Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 10th Lesson Preparation of Final Accounts Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 10th Lesson Preparation of Final Accounts
Essay Questions:
Question 1.
Describe the various types of adjustments with suitable examples.
Ans.
The following are the various adjustments :
1. Outstanding expenses:
Outstanding expenses are the expenses relating to the current year but unpaid during the year and are to be paid in the next year is known as outstanding expenses. E.g. Salary or rent for the month of March is due but not paid. These expenses are added to the concerned expenditure either in trading or profit and loss account debit side. These expenses are again shown as liability in balance sheet.
2. Prepaid expenses :
Prepaid expenses are the expenses relating to the next year but paid during the year. E.g. Insurance or taxes are paid for the next year. These expenses are deducted from the concerned expenditure either in trading or profit and loss account debit side. These expenses are shown as assets in the balance sheet.
3. Income to be received :
It is also known as accured income. It is the income relating to the current year which is not received but to be received in the next year. These incomes are added to the concerned income in profit and loss account credit side. These incomes are shown as assets in the balance sheet.
4. Income received in advance:
Income relating to the next year but received in advance during the current year. These incomes are deducted from the concerned income in profit and loss account credit side. These incomes are shown as liability on the Balance Sheet.
5. Depreciation on fixed assets:
The value of fixed assets like machinery, plant, buildings will decrease year after year due to reasons like wear and tear, obsolescence etc. Such decline is called as depreciation. It is considered as an expense and generally calculated as a percentage on the value of asset. It is debited to profit and loss account and again deducted from the asset on the balance sheet.
6. Interest on capital :
Interest paid on the owners capital is treated as expenditure is debited profit and loss account. It is added to the capital on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
7. Interest on drawings :
The amount of cash or goods taken for personal use are known as drawings. Interest on such drawings is credited to profit and loss a/c and again it should be deducted from capital in balance sheet.
8. Closing stock :
If the closing stock is given as adjustment, it is credited to trading a/c and shown as an asset in the balance sheet.
9. Bad debts :
The debts which cannot be recovered are called as bad debts.
i) If the bad debts are given in the trial balance. It is debited to profit and loss account only.
ii) If the bad debts are given as adjustment, they should be debited to profit and loss account and deducted from the sundry debtors on the asset side of the balance sheet.
10. Provision for bad debts :
Some of the debts of a year may or may not be recovered in the next year. These are known as doubtful debts. So, the trader create some amount on current year to meet the doubtful debts of the next year which is called provision for bad and doubtful debts when the provision is given as an adjustment, the amount so calculated on debtors is debited to profit and loss a/c. It is again deducted from the debtors on the asset side of the balance sheet.
11. When provision for doubtful debts is given in the trial balance and also in adjustments. The provision given in the trial balance is created in the last year, is the old reserve. If the new provision is more than the old provision the difference is debited to profit and loss account, and the new provision is deducted from the debtors in the balance sheet.
On the other hand, if the new provision is less than old provision. The difference is credited to profit and loss account. New provision only deducted form sundry debtors in the balance sheet.
![]()
Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What do you mean by Adjustments ? State the importance of Adjustments.
Answer:
On the date of preparing the final accounts, all the expenses whether paid or not and all incomes whether received or not should be taken, similarly, expenses and incomes relating to next year should not taken. All these items are to be adjustment in final accounts by way of adjustments entries. Addition or subtraction of the amounts from revenue items is called adjustment.
Importance of adjustments :
- Expenses or incomes relating to the accounting period can be ascertained accurately.
- Profit or loss can be calculated accurately.
- True value of assets and liabilities can be ascertained easily.
- Unrecorded transactions can be brought into the books of accounts.
Question 2.
Write the following :
a) Interest on capital.
b) Interest on Drawings.
Answer:
a) Interest on capital :
It is the amount of interest payable on owner’s capital by the business firm. It is an expenditure.
Adjustment entry :
Interest on capital a/c Dr
To Capital a/c (Being the interest payable capital)
Calculate interest on capital at a given percentage and is debited to profit and loss account. Interest on capital is added to capital on the liabilities side of balance sheet.
b) Interest on drawings:
The amount of cash or goods taken by the proprietor for personal use is called drawings. Interest should be calculated at a given rate and it is credited to profit and loss account as it is income to business. The interest on drawings is deducted from the capital on the liabilities side of balance sheet.
Interest on Drawings entry :
Capital / Drawings a/c Dr
To Interest on Drawings a/c (Being interest receivable on drawings).
![]()
Question 3.
Briefly explain about the following.
a) Depreciation
b) Loss of stock by Fire.
Answer:
a) Depreciation :
The value of fixed assets such as Buildings, Machinery, Furniture, Loose tools etc., will decrease year after year due to various reasons, such as wear and tear, obsolescence etc. Such decline in the value of fixed asses is called “Depreciation”.
Depreciation may be defined as “the gradual decrease in the value of an asset”. Depreciation should be considered as a business expense and is to be charged to the Profit and Loss Account. Generally depreciation is calculated as a percentage on the value of the asset given in Trial Balance.
Adjustment Entry :
Depreciation a/c Dr XX
To Asset a/c (individually) XX
(Being the depreciation provided on asset)
b) Loss of stock by Fire Accident:
Sometimes business stock may be lost due to fire accident. A provision has to be made for such loss. Stock lost by fire accident is an abnormal loss and hence it should be treated properly in the final accounts. Firstly, the total loss of stock by fire should be shown on credit side of the Trading Account. Again, it should be treated according to the following situations :
a) When Stock is fully insured.
b) When Stock is partly insured.
c) When Stock is not insured at all.
a) When Stock is fully insured and full claim is admitted by the Insurance Company : Adjustment Entries
i) Loss of Stock by Fire Accident a/c …………. Dr XX
To Trading a/c XX
(Being loss of stock by fire accident)
ii) Insurance company a/c …………. Dr XX
To Loss of stock by Fire Accident a/c XX
(Being claim admitted by the Insurance Company)
b) When stock is partly insured and Insurance company admits a part of the claim :
i) Loss of Stock by Fire Accident a/c …………. Dr XX
To Trading a/c XX
(Being loss of stock by fire accident)
ii) Insurance company a/c …………. Dr XX
Profit and Loss a/c …………. Dr XX
To Loss of stock by fire accident a/c XX
(Being part of the claim admitted by the Insurance Company and remaining loss transferred to P & L a/c)
c) When Stock is not insured at all:
i) Loss of Stock by Fire Accident a/c …………. Dr XX
To Trading a/c XX
(Being loss of stock by Fire Accident)
ii) Profit and Loss a/c …………. Dr XX
To Loss of Stock by Fire Accident a/c XX
(Being loss of stock transferred to P & L a/c).
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the treatment of Adjustment on Debtors in Final accounts.
Answer:
In final accounts, Bad Debts, Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts and Provision for Discount on Debtors may be given as adjustments relating to Debtors.
I. Bad Debts :
When goods are sold on credit basis, some cf the customers may not pay die amount. The debts which are not collected and irreco\s ole are known as Bad Debts which are a loss.
After preparing the Trial Balance, the trader may notice some amounts are irrecoverable debts. These bad debts are called Further Bad Debts or Additional Bad Debts.
Adjustment Entry :
Bad Debts a/c Dr XX
To Sundry Debtors a/c XX
(Being bad debts written off)
Accounting Treatment in Final Accounts :
a) When bad debts are given only in the adjustments :
Accounting Treatment :
- Bad Debts are to be shown on debit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
- Bad Debts should be deducted from the debtors on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
If the Bad debts are given in Trial Balance only, it should be shown on debit side of the Profit & Loss Account as a loss and need not be shown in Balance sheet.
b) When Bad Debts are given in both Trial Balance and Adjustments :
Accounting Treatment in Final Accounts :
- Both the bad debts (Bad debts given in Trial Balance and given in adjustment) are ~ to be shown on debit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
- Bad debts given only in the adjustments are to be deducted from debtors on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
II. Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts :
According to the principle of Conservatism, anticipated losses must be provided. Therefore, the trader creates some provision on the basis of some percentage which is fixed on the basis of past experience. Such provision is called as Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts. It is also termed as Reserve for Bad and Doubtful Debts.
![]()
a) When provision is given as an adjustment:
Adjustment entry:
Profit and Loss a/c Dr XX
To provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts a/c XX
(Being provision for bad and doubtful debts created on debtors)
Accounting Treatment in Final Accounts :
- Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts should be shown on debit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
- It will be deducted from the Debtors on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
When Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts is give in the Trial Balance, it should be deducted from the Debtors on the assets side of the Balance Sheet and need not be shown in the Profit and Loss Account.
b) When provision for doubtful debts is given in Trial Balance and also in adjustments :
The provision for doubtful debts given in Trial Balance is created as created in the last year and is known as the old provision or existing provision.
The provision for doubtful debts given in the adjustments is treated as to be created in the current year and is known as the new provision or provision required.
Accounting Treatment in Final Accounts :
1. Compare the old provision (given in trial balance) with new provision (given in the adjustments), if the new provision for doubtful debts is more than the old provision for doubtful debts, the difference amount (New provision – old provision) should be debited to the Profit and Loss Account.
On the other hand, new provision for doubtful debts is less than the old provision for doubtful debts, the difference amount (old provision – new provision) should be recorded on the credit side of the Profit & Loss Account.
2. Deduct only the amount of new provision for bad and doubtful debts from sundry debtors on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
c) If tne bad debts are given both in trial balance and in adjustments, and also provision for bad and doubtful debts given in adjustments:
Accounting Treatment in Final Accounts :
1. Firstly, calculate the provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts as per the percentage given in the adjustments after deducting the further bad debts given in the adjustments from the debtors. Then both the Bad Debts (given in Trial Balance and in adjustments) and provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts should be shown on debit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
2. Further, Bad Debts given in the adjustments and Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts should be deducted from the Debtors on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
III. Provision for Discount on Debtors :
When a customer (debtor) pays the amount of sales within certain period, trader normally allows certain percentage of discount. The provision created towards the discount on debtors is called as “Provision for Discount on Debtor”.
Adjustment Entry :
Profit and Loss a/c Dr XX
To provision for Discount on Debtor a/c X X
(Being provision for discount on debtors created)
Accounting Treatment in Final Accounts :
- Provision for Discount on Debtors is shown on debit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
- It will be again shown by way of deduction from the Debtors on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
However, if Provision for Discount on Debtors is given in the Trial Balance, it should be deducted directly from the Debtors on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the following.
a) Goods Distributed as Free Samples.
b) Accrued Income.
Answer:
a) Goods Distributed as Free Samples :
With a view to promote the sales, some of the goods are distributed among customers at free of cost. These free samples are treated as advertisement expenses.
Adjustment Entry:
Advertisement a/c …………. Dr XX
To Purchases a/c XX
(Being goods distributed as free samples)
Accounting Treatment in Final Accounts :
1. Goods distributed as Free Samples should be deducted from the purchases on debit side of the Trading Account.
2. These Free Sample should be treated as Advertisement Expense and is to be shown on debit side of the Profit and Loss a/c. No need to be shown in the Balance Sheet.
b) Accrued Income :
The income which is earned but not received during the accounting year is called Accrued Income or Income Receivable.
Adjustment Entry :
Accrued Income a/c Dr X X
To Income a/c XX
(Being the income receivable)
Accounting Treatment in Final Accounts :
- Accrued Income should be added to the concerned income on credit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
- It will be shown on the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
If Accrued income is given in the Trial Balance, the amount should be shown only once on the assets side of the Balance Sheet, i.e., need not be shown in the Profit & Loss a/c.
![]()
Very Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What is the meaning of Adjustment ?
Answer:
On the date of preparing the final accounts, all the expenses whether paid or not and all incomes whether received or not should be taken, similarly, expenses and incomes relating to next year should not taken. All these items are to be adjustment in final accounts by way of adjustments entries. Addition or substraction of the amounts from revenue items is called adjustment.
Question 2.
Explain the importance of Adjustment.
Answer:Importance of adjustments :
- Expenses or incomes relating to the accounting period can be ascertained accurately.
- Profit or loss can be calculated accurately.
- True value of assets and liabilities can be ascertained easily.
- Unrecorded transactions can be brought into the books of accounts.
Question 3.
Give the meaning of bad debts.
Answer:
- The trader sells the goods on credit to some of the customers. The customer who has taken the credit may not pay the amount. These debts which are not collected and irrecoverable are known as bad debts.
- Bad debts is a loss to the business. It shown in debit side of the Profit & Loss a/c.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe provision for Discount on Creditors.
Answer:
When the payment is made to creditors within the scheduled period, the discount is likely to be earned. Such discount on creditors is an anticipated profit. The reserve created on creditors is known as Reserve for Discount on Creditors.
Adjustment Entry :
Reserve for Discount on Creditors a/c …………. Dr XX
To Profit and Loss a/c XX
(Being reserve for discount on creditor created)
Question 5.
Explain the accounting treatment of Manager’s Commission.
Answer:
Manager’s Commission: In order to encourage the manager to work more and to increase the profits, manager may be given commission on net profits of the business. It can be given at a certain percentage on the net profits in any of the following two ways :
Manager’s Commission paid on :
a) Net Profit before charging such commission.
b) Net Profit after charging such commission.
Adjustment Entry :
Profit and Loss a/c ………… Dr XX
To Commission Payable a/c XX
(Being commission payable to manager).
![]()
Problems:
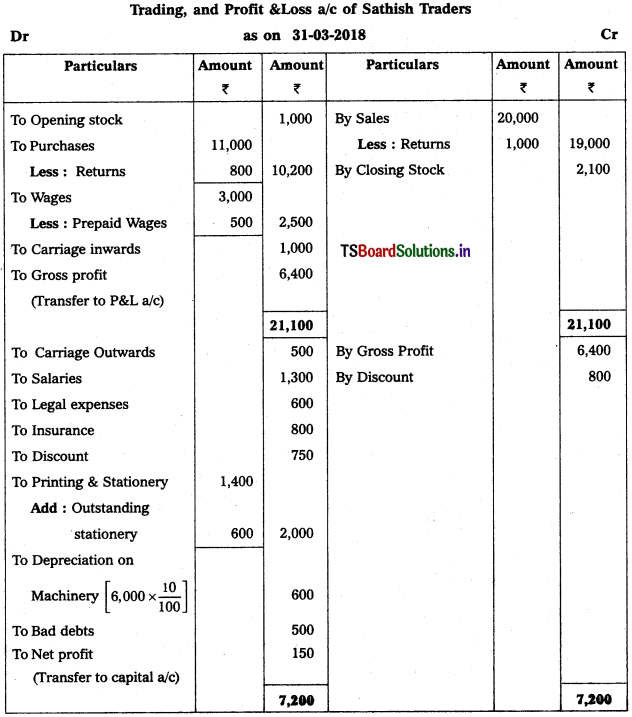
Question 1.
From the following Trial Balance, prepare final accounts of SathishTraders as on 31-12-2013.
