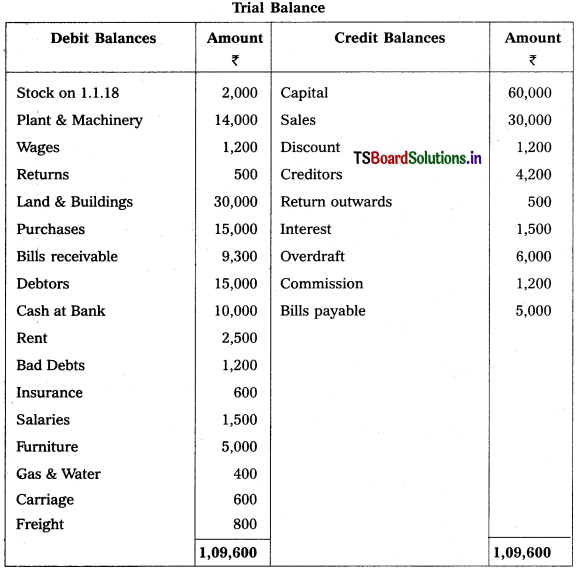
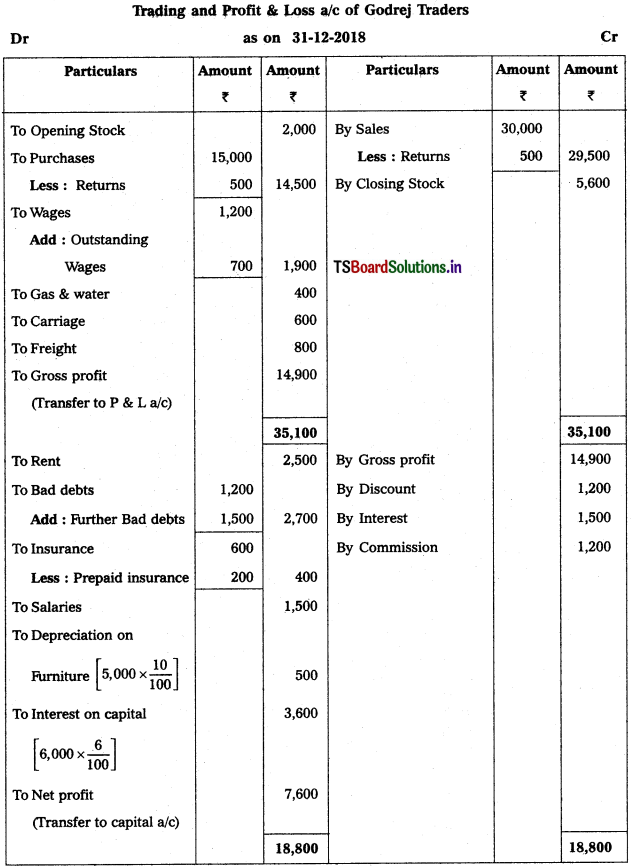
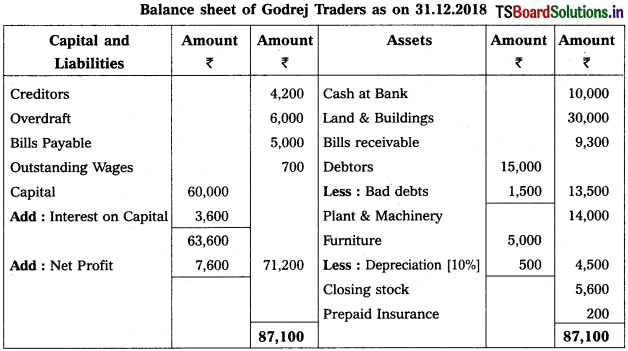
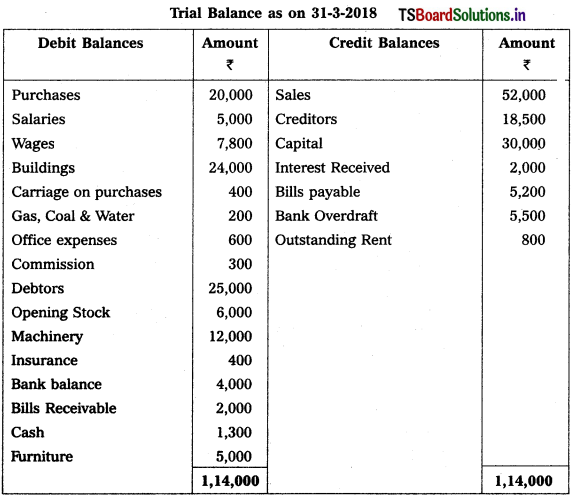
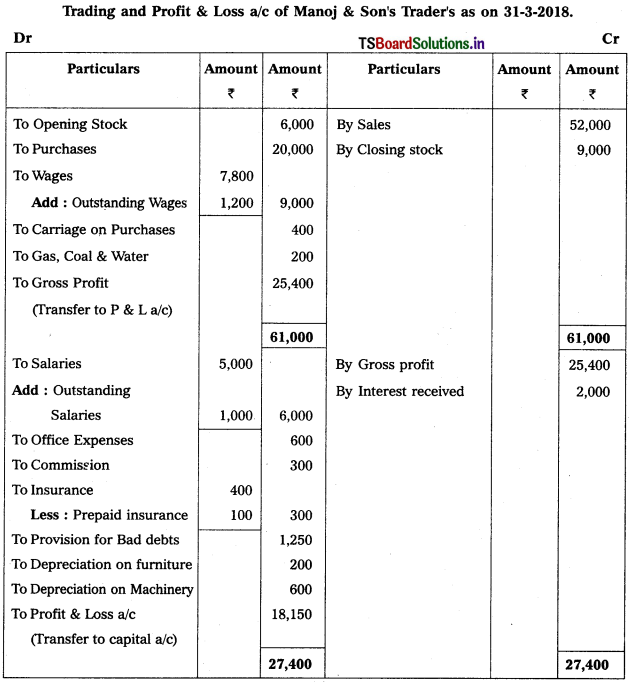
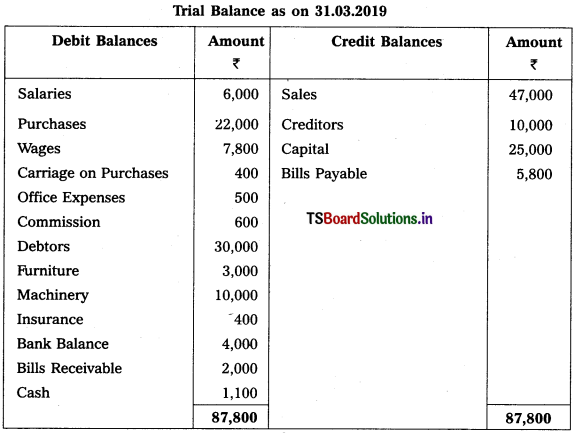
