The multiple-choice format of TS 6th Class Science Bits with Answers 11th Lesson Water in Our Life allows students to practice decision-making and selecting the most appropriate answer.
TS 6th Class Science Bits 11th Lesson Water in Our Life
Question 1.
A unit for measuring volumes of liquids
A) gallon
B) litre
C) cusecs
D) all
Answer:
D) all
![]()
Question 2.
Water level in the reservoirs is measured in ………………….
A) miles
B) feet
C) centimetres
D) milli metres
Answer:
B) feet
Question 3.
Water released from dams and projects during floods is measured in
A) cusec
B) litres
C) gallons
D) A and C
Answer:
A) cusecs
Question 4.
Liquids are measured in ……………..
A) centimetres
B) milli metres
C) gallons
D) metres
Answer:
C) gallons
Question 5.
Long periods of less rainfall causes
A) floods
B) droughts
C) cyclones
D) mansoons
Answer:
B) droughts
Question 6.
One of the following is not a reason for scarcity of water
A) deforestation
B) lack of rains
C) drying of water bodies
D) heavy floods
Answer:
D) heavy floods
![]()
Question 7.
Excessive rainfall in an area leads to
A) drought
B) floods
C) migration
D) none
Answer:
B) floods
Question 8.
Factors responsible for floods are
A) Intensity and duration of rainfall
B) Soil condition
C) Presence of plants or trees on the ground
D) All of them
Answer:
D) All of them
Question 9.
Find the mis-matched pair
1. Water in reservoir is measured in – feet
2. Water released from dams – liters
3. Liquids are measured in – liters or milliliters
A) 1
B) Both 1 & 2
C) 2
D) 3
Answer:
C) 2
Question 10.
Read the following.
1. Sea water is readily available for drinking
2. River water should be purified before drinking
3. Water in ponds and puddles is usually fresh water
Find the correct sentences from above
A) 1 & 2
B) 2 & 3
C) 1
D) 1 & 3
Answer:
B) 2 & 3
Question 11.
One of the following is not a fresh water body?
1. Puddle
2. Pond
3. River
4. Ocean
A) 4
B) 3
C) 1
D) 2
Answer:
A) 4
![]()
Question 12.
The consequences of drought
1. Very difficult to get food and fodder
2. Drinking water is sufficient
3. People travel long distances for water
4. Soil becomes wet and fertile
A) 1 & 2 are correct
B) 2 & 4 are correct
C) 1 & 3 are correct
D) 3 & 4 are correct
Answer:
C) 1 & 3 are correct
Question 13.
Area of the earth’s surface covered by water.
A) 34
B) 23
C) 14
D) 13
Answer:
A) 34
Question 14.
The percentage of water by weight in the human body is…………
A) 50%
B) 60%
C) 70%
D) 80%
Answer:
C) 70%
Question 15.
Fruit that contains large amount of water.
A) Mango
B) Apple
C) Watermelon
D) Guava
Answer:
C) Watermelon
Question 16.
Of the water available on the earth, the percentage of fresh water ……………
A) 1%
B) 2%
C) 3%
D) 4%
Answer:
A) 1%
Question 17.
The taste of sea water is ……
A) sweet
B) salty
C) sour
D) bitter
Answer:
B) salty
![]()
Question 18.
Why don’t we drink sea water?
A) because of sweet taste
B) because of salinity
C) because of sour taste
D) sea water with more minerals
Answer:
B) because of salinity
Question 19.
If several borewells are dug and underground water is tapped constantly what will happen to the source of ground water?
A) depletion of ground water occurs
B) depletion of rain
C) sudden decrease in water level of rivers
D) sudden increase in underground waters
Answer:
A) depletion of ground water occurs
Question 20.
Why are people ready to pay money for water along with other commodities?
A) Water is available in excessive amounts.
B) Water scarcity occurs
C) Water bodies became dry
D) Water bodies became contaminated
Answer:
D) Water bodies became contaminated
Question 21.
Water level in well increases during rainy season. Why?
A) due to direct rainfall into the well
B) over flow of river water to wells
C) rise of ground water revel leads to rise in water level of wells
D) A or B options
Answer:
C) rise of ground water revel leads to rise in water level of wells
Question 22.
What will happen if the source of ground water is tapped constantly?
A) Ground water level decreases
B) Ground water level increases
C) More rainfall occurs
D) Earth will be free of pollution
Answer:
A) Ground water level decreases
![]()
Question 23.
What happens if there is less rainfall or too much rainfall?
A) Water bodies are filled with rain water
B) Scarcity of food and drinking water problem will arise
C) All the crops are grown easily
D) Water will be useful for several years
Answer:
B) Scarcity of food and drinking water problem will arise
Question 24.
i) Water level in the water bodies depends on rainfall.
ii) Water level in the water bodies go up in summer.
A) Both the sentences are true
B) Both the sentences are false
C) Sentence – (i) is false, sentence – (ii) is true
D) Sentence – (i) is true, sentence – (ii) is false
Answer:
D) Sentence – (i) is true, sentence – (ii) is false
Question 25.
i) Sea water is salty and is not fit for drinking.
ii) Water used by us in our daily life is not salty.
A) Both sentences are false
B) Both sentences are true
C) Sentence – (i) is true, sentence – (ii) is false
D) Sentence – (i) is false, sentence – (ii) is true
Answer:
B) Both sentences are true
Question 26.
What have you done to measure the amount of water wasted by you?
A) Measured the time the tap was left open
B) A bucket was kept under the tap while using water
C) Measured the water used and wasted by other students
D) All the above
Answer:
D) All the above
Question 27.
The sequence of steps properly involved in observing the quantity of water mentioned on the label?
i) Water bottles are collected
ii) Labels are observed
iii) Observing their quantity
A) i, ii, iii
B) iii, ii, i
C) ii, iii, i
D) i, iii, ii
Answer:
A) i, ii, iii
Question 28.
What activities are considered to measure the amount of water used by us daily?
1. Drinking
2. Toilets
3. Bathing
4. Washing
The related activities for measuring?
A) 1,2,3
B) 2,3,4
C) 1,2,3,4
D) 2&3
Answer:
C) 1,2,3,4
![]()
Question 29.
Tapping of ground water by………………. is a tough job.
A) digging pit
B) digging well or borewell
C) fish tank
D) reservoir
Answer:
B) digging well or borewell
Question 30.
Rainfall is less and farmers are largely dependent on irrigation using to raise crops.
A) underground water
B) river water
C) salty water
D) lake water
Answer:
A) underground water
Question 31.
You found that paid water is purchased in shops through
A) Packets
B) Disposable bottles
C) Cans
D) All the above
Answer:
D) All the above
Read the given lines.
Sea water is salty but water used by us for our daily purposes is not salty. Water in ponds, pudd’es, rivers is fresh water.
Question 32.
Which water is not useful for drinking?
A) sea water
B) ocean water
C) well water from saline sou
D) all the above
Answer:
D) all the above
Read the given lines
Water level in the water sources depends on rainfall. Water levels in wells go up in the rainy season and go down in the summer season. :
Question 33.
Generally the water level in water sources depends upon
A) Rainfall during rainy season
B) Rainfall during winter season
C) Rainfall during summer season
D) Rainfall during dry condition
Answer:
A) Rainfall during rainy season
![]()
Question 34.
What are the places in which water is widely used other than our domestic purposes?
A) Vehicle washing shed
B) Industries
C) Houses
D) A & B
Answer:
D) A & B
Question 35.
These districts are treated as drought prone areas
A) Anantapur
B) Prakasham
C) A and B
D) Vest Godavari
Answer:
C) A and B
Question 36.
The place is determined as drought hit area by no rain fall for a period of
A) 1 to 2 years
B) 2 or 3 years
C) 4 to 5 ears
D) 6 months to 1 year
Answer:
C) 4 to 5 ears
Question 37.
Read the passage and answer the question.
During droughts it is very difficult to get food and fodder. Drinking water is scarce. What will people do in drought hit areas? ( )
A) People migrate longer distances for work
B) People stay back to get water
C) Nothing will happen to people in drought hit areas
D) People pray to god to get rains
Answer:
A) People migrate longer distances for work
Question 38.

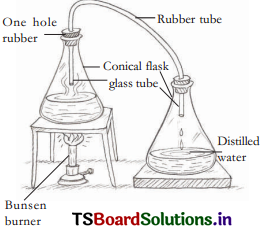
What is the method to be implemented in the place of ‘?‘ empty box?
A) cleaning
B) aeration
C) sublimation
D) distillation
Answer:
B) aeration
![]()
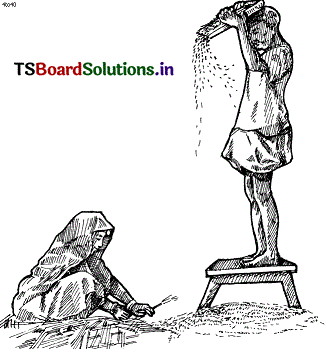
Question 39.
The above picture tells us

A) floods
B) walk in sea
C) tap water burst
D) water in the summer
Answer:
B) walk in sea
Question 40.
Everyone should have the aim for conserving this resource for future generations .
A) water
B) plastic
C) synthetic material
D) polymers
Answer:
A) water
Question 41.
These are the suitable slogans for conserving water resources …..
1. Save water for future
2. Use water unnecessarily as much as possible
3. Every drop of water counts – let us save
4. Let us save water – save our lives
Suitable slogans are
A) 1,2 & 3
B) 2,3 & 4
C) 1,3 & 4
D) 1,2 & 4
Answer:
C) 1,3 & 4