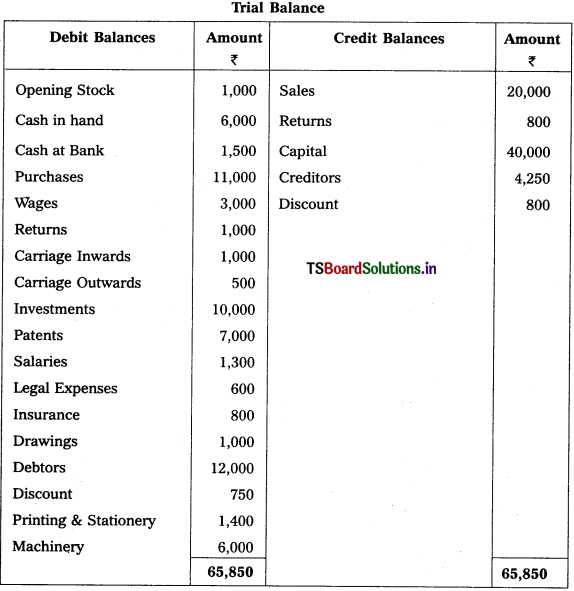
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 2,100
2) Outstanding Stationery : ₹ 600
3) Depreciationof Machinery : 10%
4) Bad Debts : ₹ 500
5) Prepaid Wages : ₹ 500
Solution:
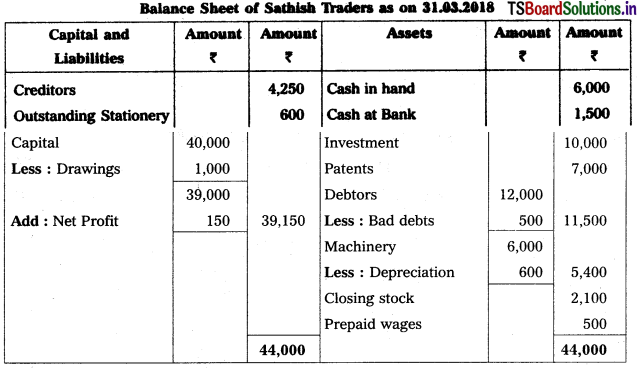
![]()
Question 2.
From the following particulars, prepare final accounts of Godrej Traders for the year ending 31.12.2018:
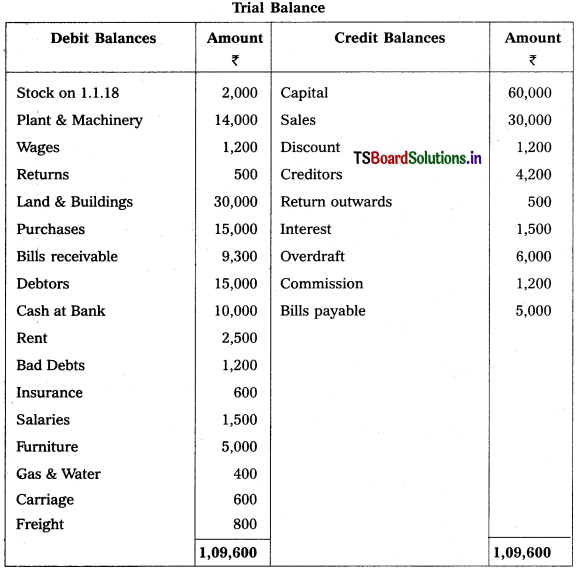
Solution:
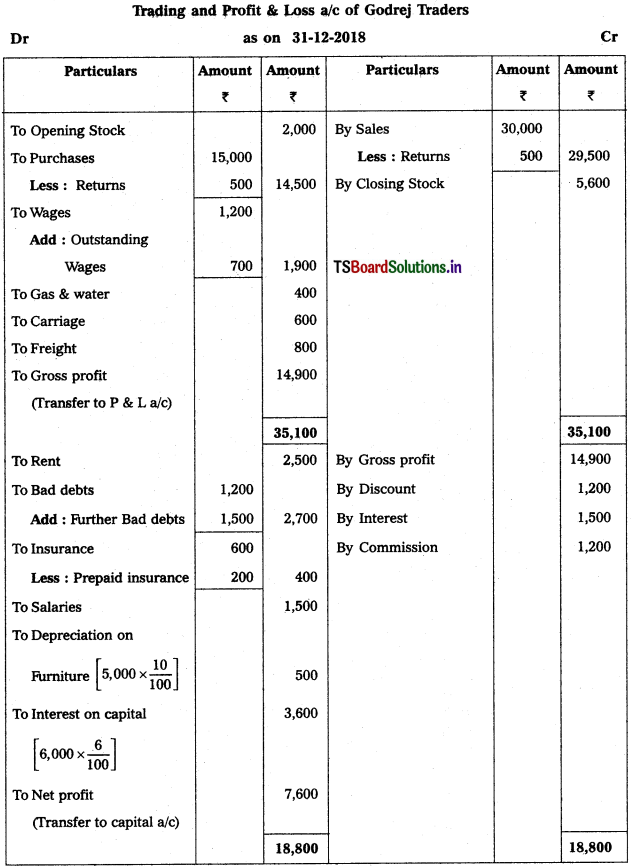
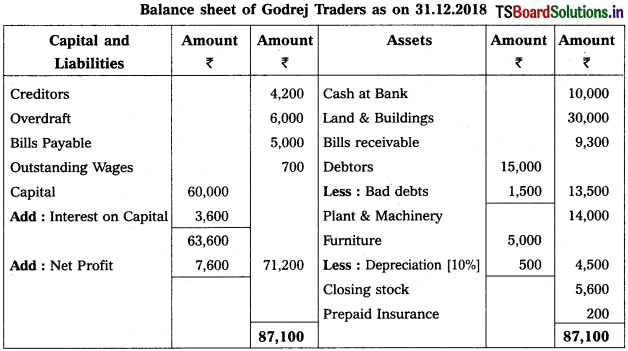
![]()
Question 3.
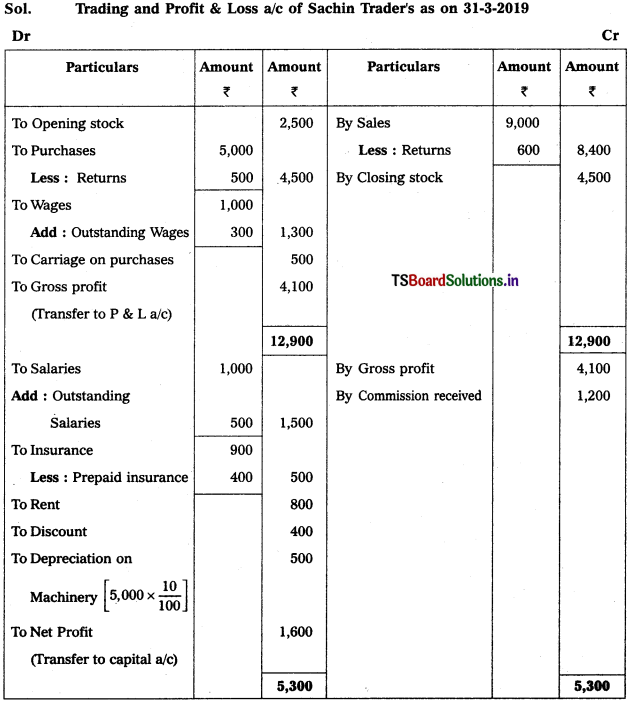
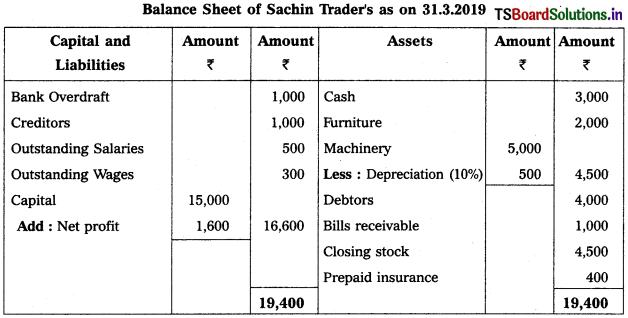
From the following Trial Balance, prepare final accounts of Sachin Trader’s for the year ended 31-3-2019.
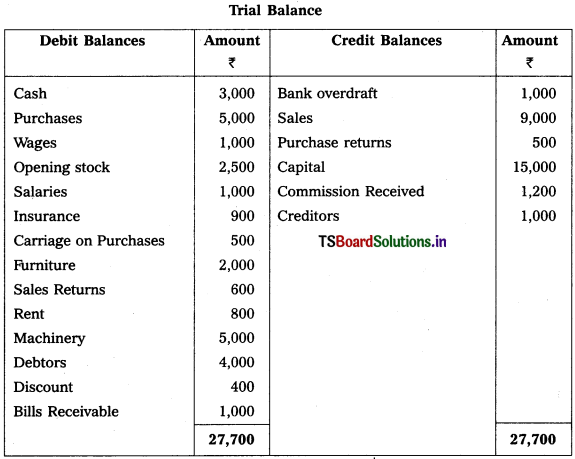
Adjustments :
1) Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 500
2) Closing Stock : ₹ 4,500
3) Prepaid Insurance : ₹ 400
4) Outstanding Wages : ₹ 300
5) Depreciation on Machinery : 10%.
Solution:
![]()
Question 4.
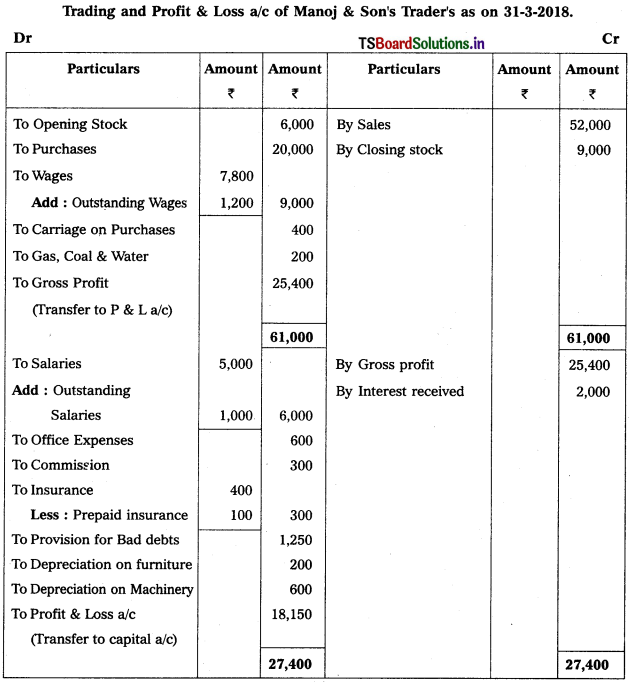
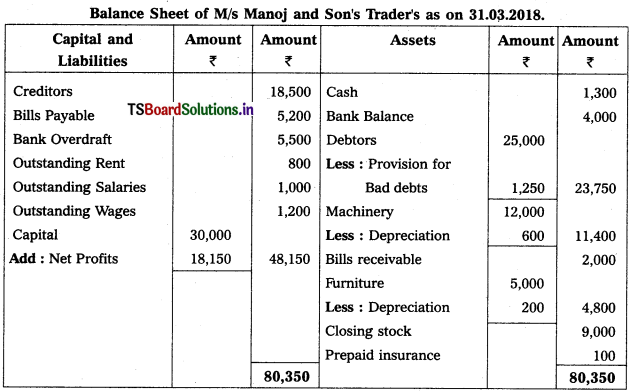
From the following Trial Balance of M/s Manoj & Son’s Trader’s prepare Trading, Profit & Loss a/c and Balance Sheet for the year ended 31-3-2018.
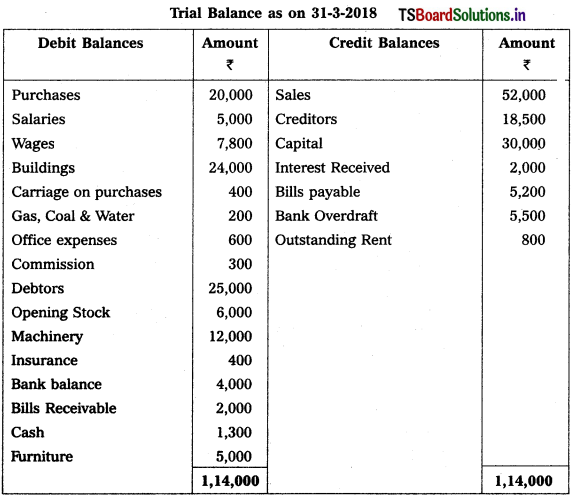
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 9,000
2) Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 1,000
3) Prepaid insurance : ₹ 100
4) Create 5% Provision for Bad Debts
5) Depreciation on Furniture : 200 and on Machinery : 600
6) Outstanding Wages : ₹ 1,200.
Solution:
![]()
Question 5.
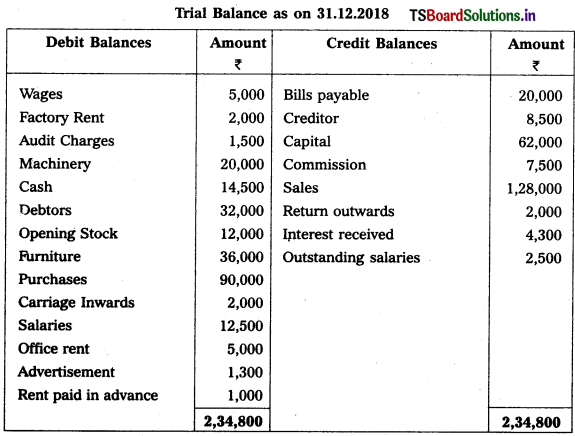
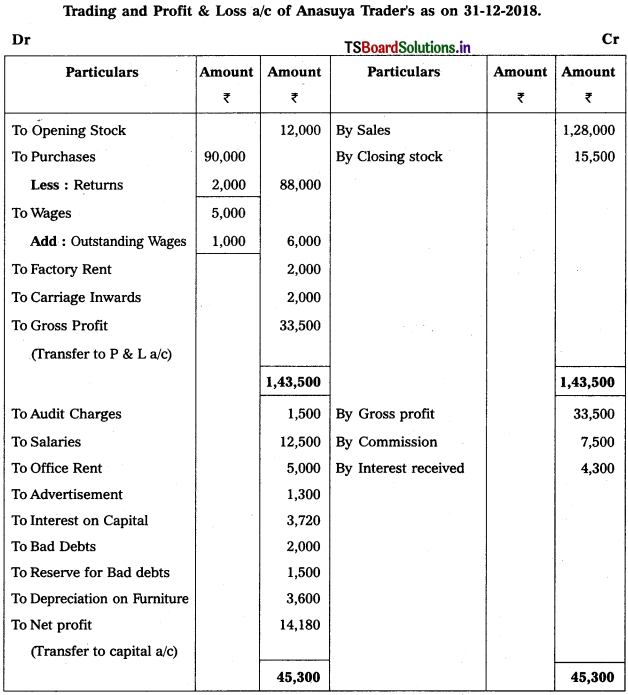
From the following particulars of Anasuya Traders, prepare final accounts for the year ended 31-12-2018.