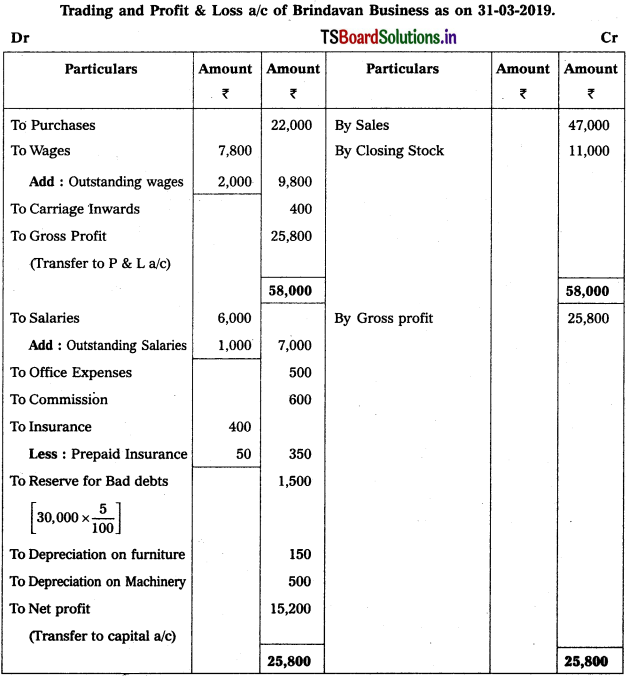
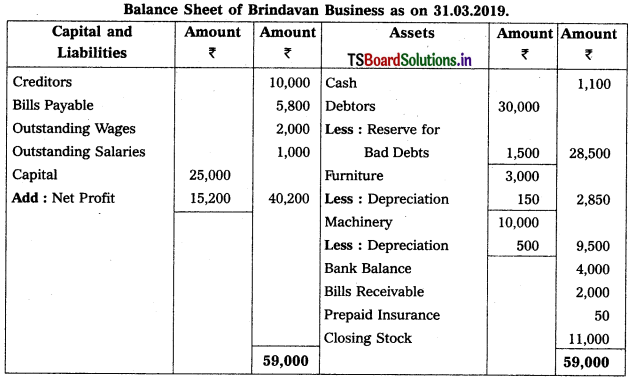
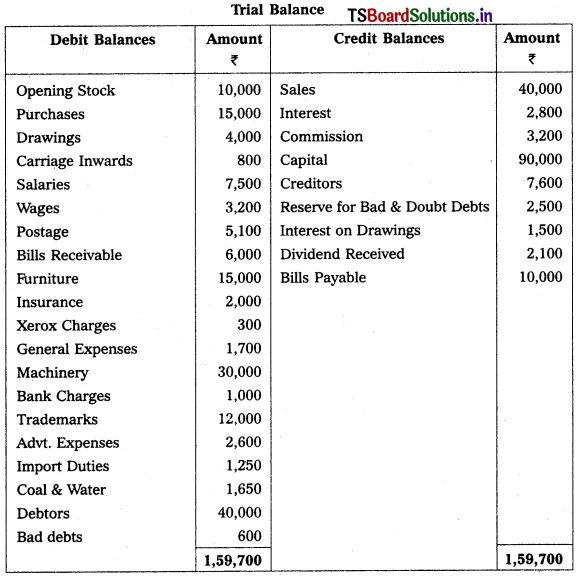
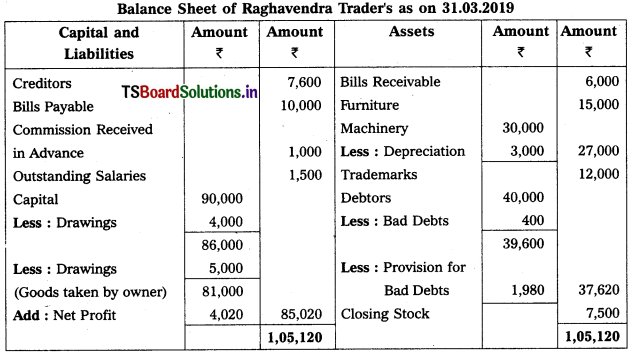
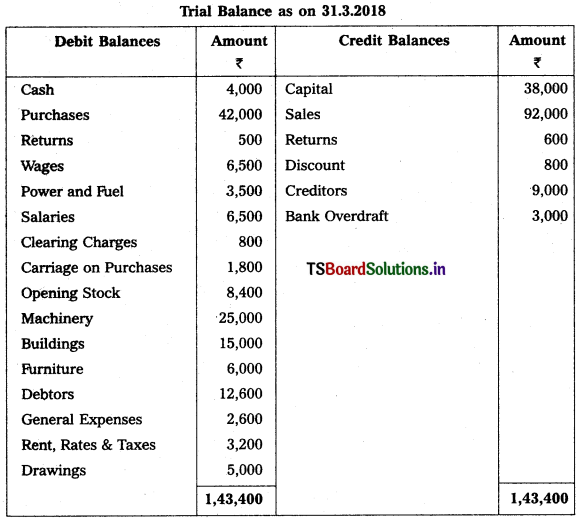
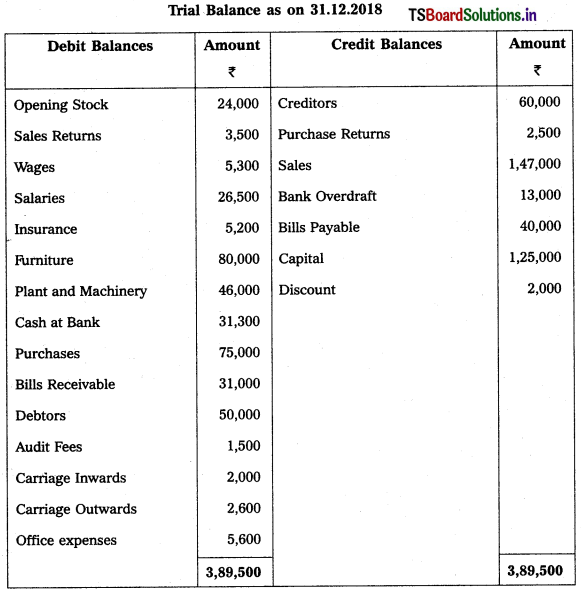