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 15,500
2) Interest on Capital: 6%
3) Write off ₹ 2,000 as Bad Debt and provide 5% Reserve for Doubtful Debts
4) Outstanding Wages : ₹ 1,000
5) Depreciation on Furniture : 10%.
Solution:
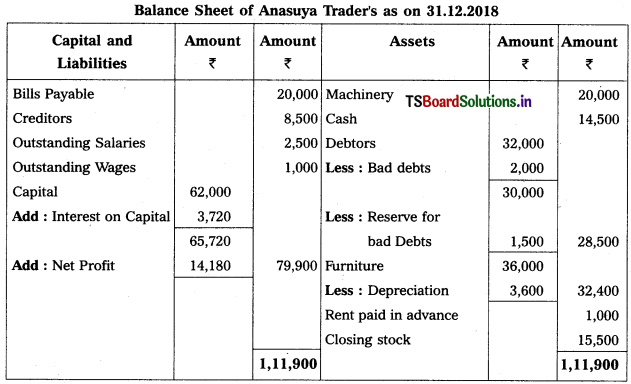
![]()
Question 6.
Prepare Final Accounts from the Trial Balance of Brindavan Business for the year ended 31-3-2019.
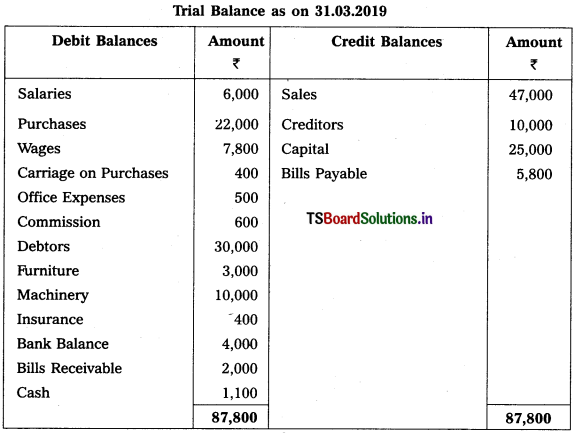
Adjustments :
1) Outstanding Wages : ₹ 2,000.
2) Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 1,000.
3) Prepaid Insurance: ₹ 50.
4) Create 5% Reserve for Bad Debts on Debtors.
5) Depreciation on Furniture ₹ 150 and on Machinery ₹ 500.
6) Closing Stock ₹ 11,000.
Solution:
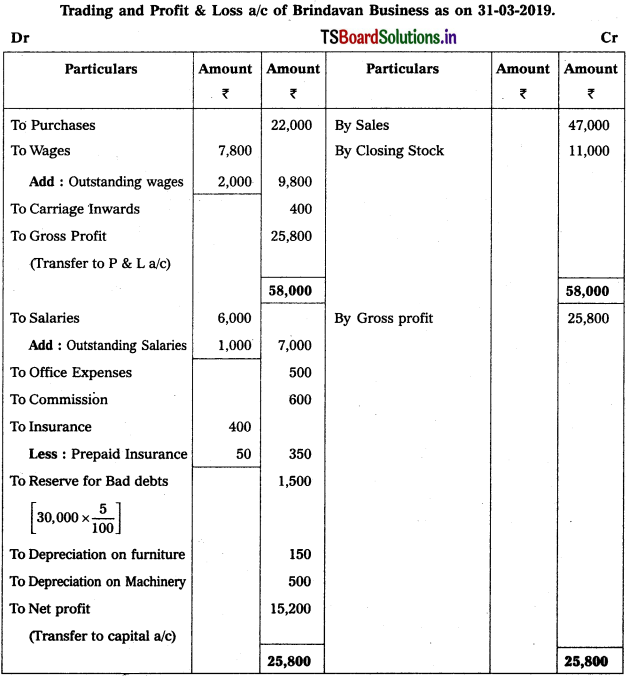
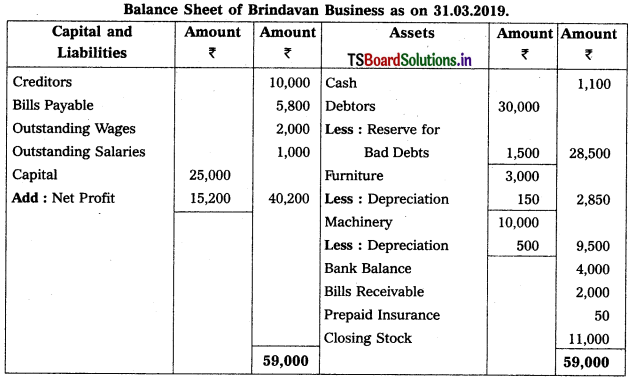
![]()
Question 7.
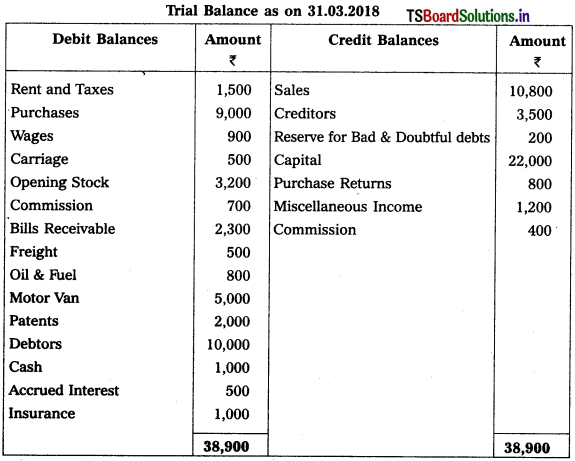
Prepare Final Accounts of Pawan Enterprises for the ending 31-3-2018.
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 6,800.
2) Depreciation of Motor Van : 5%.
3) Reserve for Bad & Doubtful Debts : 6%.
4) Outstanding Rent: ₹ 500
5) Prepaid Insurance ₹ 300
6) Create Reserve for Discount on Creditors : 3%.
Solution:
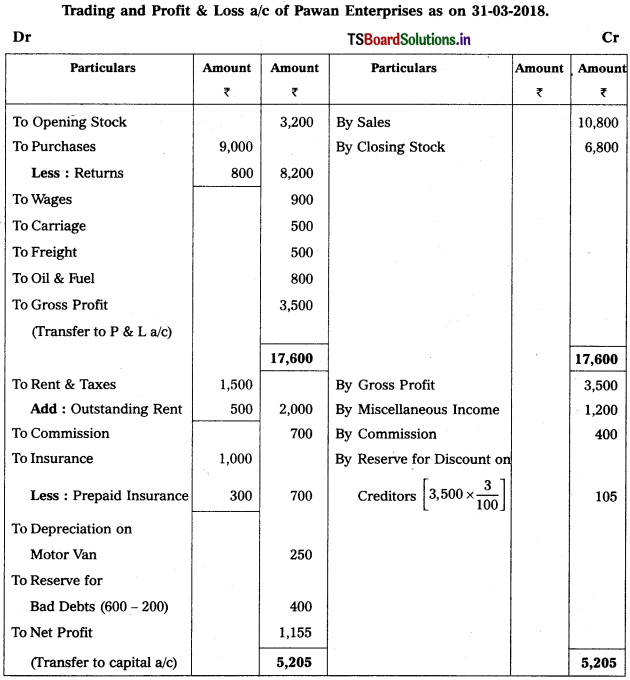
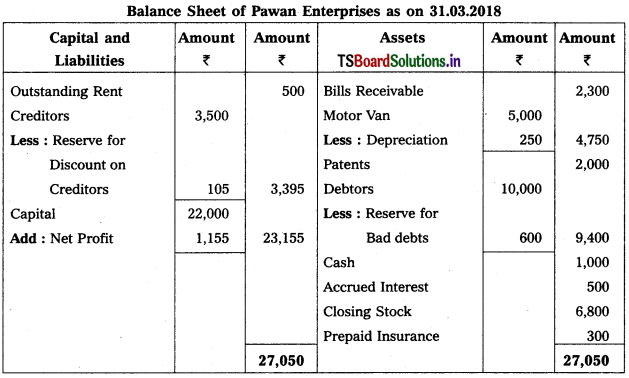
Working Note :
Accounting for Reserve for Bad & Doubtful Debts :
Old Reserve for Bad & Doubtful Debts 200
New Reserve for Bad & Doubtful Debts [10,000 × \(\frac{6}{100}\)] = 600
New RBD is > Old RBD
⇒ 600 – 200 = 400
Accounting Treatment :
1. Debit the difference (New Reserve – Old Reserve) to the Profit & Loss a/c
2. Deduct new provision for bad debts from debtors on assets side of Balance Sheet.
![]()
Question 8.
Prepare Final Accounts from the following Trial Balance of Mamaji Trader’s for the year ended 31-12-2018.
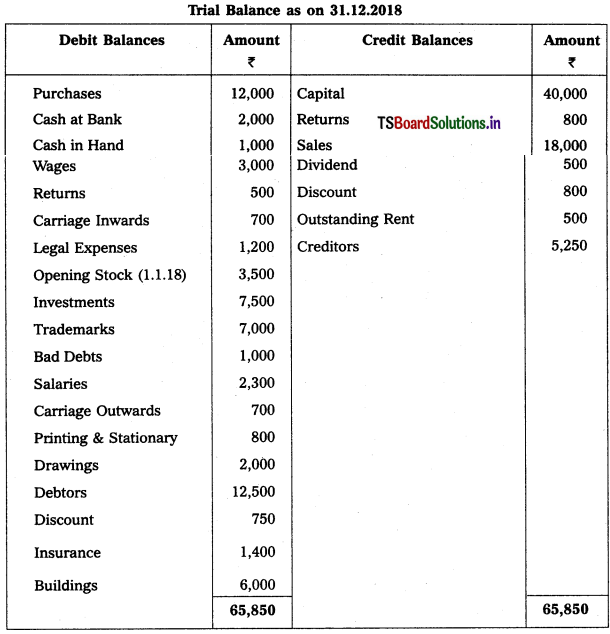
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock (31-12-2018) : ₹ 2,500.
2) Outstanding Stationary : ₹ 600
3) Depreciation on Buildings : 10%.
4) Bad Debts : ₹ 500 and Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts : 5%
5) Prepaid Wages : ₹ 500
6) Interest on Drawings : 6%.
Solution:
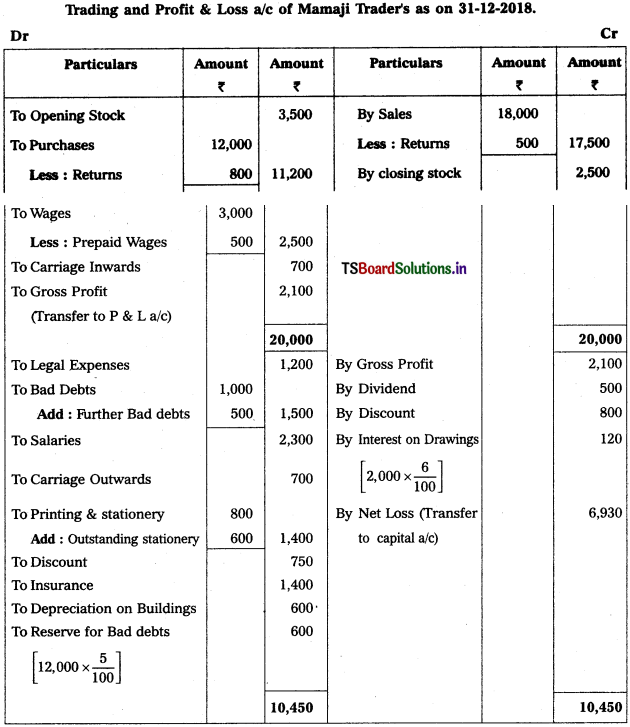
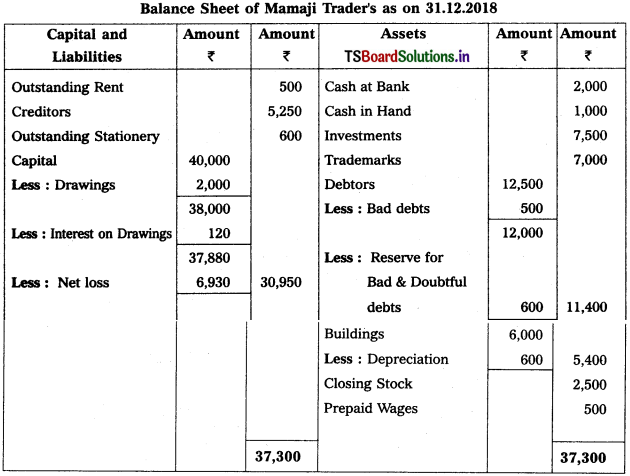
Working Note :
i) Accounting Related with Debtors :
Calculation of Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts = (Debtors – New Bad Debts) (Rate of PBD / 100)
= (12,500 – 500) \(\frac{5}{100}\)
= 12,000 × \(\frac{5}{100}\) = 600
∴ PB & DD = 600.
![]()
Question 9.
From the following Trial Balance of Vinayaka Enterprises, prepare Final Accounts for the year ending 31-12-2018.
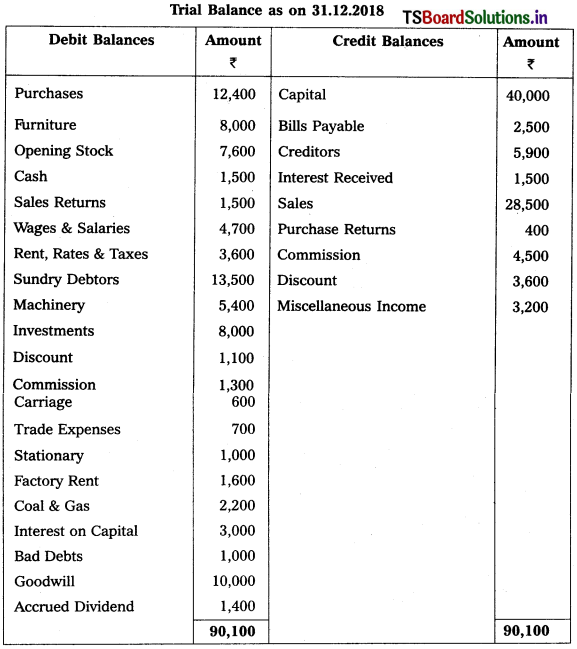
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 10,500.
2) Bad Debts : ₹ 1,500 and Provide Reserve for Doubtful Debts : 5%.
3) Outstanding Factory Rent: ₹ 400.
4) Depreciation of Furniture : 10%.
5) Interest received in advance : ₹ 500.
6) Stock worth of: 10,000 destroyed in fire and Insurance Co. admitted a claim of ? 7,500.
Solution:
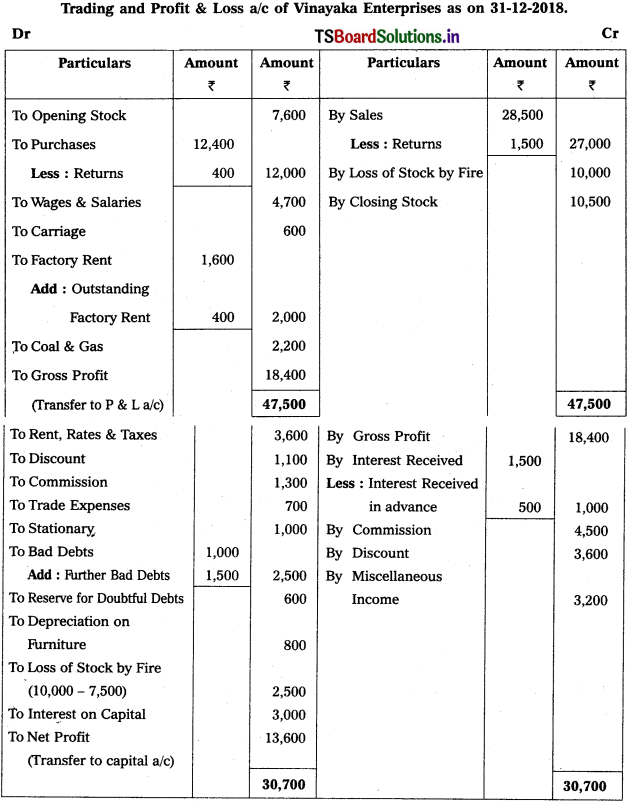
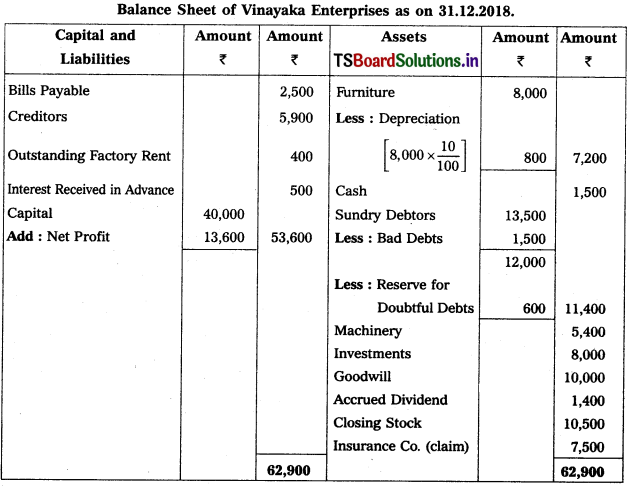
Working Note:
1) Renne for Doubtfùl Debts = (Debtors – New Bad debts) (RDD Rate / 100)
= (13,500 – 1,500) × \(\frac{5}{100}\)
= 12000 × \(\frac{5}{100}\)
∴ RDD = 600.
2) Calculation of actual loss on stock destroyed by fire :
Value of stock destroyed = 10,000
(-) Insurance claim = (-) 7,500
Actual loss = 2,500 (Transfer to P & L a/c).
![]()
Question 10.
Prepare Final Accounts of Raghavendra Trader’s for the year ended 31-12-2019.
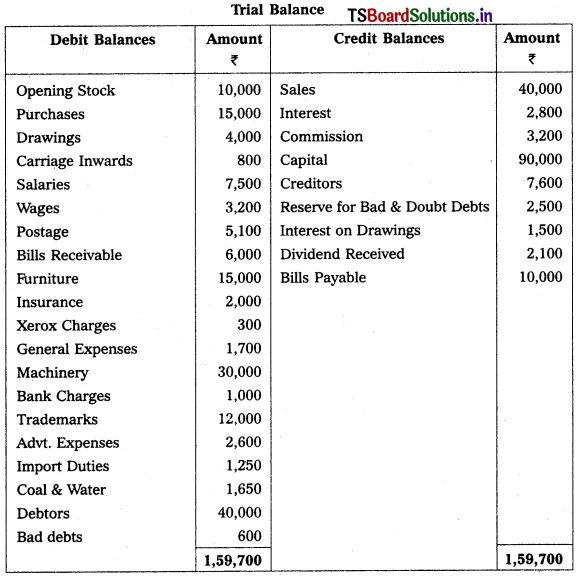
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock Value : ₹ 7,500.
2) Depreciation on Machinery : 10%
3) Commission Received in Advance: ₹ 1,000.
4) Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 1,500.
5) Further Bad Debts : ₹ 400 and Provision for Bad & Doubtful Debts : 5%
6) Good worth of ₹ 5,000 withdrawn by the owner for his personal use.
Solution:

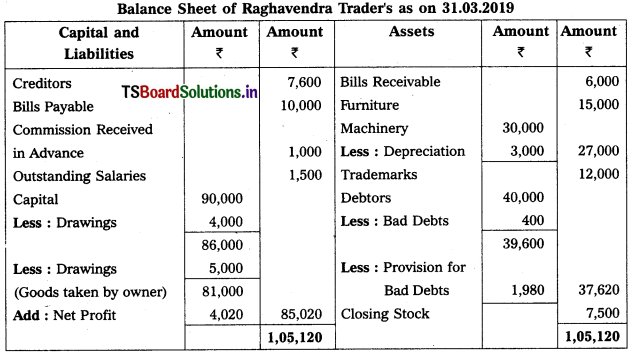
Working Note :
Accounting treatment for provision for Bad & Doubtful debts (PB & DD) :
i) Calculation of new PB & DD = (Debtors – Bad debts) (Rate of PB & DD / 100)
= (40,000 – 400) × \(\frac{5}{100}\)
= 39,600 × \(\frac{5}{100}\) = 1,980
ii) Accounting : Old PB & DD (2,500) > New PB & DD (1,980)
Difference is record on Cr. side of P & L a/c [i.e., 2,500 – 1,980 = 520]
Deduct new PB & DD from Debtors in Balance Sheet [i.e., 1,980].
![]()
Question 11.
Prepare final accounts of Yadadri Trader’s as on 31-12-2018.
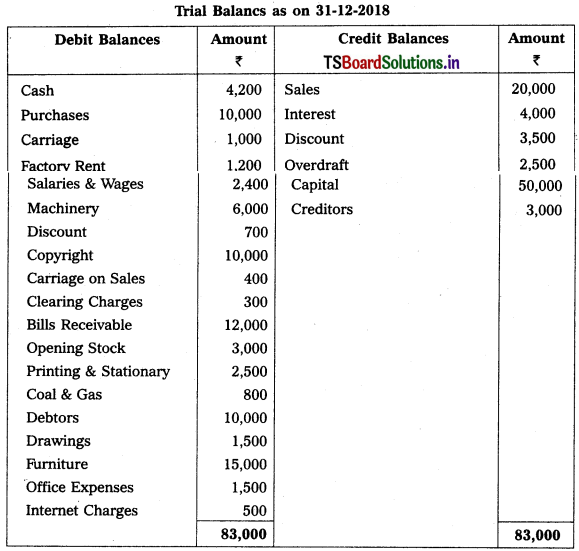
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 6,500.
2) Prepaid Salaries & Wages : ₹ 400
3) Create 6% for Provision for Bad & Doubtful Debts.
4) Depreciation on Machinery : 10%.
5) Interest on Capital: 6%
6) MD’s Commission on Net Profit is 10% before charging such commission.
Solution:
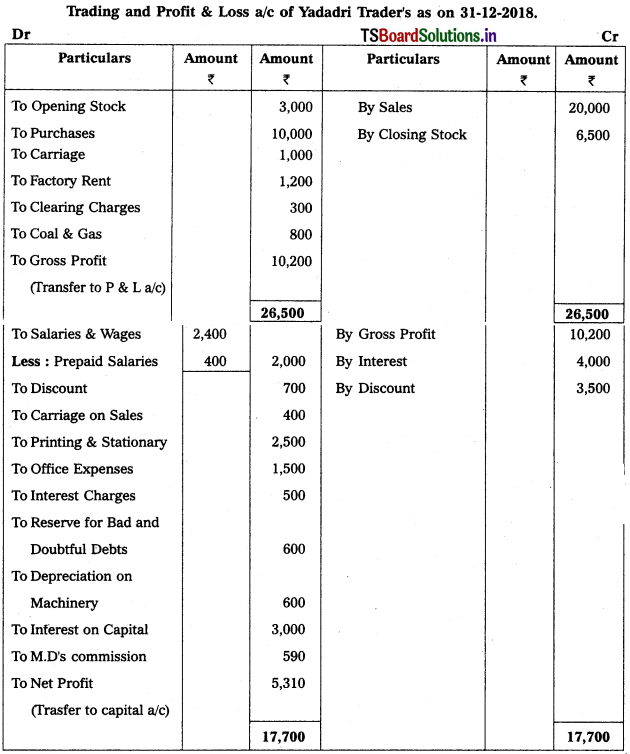
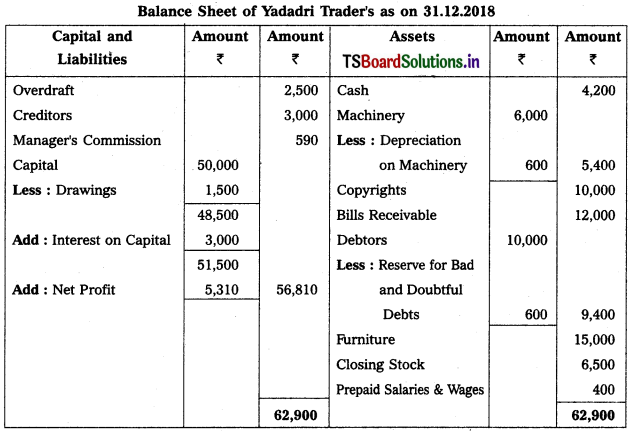
![]()
Working Note :
Calculation of MD’s Commission :
M.D’s commission on Net profit before charging commission
= Net profit before commission × (Rate of commission / 100)
= 5,900 × \(\frac{10}{100}\)
∴ M.D’s Commission = 590.
Question 12.
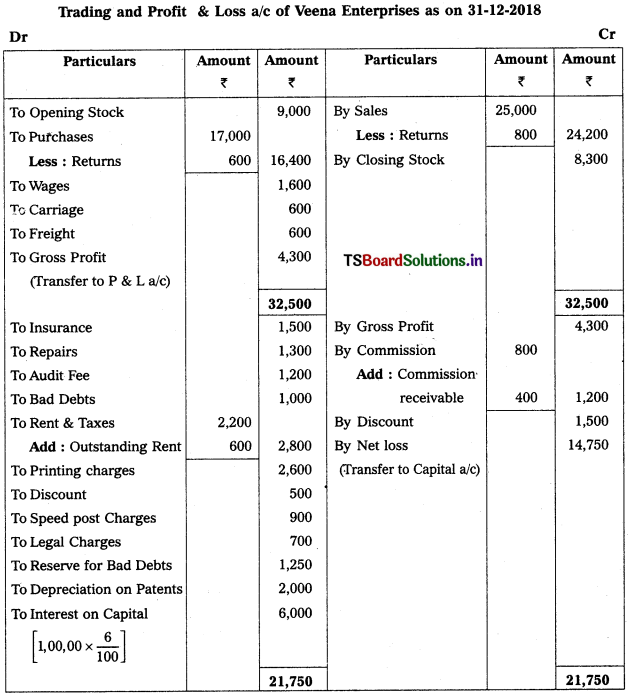
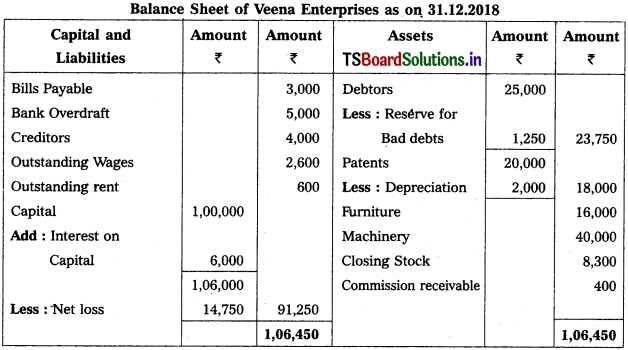
Prepare Veena Enterprises Final Accounts for the year ended 31-12-2018.
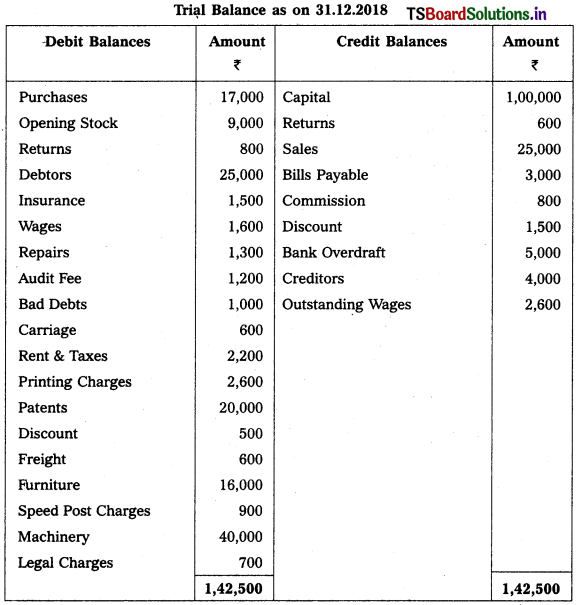
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock Value : ₹ 8,300.
2) Reserve for Bad Debts : 5%
3) Depreciation on Patents 10%
4) Outstanding Rent: ₹ 600
5) Commission Receivable : ₹ 400
6) Interest on Capital: 6%.
Solution:
![]()
Question 13.
Prepare Final Accounts of Srivasthava Traders as on 31-12-2018.
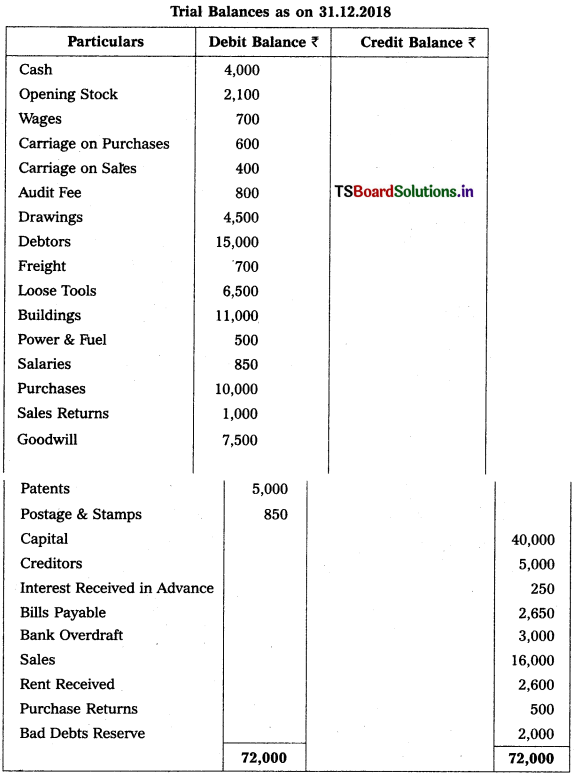
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock Value : ₹ 6,000
2) Outstanding Salary : ₹ 450
3) Interest on Drawings : 10%
4) Provide Reserve for Doubtful Debts : 5% and Create Provision for Discount on Debtors 2%.
5) Depreciation on Buildings : 10%
6) Goods worth of ₹ 2,000 distributed as free samples.