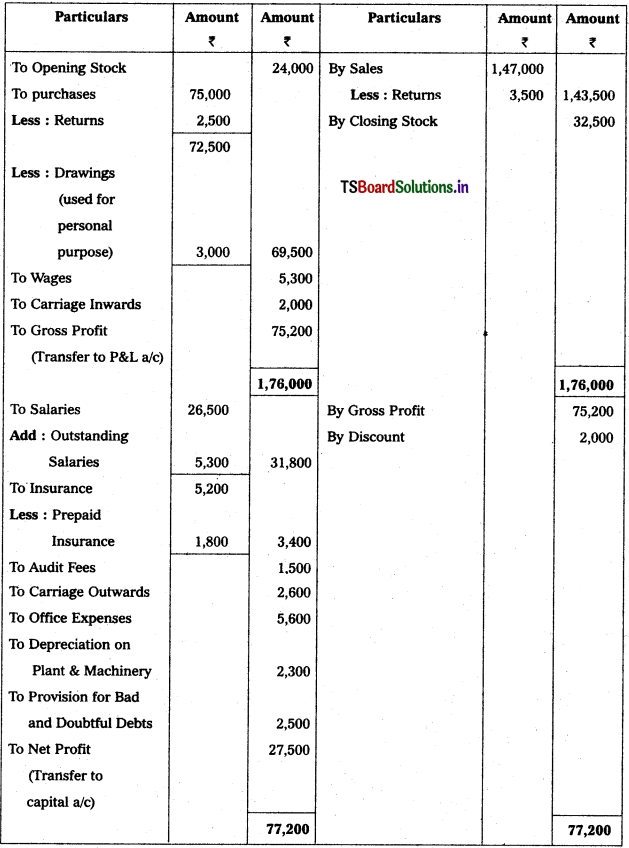
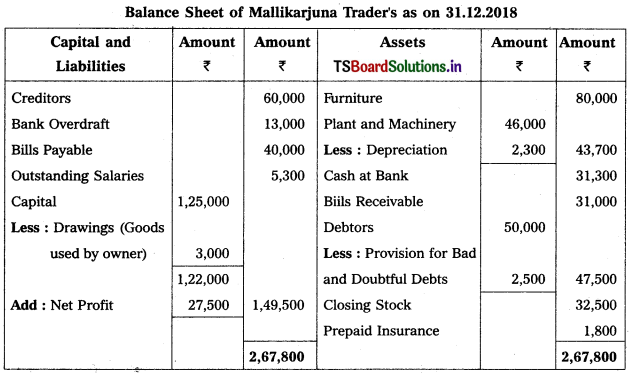
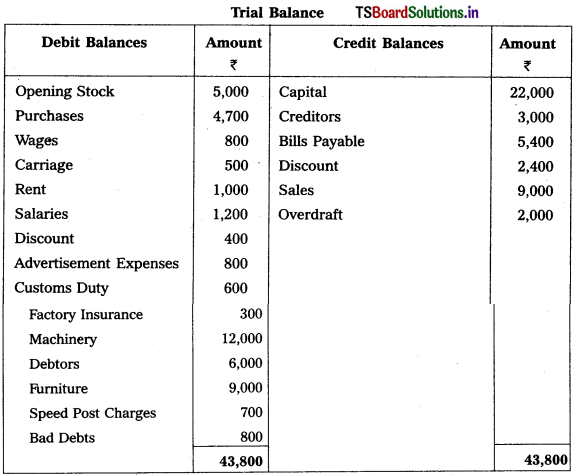
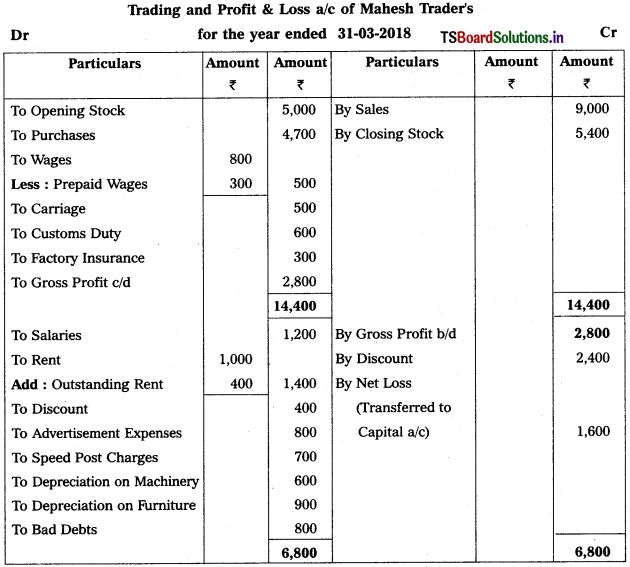
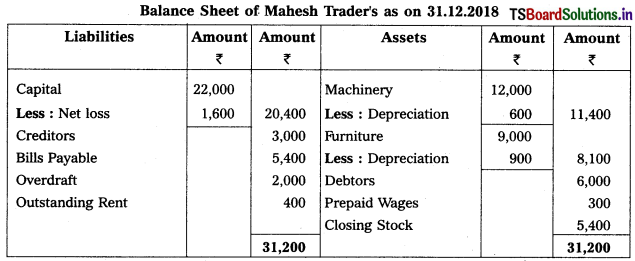