Solution:
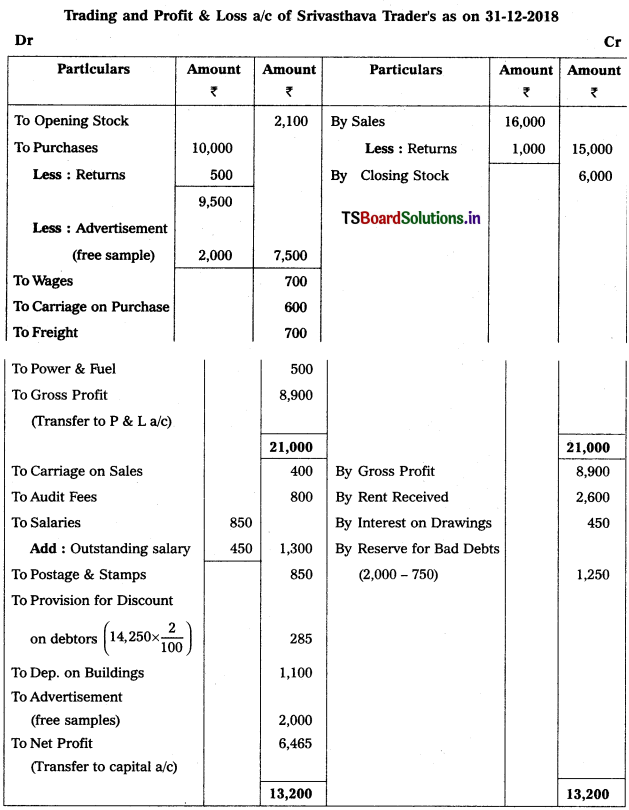
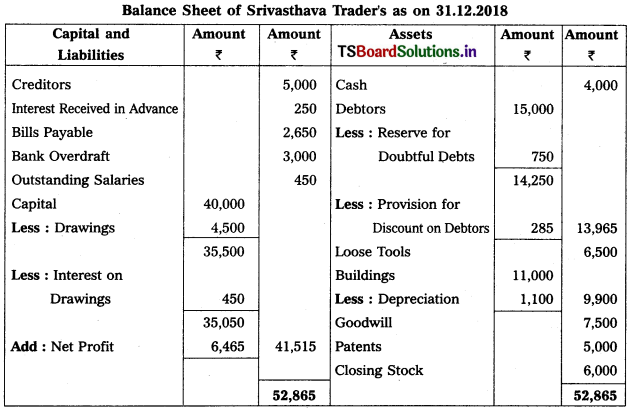
Working Note :
Treatment of Reserve for Doubtful Debts :
Old RDD = 2,000
NewRDD = 15,000 = 750
Old RDD > New RDD
Accounting Treatment :
Difference of Old & New RDD record on Cr. side in profit and loss a/c New RDD deduct from Debtors in Balance Sheet.
![]()
Question 14.
From the following Trial Balance, prepare Final Accounts for the year ended 31-03-2019.
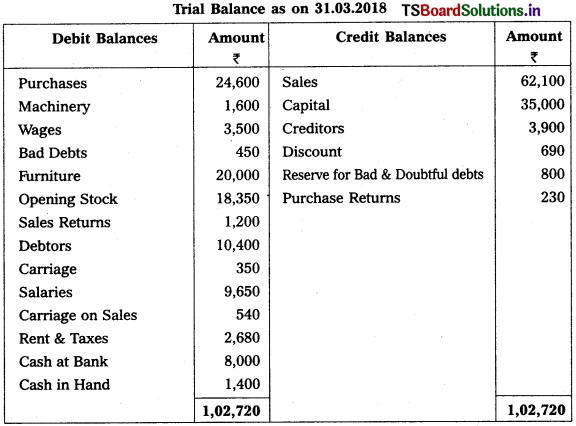
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock Value : ₹ 17,800
2) Outstanding Wages : ₹ 400
3) Prepaid Rent & Taxes : ₹ 380
4) Provide Reserve for Bad & Doubtful Debts on Sundry Debtors 5%.
5) Depreciation on Furniture : 10%
6) Reserve for Discount on Creditors : 5%
Solution:
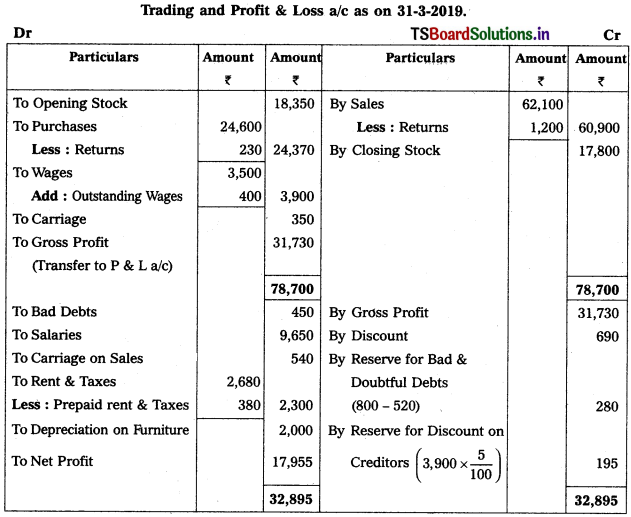
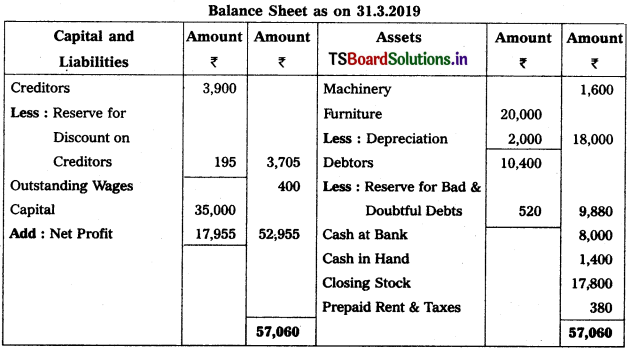
Working Note :
Calculation of New Reserve for Bad & Doubtful Debts (RB & DD) :
New RB & DD = Debtors × RB & DD Rate / 100
= 10,400 × \(\frac{5}{100}\) = 520.
Accounting Treatment :
Old RB & DD <800) > New RB & DD (520)
∴ → Credit the difference (i.e., 800 – 520 = 280) in Profit & Loss a/c.
→ Deduct New RB & DD from Debtors in Balance Sheet.
![]()
Question 15.
From the following Trial Balance of Sudheer Trader’s prepare Final Accounts for the year ended 31-03-2018.
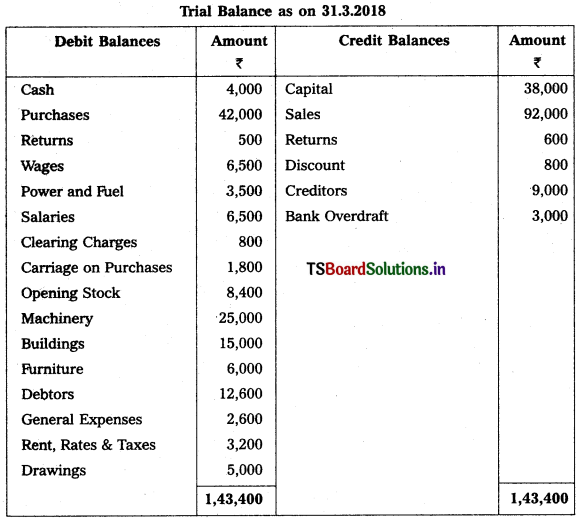
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock Value : ₹ 16,400.
2) Depreciation on Furniture : 5%, on Machinery : 10%
3) Outstanding Wages : ₹ 500.
4) Write off ₹ 600 as Bad Debts and create Provision for Bad & Doubtful Debts : 6%
5) Interest on Drawings : 5%
6) Stock worth of ₹ 12,000 destroyed by fire and Insurance Company admitted a cliam of ₹ 8,500.
Solution:
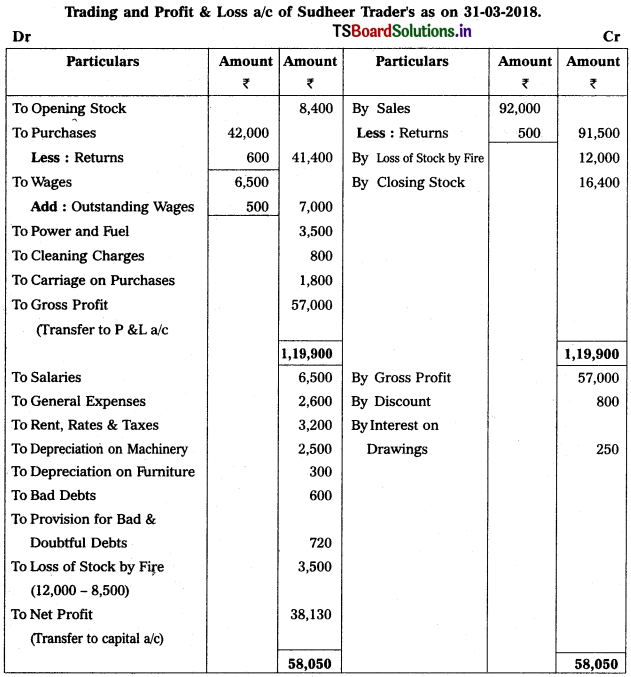
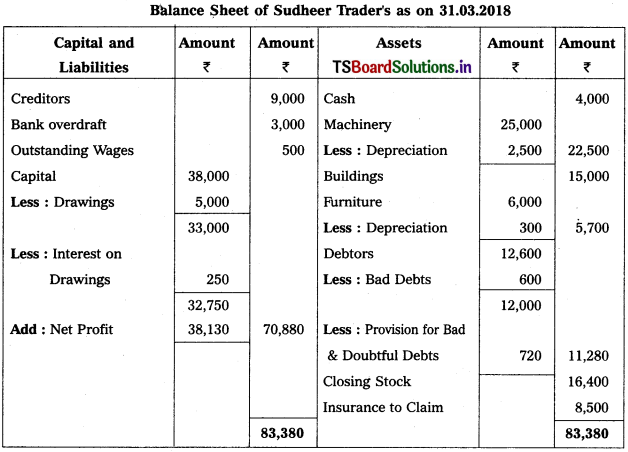
Working Note :
Calculation of Actual loss of goods by fire :
Value of goods/stock destroyed by fire = 12,000
(-) Insurance claim = (-) 8,500
Actual loss = 3,500
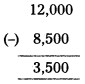
Accounting Treatment :
→ Deduct total loss from purchases in trading a/c (i.e., 12,000)
→ Debit actual loss (ie 3,500) in Profit & Loss a/c.
![]()
Question 16.
Prepare Final Accounts for the year ended 31-03-2018.
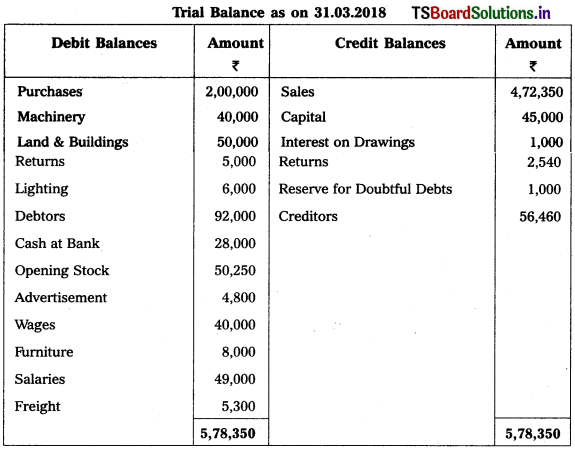
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock Value : ₹ 53,000.
2) Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 5,000.
3) Bad Debts : ₹ 2,000, Create Reserve for Bad Debts : 5% and Provision for Discount on Debtors : 2%.
4) Depreciation on Machinery : 5%
5) Lighting : Factory ₹ 4,000 and Office ₹ 2,000.
6) Manager’s Commission is 10% on Net Profit after charging such commission.
Solution:
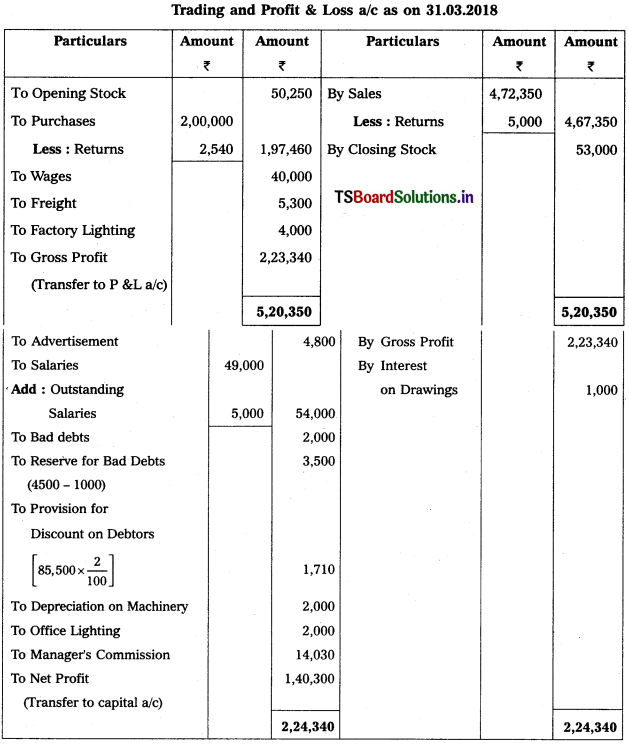
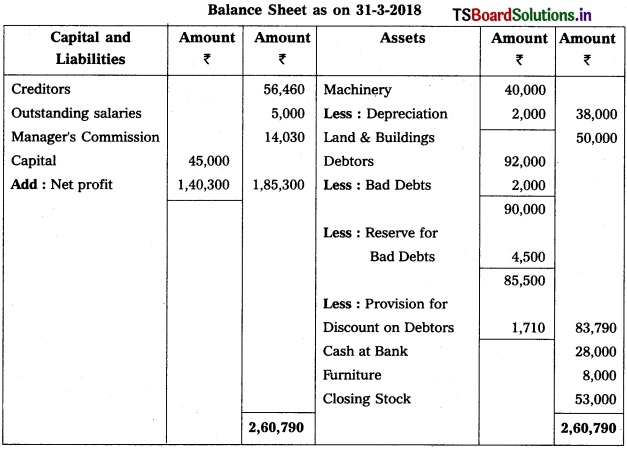
Working Note :
1. Calculation of Manager’s commission on net profit after charging such commission:
Manager s commission = Net profit before commission × (Rate of commission / (100 + Rate of commission))
= 1,54,330 × \(\frac{10}{100+10}\)
= l,54,330 × \(\frac{10}{110}\) = 14,030.
2. Accounting treatment for RDD :
Old RDD (1000) < New RDD (4500)
→ Debit the difference (3,500) on Profit & Loss a/c.
→ Deduct New RDD (4,500) from Debtors in Balance Sheet.
![]()
Question 17.
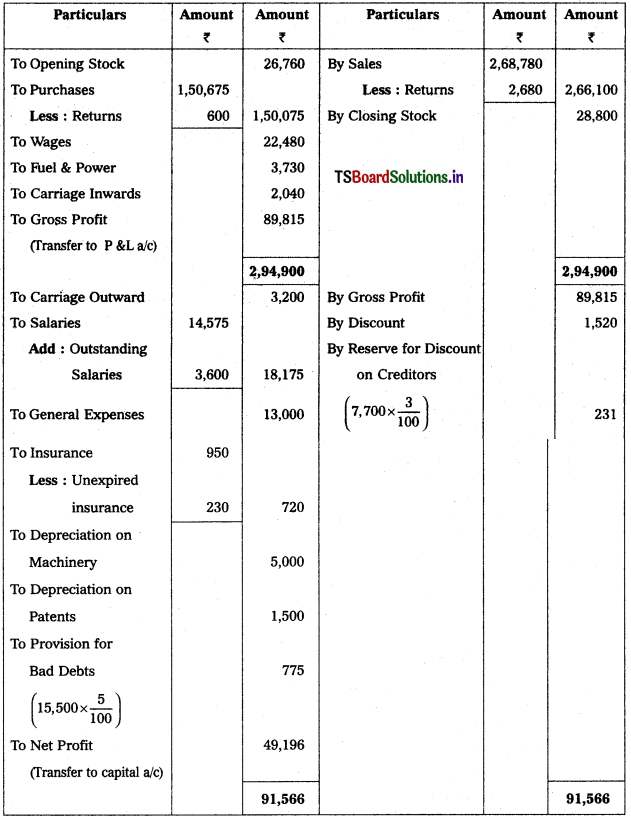
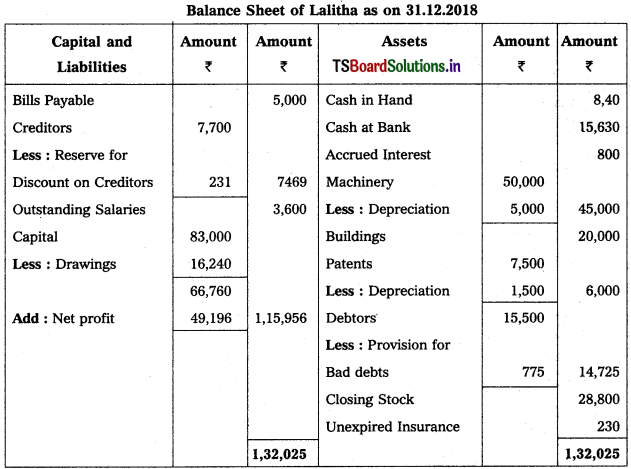
From the following Trial Balance and additional information of Lalitha, prepare Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st Dec. 2018 and Balance Sheet as on that date.
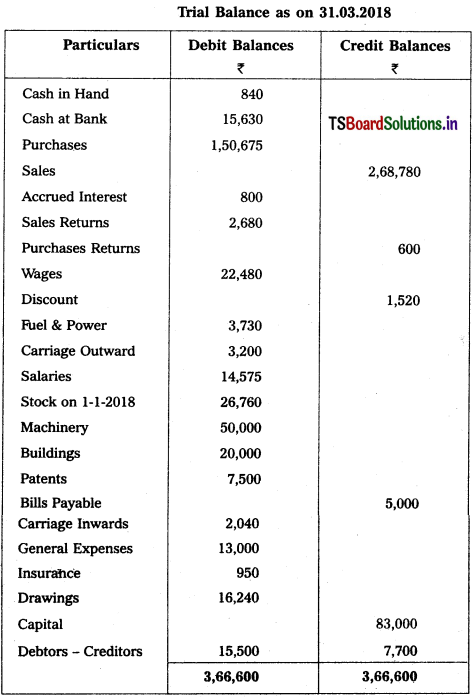
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 28,800.
2) Depreciate 10% on Machinery and 20% on Patents.
3) Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 3,600.
4) Unexpired Insurance : ₹ 230.
5) Create 5% Provision for Bad Debts on Debtors.
6) Create 3% Resere for Discount on Creditors.
Solution:
Trading and Profit & Loss a/c of Lalitha as on 31.12.2018.
![]()
Question 18.
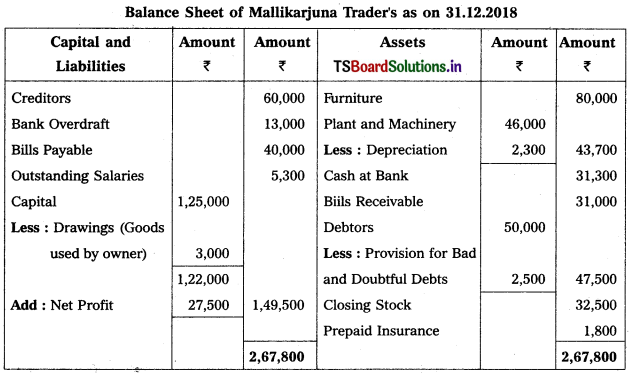
From the following Trial Balance of Mallikaijuna Trader’s prepare the Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet for the year ended 31-12-2018.
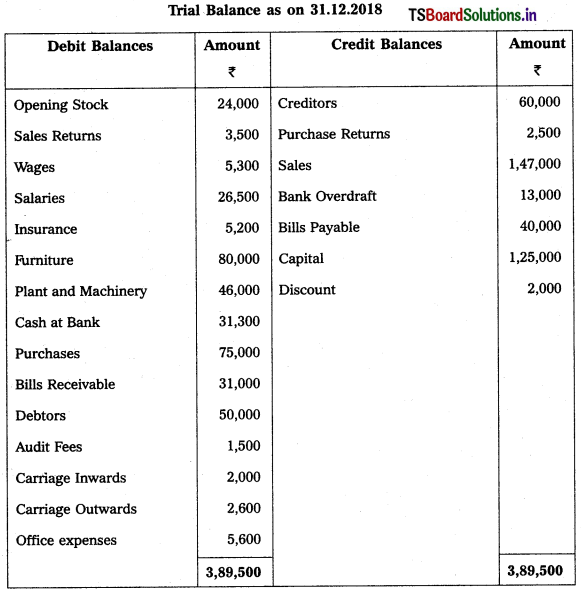
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 32,500.
2) Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 5,300.
3) Depreciate Plant and Machinery by 5%.
4) Prepaid Insurance ₹ 1,800.
5) 5% Provision is to be made for Bad and Doubtful Debts.
6) Goods worth of ₹ 3,000 used by Owner for his personal use.
Solution:
Trading and Profit & Loss a/c of Mallikaijuna Trader’s as on 31.12.2018
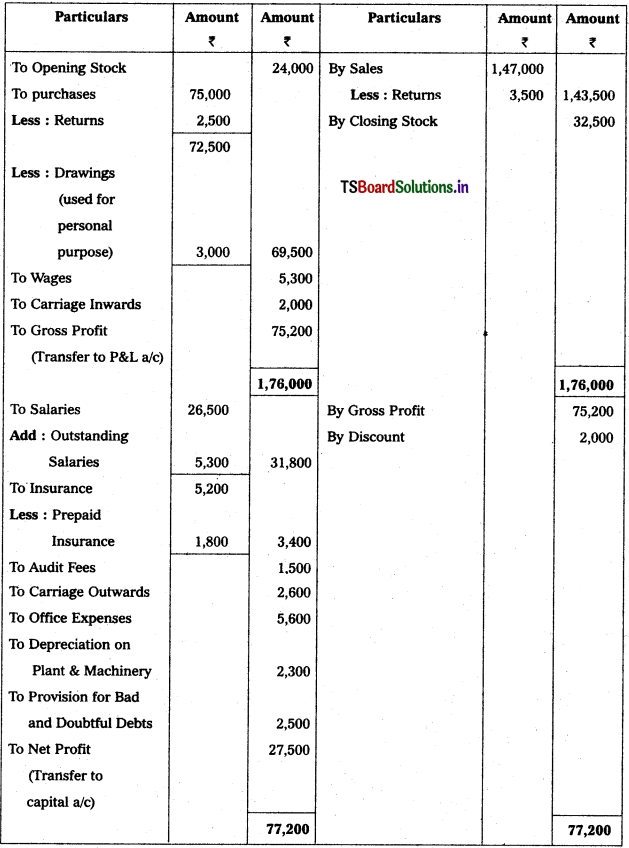
![]()
Question 19.
From the following Trial Balance, prepare final accounts of Sri Raja Rajeshwara Traders as on 31-3-2019.
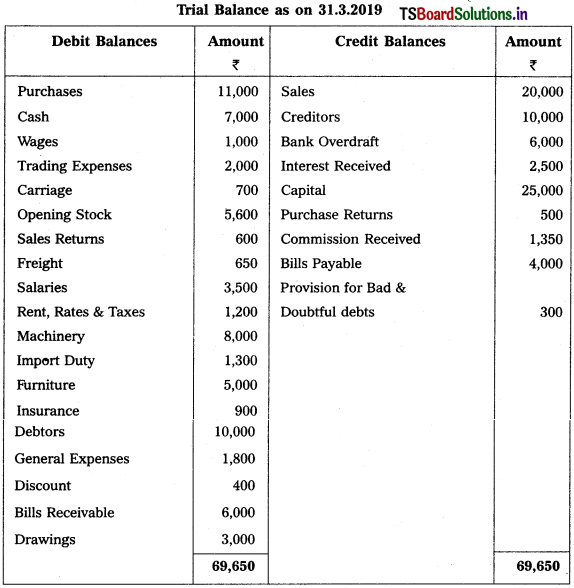
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 7,500.
2) Outstanding Wages : ₹ 400.
3) Accrued Interest: ₹ 600
4) Interest on Capital: 6%.
5) Write off ₹ 1,000 as Bad Debts and create 6% Provision for Bad & Doubtful Debts
6) Depreciation on Furniture : 10%.
Solution:
Trading and Profit & Loss a/c of Sri Raja Rajeswara Trader’s as on 31.3.2019
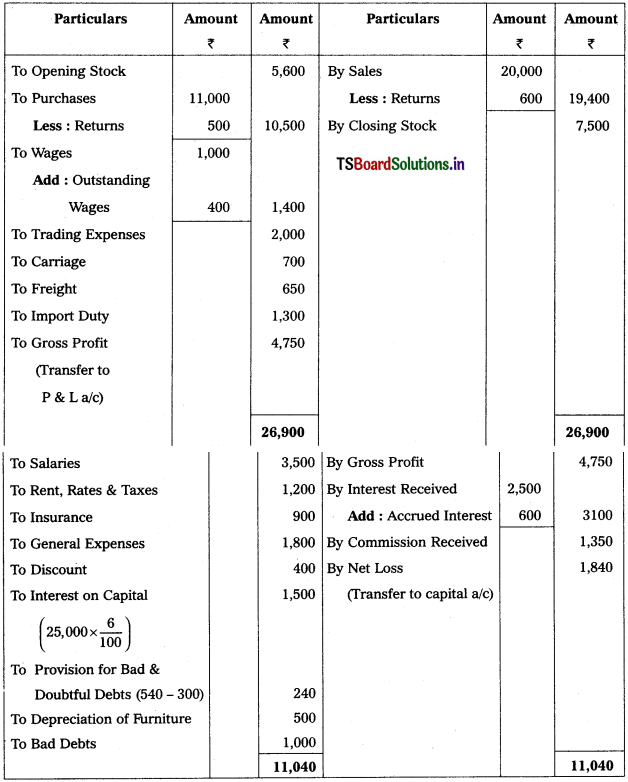
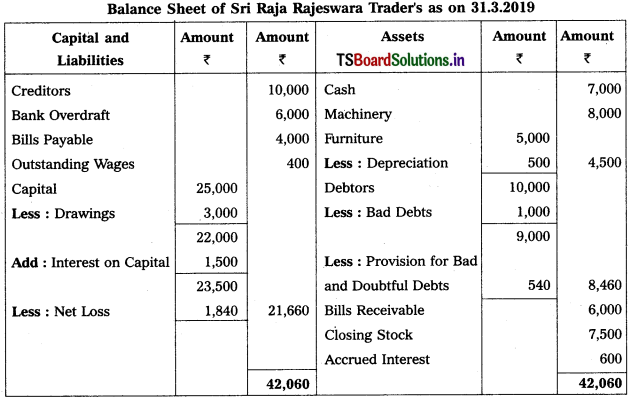
Working Note :
Calculation of New provision for Bad & Doubtful Debts (PB&DD)
New PB & DD = (Debtors – Bad debts) × (Rate of PB&DD / 100)
= (10,000 – 1,000) \(\frac{6}{100}\)
= 9000 × \(\frac{4}{4}\) = 540.
Accounting Treatment:
Old PB & DD (300) < New PB & DD (540)
→ Debit the difference (540 – 300 = 240) in profit & loss a/c.
→ Deduct New PB & DD (540) from Debtors in Balance Sheet.
![]()
Question 20.
From the Trial Balance of M/s Sathyam Trader’s, prepare Trading and Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet for the year ended 31-3-2018.
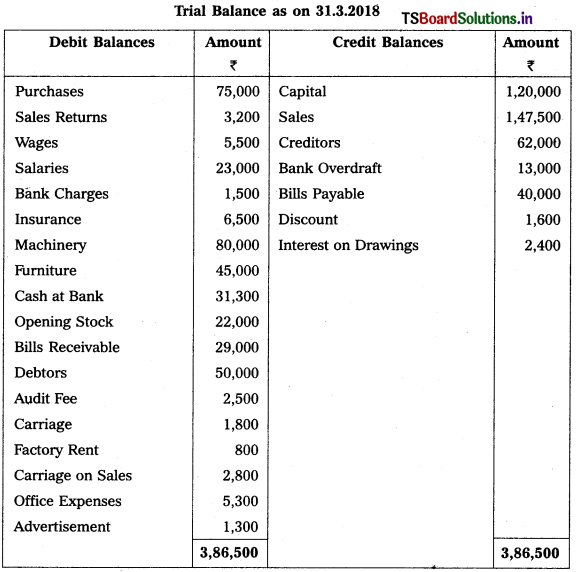
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 34,500.
2) Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 5,500.
3) Depreciation on Machinery : 5%.
4) Prepaid Insurance : ₹ 1,500.
5) Provide for Bad Debts : 5%.