From the following Trial Balance, prepare Trading, P & L Account and Balance Sheet.
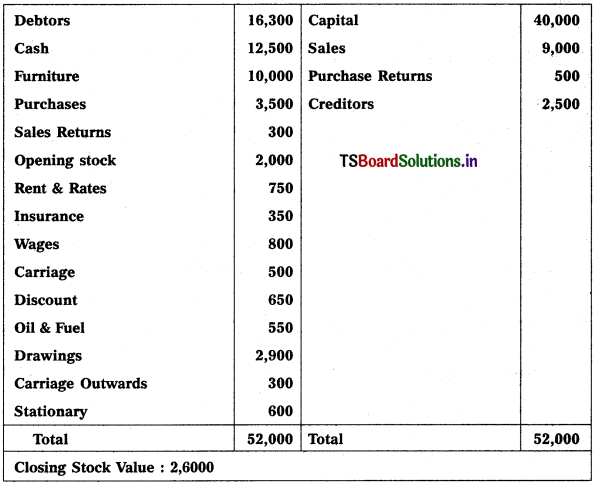
Solution:
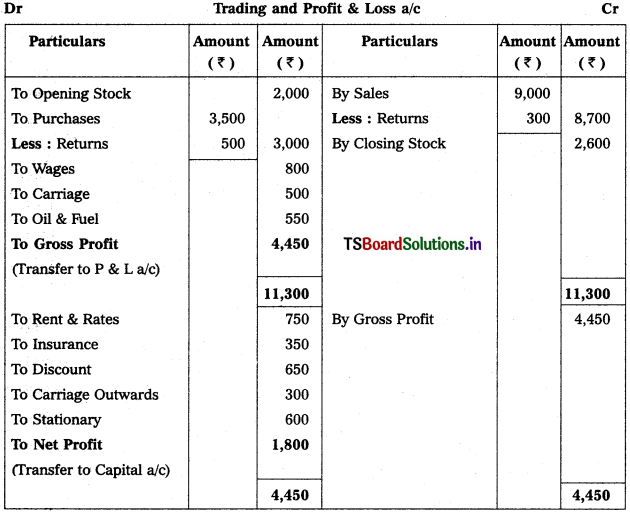
Balance Sheet
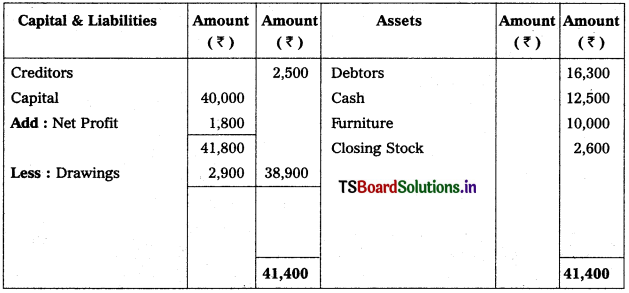
![]()
Question 15.