Solution:
Trading and Profit & Loss a/c of M/s Sathyam Trader’s as on 31.3.2018
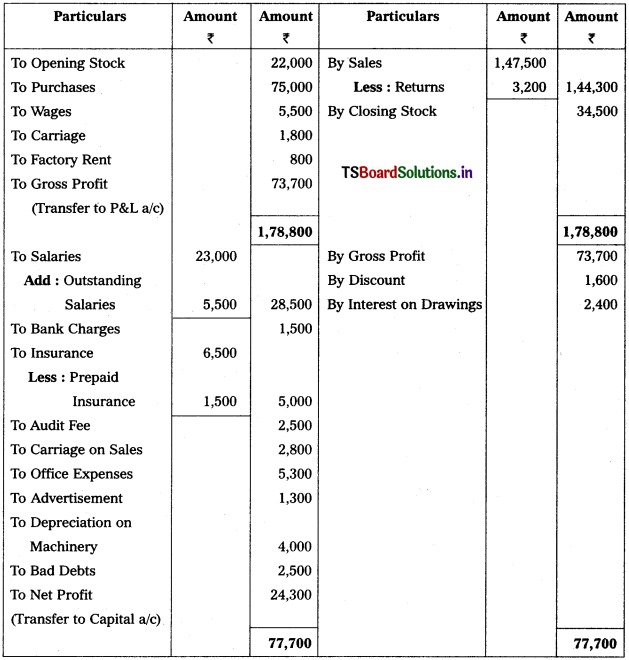
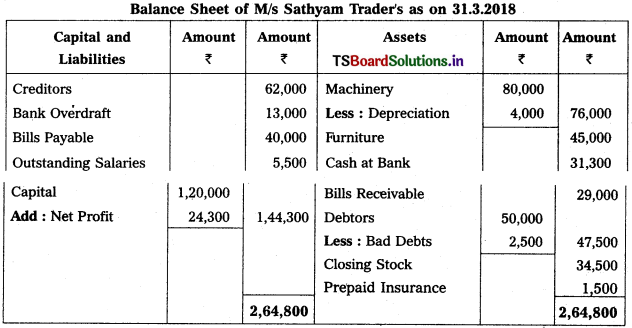
Working Note :
1. Calculation of Depreciation on Machinery = 80,000 × \(\frac{5}{100}\) = 4,000.
2. Calculation of Bad Debts = 50,000 × \(\frac{5}{100}\) = 2,500.
![]()
Textual Examples:
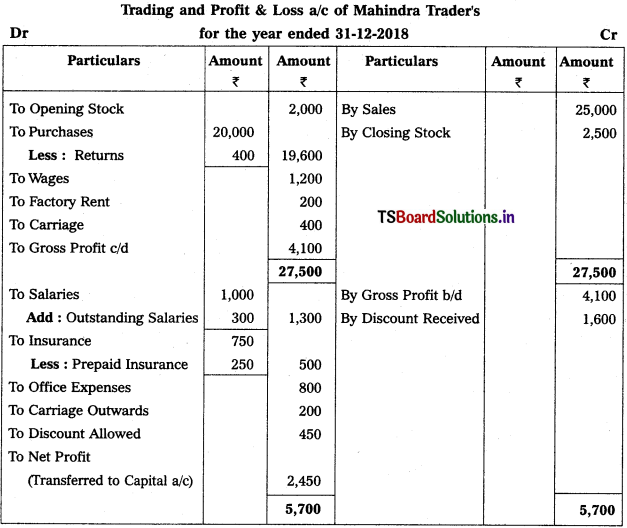
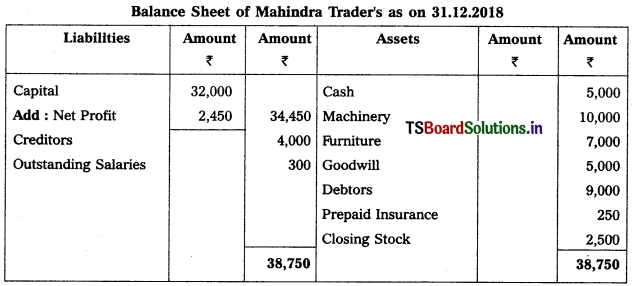
Question 1.
From the following trial balance of Mahindra Traders, prepare final accounts for the year ended 31.12.2018.
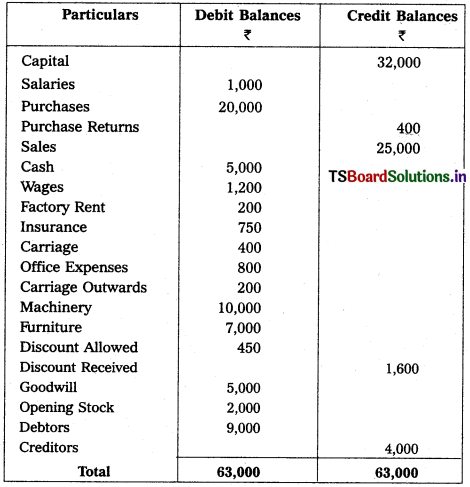
Adjustments :
(1) Value of Closing Stock ₹ 2,500
(2) Prepaid Insurance ₹ 250
(3) Outstanding Salaries ₹ 300
Solution:
![]()
Question 2.
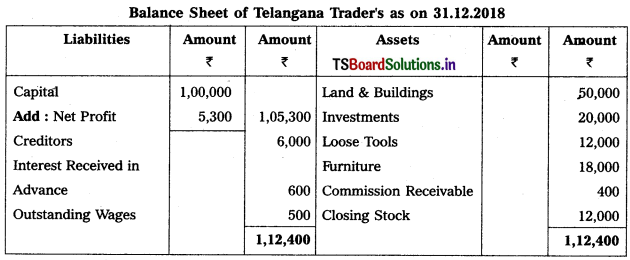
Prepare Final Accounts of Telangana Traders for the year ended 31.12.2018.
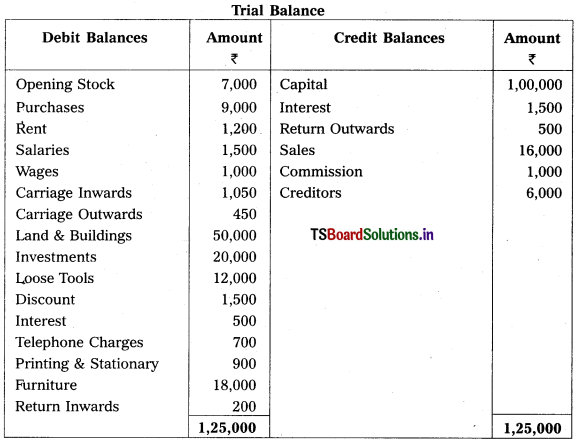
Solution:
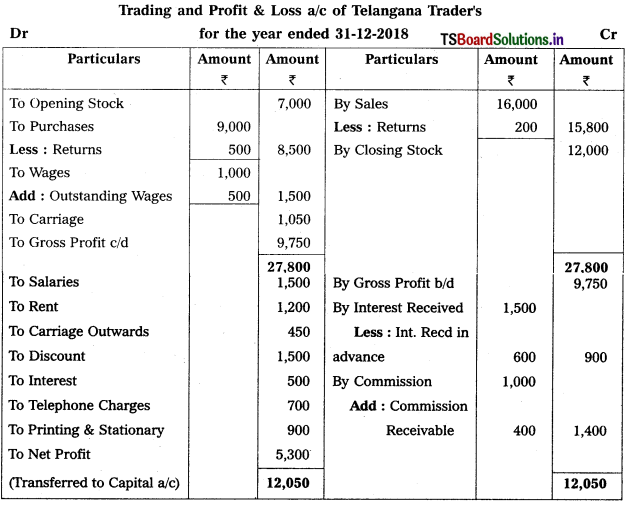
![]()
Question 3.
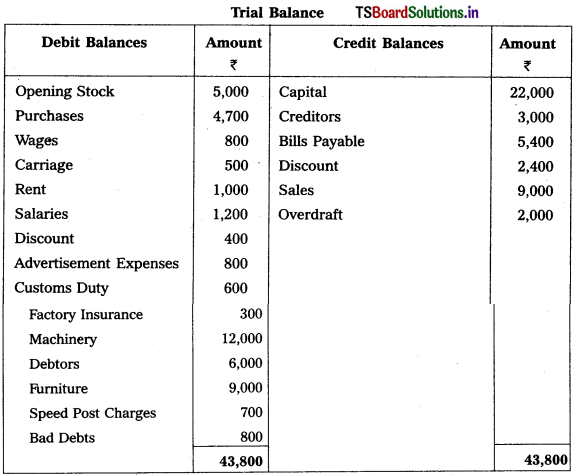
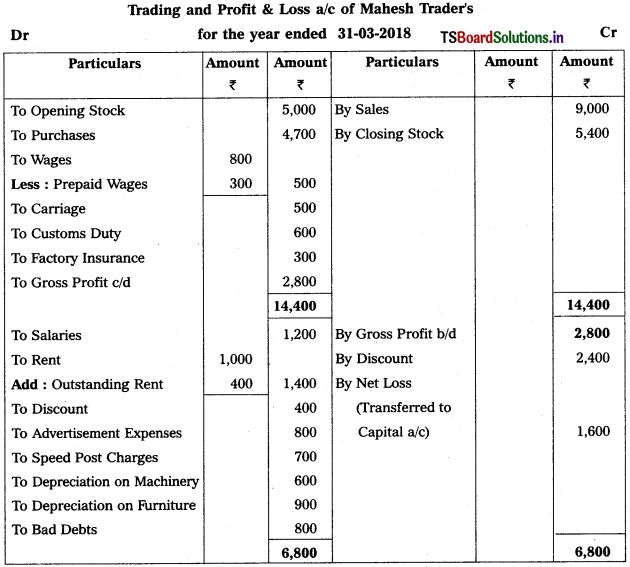
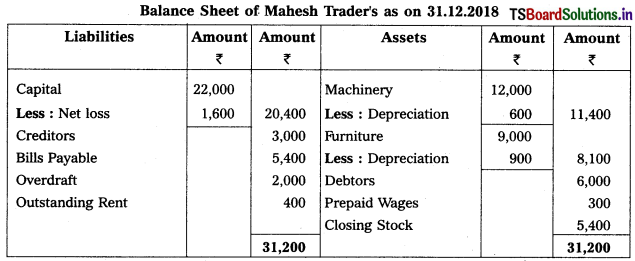
From the following trial balance, prepare Mahesh Trader’s final accounts for the year ended 31.03.2018 :
Adjustments :
1) Values of Closing Stock : ₹ 5,400
2) Prepaid Wages : ₹ 300
3) Outstanding Rent: ₹ 400
4) Depreciation on Machinery : 5%, Depreciation on Furniture : 10%.
Solution:
![]()
Question 4.
From the following Trial Balance of Warangal Trader’s, prepare final accounts for the year ended 31.12.2018.
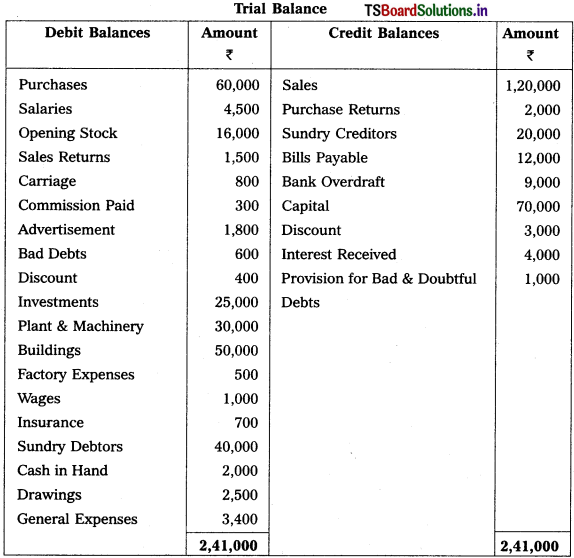
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock ₹ 15,000.
2) Outstanding Wages ₹ 600; Accrued Interest ₹ 1,000.
3) Unexpired Insurance ₹ 200.
4) Depreciation on Plant & Machinery is 10%.
5) Bad Debts to written off ₹ 1,000 and provide 5% for Bad and Doubtful Debts.
6) Create 2% Provision for Discount on Debtors and on Creditors.
Solution:
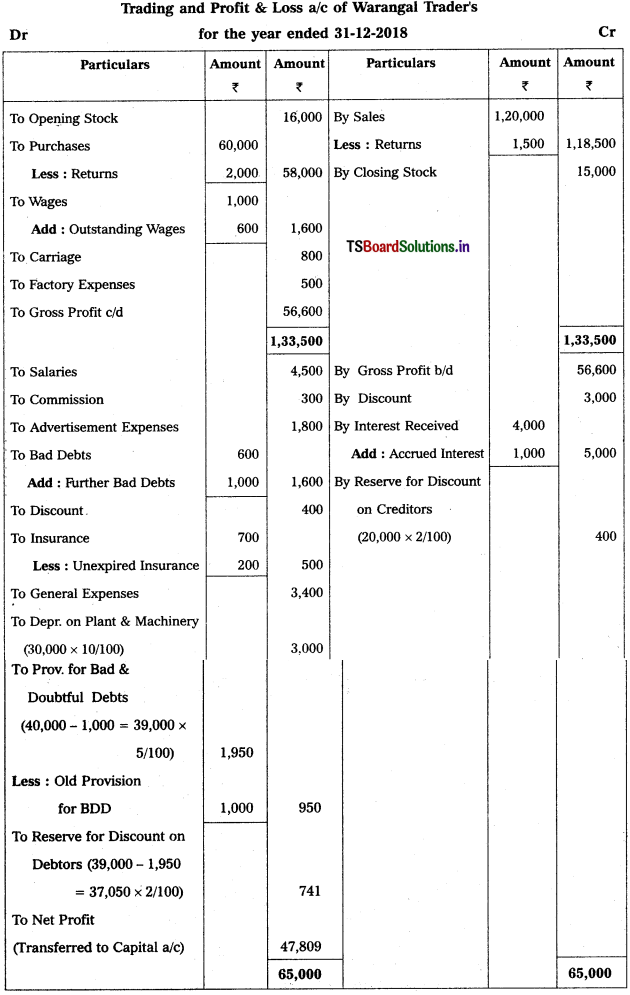
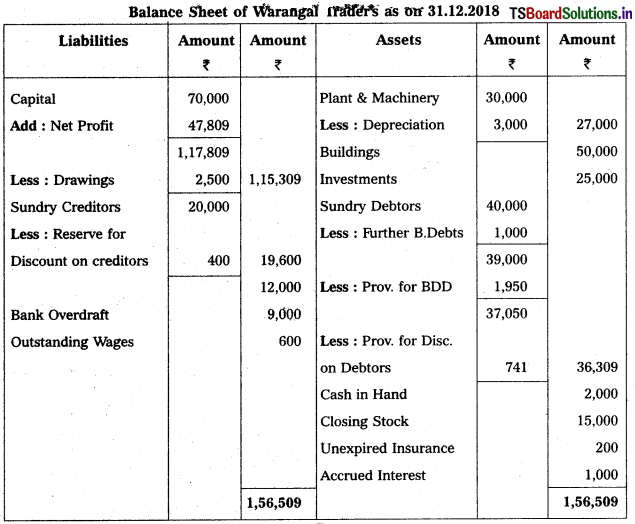
![]()
Question 5.
From the following trial balance, and adjustments, prepare final accounts of Revanth Traders as on 31.03.2019.