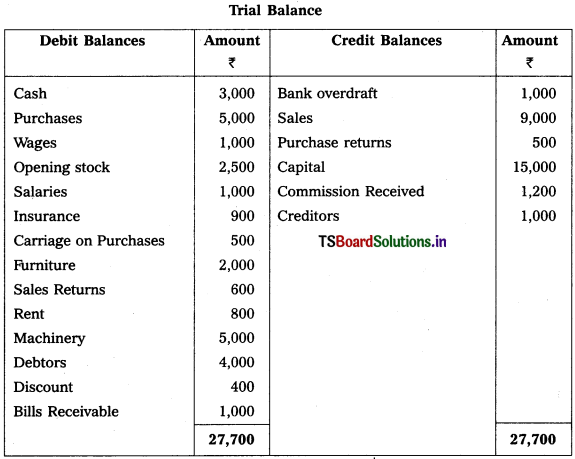
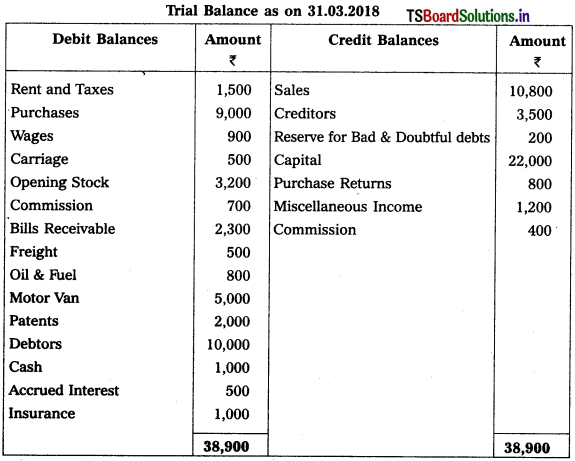
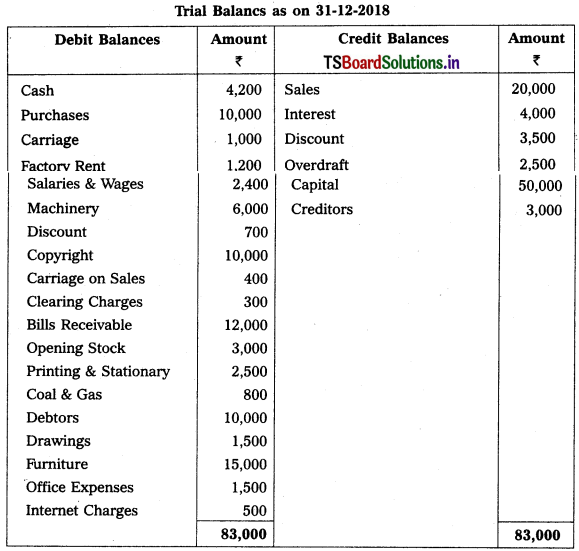
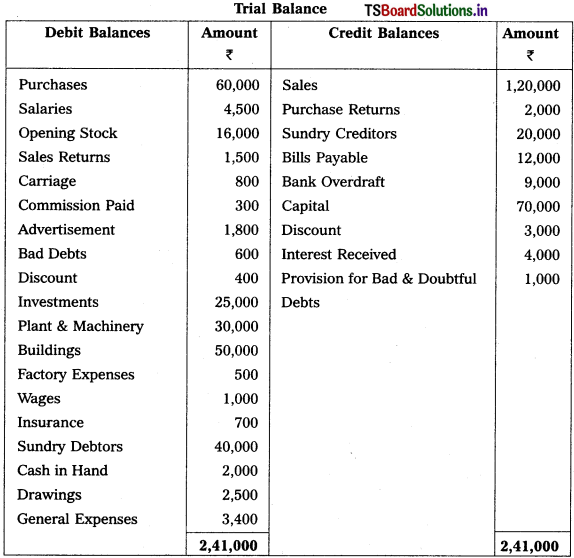
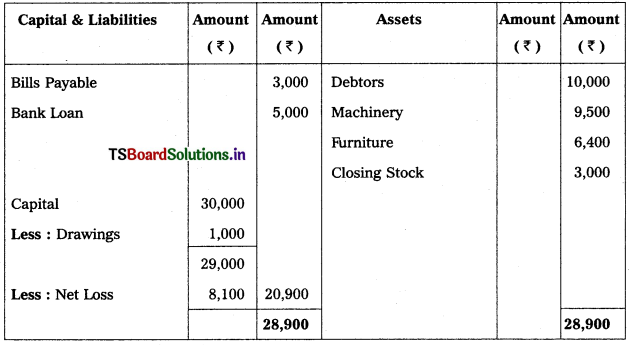
From the following trial balances prepare final accounts for the year ending 31.03.2015.
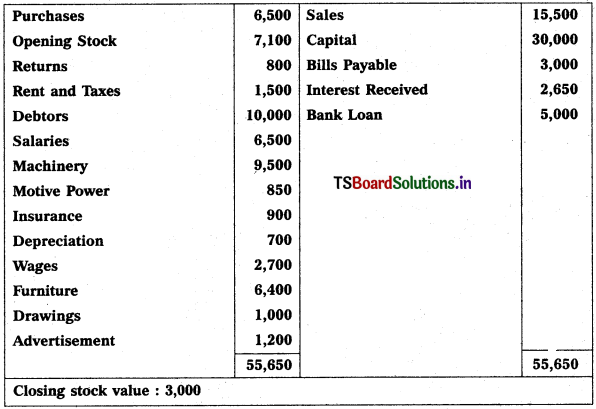
Solution:
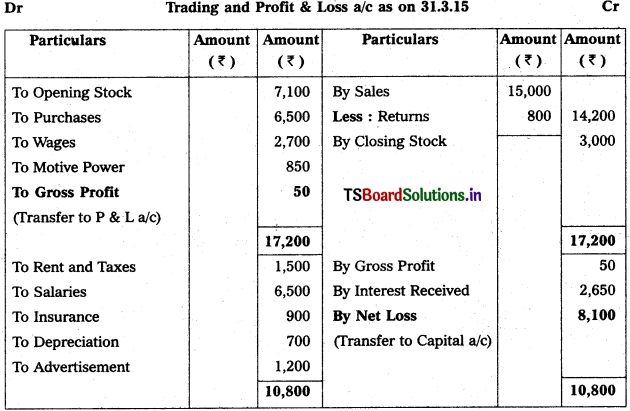
Balance Sheet
![]()
Textual Questions:
Question 1.
From the following information, prepare Trading Account of Shylaja Traders for the year ending 31.12.2018:
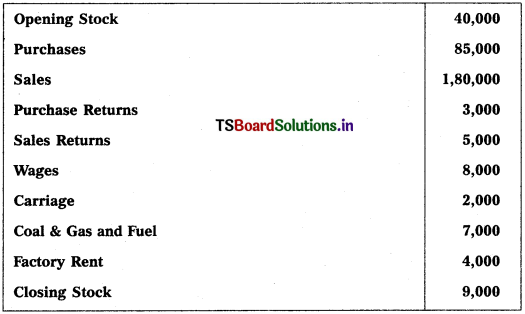
Solution:
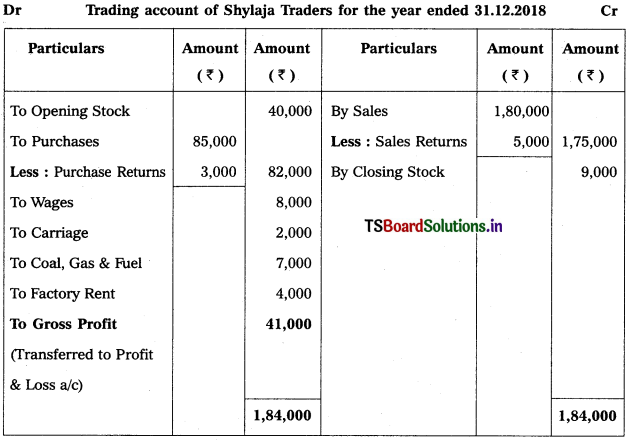
Question 2.
From the following information, prepare Trading Account of Swamy as on 31.12.2018 :
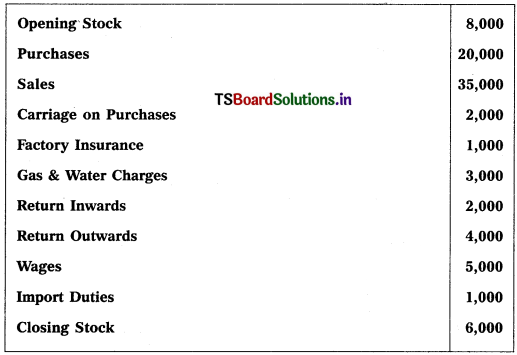
Solution:
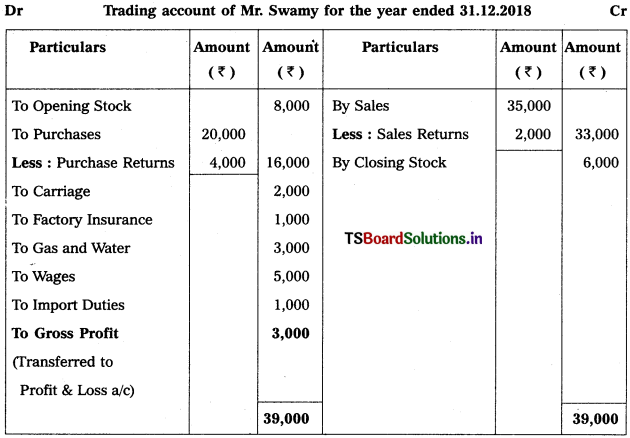
![]()
Question 3.
Prepare Trading Account of Ayyappa Traders for the year ending 31.12.2018.
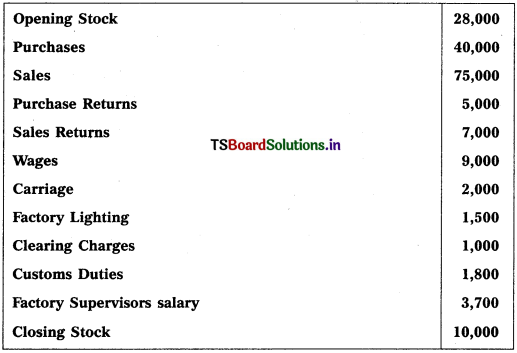
Solution:
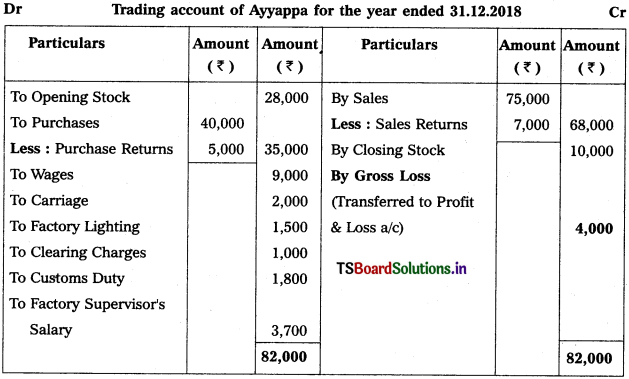
Question 4.
From the following particulars, prepare Profit & Loss a/c of Sathwlka for the year ending 31.12.2018 :
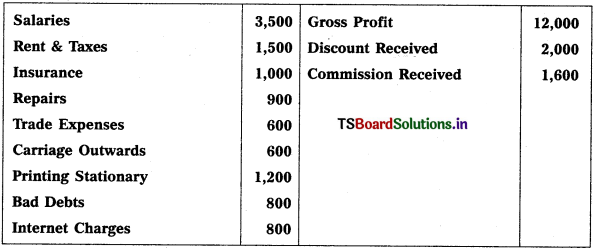
Solution:
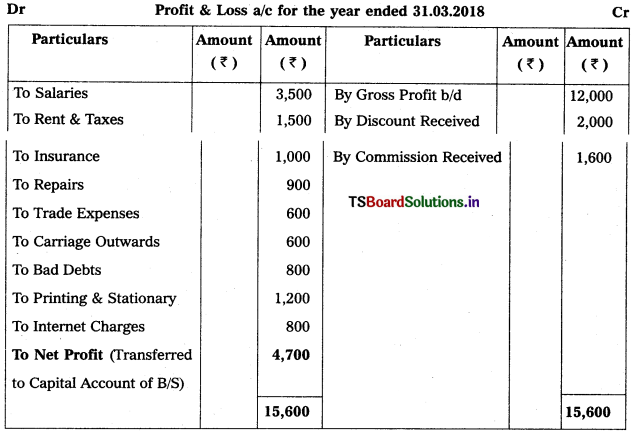
![]()
Question 5.
Prepare Profit & Loss a/c of Naveen Kumar Traders as on 31.03.2018.
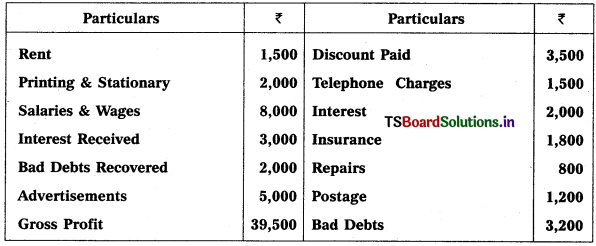
Solution:
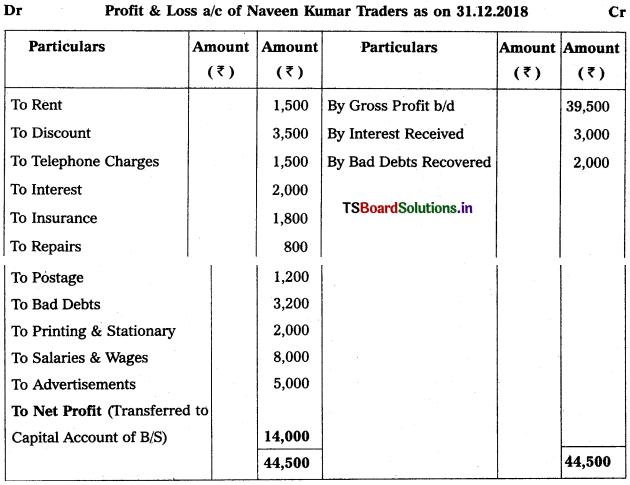
Question 6.
From the following balances, prepare Profit & Loss a/C of Harini for the year ended 31.12.2018.
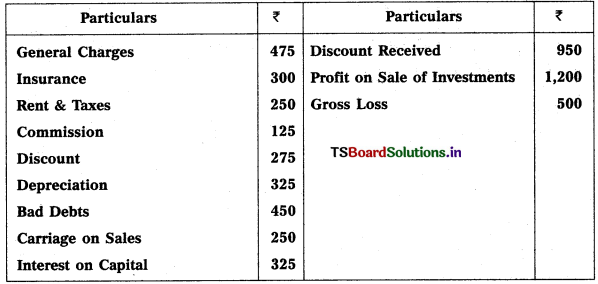
Solution:
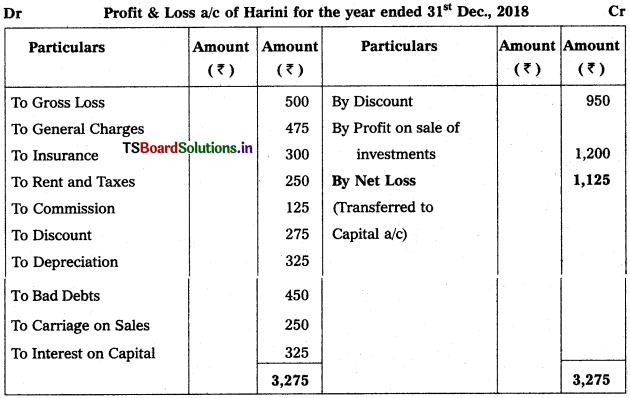
![]()
Question 7.
Prepare leading Account and Profit & Loss a/c from the following particulars.
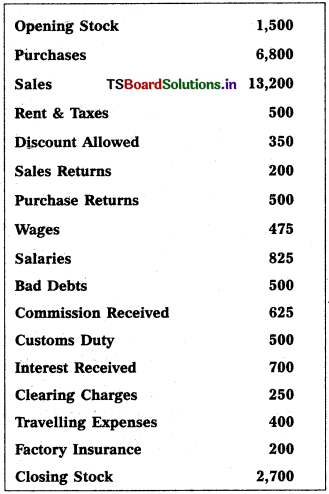
Solution:
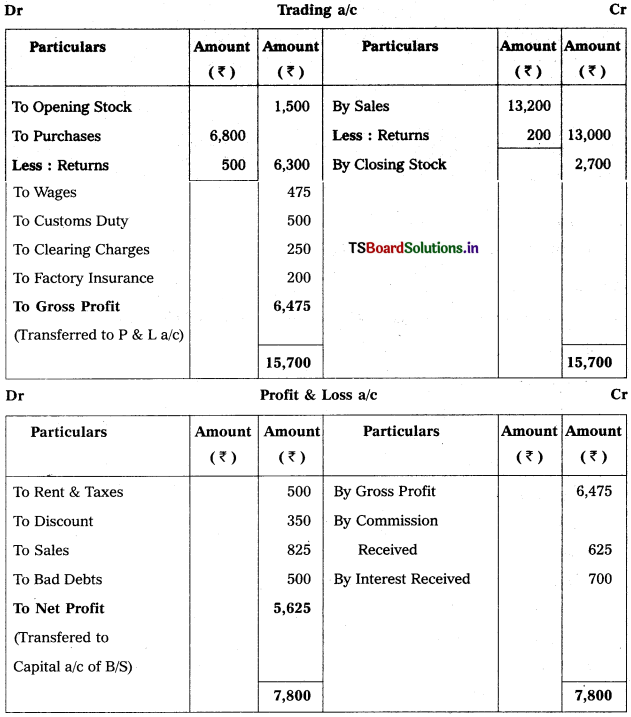
![]()
Question 8.
Prepare Balance Sheet of Srinivas from the following particulars as on 31.12.2017 :
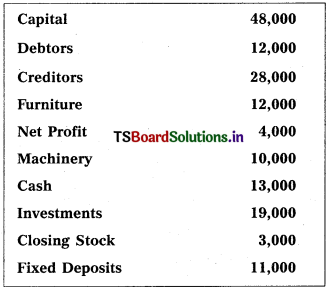
Solution:
Balance Sheet of Srinivas as on 31.12.2018