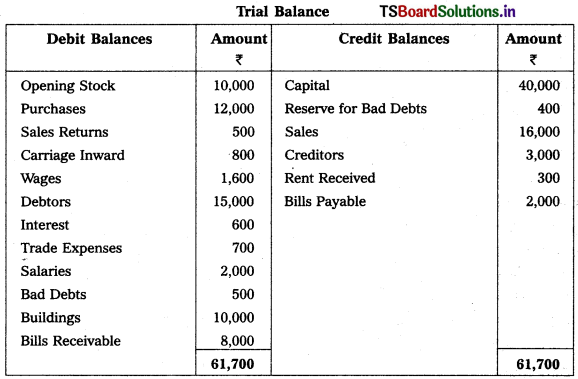
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : 15,000.
2) Reserve for Bad Debts : 5%.
3) Goods worth of ₹ 1,000 withdrawn by owner for his personal use.
4) Stock destroyed by fire ₹ 6,000 and Insurance company admitted a claim to the extent of ₹ 4,500.
5) Manager’s Commission is 5% on net profit after charging such commission.
6) Goods worth of ₹ 300 distributed as free samples.
Solution:
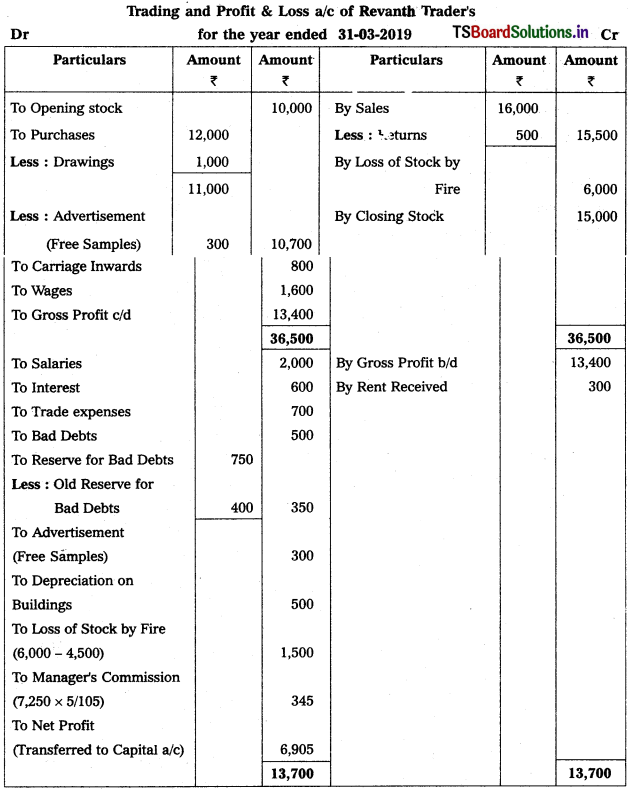
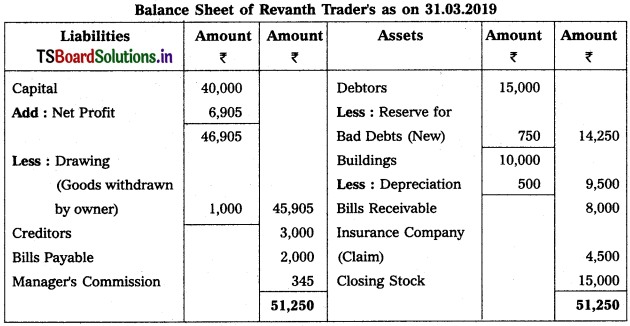
![]()
Question 6.
Prepare final accounts of Mahathi Trader for the year ending 31.03.2018.
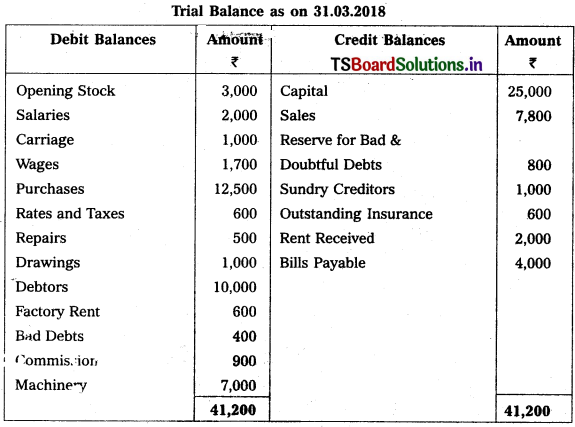
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 6,000
2) Reserve for Bad and Doubtful Debts : 5%
3) Interest on Capital: 5%
4) Outstanding Wages : ₹ 300
5) Depreciation on Machinery : 5%.
Solution:
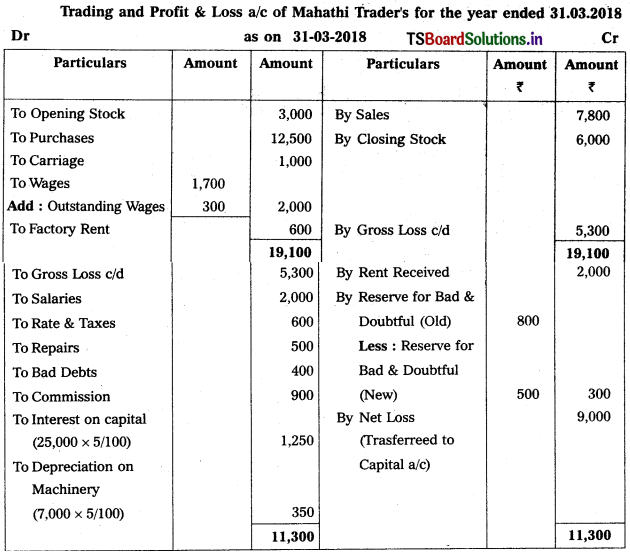
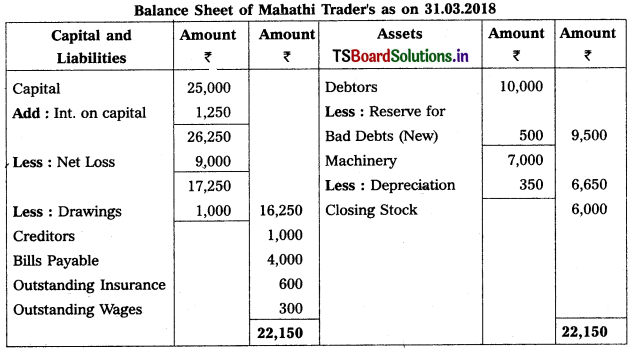
![]()
Question 7.
From the following trial balance, prepare final accounts of Shankari Traders for the year ending 31.12.2018.
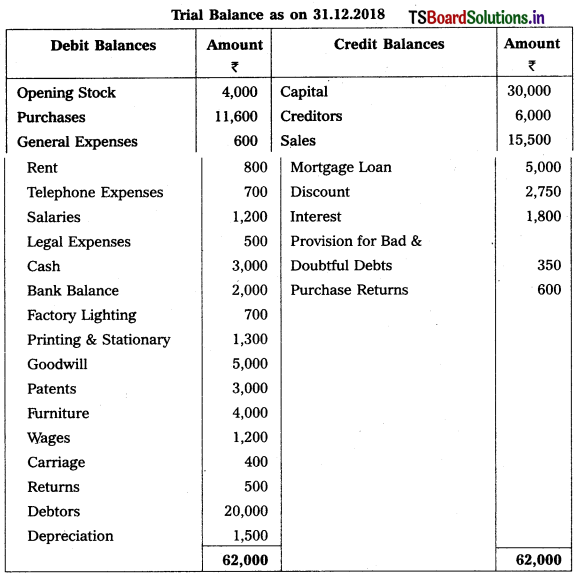
Adjustments :
1) Closing Stock : ₹ 6,500
2) Prepaid Salaries : ₹ 600
3) Accrued Interest: ₹ 200
4) Write off Bad Debts : ₹ 1,000, Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts : 5% and Provision for Discount on Debtors : 2%.
5) Reserve for Discount of Creditors : 2%.
6) Stock of worth ₹ 3,000 destroyed in Fire and Insurance Company admitted a claim of ₹ 1,500
Solution:
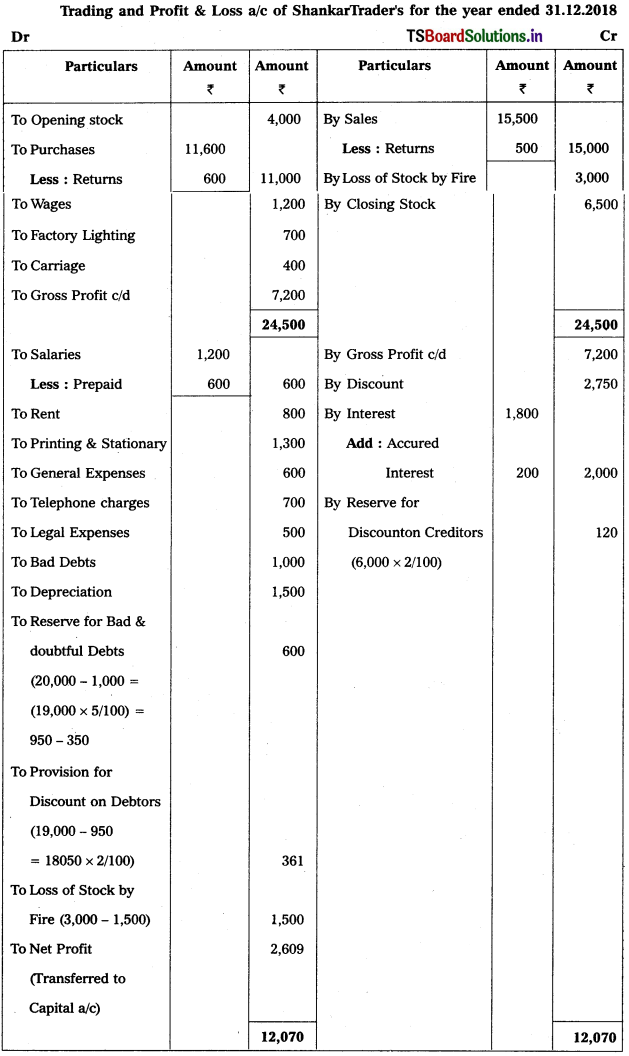
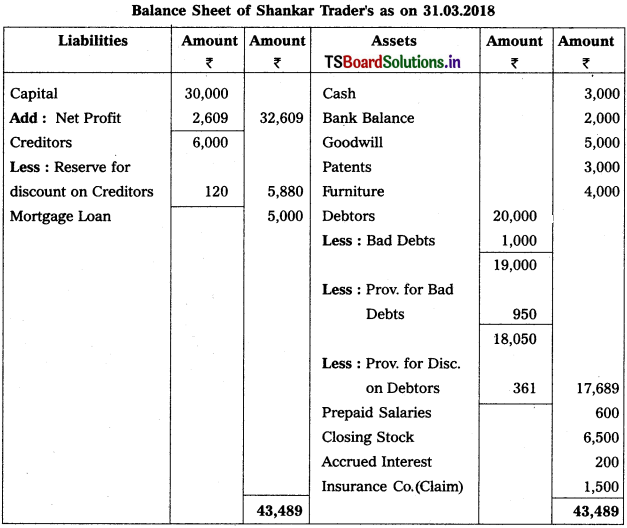
Question 8.
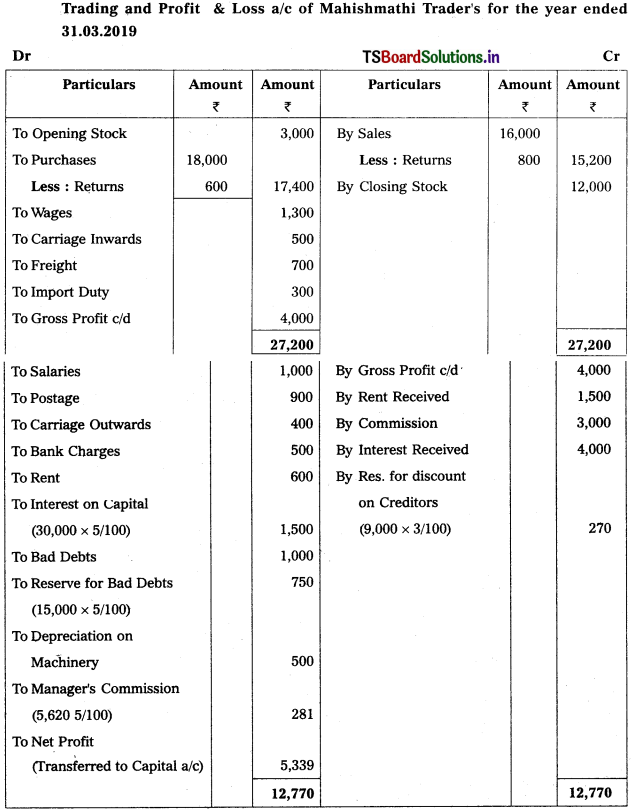
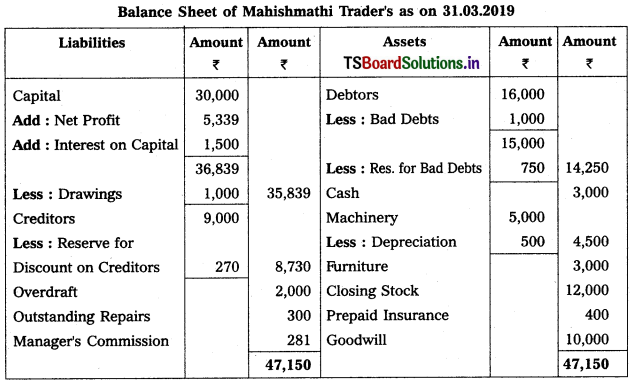
From the following trial balance of Mahishmathi Traders, prepare final accounts for the year ended 31.03.2019.
Trial Balance as on 31.03.2019
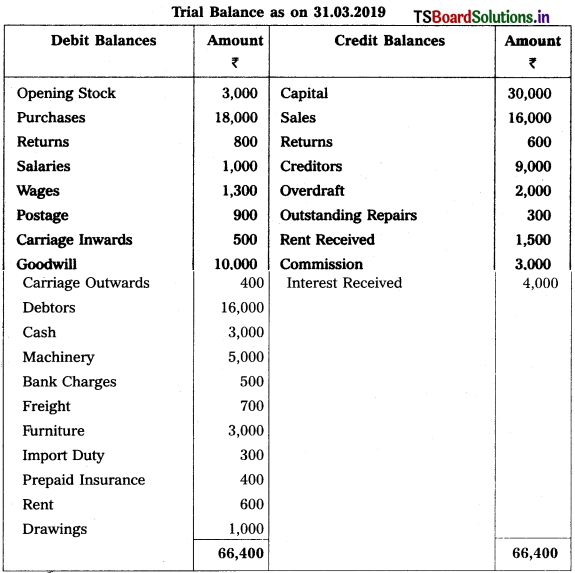
Adjustments :
1) Closing stock : ₹ 12,000
2) Interest on capital : 5%
3) Bad Debts : 1000 and Reserve for Bad Debts : 5%
4) Depreciation on Machinery : 10%
5) Manager’s Commission is 5% on net profit before charging such commission.
6) Reserve for Discount on Creditors : 3%
Solution: