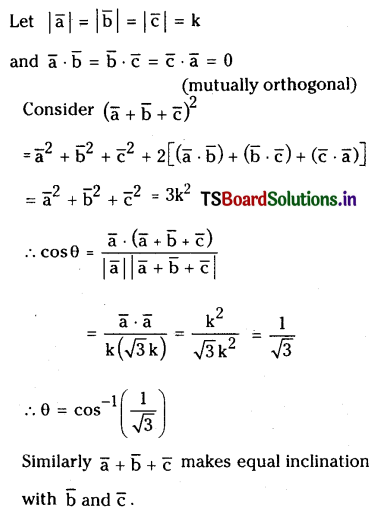
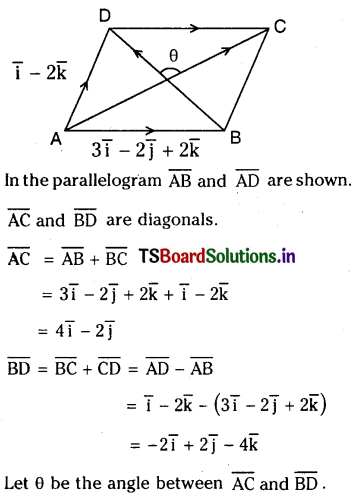
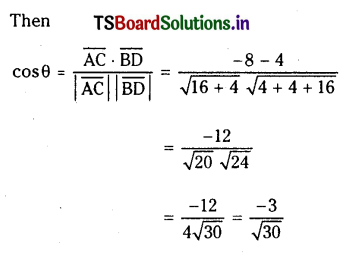
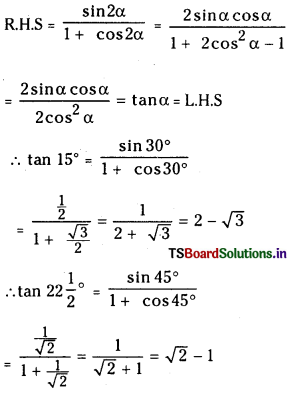
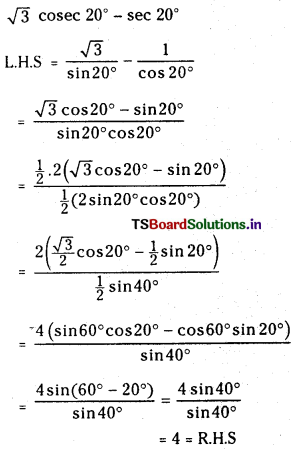
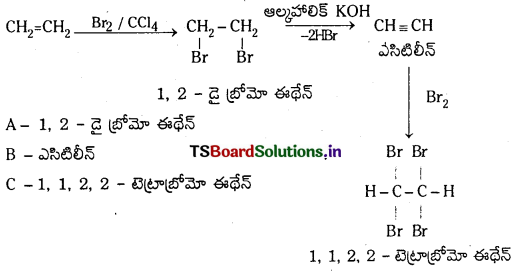
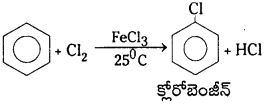
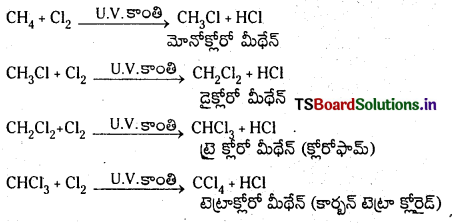
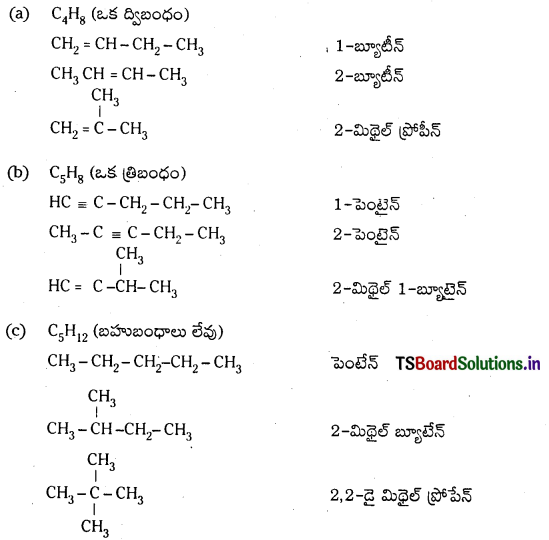
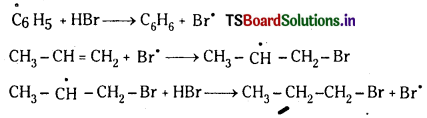
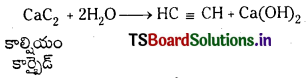
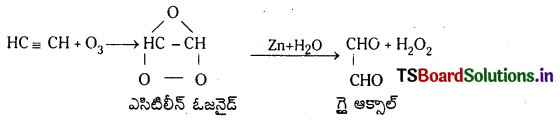
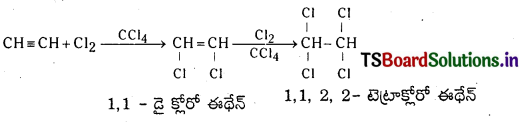
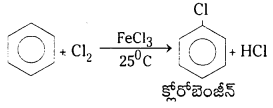
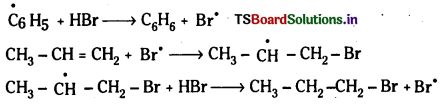
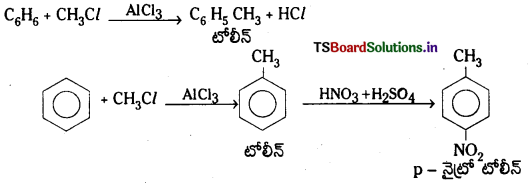
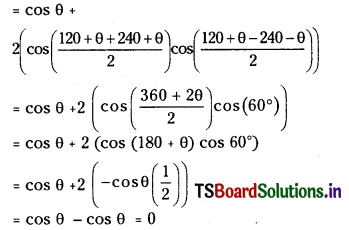
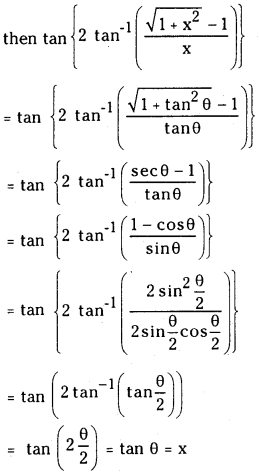
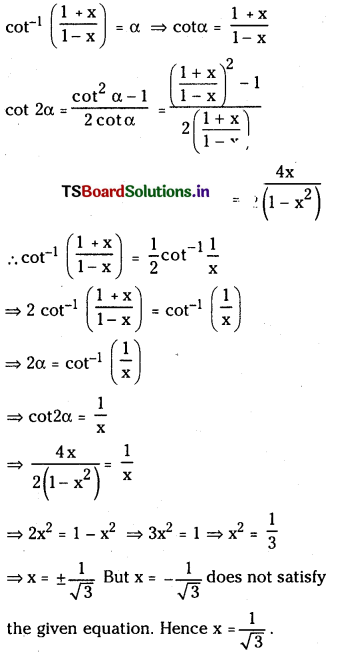
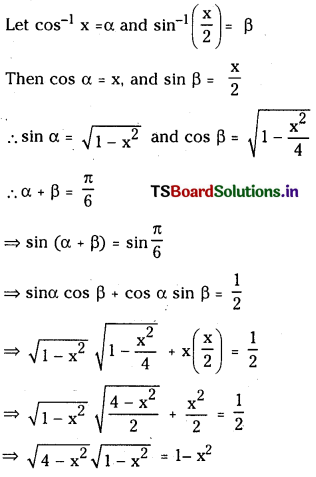
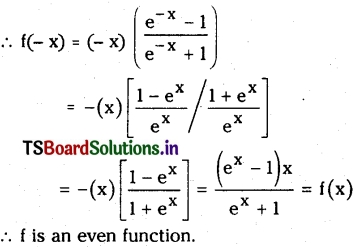
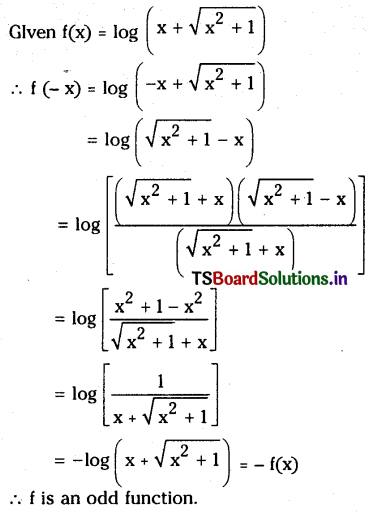
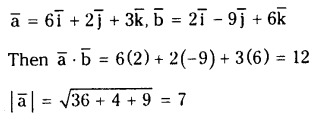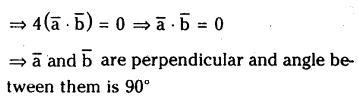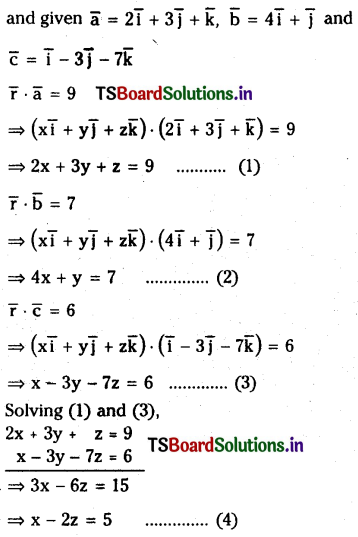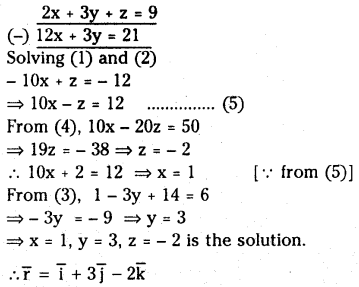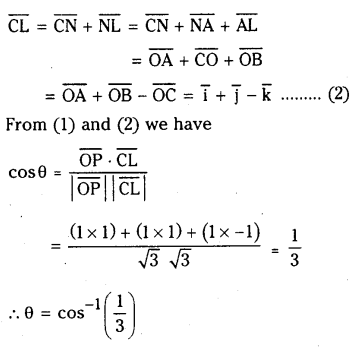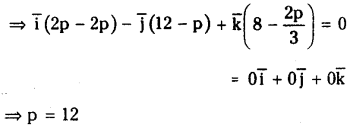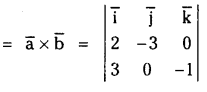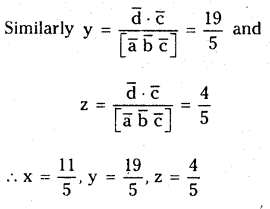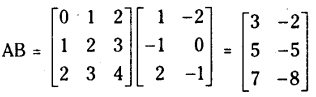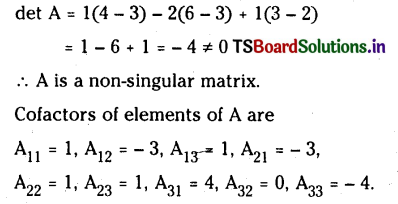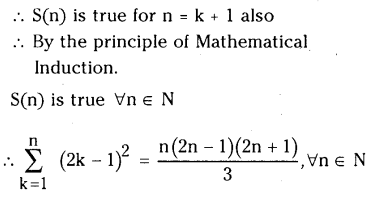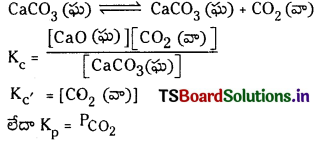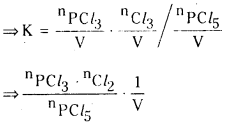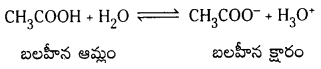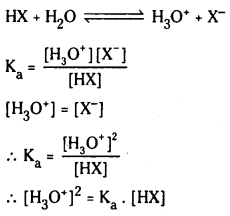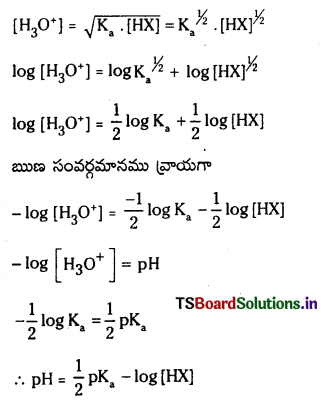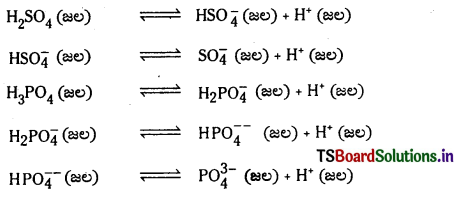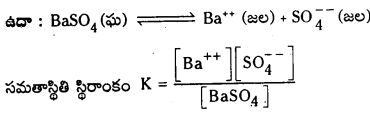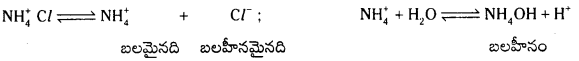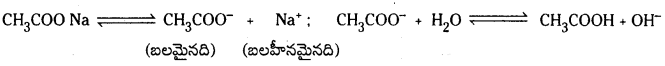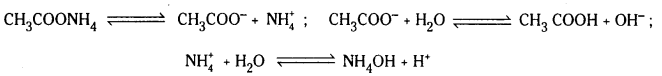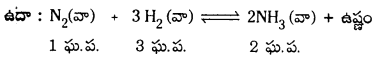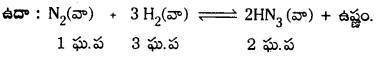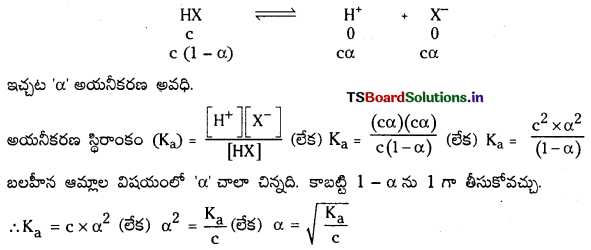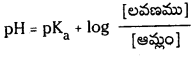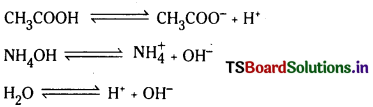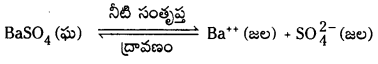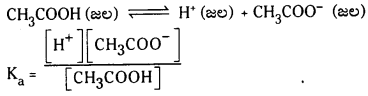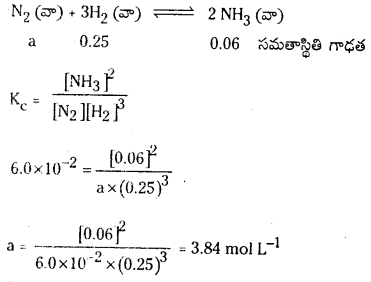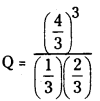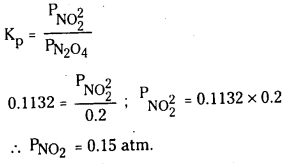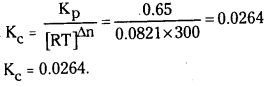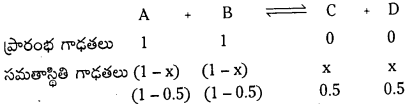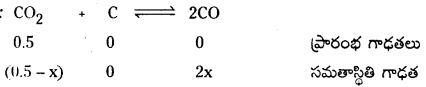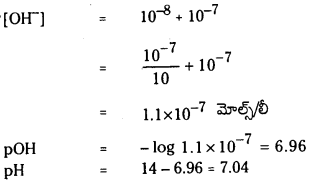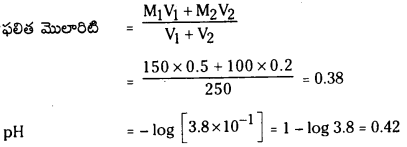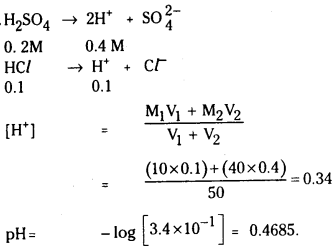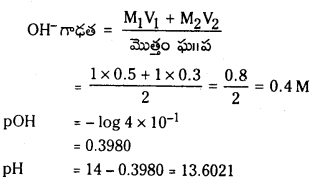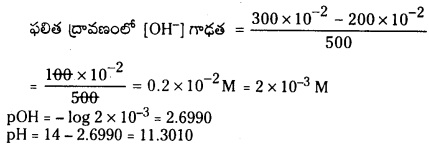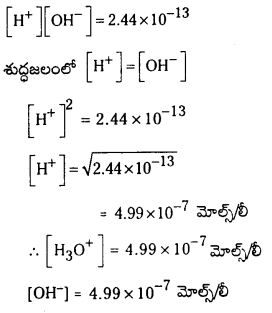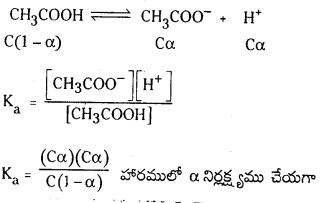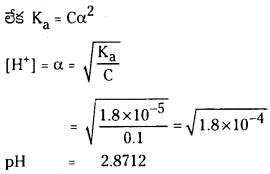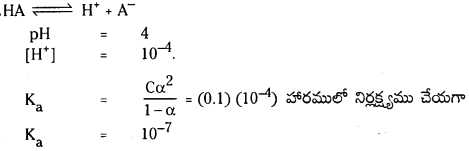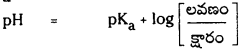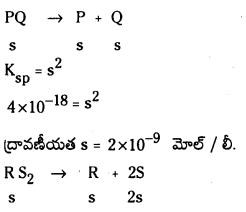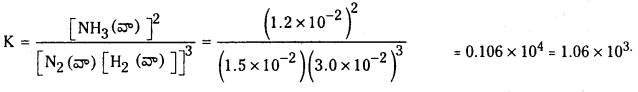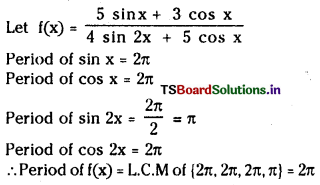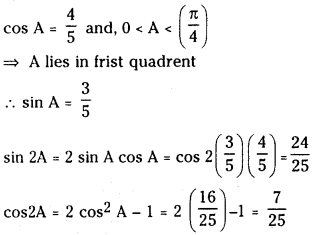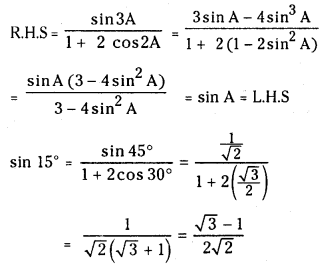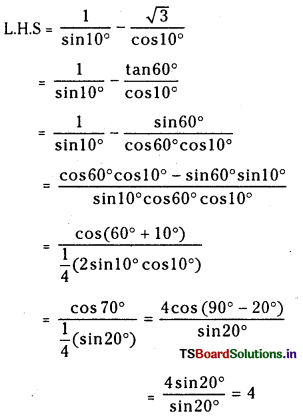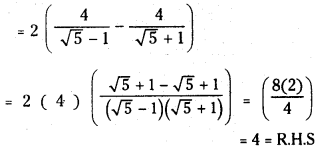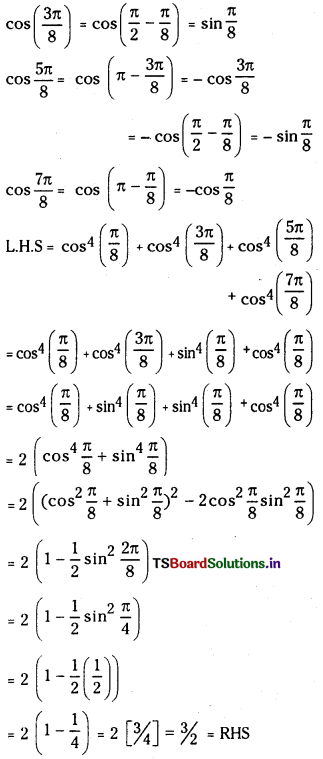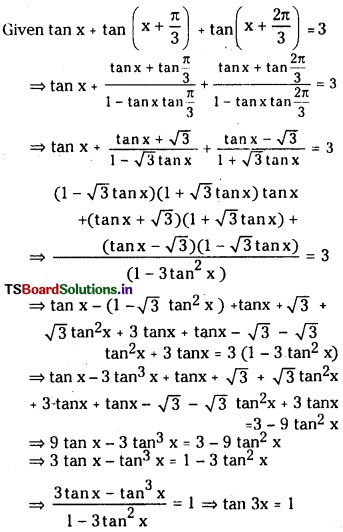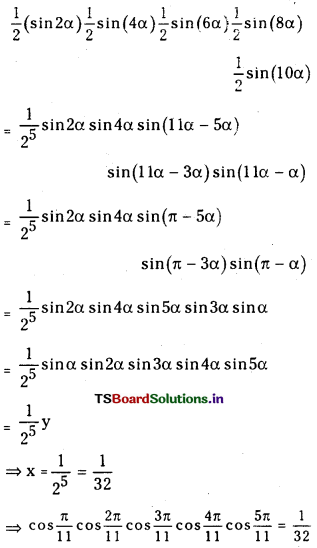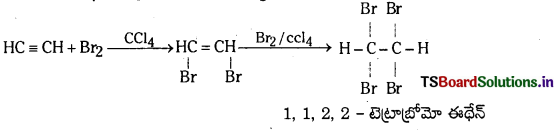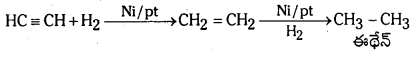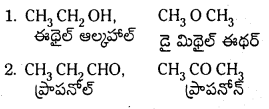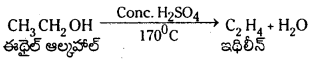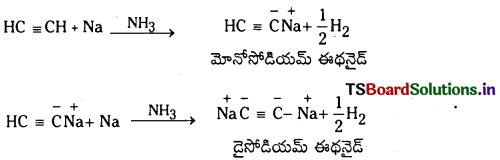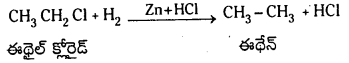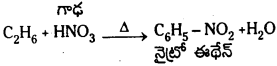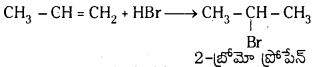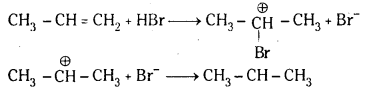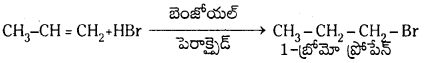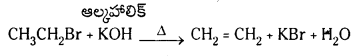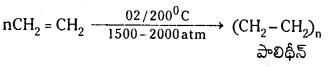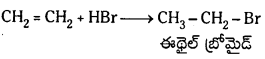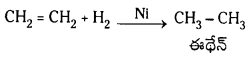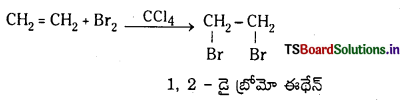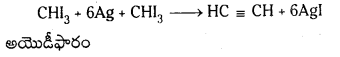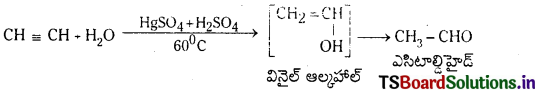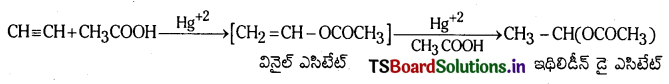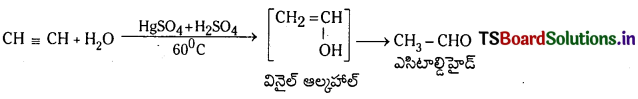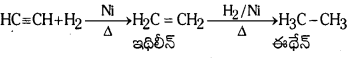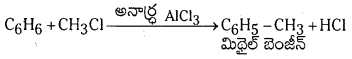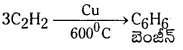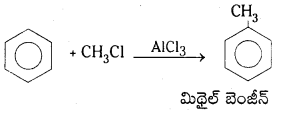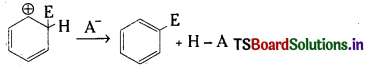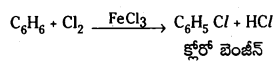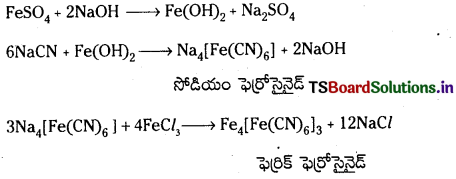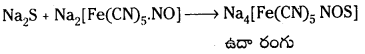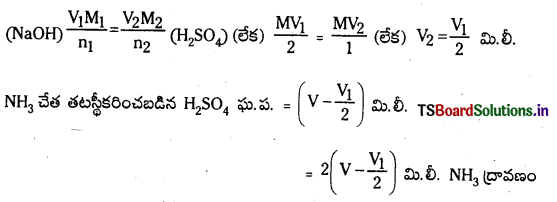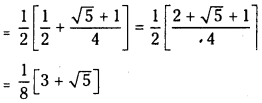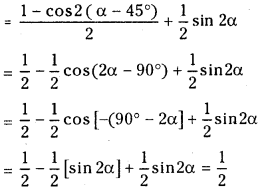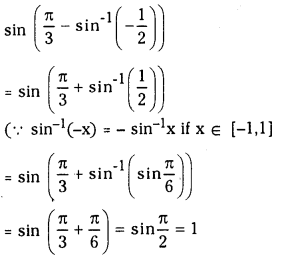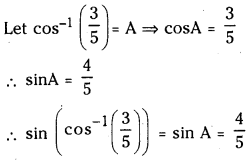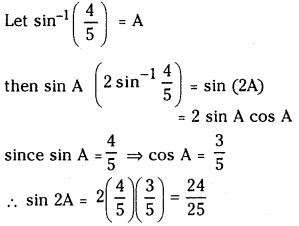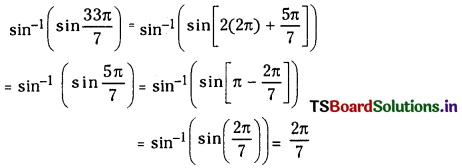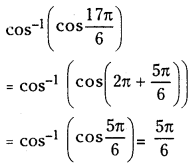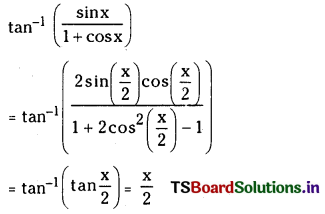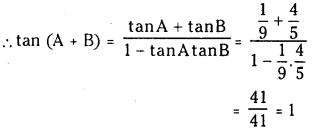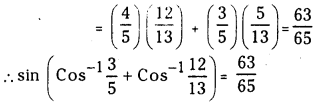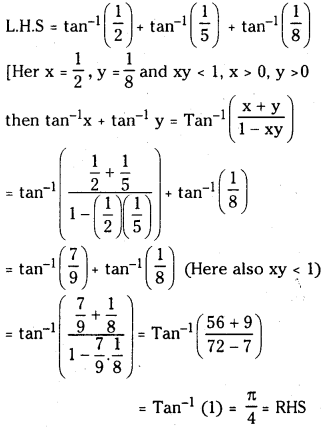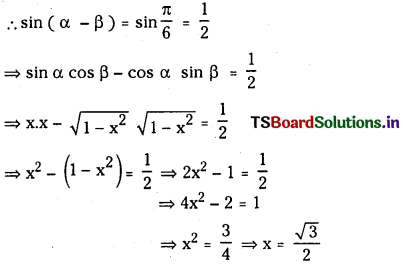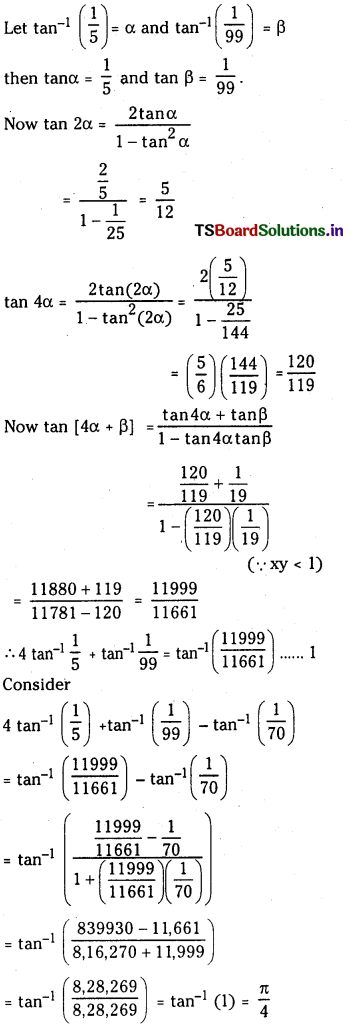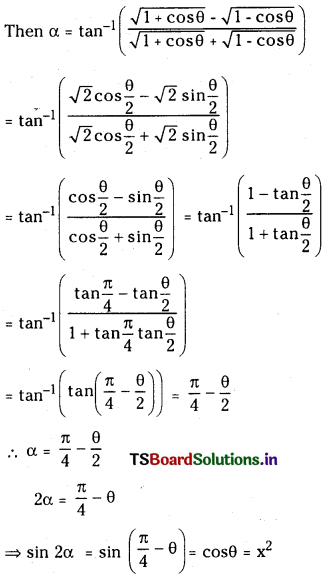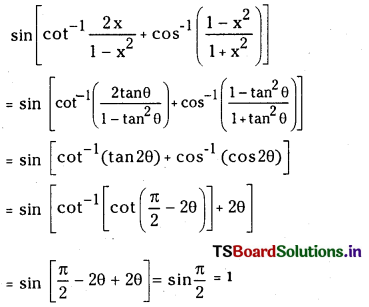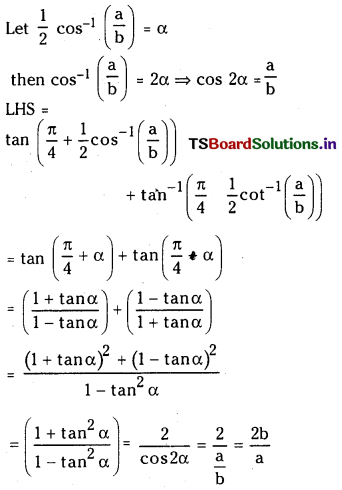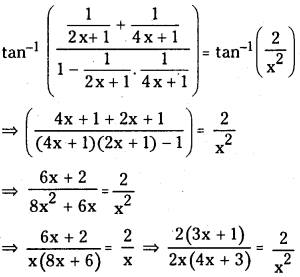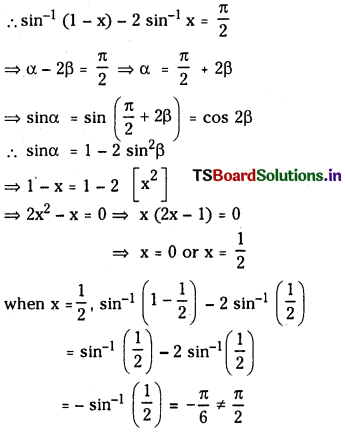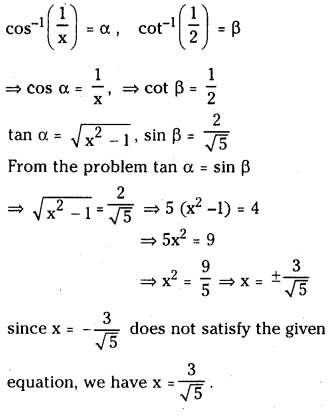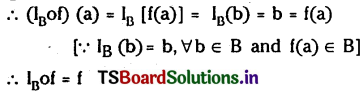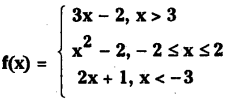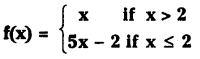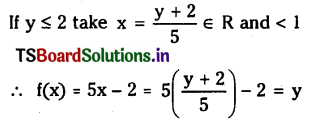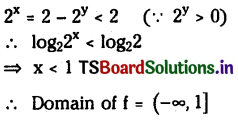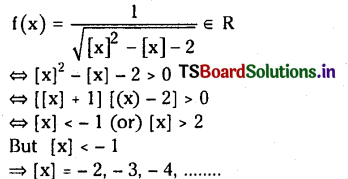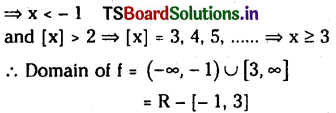Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material 7th Lesson రసాయనిక సమతాస్థితి, అమ్లాలు – క్షారాలు Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material 7th Lesson రసాయనిక సమతాస్థితి, అమ్లాలు – క్షారాలు
అత్యంత లఘు సమాధాన ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 1.
రసాయన సమతాస్థితి నియమం తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
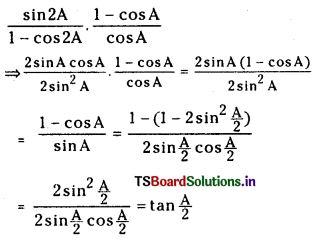
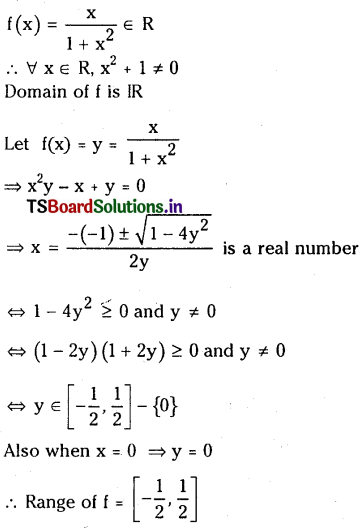
నిర్దిష్ట ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద, సమతుల్యం చేయబడిన రసాయన సమీకరణంలోని, క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతలను సూచించే పదాలకు, వాటి సంబంధిత స్థాయికియోమెట్రిక్ గుణకాలను ఘాతాలుగా రాసి ఏర్పడిన గాఢత పదాల అంకగణిత లబ్ధాల విలువను సమీకరణంలోని క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతలను సూచించే పదాలకు వాటి స్థాయికియోమెట్రిక్ గుణకాలను ఘాతాలుగా రాసి, ఏర్పడిన గాఢత పదాల అంకగణిత లబ్ధం విలువతో భాగిస్తే, స్థిర విలువ లభిస్తుంది. దీనినే సమతాస్థితి నియమం లేదా రసాయన సమతాస్థితి నియమం అంటారు.
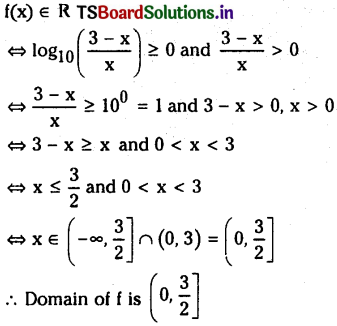
[A], [B], [C], [D] లు వరుసగా క్రియాజనకాల, క్రియాజన్యాల సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలు. K ను సమతా స్థిరాంకం అంటారు.
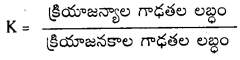
ప్రశ్న 2.
తెరచిన పాత్రలో నీరు, దాని బాష్పం మధ్య సమతాస్థితిని పొందగలమా ? వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడదు. బాష్పం తెరచి ఉన్న పాత్ర నుండి వాతావరణంలోనికి తప్పించుకొనిపోవుట వలన సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడదు.

ప్రశ్న 3.
సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం సమాసాలలో శుద్ధ ద్రవాల, శుద్ధ ఘనపదార్థాల గాఢతను ఎందుకు విస్మరిస్తాం ?
జవాబు:
విజాతీయ సమతాస్థితులలో శుద్ధద్రవాల, శుద్ధ ఘనపదార్థాల మోలార్ గాఢత స్థిరంగా ఉంటుంది. అందువల్ల సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాల సమాసాలలో శుద్ధద్రవాల, శుద్ధ ఘనపదార్థాల గాఢతలను విస్మరించవచ్చు.
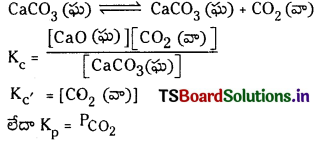
ప్రశ్న 4.
సమజాతి సమతాస్థితి అంటే ఏమి ? సమజాతి సమతాస్థితి చర్యలకు రెండు ఉదాహరణలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
సమతాస్థితిలో ఉన్న అన్ని పదార్థాలు ఒకే ప్రావస్థలో ఉంటే ఆ సమతాస్థితిని సమజాతి సమతాస్థితి అంటారు.
ఉదా : N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ⇌ 2NH3 (వా)
CH3COOH (ద్ర) + C2H2 OH (ద్ర) ⇌ CH3COO C2H5 (ద్ర) ⇌ H2O (ద్ర)
ప్రశ్న 5.
విజాతి సమతాస్థితి అంటే ఏమిటి ? విజాతి సమతాస్థితి చర్యలకు రెండు ఉదాహరణలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
సమతాస్థితిలో ఉన్న పదార్థాలు భిన్న ప్రావస్థలలో ఉంటే, అటువంటి సమతాస్థితిని విజాతి సమతాస్థితి అంటారు.
ఉదా : CaCO3 (ఘ) ⇌ CaO (ఘ) + CO2 (వా)
H2O (ద్ర) ⇌ H2O (వా)
ప్రశ్న 6.
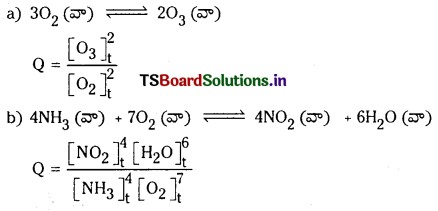
కింది చర్యలకు, చర్యా భాగఫలం Q విలువను రాయండి.
a) 3O2 (వా) ⇌ 2O3 (వా)
b) 4NH3 (వా) + 7O2 (వా) ⇌ 4NO2 (వా) + 6H2O (వా)
జవాబు:
చర్యా భాగఫలం :
ప్రశ్న 7.
సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం నిర్వచించండి.
జవాబు:
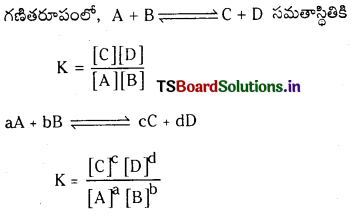
సమతాస్థితిలో ఉన్న వ్యవస్థలో క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతల లబ్ధానికి, క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతల లబ్ధానికి గల నిష్పత్తిని సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం అంటారు. కింది సమీకరణంలో స్థాయికియోమెట్రిక్ గుణకాలు ఉన్నపుడు ఆ గుణకాలను సంబంధిత గాఢతా పదాలకు ఘాతాలుగా రాయవలెను.
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
Kc = \(\frac{[\mathrm{C}]^c[\mathrm{D}]^{\mathrm{d}}}{[\mathrm{A}]^{\mathrm{a}}[\mathrm{B}]^b}\) ; [A], [B], [C], [D] లు వరుసగా క్రియాజనకాల, క్రియాజన్యాల సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలు.

ప్రశ్న 8.
ఒక వాయుస్థితి చర్యకు, సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంక సమాసం కింది విధంగా ఉంది.
Kc = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{NH}_3\right]^4\left[\mathrm{O}_2\right]^5}{[\mathrm{NO}]^4\left[\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}^6\right]^6}\) దీనికి సంబంధించిన సమతుల్యం చేయబడిన రసాయన సమీకరణం రాయండి.
జవాబు:
4NO (వా) + 6H2O (వా) ⇌ 4NH3 + 5O2 (వా)
ప్రశ్న 9.
Kp, Kc ల మధ్య సంబంధం రాయండి.
జవాబు:
Kp = Kc [RT]Δn.
Kp = K. (∴ Δn = 0)
వాయు స్థితిలోని క్రియాజన్యాల మోల్ల సంఖ్య, వాయుస్థితిలోని క్రియాజనకాల మోత్ల సంఖ్యకు సమానమైనపుడు Kp విలువ, Kc విలువ సమానము.
ప్రశ్న 10.
ఏ పరిస్థితులలో ఒక చర్యకు Kp, Kcలు సంఖ్యాపరంగా సమానం ?
జవాబు:
వాయుస్థితిలోని క్రియాజన్యాల మోత్ల సంఖ్య, వాయుస్థితిలోని క్రియాజనకాల మోల్ల సంఖ్యకు సమానమైనపుడు
Kp విలువ, Kc విలువ సమానము. Δn = 0;
Kp = Kc [RT]Δn
∴ Kp = Kc
ప్రశ్న 11.
Kp = Kc అయినటువంటి రెండు రసాయనిక సమతాస్థితి చర్యలను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
H2 (వా) + I2 (వా) ⇌ 2HI (వా)
N2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2NO (వా)
ప్రశ్న 12.
Kp > Kc అయినటువంటి రెండు రసాయనిక సమతాస్థితి చర్యలను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
2NOCl ⇌ 2NO (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
CaCO3 (ఘ) ⇌ CaO (ఘ) + CO2 (వా)
ప్రశ్న 13.
Kp < Kc అయినటువంటి రెండు రసాయనిక సమతాస్థితి చర్యలను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ⇌ 2NH3 (వా)
2SO2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2SO3 (వా)
ప్రశ్న 14.
Kcను Kp గా మార్చే సమీకరణాలను కింది చర్యలకు రాయండి.
a) CO (వా) + H2O (వా) ⇌ CO2 (వా) + H2 (వా)
b) C3H8 (వా) + 5O2 (వా) ⇌ 3CO2 (వా) + 4H2O (వా)
జవాబు:
a) CO (వా) + H2O (వా)
Δn = 2 – 2 = 0
b) C3H8 (వా) + 5O2 (వా) ⇌ 3CO2 (వా) + 4H2O (వా)
Δn = 7 – 6 = 1
Kp = Kc (RT)1
Kp = Kc (RT)
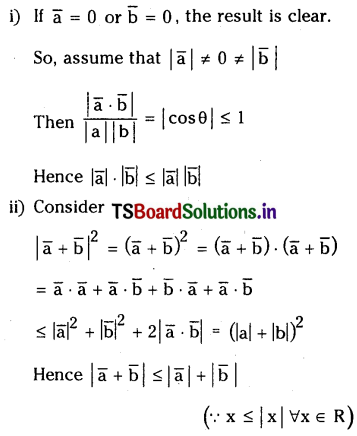
ప్రశ్న 15.
రసాయనిక సమతాస్థితిని ప్రభావితం చేసే కారణాంశాలు ఏవి ?
జవాబు:
- గాఢత
- ఉష్ణోగ్రత
- పీడనం.

ప్రశ్న 16.
వాయుస్థితి రసాయన సమతాస్థితిపై పీడనం ప్రభావం ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
వాయుస్థితి రసాయన స్థితిపై పీడన ప్రభావం, చర్యపై ఆధారపడి వుంటుంది.
a) మోల్ల సంఖ్యలో మార్పులేని చర్యలు.
N2 (వా) + O2 (వా) → 2NO (వా)
ఇటువంటి చర్యలపై పీడనం ప్రభావం ఉండదు.
b) N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) → 2NH3 (వా)
ఈ రకం చర్యలలో పురోగామి చర్యలో మోల్ల సంఖ్య తగ్గుతుంది.
Δn = ఋణాత్మకం. ఇటువంటి చర్యలలో పీడనం పెంచితే ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య అనగా పురోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
c) PCl5 (వా) ⇌ PCl3 (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
Δn = ధన్మాతకం.
ఇటువంటి చర్యలలో మోల్ల సంఖ్య పురోగామి చర్యలో పెరుగుతుంది. పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య అనగా తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 17.
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉండే రసాయన చర్యలో క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతల మార్పు ప్రభావం ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
క్రియాజనకాల గాఢత పెరిగితే పురోగామి చర్య వేగం పెరుగుతుంది (సమతాస్థితి కుడివైపుకు జరుగుతుంది). క్రియాజన్యాలను కలిపితే క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢత పెరిగి, తిరోగామీ చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 18.
సమతాస్థితిని ఉత్ప్రేరకం ప్రభావితం చేస్తుందా ?
జవాబు:
చేయలేదు. ఉత్ప్రేరకం, పురోగామి తిరోగామి చర్యలను సమానంగా ప్రోత్సహించి సమతాస్థితి త్వరితంగా ఏర్పడేటట్లు చేస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 19.
సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ ఏ కారణాంశం మీద ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది ?
జవాబు:
ఉష్ణోగ్రత. ఉష్ణోగ్రత మార్పువల్ల Kf, Kf లు ప్రభావితం అవుతాయి. అందువల్ల K = \(\frac{K_f}{K_b}\) విలువ ప్రభావితం అవుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 20.
ఒక చర్య సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాలు వరసగా 27°C, 127°C ల వద్ద 1.6 × 10-3, 7.6 × 10-2 ఈ చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్యా లేదా ఉష్ణమోచక చర్యా ?
జవాబు:
ఈ చర్యలో Kc విలువ పెరుగుతోంది. అందువల్ల ఈ చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహకచర్య. Kc = \(\frac{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{f}}}{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{b}}}\) ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే Kf విలువ పెరిగి Kc విలువ కూడా పెరుగుతుంది. ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్యలు ప్రోత్సహించబడతాయి కాబట్టి పురోగామి చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య.

ప్రశ్న 21.
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉండే వ్యవస్థపై ఉష్ణోగ్రత ప్రభావం ఏమి ?
జవాబు:
ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్యలలో ఉష్ణరాశిని కూడా క్రియాజనకంగా పరిగణించవచ్చు. ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే క్రియాజనకాలలో ఒకటైన ఉష్ణరాశి గాఢత పెరిగి, పురోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. అనగా సమతాస్థితి కుడివైపుకు జరుగుతుంది.
N2 (వా) + O2 (వా) + ఉష్ణరాశి ⇌ 2NO (వా)
ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే ఉష్ణగ్రాహకచర్య, ఉష్ణోగ్రతను తగ్గిస్తే ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 22.
ఒక ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య ఉష్ణోగ్రతను పెంచితే, ఆ చర్య సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం ఏ మార్పుకు గురవుతుంది ?
జవాబు:
Kc = \(\frac{K_f}{K_b}\) ;
ఉష్ణోగ్రతను పెంచినపుడు ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య వేగం తగ్గుతుంది (Kf తగ్గుతుంది.) ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య అయిన తిరోగామి చర్య వేగం పెరుగుతుంది (Kb పెరుగుతుంది.) అందువల్ల K విలువ తగ్గుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 23.
వాయువు మాత్రమే పాల్గొనే చర్యకు AG° ద్వారా ఏ రకపు సమతాస్థిరాంకాన్ని లెక్కించవచ్చు ?
జవాబు:
ΔG° విలువ నుండి Kp విలువను లెక్కించవచ్చు.
AG° = – RT lnK
lnK = e-ΔG°/RT
ఈ సమీకరణంలో ‘R’ ఉన్నది కనుక సమతాస్థిరాంకం Kp.
ప్రశ్న 24.
బ్రాన్ స్టెడ్ క్షారం అంటే ఏమిటి ? ఒక ఉదాహరణ తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
ప్రోటాన్ ను గ్రహించేది బ్రాన్టేడ్ క్షారం.
NH3 + HCl ⇌ \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\) + HCI–
ఈ చర్యలో NH3, HCl నుండి ప్రోటాన్ H+ ను స్వీకరిస్తుంది. అందువల్ల బ్రాన్టెడ్ క్షారం.
ప్రశ్న 25.
లూయీ ఆమ్లం అంటే ఏమిటి ? ఒక ఉదాహరణ తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను స్వీకరించేది లూయీ ఆమ్లం. ఉదా : BF3.
ప్రశ్న 26.
నీటి అయానిక అంటే ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
జలద్రావణంలో H+ అయానుల, OH– అయానుల గాఢతల లబ్ధాన్ని నీటి అయానిక లబ్ధం అంటారు.
Kw = [H+] [OH–]
ప్రశ్న 27.
Kw విలువ ఏమి ? దీని పరామితులు ఏమి ?
జవాబు:
Kw విలువ 25°C వద్ద 1.0 × 10-14.
దాని యూనిట్లు మోల్2 / లీ2
ప్రశ్న 28.
నీటి అయానిక లబ్ధం విలువపై ఉష్ణోగ్రత ప్రభావం తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే నీటి అయనీకరణం పెరిగి H+, OH– ల గాఢతలు పెరుగుతాయి. అందువల్ల Kw విలువ పెరుగుతుంది.

ప్రశ్న 29.
H2O + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + OH–
25°C, 40°C ఉష్ణోగ్రతల వద్ద వరసగా నీటి అయానిక లబ్ధం విలువలు 1 × 10–14, 3.0 × 10-14 పై చర్య ఉష్ణమోచక చర్యా ? లేదా ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్యా ?
జవాబు:
ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే నీటి అయానిక లబ్ధం విలువ పెరుగుతుంది. అందువల్ల నీటి అయనీకరణ చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య అని తెలియుచున్నది. పై చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య.
ప్రశ్న 30.
‘బ్రాన్ స్టెడ్ క్షారాలు అన్నీ లూయీ క్షారాలే’. వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
ప్రోటాను స్వీకరించేవి బ్రాన్స్టెడ్ క్షారాలు. ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను కలిగి ఉండి, దానిని దానం చేయగలిగే పదార్థాలన్నీ లూయీ క్షారాలు. ఈ పదార్థాలన్నీ ప్రోటాన్ ను స్వీకరించగలవు. అందువల్ల బ్రానెడ్ క్షారాలు లూయీ క్షారాలు ఒకటే.
H3 N: + H+ → [H3N → H]+
ప్రశ్న 31.
‘లూయీ ఆమ్లాలు అన్నీ బ్రానెడ్ ఆమ్లాలు కావు’. ఎందువల్ల ?
జవాబు:
ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను స్వీకరించే పదార్థాలు లూయీ ఆమ్లాలు.
ఉదా : BF3 ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంట స్వీకరించగలదు. అందువల్ల లూయీ ఆమ్లం.
ప్రోటాన్ ను దానం చేయగలిగే పదార్థాలు బ్రాన్డెడ్ ఆమ్లాలు. ఉదా : HCl.
BF3 లూయీ ఆమ్లం అయినప్పటికి దానియందు ప్రోటాన్ లేకపోవుట వలన బ్రాన్డెడ్ ఆమ్లం కాదు. అందువల్ల లూయీ ఆమ్లాలు బ్రాన్టెడ్ ఆమ్లాలు కానక్కరలేదు.
ప్రశ్న 32.
అయనీకరణం అవధి అంటే ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
అయనీకరణం చెందిన అణువుల సంఖ్యకు, మొత్తం అణువుల సంఖ్యకు గల నిష్పత్తిని అయనీకరణ అవధి అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 33.
ఒక ఆమ్లం లేదా క్షారం బలాన్ని వ్యక్తం చేసే రాశి ఏది ?
జవాబు:
ఆమ్లము యొక్క విఘటన స్థిరాంకం Ka విలువ ఎక్కువగా ఉంటే అది బలమైన ఆమ్లము. అదేవిధంగా క్షారము యొక్క విఘటన స్థిరాంకం Kb విలువ ఎక్కువగా ఉంటే అది బలమైన క్షారం.
ప్రశ్న 34.
వాటి జలద్రావణాలలో, క్షార స్వభావం చూపే రెండు లవణాలను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
- సోడియం కార్బొనేట్ జలద్రావణం క్షారత్వాన్ని చూపుతుంది.
- సోడియం ఎసిటేట్ జలద్రావణం క్షారత్వాన్ని చూపుతుంది.

ప్రశ్న 35.
వాటి జలద్రావణాలలో, ఆమ్ల స్వభావం చూపే రెండు లవణాలను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
- AlCl3 జలద్రావణం ఆమ్ల స్వభావాన్ని చూపుతుంది.
- CuSO4 జలద్రావణం ఆమ్ల స్వభావాన్ని చూపుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 36.
ఆమ్ల బఫర్ ద్రావణం pH ను లెక్కించడానికి ఏ సమీకరణాన్ని ఉపయోగిస్తారు ?
జవాబు:
ఆమ్ల బఫర్ ద్రావణం pH ను కనుక్కోవడానికి సమీకరణం :
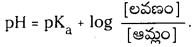
ప్రశ్న 37.
ఫాస్ఫారిక్ ఆమ్లం (H3PO4) కు మూడు అయనీకరణ స్థిరాంకాలు ఉన్నాయి. ఇవి Ka1, Ka2, Ka3. వీటిలో దేనికి కనిష్ఠ విలువ ఉంటుంది ? కారణాలు తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
Ka3 విలువ కనిష్ఠంగా ఉంటుంది. ఋణ అయాను (HP\(\mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\)) నుండి ప్రోటానును తొలగించుట కష్టం. దీనికి కారణం ఋణ అయానులో ప్రోటాను బలమైన స్థిర విద్యుదాకర్షణకు లోను కావడమే.
ప్రశ్న 38.
ఎత్తు ప్రదేశాలలో ఐస్ నెమ్మదిగా కరుగుతుంది. దీనికి కారణం వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
నీటికన్నా ఐస్కు ఘనపరిమాణం ఎక్కువ. పీడనం పెరిగితే ఐస్ నేరుగా మారే చర్య జరుగుతుంది. పీడనాన్ని తగ్గిస్తే ఈ చర్య నెమ్మదిగా జరుగుతుంది. ఎత్తు ప్రదేశాలలో పీడనం తక్కువగా ఉండడం వల్ల ఐస్ నెమ్మదిగా కరుగుతుంది.
లఘు సమాధాన ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 39.
కింది చర్యలు ప్రతీదానికి సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం Kc కు సమీకరణాలు రాయండి.
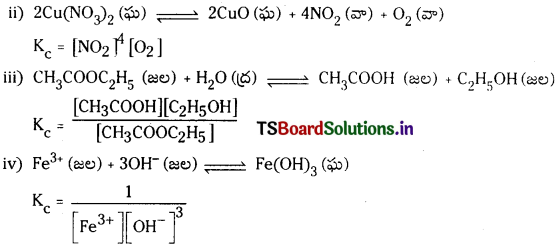
(i) 2NOCl (వా) ⇌ 2NO (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
(ii) 2Cu (NO3)2 (ఘ) ⇌ 2CuO (ఘ) + 4NO2 (వా) + O2 (వా)
(iii) CH3COOC2H5 (జల) + H2O (ద్ర) ⇌ CH3COOH (జల) + C2H5OH (జల)
(iv) Fe+3 (జల) + 3OH– (జల) ⇌ Fe (OH)3 (ఘ)
జవాబు:
i) 2NOCl (వా) ⇌ 2NO (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
Kc = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{NO}^2\left[\mathrm{Cl}_2\right]\right.}{[\mathrm{NOCl}]^2}\)
ప్రశ్న 40.
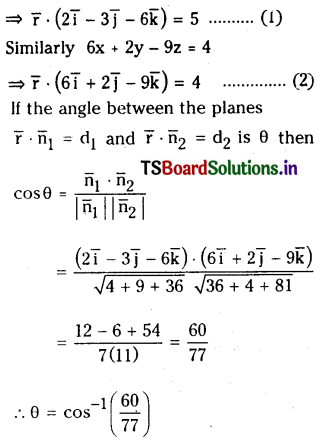
కింది సమతాస్థితి చర్యకు Kp, Kc ల మధ్య గల సంబంధాన్ని ఉత్పాదించండి. (March 2013)
N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ⇌ 2H3 (వా)
జవాబు:
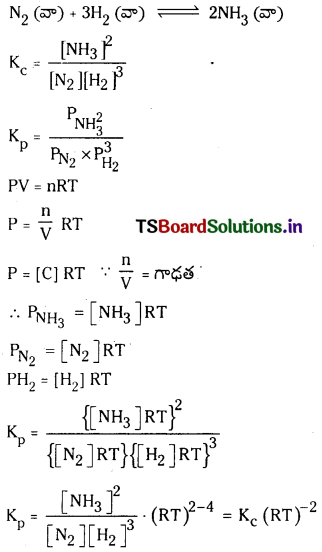

ప్రశ్న 41.
సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాన్ని నిర్వచించండి. కింది చర్యకు, దాని ఉత్ర్కమణీయ చర్యకు సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాన్ని రాయండి.
H2 (వా) + I2 (వా) ⇌ 2HI (వా)
ఈ రెండు స్థిరాంకాలు ఏ విధంగా సంబంధం కలిగి ఉన్నాయి ?
జవాబు:
సమతాస్థితిలో ఉన్న వ్యవస్థలో, క్రియాజన్యాల మోలార్ గాఢతల లబ్ధానికి, క్రియాజనకాల మోలార్ గాఢతల లబ్ధానికి గల నిష్పత్తిని సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం అంటారు.
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
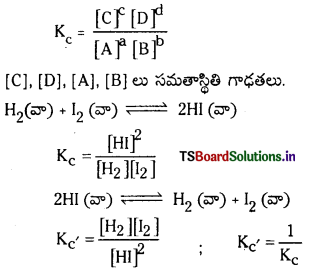
ప్రశ్న 42.
ఒక చర్య విస్తృతిని, సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం ఏ విధంగా ఊహిస్తుంది ?
జవాబు:
ఒక చర్య సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం సంఖ్యాత్మక విలువ, ఆ చర్య విస్తృతిని తెలుపుతుంది. Kc లేదా Kp ల పరిమాణం క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతలకు అనులోమానుపాతంలోను, క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతలకు విలోమానుపాతంలోను ఉంటాయి. దీనిని అనుసరించి K విలువ అధికంగా ఉంటే క్రియాజన్యాలు అధికంగా ఏర్పడతాయి అని తెలుపుతుంది. అదేవిధంగా అల్పంగా ఉంటే క్రియాజన్యాలు అల్పంగా ఏర్పడతాయని తెలుస్తుంది.
Kc > 103 అయితే క్రియాజనకాల కంటే క్రియాజన్యాలు అధికంగా వుంటాయి. అంటే Kc విలువ అత్యధికంగా ఉన్నట్లైతే చర్య సుమారుగా పూర్తిగా జరుగుతుందని ఊహించవచ్చు.
ఉదా : 500 K వద్ద H2, O2 తో జరిపే చర్యకు సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ అత్యధికంగా ఉంది.
Kc = 2.4 × 1047
Kc < 10-3 అయితే క్రియాజనకాలు, క్రియాజన్యాల కంటే అధికంగా ఉంటాయి. Kc విలువ అతి తక్కువ అయితే ఆ చర్య అరుదుగా జరుగుతుంది.
ఉదా : 298 K వద్ద N2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2NO (వా) చర్యకు Kc = 4.8 × 10-31
Kc విలువ 10-3 కు మధ్యగా ఉండినట్లైతే చర్యలో గమనించదగిన గాఢతలలో క్రియాజన్యాలు, క్రియాజనకాలు కూడా ఉంటాయి.
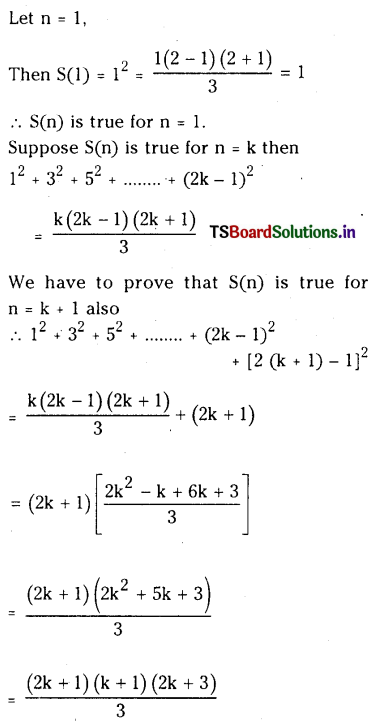
ప్రశ్న 43.
సమతాస్థితి నియమాన్ని వివరించండి. సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలు కింది విధంగా ఉండే సమతాస్థితికి Kcను లెక్కించండి.
[SO2] = 0.60 M, [O2] = 0.82 M, [SO3] = 1.90 M ?
2SO2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2SO3 (వా)
జవాబు:
సమతాస్థితి నియమం : నిర్దిష్ట ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద, సమతుల్యం చేయబడిన రసాయన సమీకరణంలోని, క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతలను సూచించే పదాలకు, వాటి సంబంధిత స్థాయికియోమెట్రిక్ గుణకాలను ఘాతాలుగా రాసి ఏర్పడిన గాఢత పదాల అంకగణిత లబ్ధాల విలువను సమీకరణంలోని క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతలను సూచించే పదాలకు వాటి స్థాయికియోమెట్రిక్ గుణకాలను ఘాతాలుగా రాసి, ఏర్పడిన గాఢత పదాల అంకగణిత విలువతో భాగిస్తే, స్థిర విలువ లభిస్తుంది. దీనినే సమతాస్థితి నియమం లేదా రసాయన సమతాస్థితి నియమం అంటారు.
2SO2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2SO3 (వా)
Kc = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{SO}_3\right]^2}{\left[\mathrm{SO}_2\right]^2\left[\mathrm{O}_2\right]}\) = \(\frac{(1.9)^2}{(0.6)^2(0.82)}\) = 12.229 mol L-1
ప్రశ్న 44.
సీలు చేయబడి ఉన్న సోడా నీటి సీసాను తెరచినప్పుడు ఎందుకు వాయువు బుసబుస పొంగుతూ బయటకు వస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
సీలు చేయబడిన సోడా నీటి సీసాలో పీడనం అధికం. CO2 అధికంగా నీటియందు కరిగి ఉండి, సమతాస్థితిలో ఉంటుంది.
CO2 (వా) + H2O (ద్ర) ⇌ H2CO3 (వా)
పీడనం అధికంగా ఉన్నపుడు, సమతాస్థితి కుడివైపుకు జరిగి, CO2 అధికంగా నీటిలో కరిగి ఉంటుంది. పీడనాన్ని తగ్గిస్తే, అంటే సీసా మూతను తెరిస్తే సమతాస్థితి ఎడమవైపుకు జరిగి, CO2 ఏర్పడి బుసబుసమని పొంగుతూ బయటకు వస్తుంది.

ప్రశ్న 45.
కింది వాటి ప్రాముఖ్యం తెలపండి.
a) అతి ఎక్కువ K విలువ
b) అతి తక్కువ K విలువ
c) K విలువ 1.0 గా ఉన్నది.
జవాబు:
a) K విలువ అధికంగా వున్నపుడు క్రియాజనకాల కంటే క్రియాజన్యాలు అధికంగా వుంటాయి. అంటే K విలువ అత్యధికంగా వున్నట్లైతే చర్య సుమారుగా పూర్తిగా జరుగుతుంది.
b) K విలువ అల్పంగా ఉంటే క్రియాజనకాలు, క్రియాజన్యాల కంటే అధికంగా వుంటాయి. K విలువ అతి తక్కువ అయితే, ఆ చర్య అరుదుగా జరుగుతుంది.
c) K విలువ 1.0 అయితే క్రియాజనకాలు 50% వరకు క్రియాజన్యాలుగా మారినవని అర్థము. పురోగామి, తిరోగామి వేగ స్థిరాంకాలు సమానం అని అర్థము.
ప్రశ్న 46.
Q, K లను సరిపోల్చడం ఎందుకు ఉపయోగపడుతుంది ? కింది వాటిలో పరిస్థితులు ఏమి ?
(a) Q = K
(b) Q < K (c) Q>K
జవాబు:
క్రియాజన్యాల మోలార్ గాఢతల లబ్ధానికి, క్రియాజనకాల మోలార్ గాఢతల లబ్ధానికి గల నిష్పత్తిని చర్య యొక్క భాగఫల స్థిరాంకం Q అంటారు. Qను లెక్కించేటపుడు సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలను వాడనవసరం లేదు.
Q విలువను సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం K తో పోలిస్తే, చర్య జరిగే దిశను ఊహించవచ్చు.
- Q > K అయితే తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. (ఉత్రమ చర్య)
- Q < K అయితే సమతాస్థితిని తిరిగి పొందే విధంగా చర్య పురోగామి దిశలో పయనిస్తుంది.
- Q = K అయితే, చర్య సమతాస్థితిలో ఉంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 47.
Cl2 (వా) + F2 (వా) ⇌ 2Cl F (వా), Kc = 19.9
పై చర్యలోని పదార్థాల గాఢతలు కింది విధంగా ఉంటే చర్య ఏ విధంగా జరుగుతుంది ?
[Cl2] = 0.4 mol L–; [F2] = 0.2 mol L-1, [Cl F] = 7.3 mol L–?
జవాబు:
Q = \(\frac{[\mathrm{ClF}]^2}{\left[\mathrm{Cl}_2\right]\left[\mathrm{F}_2\right]}\) = \(\frac{(7.3)^2}{0.04 \times 0.2}\)
= 6.66 × 103
Kc విలువ కన్నా Q విలువ చాలా ఎక్కువగా ఉన్నది. అందువల్ల మరల సమతాస్థితిని ఏర్పరచడానికి తిరోగామి దిశలో చర్య జరుగుతుంది.

ప్రశ్న 48.
కింది వాటిలో దేనిలో క్రియాజనకాలు, క్రియాజన్యాలు గుర్తించగలిగిన గాఢతలలో ఉంటాయి ?
a) Cl2 (వా) ⇌ 2Cl(వా) Kc = 5 × 10-39
b) Cl2 (వా) + 2NO (వా) ⇌ 2NOCl (వా) Kc = 3.7 × 108
c) Cl2 (వా) + 2NO2 (వా) ⇌ 2NO2(వా) Kc = 1.8
జవాబు:
a) Cl2 (వా) ⇌ 2Cl(వా) Kc = 5 × 10-39
ఈ చర్యకు Kc విలువ చాలా స్వల్పం. అందువల్ల పురోగామి చర్య చాలా స్వల్పంగా జరుగుతుంది. అందువల్ల సమతా వ్యవస్థలో క్రియాజనకమైన క్లోరిన్ ప్రధానంగా ఉంటుంది.
b) Cl2 (వా) + 2NO (వా) ⇌ 2NOCl (వా) Kc = 3.7 × 108
Kc విలువ ఎక్కువగా ఉన్నందున, పురోగామి చర్య అధికంగా జరిగి, సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉత్పన్నాలు అధికంగా వుంటాయి. ఉత్పన్నాల గాఢత అధికంగా వుంటుంది.
c) Cl2 (వా) + 2NO2 (వా) ⇌ 2NO2(వా) Kc = 1.8
ఈ చర్యలో పురోగామి చర్య 50% కన్నా కొద్దిగా ఎక్కువ జరుగుతుంది. అందువల్ల ఈ చర్యలో క్రియాజనకాలు, క్రియాజన్యాలు గుర్తింపదగిన గాఢతలో ఉంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 49.
సమతాస్థితిలో ఉండే వ్యవస్థ పీడనం మార్పు ద్వారా ప్రభావితం అయ్యే పరిస్థితులను ఏ విధంగా తెలుసుకొంటాం?
జవాబు:
సమతాస్థితిలో ఉండే వ్యవస్థపై పీడన ప్రభావాన్ని లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ద్వారా తెలుసుకోవచ్చు.
i) ఒక చర్యలో వాయుస్థితిలో ఉండే క్రియాజనకాల మొత్తం మోల్ల సంఖ్య వాయుస్థితిలో ఉండే క్రియాజన్యాల మొత్తం మోల్ల సంఖ్యకు సమానంగా ఉంటే, సమతాస్థితిపై పీడన ప్రభావం ఉండదు.
ఉదా : N2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2NO (వా)
ఈ చర్యపై పీడన ప్రభావం ఉండదు.
ii) క్రియాజనకాల, క్రియాజన్యాల మోత్ల సంఖ్య సమానంగా లేనపుడు పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు మోత్ల సంఖ్య తగ్గేదిశగా (ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే దిశలో చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది).
a) N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ⇌ 2NH3 (వా)
ఈ చర్యలో అమ్మోనియా ఏర్పడుటలో మోల్ల సంఖ్య తగ్గుతుంది. అందువల్ల పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే దిశలో జరుగుతున్న పురోగామి చర్య జరుగుతుంది. అమ్మోనియా అధికంగా ఏర్పడుతుంది. పీడనాన్ని తగ్గిస్తే ఉత్రమచర్య జరిగి అమ్మోనియా విడిపోతుంది.
b) PCl5 (వా) ⇌ PCl3 (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
ఈ చర్య పురోగామి దిశలో మోల్ల సంఖ్య మరియు ఘనపరిమాణం పెరుగుతాయి. పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య అయిన ఉత్రమచర్య జరిగి PCl5 (వా) విఘటనం తగ్గుతుంది. పీడనం తగ్గిస్తే పురోగామి చర్య జరుగుతుంది.
లీచాట్లీయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం సమతాస్థితి వ్యవస్థపై పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. అనగా మోల్ల సంఖ్య తగ్గే దిశలో జరిగే చర్య జరుగుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 50.
సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ పరిమాణంపై ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో మార్పు ప్రభావాన్ని తెలుసుకొనేందుకు చర్య ఏ ధర్మం ఉపయోగపడుతుంది ?
జవాబు:
చర్య ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో మార్పు తటస్థపడితే సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాకం Klc విలువ కూడా మారుతుంది. సాధారణంగా సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం ఉష్ణోగ్రతపై ఆధారపడే విషయం చర్య ΔH విలువ సంజ్ఞను అనుసరించి ఉంటుంది.
- ఉష్ణమోచక చర్యల (ఋణ ΔH విలువ గలవి) ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరుగుదలతో సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ తగ్గుతుంది.
- ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్యలలో (ధన ΔH విలువ గలవి) ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరుగుదలతో సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ కూడా పెరుగుతుంది.
ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో నూర్పులు సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాలను, చర్యల రేటులను కూడా ప్రభావితం చేస్తాయి.
N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ⇌ 2NH3 (వా)
ΔH = 92.38 K.J mol-1 చర్య ఆధారంగా జరిగే అమ్మోనియా ఏర్పడే చర్య ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య. లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం అనుసరించి చర్య ఉష్ణోగ్రతను పెంచినట్లైతే చర్య సమతాస్థితి ఎడమవైపుగా జరుగుతుంది. ఫలితంగా అమ్మోనియా సమతాస్థితి గాఢత తగ్గుతుంది. మరో విధంగా తెలపాలి అంటే అల్పస్థాయి ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు అమ్మోనియా దిగుబడిని పెంచుతాయి. కానీ అల్ప ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు చర్యవేగాన్ని తగ్గిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 51.
ఘనపరిమాణాన్ని పెంచడం ద్వారా పీడనాన్ని తగ్గించే ప్రక్రియకు కింది సమతాస్థితులను గురిచేస్తే చర్యలోని క్రియాజనకాల, క్రియాజన్యాల మోల్ల సంఖ్య పెరుగుతుందా ?
i) PCl5 (వా) ⇌ PCl3 (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
ii) CaO (ఘ) + CO2 (వా) ⇌ CaCO3 (ఘ)
జవాబు:
i) PCl5 (వా) ⇌ PCl3 (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం సమతాస్థితిలో ఉన్న వ్యవస్థ పీడనాన్ని తగ్గిస్తే ఘనపరిమాణం, పెరిగే దిశలో సమతాస్థితి జరుగుతుంది. PCl5 పై విఘటనలలో PCl3, Cl2 ఏర్పడి మోల్లసంఖ్య మరియు ఘనపరిమాణం పెరుగుతుంది. కనుక ఈ చర్యలో పీడనాన్ని తగ్గిస్తే క్రియాజన్యాల మోత్ల సంఖ్య పెరుగుతుంది.
ii) CaO (ఘ) + CO2 (వా) ⇌ CaCO3 (ఘ)
ఈ చర్యలో పీడనాన్ని తగ్గించినపుడు CO2 అణువుల సంఖ్య పెరుగుతుంది. CO2 అణువుల సంఖ్య పెరగడం విఘటనం వల్ల జరుగుతుంది. అందువల్ల పీడనాన్ని తగ్గించినపుడు CaCO3 విఘటనం చెందడం వల్ల CaCO3 మోల్లల సంఖ్య తగ్గుతుంది.

ప్రశ్న 52.
పీడనం పెంపు ద్వారా కింది వాటిలో ఏ చర్యలు ప్రభావితం అవుతాయి ? ఈ ప్రభావం ద్వారా చర్య పురోగామి దిశలో జరుగుతుందా ? లేదా ? తిరోగామి దిశలో జరుగుతుందా ? తెలపండి.
i) COCl2 (వా) ⇌ CO (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
ii) CH4 (వా) ⇌ CS2 (వా) + 2H2S (వా)
iii) CO2 (వా) + C (ఘ) ⇌ 2 CO (వా)
iv) 4NH3 (వా) + 5O2 (వా) ⇌ 4 NO (వా) + 6H2O (వా)
జవాబు:
i) COCl2 (వా) ⇌ CO (వా) + Cl2 (వా)
ఈ చర్యలో పీడనం పెంపువల్ల తిరోగామి చర్య జరుగుతుంది. క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతలు తగ్గుతాయి.
ii) CH4 (వా) ⇌ CS2 (వా) + 2H2S (వా)
ఈ చర్యలో మోల్ సంఖ్య సమానం. అందువల్ల పీడన ప్రభావం ఉండదు.
iii) CO2 (వా) + C (ఘ) ⇌ 2 CO (వా)
ఈ చర్యలో పురోగామి దిశలో వాయుస్థితిలోని అణువుల సంఖ్య పెరుగుతున్నది. తిరోగామి దిశలో తగ్గుచున్నది. లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం పీడనాన్ని పెంచితే ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. అంటే ఇవ్వబడిన సమతాస్థితి చర్యలో తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహింపబడుతుంది.
iv) 4NH3 (వా) + 5O2 (వా) ⇌ 4 NO (వా) + 6H2O (వా)
ఈ చర్యలో వాయుస్థితిలోని క్రియాజనకాల మోత్ల సంఖ్య (9), క్రియాజన్యాల మోల్ సంఖ్య (10) కన్నా తక్కువ. లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం పీడనాన్ని పెంచితే సమతాస్థితి వ్యవస్థలో ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య ప్రోత్సహింపబడుతుంది. అనగా తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహింపబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 53.
కింది సమతాస్థితులను పీడనం పెరుగుదల ఏ విధంగా ప్రభావితం చేస్తుంది ? అదేవిధంగా ఉష్ణోగ్రతలలో పెరుగుదల ఏ విధంగా ప్రభావితం చేస్తుంది ?
i) 2NH3 (వా) ⇌ N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ΔH = 92 kJ
ii) N2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2 NO (వా) ΔH = -176 kJ
iii) 2O3 (వా) ⇌ 3O2 (వా) ΔH = -285 kJ
iv) CaO (ఘ) + CO2 (వా) ⇌ CaCO3 (ఘ) ΔH = – 176 kJ
జవాబు:
పీడన ప్రభావం : లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం పీడనాన్ని పెంచితే ఘనపరిమాణం కగ్గే చర్య ప్రోత్సహింపబడుతుంది. ఉష్ణోగ్రతా ప్రభావం : లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో పెరుగుదల ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్యను ప్రోత్సహిస్తుంది.
i) 2NH3 (వా) ⇌ N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ΔH = 92 kJ
ఈ సమతాస్థితిలో అమ్మోనియా విఘటన చర్య అయిన పురోగామి చర్యలో ఘనపరిమాణం పెరుగుచున్నది. పీడనాన్ని పెంచితే ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. అంటే నైట్రోజన్, హైడ్రోజన్ కలసి NH3.
ఏర్పడే చర్య జరుగుతుంది. ఈ చర్యలో పురోగామి చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య. ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో పెరుగుదల ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్యను ప్రోత్సహిస్తుంది. అంటే అమ్మోనియా విఘటనం చెందుతుంది. అంటే పై చర్యలో పురోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
ii) N2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2 NO (వా) ΔH = 181 kJ
ఈ సమతావ్యవస్థలో మోల్ల సంఖ్యలో మార్పు లేదు. ఇటువంటి చర్యలపై పీడన ప్రభావం ఉండదు. పురోగామి చర్యలో ఉష్ణం గ్రహించబడుతున్నది. ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో పెరుగుదల ఉష్ణగ్రాహకచర్యను ప్రోత్సహిస్తుంది. అందువల్ల ఉష్ణోగ్రతను పెంచడం వల్ల NO ఏర్పడే చర్య జరుగుతుంది.
iii) 2O3 (వా) ⇌ 3O2 (వా) ΔΗ = -285 kJ
పీడన ప్రభావం : ఈ సమతాస్థితిలో ఓజోన్ విఘటన చర్య అయిన పురోగామి చర్యలో మోల్ల సంఖ్య పెరుగుట వలన ఘనపరిమాణం పెరుగుతుంది. తిరోగామి చర్యలో ఓజోన్ ఏర్పడి, ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గుతుంది.
లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం అధిక పీడనాల వద్ద ఓజోన్ ఏర్పడే తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. సమతాస్థానం ఎడమవైపు జరుగుతుంది.
ఉష్ణోగ్రత ప్రభావం : ఓజోన్ విఘటన చర్య ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య. (ΔH = ఋణాత్మకం). పురోగామి చర్య ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య. తిరోగామి చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య. లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం అధిక ఉష్ణోగ్రతల వద్ద ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య అయిన తిరోగామి చర్య అయిన ఓజోన్ ఏర్పడే చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
iv) CaO (ఘ) + CO2 (వా) ⇌ CaCO3 (ఘ) ΔH = – 176 kJ
ఈ చర్యలో ఒకే ఒక వాయుస్థితిలోని క్రియాజనకం ఉన్నది. పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య అయిన పురోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
ఈ చర్యలో పురోగామి చర్య ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య. తిరోగామిచర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య. ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే తిరోగామి దిశగా సమతాస్థానం జరుగుతుంది. తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
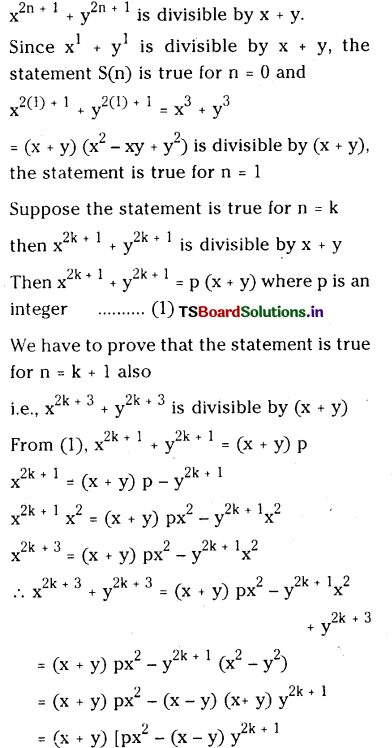
ప్రశ్న 54.
HI విఘటనం చర్యపై అనువర్తితన పీడనం ఎటువంటి ప్రభావం చూపదు. అయితే PCl5 విఘటనంపై ప్రభావం చూపుతుంది. వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
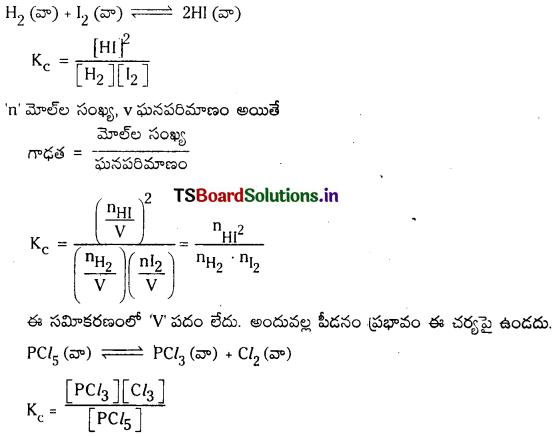
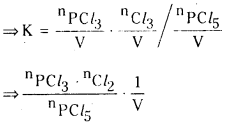
ఈ సమీకరణంలో ‘V’ పదం లేదు. అందువల్ల పీడనం ప్రభావం ఈ చర్యపై ఉండదు.
ఈ సమీకరణంలో ‘V’ పదం ఉంది. కనుక పీడనం వల్ల ఈ చర్య ప్రభావితం అవుతుంది.
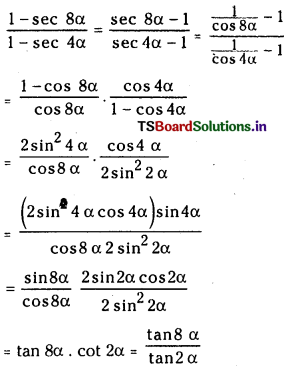
స్థిర ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద Kc విలువ స్థిరం. స్థిర ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు \(\frac{1}{v}\) విలువ పెరుగుతుంది. కాని Kc విలువ స్థిరంగా ఉండుట కోసం \({ }^{{ }^n} \mathrm{Cl}_2\) ల విలువలు తగ్గాలి. అందువల్ల తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 55.
కింది పదాలను వివరించండి.
(i) విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యకం
(ii) అవిద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యకం
(iii) బలహీన బలమైన విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యకాలు
(iv) అయానిక సమతాస్థితి
జవాబు:
i) విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యకం : కొన్ని పదార్థాలు తమ జలద్రావణాల గుండా విద్యుత్ను ప్రవహింపచేస్తాయి. వీటిని విద్యుత్ వాహకాలు అంటారు లేదా విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యకాలు అంటారు. వీటి గుండా విద్యుత్ ప్రవహింపచేసినపుడు విద్యుత్ ప్రవాహంతోబాటు రసాయన మార్పును కూడ పొందుతాయి.
ii) కొన్ని పదార్థాలు తమ జలద్రావణాల ద్వారా విద్యుత్ను ప్రవహింపచేయవు. వీటిని అవిద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యకాలు అంటారు.
iii) బలమైన విద్యుత్ వాహకాలను నీటిలో కరిగించినపుడు అవి సుమారు సంపూర్ణంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతాయి.
బలహీన విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యాలు జలద్రావణాలలో పాక్షికంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతాయి. ఉదా : సోడియం క్లోరైడ్ జలద్రావణంలో సోడియం అయాన్లు క్లోరైడ్ అయాన్లు మాత్రమే ఉంటాయి. ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల జలద్రావణంలో ప్రధానంగా అయనీకరణం చెందని ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల అణువులు, కొద్ది పరిమాణంలో ఎసిటేట్ అయాన్లు, హైడ్రోనియం అయాన్లు ఉంటాయి. దీనికి కారణం సోడియం క్లోరైడ్ బలమైన విద్యుత్ వాహకం కాబట్టి 100% అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది. ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం బలహీన విద్యుత్ వాహకం కాబట్టి 5% కంటే తక్కువ పరిమాణంలో మాత్రమే అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది.
iv) బలహీన విద్యుత్ వాహకాల జలద్రావణాలలో, అయాన్లు అయనీకరణం చెందలేని అణువుల మధ్య సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడి ఉంటుంది. అయాన్లు పాల్గొని ఏర్పడిన సమతాస్థితిని అయానిక సమతాస్థితి అంటారు.
CH3COOH (జల) + H2O (ద్ర) ⇌ CH3COO– (జల) + H3O+ (జల)
ప్రశ్న 56.
కింది పదాలను వివరించండి :
(i) అయనీకరణం విస్తృతి, అది ఏ కారణాంశాలపై ఆధారపడుతుంది
(ii) విఘటనం
(iii) అయనీకరణం
జవాబు:
i) బలహీన విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యాలు పాక్షికంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతాయి. అయనీకరణం వల్ల ఏర్పడిన అయాన్లకు, అయనీకరణం చెందని అణువులకు మధ్య గతిక సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడుతుంది.
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద అయనీకరణం చెందిన అణువుల సంఖ్యకు మొత్తం అణువుల సంఖ్యకు గల నిష్పత్తిని అయనీకరణ అవధి అంటారు. అయనీకరణ అవధిని శాతంగా మార్చితే అయనీకరణ విస్తృతి అంటారు.
అయనీకరణ విస్తృతి తి కింది అంశాలపై ఆధారపడుతుంది.
a) గాఢత : ద్రావణం గాఢత తక్కువగా వుంటే అయనీకరణ విస్తృతి ఎక్కువగా వుంటుంది.
b) ఉష్ణోగ్రత : ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే అయనీకరణం పెరుగుతుంది.
ii) విఘటనం : కొన్ని పదార్థాలను వేడిచేస్తే అవి రెండు లేక అంతకంటే ఎక్కువ విభిన్న పదార్థాలుగా విడిపోతాయి. ఈ ప్రక్రియను విఘటనం అంటారు.
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
iii) తటస్థ అణువు ద్రావణంలో విద్యుత్ ఆవేశపు అయాన్లుగా విచ్ఛిన్నం అయ్యే ప్రక్రియను అయనీకరణం అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 57.
ఆర్హీనియస్ ఆమ్లాల, క్షారాల భావనలను వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
1) నీటిలో కరిగించినపుడు, వియోగం చెంది H+ (జల) అయాన్లను ఏర్పరచే పదార్థాలను ఆమ్లాలు అనీ, హైడ్రాక్సిల్ అయాన్లను ఏర్పరచే పదార్థాలను క్షారాలు అని ఆర్హీనియస్ ప్రతిపాదన.
HX (జల) ⇌ H+ (జల) + X (జల)
MOH (జల) ⇌ M (జల) + OH– (జల)
2) HCl, HNO3 వంటి ఆమ్లాలు జలద్రావణాలు దాదాపు సంపూర్ణంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతాయి. అవి బలమైన ఆమ్లాలు. ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం వంటి ఆమ్లాలు పాక్షికంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతాయి. అవి బలహీన ఆమ్లాలు. అదేవిధంగా జలద్రావణంలో పూర్తిగా అయనీకరణం చెందే క్షారాలు బలమైన క్షారాలు. పాక్షిక అయనీకరణం చెందే క్షారాలు బలహీన క్షారాలు.
3) ఈ సిద్ధాంతం ప్రకారం ఆమ్ల, క్షార తటస్థీకరణ చర్య అనగా, H+, OH– లు కలిసి నీరు ఏర్పడుటయే.
H+ (వా) + OH– (వా) ⇌ H2O (ద్ర)
ప్రశ్న 58.
కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్ల క్షార జంట అంటే ఏమిటి ? ఒక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
ఆమ్ల-క్షారాల మధ్య తేడా ప్రోటాన్ మాత్రమే అయితే, ఆమ్ల క్షార జంటను సంయుగ్మ ఆమ్ల, క్షార జంట లేదా కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్లక్షార జంట అంటారు.
ఉదా :
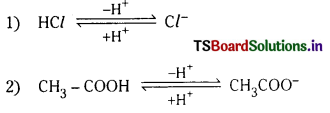

ప్రశ్న 59.
ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం బలహీన ఆమ్లం. 1 M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల జలద్రావణంలో ఉండే అన్ని అయానిక అణు జాతుల గాఢతల అవరోహణ క్రమాన్ని తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం అయనీకరణం

ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం బలహీన ఆమ్లం. అది అల్పంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది. అందువల్ల 1 M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల జలద్రావణంలో అన్ని అయానిక అణుజాతుల గాఢతల అవరోహణ క్రమం
[H2O] > [CH3COOH] > [CH3COO –] = [H3O+] > [OH–]
ప్రశ్న 60.
తగిన సమీకరణాలతో కింది వాటిలో ప్రతీ జాతి బ్రానెడ్ ఆమ్లంగా ప్రవర్తిస్తుంది అని తెలపండి.
a) H3O+
b) HCl
c) NH3
d) HS\(\mathrm{O}_{\overline{4}}\)
జవాబు:
బ్రాన్ డ్ సిద్ధాంతం ప్రకారం హైడ్రోజన్ అయాన్ (H+) ను దానం చేయగలిగే పదార్థాలు ఆమ్లాలు.
a) H3O+ + OH– ⇌ 2H2O
H3O+, OH–కు H+ ను దానం చేస్తుంది. అందువల్ల H3O+ బ్రాన్డెడ్ ఆమ్లం.
b) HCl + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + Cl–
HCl, H2O కు H+ ను దానం చేస్తుంది. అందువల్ల HCl బ్రానెడ్ ఆమ్లం.
c) NH3 + NH3 ⇌ \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\) + \(\mathrm{NH}_2^{-}\)
NH3 మరియొక NH3 కు H+ ను దానం చేస్తుంది. అందువల్ల NH3 బ్రాన్టెస్టెడ్ ఆమ్లం.
d) HS\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{-}\). అందువల్ల \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{-}\) బ్రాన్డెడ్ ఆమ్లం.
ఈ చర్యలో H\(\mathrm{SO}_4^{-}\), H2O కు H+ ను దానం చేస్తున్నది. కావున ఆమ్లం.
ప్రశ్న 61.
తగిన సమీకరణాలతో కింది వాటిలో ప్రతీ జాతి బ్రాన్టెడ్ క్షారంగా ప్రవర్తిస్తుంది అని తెలపండి.
a) H2O
b) OH–
c) C2H5OH
d) HP\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-2}\)
జవాబు:
a) H2O + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + OH–.
నీటి అణువు మరియొక నీటి అణువు నుండి ప్రోటాన్ను స్వీకరిస్తుంది. అందువల్ల H+ స్వీకరిస్తున్న అణువు బ్రాన్ స్టెడ్ క్షారం.
b) HCl + OH– → H2O + Cl–
OH–, HCl నుండి ప్రోటాను స్వీకరిస్తుంది. అందువల్ల OH– బ్రాన్టెడ్ క్షారం.
c)
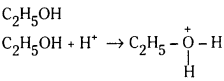
ఇథైల్ ఆల్కహాల్, ప్రోటాను స్వీకరిస్తున్నది. అందువల్ల బ్రాన్డ్ క్షారం.
d) HP\(\mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\)
HP\(\mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\) + HCl → H2P\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) + Cl–
HP\(\mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\), HCl నుండి ప్రోటాను స్వీకరిస్తుంది. కనుక బ్రాన్ స్టెడ్ క్షారం.
ప్రశ్న 62.
H2O, HC\(O_3^{-}\), HS\(O_4^{-}\), NH3 లు బ్రానెడ్ ఆమ్లాలు, బ్రాస్టెస్టెడ్ క్షారాలుగా ప్రవర్తిస్తాయి. వాటికి సంబంధించిన కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్లం, క్షారం రాయండి.
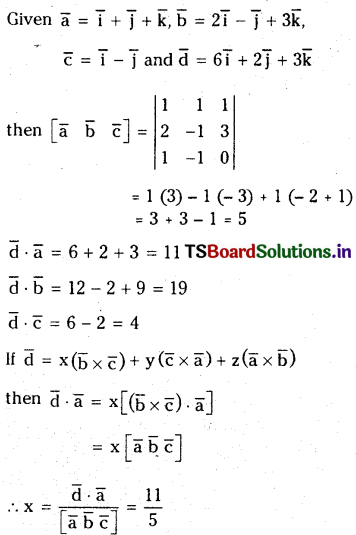
జవాబు:
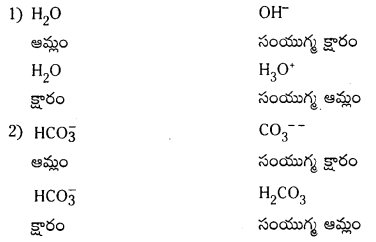

ప్రశ్న 63.
H2P\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) ఆమ్లంగాను, క్షారంగాను ప్రవర్తిస్తుంది అని తెలపడానికి సమీకరణం రాయండి.
జవాబు:
H2P\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) + H2O ⇌ HP\(\mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\) + H3O+
H2P\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) నీటికి ప్రోటాన్ను దానం చేస్తున్నది కనుక ఆమ్లం.
H2\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) + HCl ⇌ H3PO4 + Cl–
H2P\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) ప్రోటాన్ ను HCl నుండి స్వీకరిస్తుంది. కావున క్షారం.

ప్రశ్న 64.
కింది వాటికి కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్లాన్ని, కాంజుగేటు క్షారాన్ని రాయండి.
a) OH–
b) H2O
c) HC\(\mathrm{O}_3^{-}\)
d) H2O2
జవాబు:
a) OH– సంయుగ్మ క్షారం O2-
OH– సంయుగ్మ ఆమ్ల H2O
b) H2O సంయుగ్మ ఆమ్లం H3O+
H2O సంయుగ్మ క్షారం OH–
c) HC\(\mathrm{O}_3^{-}\)
HC\(\mathrm{O}_3^{-}\) సంయుగ్మ ఆమ్ల H2CO3
HC\(\mathrm{O}_{\overline{3}}\) సంయుగ్మ క్షారం C\(\mathrm{CO}_3^{-}\)
d) H2O2
H2O2 సంయుగ్మ ఆమ్లం H3[laex]\mathrm{O}_2^{+}[/latex]
H2O2 సంయుగ్మ క్షారం H\(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\)
ప్రశ్న 65.
బ్రాన్టెస్టెడ్ ఆమ్లం, దాని కొంజుగేటు క్షారం, అదేవిధంగా బ్రానెడ్ క్షారం, దాని కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్లం, వీటిని కింది సమీకరణాలలో గుర్తించండి.
a) HSO4 + Cl– → HCl + HS\(O_4^{-}\)
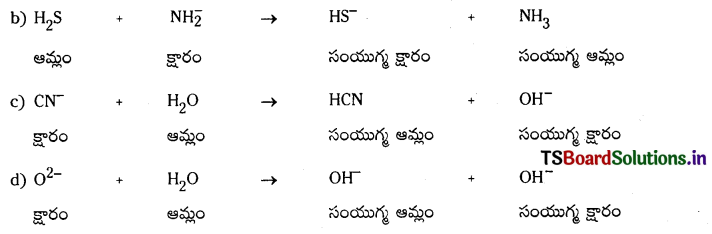
b) H2S + N\(\mathrm{H}_2^{-}\) → HS– + NH3
c) CN– + H2O → HCN + OH–
d) O-2 + H2O → 2OH–
జవాబు:
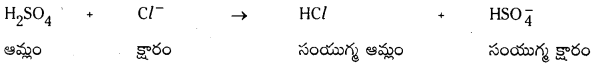
a)
ప్రశ్న 66.
AlCl3, NH3, Mg+2, H2O లను లూయీ ఆమ్లాలు, లూయీ క్షారాలుగా వర్గీకరించండి. జవాబును సమర్ధించండి.
జవాబు:
ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంట దాత క్షారం. ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ స్వీకర్త ఆమ్లం.
AlCl3 ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను స్వీకరించగలదు. కనుక లూయీ ఆమ్లం.
NH3 ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను దానం చేయగలదు. కనుక లూయీ క్షారం. కేటయాన్లు ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను స్వీకరించగలవు. కనుక Mg++ లూయీ ఆమ్లం.
H2O ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను దానం చేయగలదు కనుక లూయీ క్షారం.
ప్రశ్న 67.
బలమైన ఆమ్లం, బలహీన ఆమ్లం, వీటి కాంజుగేటు క్షారాల బలాలను వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
HCl + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + Cl–
ఈ చర్యలో HCl బలమైన ఆమ్లం. దీని సంయుగ్మ క్షారం బలహీనమైనది.
అందువల్ల Cl–, H3O+ నుండి H+ ను స్వీకరించే చర్య చాలా స్వల్పం.
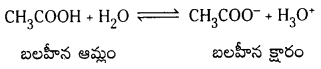
CH3COOH బలహీన ఆమ్లం. దాని సంయుగ్మ క్షారం CH3COO– బలమైన క్షారం.

ప్రశ్న 68.
బలమైన క్షారం, బలహీన క్షారం, వీటి కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్లాల బలాలను వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
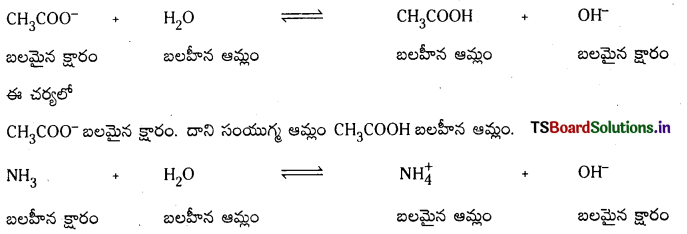
ప్రశ్న 69.
“నీటి అయానిక లబ్ధం”, దీనిని వివరించండి. గది ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద దీని విలువ ఎంత ?
జవాబు:
స్థిర ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద శుద్ధ జలంలో లేదా జలద్రావణాలలో హైడ్రోజన్, హైడ్రాక్సైడ్ అయాన్ల గాఢతల లబ్ధాన్ని నీటి అక అంటారు. దీనిని K తో సూచిస్తారు. దీని విలువ 25°C వద్ద 1.0 × 10-14 మోల్స్ 2/లీ2
శుద్ధ నీరు బలహీన విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యం. దాని అయనీకరణ స్థితిని కింది విధంగా రాస్తారు.
H2O ⇌ H+ + OH–
సమతా స్థితి స్థిరాంకం Kc = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]\left[\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\right]}\)
Kc × [H2O] = [H+] [OH–]
[H2O] విలువ స్థిరం. కాబట్టి Kc . [H2O] విలువ కూడా స్థిరమే. దానిని Kw తో సూచిస్తారు.
Kw = [H+] [OH–]
Kw ను నీటి అయానిక లబ్ధం అంటారు.
Kw విలువ ఉష్ణోగ్రత మీద ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది. ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే Kw విలువ పెరుగుతుంది. దీని కారణం నీటి అయనీకరణం పెరగడమే. నీరు తటస్థ ద్రావణి. కాబట్టి దానిలోని H+, OH– అయాన్ల గాఢత సమానంగా ఉంటుంది.
Kw = [H+] [OH–] = 1.0 × 10-14 మోల్2/లీ2
∴ శుద్ధ నీటిలో [H+] = [OH–] = 1.00 × 10-7 మోల్/లీ
ఆమ్ల ద్రావణంలో [H+] > 1.0 × 10-7 మోల్స్/లీ
క్షారద్రావణంలో [H+] < 1.0 × 10-7 మోల్స్ / లీ లేదా క్షారద్రావణంలో [OH] > 1.00 × 10-7 మోల్/లీ
ప్రశ్న 70.
pH ను నిర్వచించండి. బలహీన ఆమ్లం, బలహీన క్షారం వీటి మోలార్ గాఢతల నుంచి pH ను లెక్కించలేం. ఎందువల్ల ? బలహీన ఆమ్లం pH కు సమీకరణం ఉత్పాదించండి.
జవాబు:
pH = -log10[H+]
H+ అయాన్ గాఢత యొక్క ఋణ సంవర్గమానాన్ని ఉదజని సూచిక pH అంటారు.
బలమైన ఆమ్లం, బలమైన క్షారం జల ద్రావణంలో పూర్తిగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతాయి. అందువల్ల H+, OH– ల గాఢతలు వాటి మోలార్ గాఢతలకు సమానం.
బలహీన క్షారాలు, బలహీన ఆమ్లాలు పాక్షికంగా మాత్రమే అయనీకరణం చెందుతాయి. అందువల్ల H+, OH– అయాన్ల గాఢతలు బలహీన ఆమ్లం, బలహీనక్షారం మోలార్ గాఢతలకు సమానం కావు. అందువల్ల బలహీన ఆమ్లం, బలహీన క్షారాల pH విలువలు వాటి మోలార్ గాఢతల నుండి లెక్కించలేము.
బలహీన ఆమ్లం pH :
HX బలహీన క్షారం. అయనీకరణం కింది విధంగా వ్రాయవచ్చు. బలహీన ఆమ్ల గాఢత ‘C’
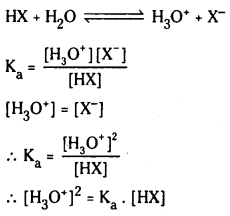
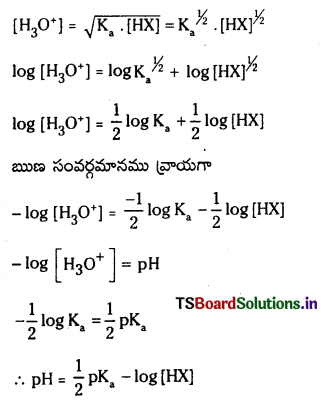
బలహీన ఆమ్లం అల్పంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది కాబట్టి బలహీన ఆమ్ల గాఢతనే సమతాస్థితి వద్ద HX గాఢతకు సమానంగా తీసుకోవచ్చు.
∴ pH = \(\frac{1}{2}\)pKa – \(\frac{1}{2}\) log c

ప్రశ్న 71.
పాలిప్రోటిక్ ఆమ్లాలు H2SO4, H3PO4 ల అంచెలవారీ అయనీకరణాలను తెలిపే సమీకరణాలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
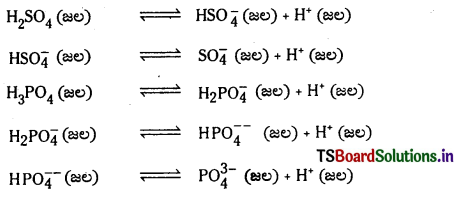
ప్రశ్న 72.
కింది వానిలో ఆమ్ల బలం ఏ విధంగా మారుతుంది ? వివరించండి. ఆవర్తన పట్టికలో
i) గ్రూపులోని మూలకాల హైడ్రైడ్లు
ii) పీరియడ్లోని మూలకాల హైడ్రేడ్లు
జవాబు:
ఒక గ్రూపులో పై నుంచి కిందకు మూలక పరమాణు పరిమాణం పెరుగుతుంది. అందువల్ల బంధ దూరం పెరిగి బంధ బలం తగ్గుతుంది. అందువల్ల అయనీకరణం సులభంగా జరుగుతుంది. అందువల్ల ఆమ్లబలం పెరుగుతుంది.
ఉదా : H-F < HCl < HBr < HI క్రమంలో ఆమ్ల బలం పెరుగుతుంది.
ఆవర్తన పట్టికలో ఎడమ నుంచి కుడికి బంధ ధ్రువణం పెరుగుతుంది. అందువల్ల H – A బంధం సులభంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది. అందువల్ల ఆమ్ల బలం పెరుగుతుంది.
CH4 < NH3 < H2O < HF
ఋణ విద్యుదాత్మకత విలువలు పెరగడం వల్ల ఆమ్ల బలం పెరుగుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 73.
ప్రోటోనిక్ భావన ఆధారంగా నీరు ఆమ్లంగాను, క్షారంగాను కూడా ప్రవర్తిస్తుంది అని తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
- HCl (aq) + H2O (aq) → H3\(\mathrm{O}^{+}\)(జల) + Cl– (జల) ఈ చర్యలో నీరు ప్రోటాన్ ను స్వీకరించి ఆమ్లంగా ప్రవర్తిస్తోంది.
- CH3COO– + H2O → CH3COOH + OH– ఈ చర్యలో నీరు H+ ను దానం చేసి క్షారంగా ప్రవర్తిస్తోంది. ఈ విధంగా నీరు ఆమ్లంగాను, క్షారంగాను కూడా ప్రవర్తించగలదు.
ప్రశ్న 74.
ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాన్ ఫలితం అంటే ఏమిటి ? వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల వియోజన సమతాస్థితి :
CH3COOH (జల) ⇌ H+(జల) + CH3COO– (జల)
Ka = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\right]}\)
ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లద్రావణానికి ఎసిటేట్ అయాన్లను కలిపితే హైడ్రోజన్ అయాన్ల గాఢత [H+] తగ్గుతుంది. అలాగే బాహ్యస్థానం నుంచి H+ అయాన్లను ద్రావణానికి చేర్చితే వియోజనం చెందని ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం దిశ వైపుగా సమతాస్థితి పయనిస్తుంది. అంటే H+ అయాన్ల గాఢత తగ్గే దిశగా పయనిస్తుంది.
ఒక విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యక జలద్రావణానికి దానిలోని, ఆనయాన్ లేక కేటయాన్ ఉభయ సామాన్యంగా ఉండే వేరొక విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యకం కలిపినపుడు మొదటి విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యకం ద్రావణీయత తగ్గిపోతుంది. దీనినే ఉభయసామాన్య అయాన్ ప్రభావం అంటారు. ఉమ్మడి అయాన్ సమక్షంలో బలహీన ఆమ్ల, బలహీన క్షార లేదా బలహీన విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యం యొక్క అయనీకరణం అణచబడుతుంది.
ప్రాధాన్యత : రసాయన విశ్లేషణలో II గ్రూపులో S— గాఢతను, III గ్రూపులో OH– గాఢతను, HCl, NH4Cl లు నియంత్రిస్తాయి. దీనికి కారణం ఉభయసామాన్య అయాను ప్రభావం. H+ అయాన్ సమక్షంలో H2S అయనీకరణ అణచబడి S— గాఢత తగ్గుతుంది. NH4Cl సమక్షంలో NH4OH అయనీకరణం అణచబడి OH– గాఢత తగ్గుతుంది. సమీకరణాలను రాయండి.
ప్రశ్న 75.
“ద్రావణీయతా లబ్ధం” దీనిని నిర్వచించండి. కింది వాటికి ద్రావణీయతా
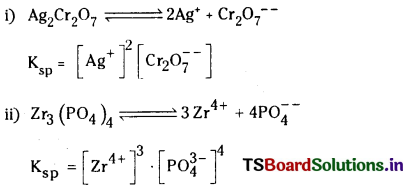
i) Ag2Cr2O7
ii) Zr3(PO4)4
జవాబు:
ద్రావణీయత లబ్ధం : గది ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద ఒక లవణం సంతృప్త ద్రావణంలో కేటయాన్ల గాఢతకు, ఆనయాన్ల గాఢతకు తో సూచిస్తారు. దీని ప్రమాణాలు మధ్యగల లబ్ధాన్ని ఆ లవణం యొక్క ద్రావణీయత లబ్ధం అంటారు. దీనిని Ksp (మోల్స్/లీటర్)”.
n = అణువు అయనీకరణంలో ఏర్పరచే మొత్తం అయాన్ల సంఖ్య. అవి
i) పదార్థం స్వభావం
ii) ఉష్ణోగ్రత మీద ఆధారపడి ఉంటాయి.
ప్రాముఖ్యత : గుణాత్మక విశ్లేషణలో అవక్షేపణ ప్రక్రియలో అవక్షేపణ ప్రాధాన్యత విషయంలో ద్రావణీయత లబ్దం ఎంతగానో ఉపయోగపడుతుంది.
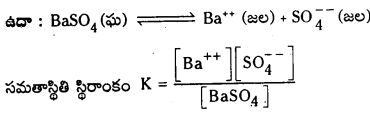
ఘనస్థితిలో గల శుద్ధ పదార్థానికి గాఢత స్థిరంగా ఉంటుంది.
Ksp = K . [BaSO4] = [Ba++] [latex]\mathrm{SO}_4^{–}[/latex]
Ksp ను ద్రావణీయత లబ్ధ స్థిరాంకం అంటారు. 298 K వద్ద Ksp విలువ 1.1 × 10-10 మోల్2 / లీ2.
ప్రశ్న 76.
లవణాలను ఎలా వర్గీకరిస్తారు ? ఏ వర్గం లవణాలు జలవిశ్లేషణం చెందుతాయి ?
జవాబు:
లవణంలోని అయాన్లు నీటితో చర్య జరిపి H+ లేదా OH– అయాన్లను విడుదల చేసే ప్రక్రియను లవణాల జలవిశ్లేషణ అంటారు. లవణాలు 4 రకాలు.
1) బలమైన ఆమ్లం – బలమైన క్షారం లవణాలు ఉదా : NaCl, KNO3
2) బలమైన ఆమ్లం – బలహీన క్షారం లవణాలు ఉదా : NH4 Cl, CuSO4
3) బలహీన ఆమ్లం – బలమైన క్షారం లవణాలు ఉదా : Na2CO3, CH3COONa
4) బలహీన ఆమ్లం – బలహీన క్షారం లవణాలు ఉదా : CH3COONH4, Ca3 (PO4)2
1) బలమైన ఆమ్లం-బలమైన క్షారం లవణాలు : ఈ లవణాలు జలవిశ్లేషణం చెందవు. జలద్రావణంలో కేటయాన్లను, ఆనయాన్లను ఇస్తాయి.
ఉదా : NaCl జల విశ్లేషణ : NaCl అయనీకరణం చెంది Na+, Cl– అయాన్లను ఇస్తుంది. ఈ అయాన్లు H2Oతో చర్య జరిపి NaOH, HCl లను ఇస్తాయి. ఇవి బలమైన విద్యుద్విశ్లేష్యాలు. కాబట్టి పూర్తిగా అయనీకరణం చెంది H+, OH– అయాన్లను ఇస్తాయి. ఇవి తిరిగి కలిసిపోయి అవిఘటిత H2O ను ఇస్తాయి. అంటే జల విశ్లేషణ చెందవు. కాబట్టి (H+) అయాన్లు [OH–] అయాన్ల గాఢతలో మార్పు ఉండదు. అందువల్ల ద్రావణం తటస్థంగా ఉంటుంది. దాని pH = 7 ఉంటుంది. [H+] = [OH–] = 1.0 × 10-7 మోల్స్ / లీటర్. లిట్మస్ కాగితాలతో ఎట్టి మార్పు చూపించదు.
2) బలమైన ఆమ్లం – బలహీన క్షారం లవణాల జలవిశ్లేషణ : ఈ లవణాలు జల విశ్లేషణం చెందే కేటయాన్లను ఇస్తాయి. అందువల్ల ఈ జలవిశ్లేషణను కేటయాన్ జలవిశ్లేషణ అంటారు.
ఉదా : NH4Cl జలవిశ్లేషణ : NH4 Cl అయనీకరణం చెంది N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\), Cl– అయాన్లను ఇస్తుంది. N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) బలమైనది. Cl– బలహీనమైనది. అందువల్ల N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) నీటితో చర్య జరుపుతుంది.
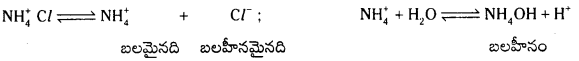
పై చర్యా ఫలితంగా ఏర్పడ్డ NH4 OH బలహీనమైనది కాబట్టి అది అంతగా విఘటనం చెందలేదు. ద్రావణంలో H+ అయాన్ల గాఢత OH– అయాన్ల కంటె ఎక్కువగా ఉంటుంది. ఫలితంగా ద్రావణానికి ఆమ్ల లక్షణం ఏర్పడుతుంది. pH < 7 ఉంటుంది. [H+] > 1.0 × 10-7 ఉంటుంది. ద్రావణం నీలి లిట్మస్ కాగితాలను ఎర్రగా మారుస్తుంది.
3) బలహీన ఆమ్లం – బలమైన క్షారం లవణాల జలవిశ్లేషణ : ఈ లవణాలు జలవిశ్లేషణ చెందే ఆనయాన్లను ఇస్తాయి అందువల్ల ఈ జలవిశ్లేషణను ఆనయాన్ జలవిశ్లేషణ అంటారు.
ఉదా : CH3COONa జలవిశ్లేషణ : CH3COONa అయనీకరణ చెంది CH3COO–, Na+ అయాన్లను ఇస్తుంది. CH3COO– బలమైనది. Na+ బలహీనమైనది. అందువల్ల CH3COO– నీటితో చర్య జరుపుతుంది.
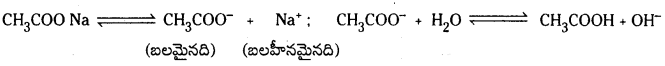
పై చర్యా ఫలితంగా ఏర్పడ్డ CH3COOH బలహీనమైనది కాబట్టి అది అంతగా విఘటనం చెందలేదు. ద్రావణంలో OH– అయాన్ల గాఢత H+ అయాన్ల కంటే ఎక్కువగా ఉంటుంది. ఫలితంగా ద్రావణానికి క్షారలక్షణం ఏర్పడుతుంది. pH > 7 ఉంటుంది. [OH–] > 1.0 × 10-7 ఉంటుంది. ద్రావణం ఎర్ర లిట్మస్ కాగితాలను నీలిరంగుగా మారుస్తుంది.
4) బలహీన ఆమ్లం – బలహీన క్షారం లవణాల జలవిశ్లేషణ : ఈ లవణాలు జలవిశ్లేషణం చెందే ఆనయాన్, కేటయాన్లను ఇస్తాయి.
ఉదా : CH3COONH4 జలవిశ్లేషణ : CH3COONH4 అయనీకరణం చెంది CH3COO–, N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\), అయాన్లను ఇస్తాయి. ఈ రెండు అయాన్లు బలమైనవే. అందువల్ల అవి నీటితో చర్య జరుపుతాయి.
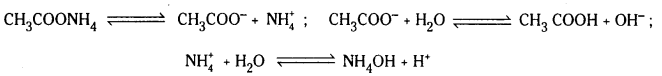
పై చర్యా ఫలితంగా ఏర్పడ్డ CH3COOH, NH4OH లు రెండూ బలహీనమైనవి. అందువల్ల అవి అంతగా విఘటనం చెందవు. ఇకపోతే ద్రావణంలో ఏర్పడ్డ H+, OH– అయాన్లు సమానంగా కాని లేదా అసమానంగా గాని ఉండవచ్చు. అందువల్ల ద్రావణం తటస్థంగా లేదా ఆమ్లంగా లేదా క్షారంగా ఉండవచ్చు. ద్రావణ లక్షణం Ka, Kb లపై ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది.
గమనిక : 2, 3, 4 రకాల లవణాలు మాత్రమే జలవిశ్లేషణ చెందుతాయి.

ప్రశ్న 77.
ఒక చర్యకు ΔG° విలువ కింది వాటిలో ఏ విధంగా ఉంటుంది ?
a) K > 1
b) K = 1
c) K < 1 జవాబు: a) K > 1 అయితే ΔG° విలువ ఋణాత్మకం. చర్య స్వచ్ఛందంగా పురోగామి దిశలో జరుగుతుంది. ఉత్పన్నాలు అధికంగా ఏర్పడతాయి.
b) K = 1 అయితే ΔG° = 0 వ్యవస్థ సమతాస్థితిలో ఉంటుంది.
c) K < 1 అయితే ΔG° విలువ ధనాత్మకం. ఈ స్థితిలో పురోగామి చర్య స్వల్పంగా మాత్రమే జరుగుతుంది. ఉత్పన్నాలు అల్ప పరిమాణంలో మాత్రమే ఏర్పడతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 78.
NH4Cl జలద్రావణం ఆమ్ల గుణం చూపిస్తుంది. వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
NH4Cl జలద్రావణం ఆమ్ల గుణం చూపిస్తుంది.
అమ్మోనియం క్లోరైడ్ జల ద్రావణంలో N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) అయానులు, Cl అయానులు ఉంటాయి. N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) అయానులు నీటితో చర్య పొందుతాయి. H3O+ అయాన్లను విడుదల చేస్తాయి. అందువల్ల NH4Cl జలద్రావణానికి ఆమ్ల లక్షణం ఉంటుంది. pH < 7.
N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) + H2O ⇌ NH3 + H3O+
NH4Cl + H2O ⇌ NH4OH + HCl
Cl– అయానులు జలవిశ్లేషణ చెందవు. H3O+ ఏర్పడుటవలన H3O+ > 1.0 × 10-7 ఉంటుంది. అందువల్ల NH4Cl జలద్రావణం ఆమ్ల లక్షణం కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 79.
CH3COONa జలద్రావణం క్షార గుణం చూపిస్తుంది. వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
సోడియం ఎసిటేటు జలద్రావణంలో CH3COO– అయానులు జలవిశ్లేషణం చెందుతాయి. Na+ అయానులు జలవిశ్లేషణ చెందవు. OH– ల గాఢత 1.0 × 10-7 కన్నా అధికమైనందున CH3COONa ద్రావణం క్షారత్వాన్ని చూపుతుంది.
CH3COO– + H2O → CH3COOH + OH–
CH3COONa + H2O → CH3COOH + NaOH
ప్రశ్న 80.
సోడియం ఎసిటేట్ ద్రావణంలో కరిగి ఉండి ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం, సోడియం క్లోరైడు ద్రావణంలో కరిగి ఉండే దానికంటే బలహీనంగా ఉంటుంది. కారణం తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల బలం అయనీకరణం వల్ల విడుదలయ్యే H+ అయాన్ల సంఖ్యపై ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది.
CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO– + H+
సోడియం ఎసిటేటు CH3COONa, CH3COOH లలో CH3COO– ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాను. సోడియం ఎసిటేటు విఘటనంలో CH3COO- అయానులు ఏర్పడతాయి.
CH3COO Na → CH3COO– + Na+
ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాన్ అయిన CH3COO– అయాను సమక్షంలో ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం విఘటనం అణచబడుతుంది. అందువల్ల బలహీనంగా వుంటుంది.
NaCl → Na+ + Cl–
NaCl సమక్షంలో CH3COOH కు ఉమ్మడి అయాను లేదు. అందు ఉభయసామాన్య ప్రభావం లేదు.
ప్రశ్న 81.
శుద్ధ నీటిలో కంటె, AgNO3 లో AgCl తక్కువగా కరుగుతుంది. దీనిని వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
AgNO3 ద్రావణంలో AgCl తక్కువగా కరుగుతుంది. ఎందులకనగా ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాన్ ప్రభావం వల్ల AgNO3 ద్రావణీయత తగ్గిపోతుంది.
శుద్ధనీటిలో AgCl ఎక్కువగా కరుగుతుంది. కారణం ఏమనగా ఇచ్చట ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాన్ ప్రభావం ఉండదు.
ప్రశ్న 82.
CH3COOH (జల) + Cl– (జల) → చర్య ఎడమవైపు నుంచి కుడివైపుకు పురోగమిస్తుందా ? తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
CH3COOH (జల) + Cl–(జల) → CH3COO– + HCl. Cl– బలహీన క్షారం. అందువల్ల అది CH3COOH నుంచి H+ ను స్వీకరించలేదు. CH3COOH బలహీన ఆమ్లం. అది ప్రోటానును బంధించి ఉంచుతుంది. అందువల్ల ఈ చర్య జరగదు.
ప్రశ్న 83.
H2S జలద్రావణంలో H2S, HS-1, S-2, H3O+, OH–, H2O భిన్న గాఢతలలో ఉంటాయి. వీటిలో ఏ జాతి క్షారంగా పనిచేస్తుంది ? ఏది ఆమ్లంగా పనిచేస్తుంది ? ఏది ఆమ్లం, క్షారం రెండింటిగా పనిచేస్తుంది ?
జవాబు:
H2O + H2S ⇌ HS– + H3O+
H2O + HS– ⇌ S— + H3O+
a) S2- క్షారంగా మాత్రమే పనిచేస్తుంది. అది ఆమ్లంగా పనిచేయదు. కారణం అది H+ లను కలిగి లేదు.
b) H2S, H3O+ లు ఆమ్లాలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి.
c) HS–, OH–, H2O లు ఆమ్లాలుగాను, క్షారాలుగాను పనిచేస్తాయి. అవి H+ ను దానం చేయగలవు మరియు గ్రహించగలవు.
దీర్ఘ సమాధాన ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 84.
సమతాస్థితి ప్రక్రియలు అంటే ఏమిటి ? భౌతిక, రసాయన ప్రక్రియలలో ఈ సమతాస్థితిని సోదాహరణంగా వివరించండి..
జవాబు:
ఉత్రమణీయ చర్యలలో ఏ స్థితి వద్ద పురోగామి చర్యావేగం తిరోగామి చర్యావేగానికి సమానం అవుతుందో ఆ స్థితిని “సమతాస్థితి” అంటారు.
భౌతిక సమతాస్థితి ప్రక్రియలు : ఏ భౌతిక ప్రక్రియలలో పదార్థం యొక్క రెండు ప్రావస్థల (భౌతిక స్థితుల) మధ్య సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడుతుందో వాటిని భౌతిక సమతాస్థితి ప్రక్రియలు అంటారు.
ఉదా : ఘన స్థితి ⇌ ద్రవస్థితి
ఘన స్థితి ⇌ బాష్పస్థితి
రసాయన సమతాస్థితి ప్రక్రియలు : ఏ రసాయన ప్రక్రియలలో క్రియాజనకాల మరియు క్రియాజన్యాల మధ్య సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడుతుందో వాటిని రసాయన సమతాస్థితి ప్రక్రియలు అంటారు.
N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2 NH3
2SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3
ప్రశ్న 85.
గతిక సమతాస్థితి అంటే ఏమిటి ? సరైన ఉదాహరణలతో వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద పురోగామి చర్యావేగం మరియు తిరోగామి చర్యావేగాలు సమానంగా ఉంటాయి. ఆ స్థితి వద్ద క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతలో గాని, క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతలో గాని ఎట్టి మార్పు కనిపించదు. ఆ పరిస్థితులలో చర్య జరగటం లేదేమోనని మనం భ్రమపడతాం. కాని చర్య జరుగుతూనే ఉంటుంది. అందువలన ఈ సమతాస్థితిని గతిక సమతాస్థితి అంటారు. అన్ని రసాయన సమతాస్థితి ప్రక్రియలు గతిక సమతాస్థితిని కలిగి ఉంటాయి.
ఉదా : N2(వా) + 3H2(వా) ⇌ 2NH3 (వా)
మూత కలిగిన ఒక పాత్రలో N2, H2 వాయువులను 1: 3 నిష్పత్తిలో తీసికోండి. చర్య జరగడానికి ముందు పాత్రలో కేవలం N2, H2 లు మాత్రమే ఉంటాయి. వాటి గాఢత గరిష్ఠంగా ఉంటుంది. అపుడు పురోగామి చర్యావేగం కూడా గరిష్ఠంగా ఉంటుంది. కాలంతో పాటు N2, H2 ల గాఢతలు క్రమంగా తగ్గుతాయి. కాబట్టి పురోగామి చర్యావేగం క్రమంగా తగ్గుతుంది. క్రియాజన్యం (NH3) గాఢత ఒక గరిష్ఠ విలువను చేరుకోగానే తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రారంభం అవుతుంది. అపుడు తిరోగామి చర్యావేగం గరిష్ఠంగా ఉంటుంది. కాలంతో పాటుగా క్రియాజన్యం (NH3) గాఢత క్రమంగా తగ్గుతుంది. అపుడు తిరోగామి చర్యావేగం క్రమంగా తగ్గుతుంది. ఈ విధంగా పురోగామి, తిరోగామి చర్యల వేగాలు తగ్గుతూ, పెరుగుతూ ఒకానొక దశలో రెండు వేగాలు సమానం అవుతాయి. ఈ స్థితినే ఈ రసాయన చర్యయొక్క సమతాస్థితి అంటారు. సమతాస్థితిని చేరుకోగానే రెండు వేగాలు (పురోగామి, తిరోగామి) సమానంగా ఉండటం వల్ల క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతలో గాని, క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతలో గాని మార్పు కనిపించదు. ఈ పరిస్థితులలో మనకు చర్య జరగటం లేదేమోనని భ్రమ కలుగుతుంది. కాని నిజానికి చర్య జరుగుతూనే ఉంటుంది. అందువలననే ఈ సమతాస్థితిని గతిక సమతాస్థితి అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 86.
భౌతిక ప్రక్రియలలోని సమతాస్థితుల సాధారణ అభిలాక్షణిక ధర్మాలను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
భౌతిక ప్రక్రియలలో సమతాస్థితి :
- ద్రవబాష్పాల మధ్య సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడుతుంది. ద్రవం ⇌ బాష్పం
- ద్రవాలలో వాయువులు కరిగినప్పుడు సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడుతుంది.
ఈ భౌతిక ప్రక్రియలలో కొన్ని అభిలాక్షణిక ధర్మాలు సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉండే అన్ని వ్యవస్థలకు ఉంటాయి.
- నిర్దిష్ట ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద సంవృత (మూసి ఉన్న) వ్యవస్థలలో మాత్రమే సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడుతుంది.
- పరస్పరం వ్యతిరేకించే రెండు చర్యలు (పురోగామి, తిరోగామి) ఒకే వేగంతో జరుగుతాయి. కాబట్టి గతిక సమతాస్థితి చోటుచేసుకొంటుంది. అయితే స్థిరపరిస్థితి కొనసాగుతుంది.
- వ్యవస్థ కొలవడానికి వీలుండే అన్ని ధర్మాలు స్థిరంగా ఉంటాయి.
- ఒక భౌతిక ప్రక్రియ సమతాస్థితిని చేరుకొన్న సందర్భంలో స్థిర ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద దాని పరామితులలో ఒకదాని విలువ స్థిరంగా ఉండే అభిలాక్షణిక స్వభావాన్ని ఈ ప్రక్రియ కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
- సమతాస్థితిని చేరుకొనక ముందుగా భౌతిక ప్రక్రియ ఎంత విస్తృతికి జరిగింది అనే విషయాన్ని ఈ పరామితుల పరిమాణాలు సూచిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 87.
సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం ముఖ్య లక్షణాలను తెలపండి. సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం అనువర్తనాలు రెండింటిని తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాల అనువర్తనాలను గురించి తెలుసుకోవడానికి ముందుగా సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాల ముఖ్య లక్షణాలివి.
- సమతాస్థితి వద్ద క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతలు, క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతలు స్థిర విలువలను చేరుకొన్న తరువాతే సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం అనువర్తిస్తుంది.
- సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ క్రియాజనకాల, క్రియాజన్యాల ఆరంభ గాఢతల మీద ఆధారపడి ఉండదు.
- సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ చర్య ఉష్ణోగ్రత మీద ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది. నిర్దిష్ట ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద ప్రతీ చర్యకు దానిదైన ప్రత్యేకమైన సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ ఉంటుంది. ఈ విలువ ఈ చర్య సమతుల్యం చేయబడిన రసాయన సమీకరణం మీద ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది.
- ఉత్రమణీయ చర్య (లేదా తిరోగామి దిశలో జరిగే చర్య) సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ పురోగామి దిశలో జరిగే చర్య సమతా స్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువకు ఉత్రమణీయ విలువగా ఉంటుంది.
- మూల సమీకరణంతో సూచింపబడని ఒక చర్య సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం K విలువ చర్య మూల సమీకరణం సూచించే సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం (K) విలువతో సంబంధం కలిగి ఉంటుంది. ఈ సంబంధం నిర్ధారించడానికి మూల సమీకరణం ద్వారా సూచింపబడిన చర్యా సమీకరణాన్ని ఒక లఘు సంఖ్య (n) తో గుణించి లేదా భాగించి ఇచ్చిన చర్య సమీకరణాన్ని రాబడతారు.
K = Kn
అనువర్తనాలు :
- చర్య స్థిరాంక పరిమాణం ద్వారా చర్య విస్తృతిని ఊహించడం.
- చర్య జరిగే దిశను (పురోగామి లేదా తిరోగామి) నిర్ధారించడం.
- సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలను లెక్కించడం.

ప్రశ్న 88.
లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం వివరించండి. సమతాస్థితిని ప్రభావితం చేసే అంశాలను వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
ప్రయోగ పరిస్థితులలో చోటుచేసుకొన్న మార్పులు సమతాస్థితిపై ఎటువంటి ప్రభావాన్ని కలుగజేస్తాయి అనే విషయాన్ని గుణాత్మకంగా తెలుసుకోవడానికి లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ఉపయోగపడుతుంది.
ఒక వ్యవస్థ సమతాస్థితిని నియంత్రించే కారణాంశాలలో దేనినైనా మార్పు చెందించినట్లైతే ఈ మార్పును తగ్గించే విధంగా లేదా పూర్తిగా ప్రతిఘటించే విధంగా లేదా తటస్థపరిచే విధంగా, వ్యవస్థ వ్యవహరిస్తుంది.
ఈ సూత్రం అన్ని భౌతిక, రసాయనిక సమతాస్థితులకు కూడా వర్తిస్తుంది.
సమతాస్థితిని ప్రభావితం చేసే అంశాలు :
గాఢతా ప్రభావం : H2 (వాయువు) + I2(వా) ⇌ 2HI(వా)
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఈ చర్యా మిశ్రమానికి H2 ను కలిపినట్లైతే చర్యా సమతాస్థితి చెదిరిపోతుంది. కాబట్టి H2 వినియోగపడే దిశలో చర్య పురోగమించి సమతాస్థితి పునరుద్ధరించబడుతుంది. అంటే HI ఏర్పడే విధంగా H2, I2 లు అధిక పరిమాణంలో చర్య జరిపి సమతాస్థితి పురోగామి దిశలో జరుగుతుంది. ఇదే విధంగా ఏర్పడిన హైడ్రోజన్ అయొడైడ్ను తొలగిస్తే కూడా పురోగామి దిశలో చర్య జరుగుతుంది.
సమతాస్థితిలో ఉండే ఒక రసాయన చర్యలోని క్రియాజనకాల లేదా క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతను మార్చినట్లైతే ఈ గాఢత మార్పును కనిష్ఠపరిచే విధంగా సమతాస్థితి మిశ్రమం సంఘటనం మార్పు చెందుతుంది.
పీడన ప్రభావం : ఒక చర్యలో వాయు స్థితిలో ఉండే క్రియాజనకాలు మొత్తం మోల్ల సంఖ్య వాయుస్థితిలో ఉండే క్రియాజన్యాల మొత్తం మోల్ల సంఖ్యకు సమానంగా లేనప్పుడు ఆ సమతాస్థితిపై పీడన ప్రభావం ఉంటుంది. లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం సమతాస్థితి వ్యవస్థపై పీడనాన్ని పెంచినప్పుడు ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే దిశలో చర్య
జరుగుతుంది.
1) పీడన ప్రభావం :
a) పీడనంలో పెరుగుదల : సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉన్న వ్యవస్థపై పీడనాన్ని పెంచితే లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం ఈ ప్రభావం రద్దు అయ్యే వైపుకు అంటే ఘ.ప.,ల సంఖ్య తగ్గే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి జరుగుతుంది.
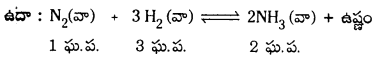
ఈ వ్యవస్థపై పీడనాన్ని పెంచితే పురోగామి చర్యవైపుకు సమతాస్థితి జరుగుతుంది.
b) పీడనంలో తగ్గుదల : సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉన్న వ్యవస్థపై పీడనాన్ని తగ్గిస్తే లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం ఈ ప్రభావం రద్దు అయ్యేవైపుకు అంటే ఘ.ప. ల సంఖ్య పెరిగే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి జరుగుతుంది.
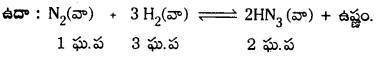
ఈ వ్యవస్థపై పీడనాన్ని తగ్గిస్తే తిరోగామిచర్య జరిగే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి జరుగుతుంది.
2) ఉష్ణోగ్రతా ప్రభావం :
a) ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో పెరుగుదల : సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉన్న వ్యవస్థపై ఉష్ణోగ్రతను పెంచితే లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం, ఈ ప్రభావం రద్దు అయ్యే వైపుకు అంటే ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య జరిగే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి స్థానం జరుగుతుంది.
ఉదా : N2(వా) + 3H2(వా) ⇌ 2NH3(వా) + ఉష్ణం.
దీనిలో పురోగామిచర్య = ఉష్ణమోచకం
తిరోగామి చర్య = ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య
ఈ వ్యవస్థపై ఉష్ణోగ్రతను పెంచితే తిరోగామిచర్య జరిగే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి జరుగుతుంది.
b) ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో తగ్గుదల : సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉన్న వ్యవస్థపై ఉష్ణోగ్రతను తగ్గిస్తే లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం, ఈ ప్రభావం రద్దు అయ్యే వైపుకు అంటే ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య జరిగే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి స్థానం జరుగుతుంది.
ఉదా : N2(వా) + 3 H2 (వా) ⇌ 2NH3 (వా) + ఉష్ణం
దీనిలో పురోగామి చర్య = ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య
తిరోగామి చర్య = ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య
ఈ వ్యవస్థపై ఉష్ణోగ్రతను తగ్గిస్తే, పురోగామి చర్య జరిగే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి జరుగుతుంది.
సమతాస్థితికి జడవాయువు చేర్చినపుడు కలిగే ప్రభావం : ఘనపరిమాణాన్ని స్థిరంగా ఉంచి ఆర్గాన్ వంటి జడవాయువును చర్యా మిశ్రమానికి చేర్చినట్లైతే అది చర్యలో పాల్గొనని కారణంగా సమతాస్థితి చెదిరిపోకుండా ఉంటుంది. స్థిరఘనపరిమాణం వద్ద చర్యలో పాల్గొనే పదార్థాల పాక్షిక పీడనాల విలువలో మార్పురాదు.
ఉత్ప్రేరక ప్రభావం : క్రియాజనకాలు క్రియాజన్యాలుగా మారేందుకు అల్ప ఉత్తేజిత శక్తిగల కొత్త మార్గాన్ని సమకూర్చడం ద్వారా ఉత్ప్రేరకం రసాయన చర్యావేగాన్ని పెంచుతుంది. ద్విగత చర్యలలో ఉత్ప్రేరకం పురోగామి, తిరోగామి చర్యల రెండింటి వేగాలను సమానంగా పెంచుతుంది. ఫలితంగా సమతాస్థితిపై ఎటువంటి ప్రభావం ఉండదు. సమతాస్థితి శీఘ్రంగా ఏర్పడడానికి ఉత్ప్రేరకం ఉపయోగిస్తుంది. అమ్మోనియా సంశ్లేషణలో ఇనుమును ఉత్ప్రేరకంగా వాడతారు.
ప్రశ్న 89.
అమ్మోనియా, సల్ఫర్ ట్రై ఆక్సైడ్ పారిశ్రామిక తయారీలలో, లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ఉపయోగాన్ని వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం : సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉన్న ఒక ఉత్రమణీయ రసాయన చర్యను, సమతాస్థితిని ప్రభావితం చేసే పీడనం లేదా ఉష్ణోగ్రత లేదా గాఢతల మార్పుకు గురిచేస్తే ఈ మార్పు ప్రభావాన్ని తగ్గించే వైపుకు లేదా రద్దు చేసే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి మారుతుంది.
హేబర్ పద్ధతి ద్వారా అమ్మోనియా సంశ్లేషణ :
N2(వా) + 3H2(వా) ⇌ 2NH3(వా) + ఉష్ణం – చర్యకు లీచాట్లియర్ సూత్రం అనువర్తన.
1) పీడన ప్రభావం : ఇవ్వబడిన చర్యలో, పురోగామి చర్య జరిగితే ఘ.ప. సంఖ్య తగ్గుతుంది. (4 ఘప → 2 ఘ. ప) తిరోగామి చర్య జరిగితే ఘ.ప. సంఖ్య పెరుగుతుంది. (2 ఘ. ప → 4 ఘ.ప)
అమ్మోనియా అధికంగా దిగుబడి కావాలంటే పురోగామి చర్య జరగాలి. అంటే ఘ.ప. సంఖ్య తగ్గే వైపుకు చర్య ప్రభావితం అవ్వాలి. దీనికి గానూ అధిక పీడనాలను ఉపయోగించాలి. ఇచ్చట ఉపయోగించవలసిన అధిక పీడనాల విలువ 200 అట్మాస్ఫియర్లు.
2) ఉష్ణోగ్రతా ప్రభావం : ఇవ్వబడిన చర్యలో
పురోగామి చర్య = ఉష్ణమోచకం
తిరోగామి చర్య = ఉష్ణగ్రాహకం
అమ్మోనియా అధికంగా దిగుబడి కావాలంటే పురోగామి చర్య జరగాలి. అంటే ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య జరిగే వైపుకు చర్య ప్రభావితం అవ్వాలి. దీనికి గానూ, అల్ప ఉష్ణోగ్రతలను ఉపయోగించాలి. ఇచ్చట ఉపయోగించవలసిన అల్ప ఉష్ణోగ్రత విలువ 725 – 775K.
3) గాఢతల ప్రభావం : క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతను పెంచినా లేదా క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతను తగ్గించినా పురోగామి చర్య ప్రభావితం అయి అధికంగా అమ్మోనియా దిగుబడి అవుతుంది. అందువలన ఇవ్వబడిన సమతాస్థితి వ్యవస్థలో N2, H2 గాఢతను పెంచడం మరియు ఏర్పడిన NH3 ని ఎప్పటికప్పుడు తీసివేయడం చేస్తూ ఉండాలి.
4) ఉత్ప్రేరక ప్రభావం : అధిక అమ్మోనియా దిగుబడి కావాలంటే ఇనుప పొడి మరియు మాలిబ్దినం పొడుల మిశ్రమాన్ని ఉత్ప్రేరకంగా వాడతారు. ఇచ్చట మాలిబ్ధినం పొడి ప్రవర్ధకంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
అధిక అమ్మోనియా దిగుబడికి కావలసిన పరిస్థితులు :
పీడనం = 200 అట్మాస్ఫియర్లు
ఉష్ణోగ్రత = 725 – 775 K
ఉత్ప్రేరకం = ఇనుము పొడి
ప్రవర్ధకం = మాలిబ్దినం పొడి
క్రియాజనకాలైన N2, H2 ల గాఢతను పెంచుతూ ఉండాలి.
క్రియాజన్యమైన NH3 ఎప్పటికప్పుడు తీసివేస్తూ ఉండాలి.
లీచాట్యర్ సూత్రం : సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ఉన్న ఒక ఉత్రమణీయ రసాయన చర్యను, సమతాస్థితిని ప్రభావితం చేసే పీడనం, లేదా ఉష్ణోగ్రత లేదా గాఢతల మార్పుకు గురి చేస్తే ఈ మార్పు ప్రభావాన్ని తగ్గించే వైపుకు లేదా రద్దు చేసే వైపుకు సమతాస్థితి మారుతుంది.
SO3 సంశ్లేషణ పద్ధతి :
2SO2(వా) + O2(వా) ⇌ 2SO3(వా) + ఉష్ణం – చర్యకు లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం అనువర్తనం.
1) పీడన ప్రభావం : ఇవ్వబడిన పురోగామి చర్య జరిగితే ఘ.ప. ల సంఖ్య తగ్గుతుంది. (3 ఘ.ప. → 2 ఘ. ప ) తిరోగామి చర్య జరిగితే ఘ.ప. ల సంఖ్య పెరుగుతుంది. (2 ఘ. ఫ → 3 ఘ.ప) సల్ఫర్ ట్రై ఆక్సైడ్ అధికంగా దిగుబడి కావాలంటే పురోగామి చర్య జరగాలి. అంటే ఘ.ప. ల సంఖ్య తగ్గే వైపుకు చర్య ప్రభావితం అవ్వాలి. దీనికి గానూ అధిక పీడనాలు ఉపయోగించాలి. ఇచ్చట ఉపయోగించవలసిన అధిక పీడనాల విలువ 1.5 అట్మా 1.7 అట్మాస్ఫియర్లు.
2) ఉష్ణోగ్రతా ప్రభావం : ఇవ్వబడిన చర్యలో
పురోగామి చర్య = ఉష్ణమోచకం
తిరోగామి చర్య = ఉష్ణగ్రాహకం
సల్ఫర్ ట్రై ఆక్సైడ్ అధికంగా దిగుబడి కావాలంటే పురోగామి చర్య జరగాలి. అంటే ఉష్ణమోచక చర్య జరిగే వైపుకు చర్య ప్రభావితం అవ్వాలి. దీనికి గానూ అల్ప ఉష్ణోగ్రతలను ఉపయోగించాలి. ఇచ్చట ఉపయోగించవలసిన అల్ప ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు 673 K.
3) గాఢతల ప్రభావం : క్రియాజనకాల గాఢతను పెంచినా లేదా క్రియాజన్యాల గాఢతను తగ్గించినా పురోగామి చర్య ప్రభావితం అయి అధికంగా SO3 దిగుబడి అవుతుంది. అందువలన ఇవ్వబడిన సమతాస్థితిలో SO2, O2 ల గాఢతలను పెంచడం మరియు ఏర్పడిన SO3 ని ఎప్పటికప్పుడు తీసివేయడం చేస్తూ ఉండాలి.
4) ఉత్ప్రేరక ప్రభావం : అధిక SO3 దిగుబడి కావాలంటే V2O5 ను ఉత్ప్రేరకంగా వాడతారు.
అధిక SO3 దిగుబడికి అనుకూల పరిస్థితులు :
పీడనం : 1.5 – 1.7 అట్మాస్ఫియర్లు
ఉష్ణోగ్రత : 673 K
ఉత్ప్రేరకం : వనేడియం పెంటాక్సైడ్ (V2O5)
క్రియాజనకాలైన SO2, O2 ల గాఢతను పెంచుతూ ఉండాలి.
క్రియాజన్యమైన SO3 ను ఎప్పటికప్పుడు తీసివేస్తూ ఉండాలి.
ప్రశ్న 90.
కింద పేర్కొన్న ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య ఆధారంగా సహజ వాయువును, నీటి ఆవిరి ద్వారా పాక్షిక ఆక్సీకరణం చర్యకు గురిచేసి డైహైడ్రోజన్ వాయువును తయారుచేస్తారు.
CH (వా) + H2O (వా) ⇌ CO (వా) + 3H2 (వా)
a) పై చర్యకు Kp కు సమీకరణం రాయండి.
b) Kp విలువ సమతాస్థితి మిశ్రమం సంఘటనం ఏ విధంగా కింది వాటి ద్వారా ప్రభావితం అవుతాయి ?
i) పీడనం పెరుగుదల
ii) ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరుగుదల
iii)ఉత్ప్రేరకం ఉపయోగం
జవాబు:
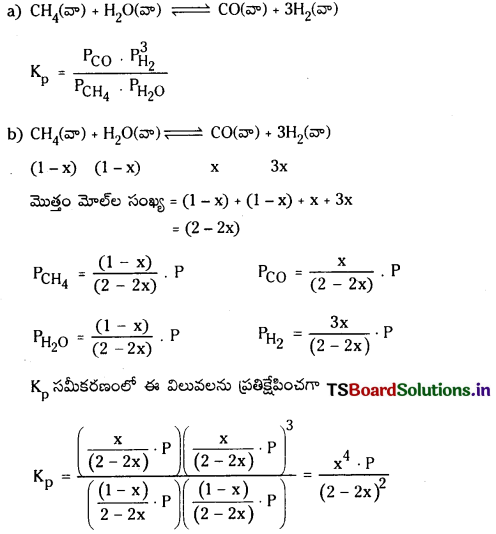
1) ఈ సమీకరణంలో ‘P’ లవంలో ఉన్నది. పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు Kp విలువను స్థిరంగా ఉంచే విధంగా హారం విలువ పెరగాలి. అందువల్ల తిరోగామిచర్య జరిగి ఉత్పన్నాల గాఢత తగ్గుతుంది.
లీచాటయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం పీడనాన్ని పెంచినపుడు ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. తిరోగామి చర్యలో ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గుచున్నది కనుక తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది.
2) ఈ చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహకచర్య కావున ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే పురోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. ఉత్పన్నాలు అధికంగా ఏర్పడతాయి.
3) ఉత్ప్రేరకం సమతాస్థానాన్ని ప్రభావితం చేయదు.
ప్రశ్న 91.
2H2 (వా) + CO (వా) ⇌ CH3 OH (వా) చర్య సమతాస్థితిపై కింది వాటి ప్రభావాన్ని తెలపండి.
a) H2 సంకలనం
b) CH3OH సంకలనం
c) CO తొలగింపు
d) CH3OH తొలగింపు
జవాబు:
a) లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం, క్రియాజనకాల గాఢత పెంచితే పురోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. H2 సంకలనం (కలుపుట) వలన CH3OH ఎక్కువగా ఏర్పడుతుంది.
b) లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం, క్రియాజన్యం కలిపినపుడు తిరోగామి చర్య జరుగుతుంది. H2 మరియు CO ల గాఢత పెరుగుతుంది.
c) CO తొలగింపు : లీచాటయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం క్రియాజనకం తొలగిస్తే, తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. CH3OH గాఢత తగ్గుతుంది.
d) CH3OH తొలగింపు : లీచాట్లెయర్ సూత్రం ప్రకారం ఉత్పన్నాన్ని తొలగిస్తే పురోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. అందువల్ల CH3OH అధికంగా ఏర్పడుతుంది.

ప్రశ్న 92.
473K వద్ద ఫాస్ఫరస్ డెంటాక్లోరైడ్ PCl5, విఘటనం చర్యకు సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ Kc = 8.3 × 10-3. ఈ విఘటన చర్యను కింది విధంగా వ్యక్తం చేస్తే.
PCl5 (వా) ⇌ PCl3 (వా) + Cl2 (వా) ΔH = 124.0 kJmol-1,
a) చర్యకు Kc ను వ్యక్తం చేసే సమాసం రాయండి.
b) అదే ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద, ఉత్రమణీయ చర్యకు Kc విలువను తెలపండి.
c) Kc పై కింది వాని ప్రభావం తెలపండి.
i) PCl5 అధిక సంకలనం
ii) పీడనం పెంచడం
iii) ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెంచడం
జవాబు:
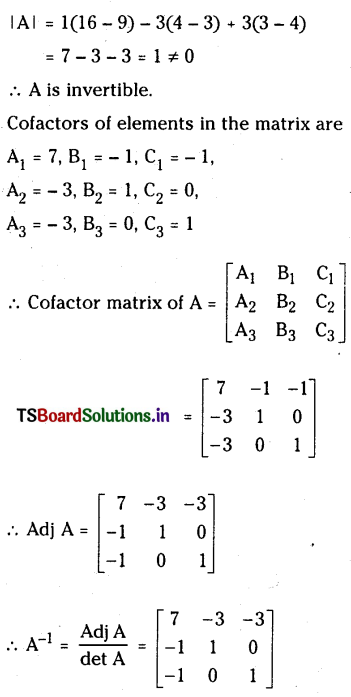
a) Kc = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{PCl}_3\right]\left[\mathrm{Cl}_2\right]}{\left[\mathrm{PCl}_5\right]}\)
b) ఉత్రమణీయ చర్యకు Kc’ = \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~K}_{\mathrm{c}}}\)
Kc’ = \(\frac{1}{8.3 \times 10^{-3}}\) = 120.28
c) i) PCl5 ను సమతాస్థితికి కలిపినపుడు పురోగామి చర్య దిశగా సమతాస్థానం కదులుతుంది. K విలువ మారదు.
ii) PCl5 విఘటన చర్య ఉష్ణగ్రాహక చర్య. ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరుగుదల ఉష్ణగ్రాహకచర్యను ప్రోత్సహించడం వల్ల PCl5 విఘటనం పెరుగుతుంది. ఉష్ణోగ్రత పెరిగితే Kc విలువ పెరుగుతుంది.
iii) పీడనాన్ని పెంచుట వలన ఘనపరిమాణం తగ్గే చర్య అయిన తిరోగామి చర్య ప్రోత్సహించబడుతుంది. Kc విలువ మారదు.
ప్రశ్న 93.
బ్రాన్ స్టెడ్ ఆమ్లాలు, బ్రాన్స్టెడ్ క్షారాలు భావనలను సోదాహరణంగా వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
బ్రాన్డ్-లౌరి సిద్ధాంతం ప్రకారం హైడ్రోజన్ అయాన్ H+ ను దానం చేసే సామర్ధ్యం గల పదార్థాలు ఆమ్లాలు. హైడ్రోజన్ అయాన్ H+ ను స్వీకరించే సామర్థ్యం గల పదార్థాలు క్షారాలు. ప్రోటాన్ దాతలు ఆమ్లాలు. ప్రోటాన్ స్వీకర్తలు క్షారాలు.
బ్రాన్టెడ్ ఆమ్లాలు రెండు రకాలు. అవి
1) బలమైన ఆమ్లం
2) బలహీన ఆమ్లం..
బలమైన ఆమ్లం : ప్రోటాన్ ను సునాయాసంగా దానం చేయగలిగే ప్రవృత్తి గల పదార్థాన్ని బలమైన ఆమ్లం అంటారు. ఉదా : HClO4, H2SO4, HCl, HNO3 మొ||వి.
బలహీన ఆమ్లం : ప్రోటాను సునాయాసంగా దానం చేయలేని పదార్థాన్ని బలహీన ఆమ్లం అంటారు.
ఉదా : HF, CH3COOH, H2CO3 మొ||వి.
బ్రాన్డ్ క్షారం : ఇతర పదార్థాల నుండి ప్రోటాను స్వీకరించే ప్రవృత్తి గల పదార్థాన్ని బ్రాన్స్టెడ్ క్షారం అంటారు.
ఉదా : H2O, Cl–, CH3COO– మొ|| వి.
బ్రాన్టెడ్ క్షారాలు రెండు రకాలు: అవి
1) బలమైన క్షారం,
2) బలహీన క్షారం.
బలమైన క్షారం : ప్రోటాను సునాయాసంగా స్వీకరించగలిగే పదార్థాన్ని బలమైన క్షారం అంటారు.
ఉదా : F–, N\(\mathrm{O}_2^{-}\), CH3COO–, HC\(\mathrm{O}_3^{-}\), CN– మొ|| వి.
బలహీన క్షారం : ప్రోటాను సునాయాసంగా స్వీకరించలేని పదార్థాన్ని బలహీన క్షారం అంటారు.
ఉదా : Cl\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\), HS\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\), Cl–, N\(\mathrm{O}_3^{-}\) మొ||వి.
తటస్థీకరణం : ఆమ్ల, క్షారముల మధ్య జరిగే ప్రోటాన్ మార్పిడిని ‘తటస్థీకరణం’ అంటారు.
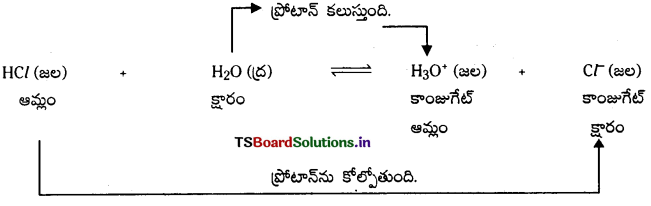
ఉదా : HCl + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + Cl–
బ్రానెడ్ సిద్ధాంతం ప్రకారం ఆమ్ల, క్షారముల మధ్య జరిగే చర్యలు ద్విగత చర్యలుగా ఉంటాయి. కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్ల-క్షార జంట : ఒక ప్రోటాన్ తేడాతో ఉండే ఆమ్లక్షార జంటను కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్ల క్షార జంట అంటారు. ఉదా : (HCl, Cl–), (H2O, OH–)
(HCl, Cl–) అనే కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్ల క్షార జంటలో HCl ఆమ్లం యొక్క కాంజుగేట్ క్షారం Cl–. అలాగే Cl– క్షారం యొక్క కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్లం HCl.
(H2O, OH–) – అనే కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్ల క్షార జంటలో H2O ఆమ్లం యొక్క కాంజుగేట్ క్షారం OH–. అలాగే OH– క్షారం యొక్క కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్లం H2O.
కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్ల-క్షార లక్షణాలు : ఒక కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్ల క్షార జంటలో ఆమ్లం బలమైనదైతే దాని కాంజుగేట్ క్షారం బలహీనమైనది అవుతుంది. అలాగే క్షారం బలమైనదైతే దాని కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్లం బలహీనమైనది అవుతుంది.
ఉదా : (HCl, Cl–) – కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్ల క్షార జంటలో HCl బలమైన ఆమ్లం. కాబట్టి దాని కాంజుగేట్ క్షారం (Cl–). బలహీనమైనది.
(CH3COOH, CH3COO–) – కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్ల క్షార జంటలో CH3COOH బలహీన ఆమ్లం కాబట్టి, దాని కాంజుగేట్ క్షారం (CH3COO–) బలమైనది.
గమనిక : ఆమ్లం నుండి ప్రోటాన్ ను తీసివేస్తే కాంజుగేట్ క్షారం వస్తుంది. అలాగే క్షారానికి ప్రోటాన్ ను కలిపితే కాంజుగేట్ ఆమ్లం వస్తుంది.
స్థాయీ ప్రభావం : నీరు, అన్ని బలమైన ఆమ్లాలు ఆమ్లశక్తిని H3O+ కు అలాగే అన్ని బలమైన క్షారాల క్షార శక్తిని OH– సమానం చేస్తుంది. దీనినే స్థాయీ ప్రభావం అంటారు.
బ్రాన్డ్ సిద్ధాంతంలోని గొప్పతనాలు :
- ఈ సిద్ధాంతం ఆమ్లాల మరియు క్షారాల స్వభావాలను జల మరియు జలేతర ద్రావణాలలో వివరిస్తుంది.
- NH3, CaO మొ||వి పదార్థాల క్షార స్వభావాన్ని, CO2, SO2 మొ||వి పదార్థాల ఆమ్ల స్వభావాన్ని చక్కగా
వివరిస్తుంది. బ్రాన్ స్టెడ్ సిద్ధాంతంలోని లోపాలు :- ప్రోటాను దానం చేయటం మరియు స్వీకరించటం ఇతర పదార్థాల సమక్షంలో మాత్రమే జరుగుతుంది.
- AlCl3, BCl3 వంటి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ కొరత గల పదార్థాల ఆమ్ల స్వభావాన్ని వివరించలేదు.
ప్రశ్న 94.
తగిన ఉదాహరణలతో లూయీ ఆమ్ల క్షార సిద్ధాంతం వివరించండి. కింది జాతులను లూయీ ఆమ్లాలు, లూయీ క్షారాలుగా వర్గీకరించండి. ఇవి లూయీ ఆమ్లం/క్షారంగా ఏ విధంగా పనిచేస్తాయి ?
a) OH–
b) F–
c) H+
d) BCl3
జవాబు:
ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను స్వీకరించే జాతిని ఆమ్లం అని, ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను దానంచేసే రసాయన జాతిని క్షారం అని లూయీ నిర్వచించెను.
ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంట స్వీకర్త ఆమ్లం. ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంట దాత క్షారం.
ఉదా :
1) హైడ్రోనియం అయాన్ ఏర్పడటం :
జలాణువు H+ తో సంయోగం చెందడం వల్ల హైడ్రోనియం అయాన్ ఏర్పడుతుంది.
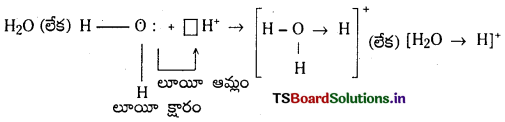
2) అమ్మోనియం అయాన్ ఏర్పడటం : అమ్మోనియా అణువు ప్రోటాన్తో సంయోగం చెందడం వల్ల అమ్మోనియం అయాన్ ఏర్పడుతుంది.
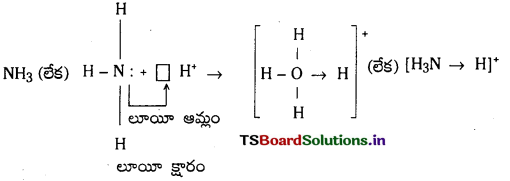
లూయీ సిద్ధాంతం పరిమితులు :
- ఆమ్లాల, క్షారాల బాలాలను వివరించలేదు.
- HCl, H2SO4 వంటి ఆమ్లాలు NaOH, KOH వంటి క్షారాలతో చర్య జరుపుతాయి. కానీ సమన్వయ సమయోజనీయ బంధాలను ఏర్పరచవు.
- సాధారణంగా ఆమ్ల క్షార చర్యలు అతి వేగంగా జరుగుతాయి. కాని లూయీ క్షారం, ఆమ్లాల మధ్య చర్యలు అతి నెమ్మదిగా జరుగుతాయి.
లూయీ ఆమ్లాలలోని రకాలు :
- అన్ని కేటయాన్లు లూయీ ఆమ్లాలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి.
ఉదా : Ag+, CO3+, Cu+, Fe3+ - ఖాళీ ఆర్బిటాల్ కలిగి ఉన్న కేంద్ర పరమాణువు గల ఎలక్ట్రాన్ కొరత గల సమ్మేళనాలు.
ఉదా : BF3, BCl3, AlCl3, FeCl3. - అష్టకాన్ని విస్తరించగల ఖాళీ ‘d’ ఆర్బిటాల్ గలవి.
ఉదా : SiF4, SnCl4, SF4 - బహుబంధాలు గల అణువులు
ఉదా : CO2, SO2, SO3, NO2
లూయీ క్షారాలలోని రకాలు :
- అన్ని ఋణ అయాన్లు. ఉదా : Cl–, OH–, CN–
- కేంద్ర పరమాణువు వద్ద ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంట గల తటస్థ అణువులు : H2O, NH3, R – OH
- బహుబంధాలు గల అణువులు : CO, NO, HC ≡ CH.
a) హైడ్రాక్సిల్ అయాన్, తాను ఒక ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను దానం చేయగలగడం చేత లూయీ క్షారంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
b) F–, దానిపై ఉండే నాలుగు ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటలలో ఒకదానిని దానంచేసి లూయీ క్షారంగా ప్రవర్తిస్తుంది.
c) హైడ్రాక్సిల్ అయాన్, ఫ్లోరైడ్ అయాన్ వంటి క్షారాల నుంచి, ఒక ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్ జంటను స్వీకరించగలిగి ఉండటం కారణంగా, ప్రోటాన్ ఒక లూయీ ఆమ్లంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
d) అమ్మోనియా లేదా ఏమీన్ అణువులనుంచి ఒక జంట ఒంటరి ఎలక్ట్రాన్లను BCl3 స్వీకరించి లూయీ ఆమ్లంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 95.
బలహీన ఆమ్లాలు, బలహీన క్షారాలు, వీటికి సంబంధించినంతవరకు అయనీకరణ అవధి ఏమిటి ? HX, బలహీన ఆమ్లం విషయంలో సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ Ka కు, అయనీకరణం అవధికి మధ్య గల సంబంధం ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
అయనీకరణ అవధి (α) : ఒక మోల్ ఆమ్లం లేక క్షారంలో ఎంత భాగం ఆమ్లం లేక క్షారం అయనీకరణం చెందుతుందో దానిని అయనీకరణ అవధి అంటారు. దీనిని α తో సూచిస్తారు. బలమైన ఆమ్లాలు లేక క్షారాలు పూర్తిగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతాయి. కాబట్టి వాటి α విలువ ‘ఒకటి’ ఉంటుంది.
‘c’ గాఢత గల బలహీన ఆమ్లం HX ను తీసికోండి. అది పాక్షికంగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది. దాని అయనీకరణ సమతాస్థితిని క్రింది విధంగా సూచిస్తారు.
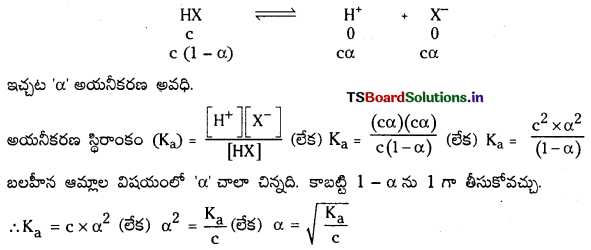

ప్రశ్న 96.
pH ను నిర్వచించండి. బఫర్ ద్రావణం అంటే ఏమిటి ? ఆమ్ల బఫర్ ద్రావణం pH విలువను లెక్కించడానికి ఉపయోగపడే హేండర్సన్ – హేజల్బాక్ సమీకరణాన్ని ఉత్పాదించండి.
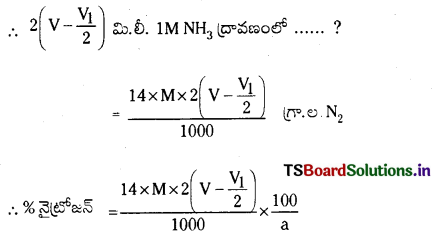
జవాబు:
ఒక జలద్రావణంలోని హైడ్రోజన్ అయాన్ క్రియాశీలత విలువ యొక్క 10 ఆధారిత సంవర్ధమానం ఋణవిలువగా, ద్రావణం pH విలువను నిర్వచించవచ్చు. హైడ్రోజన్ అయాను (H) క్రియాశీలతను దాని గాఢత విలువ పరంగా (H+)గా వ్యక్తం చేస్తారు.
\(\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{H}^{+}}\) = [H+]mol.L-1
pH : హైడ్రోజన్ అయాన్ గాఢత యొక్క ఋణ సంవర్గమానాన్ని pH అంటారు.
pH = – log\(\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{H}^{+}}\) = -log[H+]mol·L-1
బఫర్ ద్రావణం : ద్రావణాలను విలీనం చేసినపుడు లేదా వాటికి అల్పపరిమాణంలో ఆమ్లాలను లేదా క్షారాలను కలిపినప్పుడు వాటి pH లో కలిగే మార్పును నిరోధించే శక్తి గల ద్రావణాలను బఫర్ ద్రావణాలు అంటారు.
ఆమ్ల బఫర్ : ఒక బలహీన ఆమ్లము, బలమైన క్షారంతో అది ఏర్పరచిన లవణముల మిశ్రమము ఆమ్ల బఫర్గా పనిచేస్తుంది. ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం, సోడియం ఎసిటేట్ల మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం pH 4.75 పరిధిలో ఉండే బఫర్ ద్రావణంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
క్షార బఫర్ : బలహీనమైన క్షారము, బలమైన ఆమ్లంతో అది ఏర్పరచిన లవణముల మిశ్రమము క్షార బఫర్గా పనిచేస్తుంది. అమ్మోనియం క్లోరైడు, అమ్మోనియా హైడ్రాక్సైడుల మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం pH 9.25 పరిధిలో ఉండే బఫర్ ద్రావణంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
హేండర్సన్-హేజల్బాక్ సమీకరణం : నీటిలో అయనీకరణం చెందే బలహీన ఆమ్లము HA అయనీకరణం వల్ల A– ఏర్పడుతుంది.
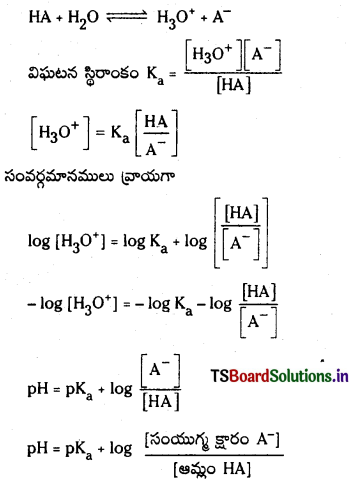
మిశ్రమంలో ఉండే ఆమ్లం యొక్క సంయుగ్మ క్షారం గాఢత, ఆమ్లం గాఢతల నిష్పత్తిని \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{A}^{-}\right]}{[\mathrm{HA}]}\) రాశి తెలుపుతుంది. ఆమ్లం చాలా బలహీనమైనది కాబట్టి అల్ప విస్తృతిలో మాత్రమే అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది. కాబట్టి బఫర్ను ఏర్పరచడానికి వాస్తవంగా ఉపయోగించిన ఆమ్లం గాఢతనుంచి సమతాస్థితి వద్ద (HA) గాఢత విలువ అల్పపరిమాణంలో మాత్రమే భేదిస్తుంది. ఈ ఆమ్ల సంబంధిత లవణం యొక్క అయనీకరణం చర్య ద్వారానే కాంజుగేటు క్షారం మొత్తం గాఢత A లభిస్తుంది. కాబట్టి లవణంగా గాఢతతో పోలిస్తే కాంజుగేటు క్షారం గాఢత ఏ మాత్రం భేదించదు. కాబట్టి పై సమీకరణాన్ని కింది రూపంలో రాయవచ్చు.
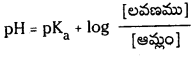
ప్రశ్న 97.
“లవణాల జలవిశ్లేషణం” పదాన్ని ఉదాహరణలతో వివరించండి. కింది లవణ ద్రావణాల pH విలువలను గురించి చర్చించండి.
i) బలహీన ఆమ్లం, బలమైన క్షారం ఏర్పరచిన లవణాలు
ii) బలమైన ఆమ్లం, బలహీన క్షారం ఏర్పరచిన లవణాలు
జవాబు:
లవణాల అయనీకరణంలో ఏర్పడిన కేటయాన్లు / ఏనయాన్లు ఆర్ద్రీకరణం చెందిన అయాన్లుగా జలద్రావణాలలో చోటు చేసుకొంటాయి. లేదా అవి నీటితో చర్య జరిపి, తిరిగి సంబంధిత ఆమ్లాలను/క్షారాలను లవణాల స్వభావాన్ని అనుసరించి ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. జలద్రావణంలో లవణాలు ఏర్పరచిన కేటయాన్లు/ఏనయాన్లు లేదా రెండు అయానులు నీటితో జరిపే అన్యోన్య చర్యను జలవిశ్లేషణం అంటారు.
బలమైన క్షారాలు ఏర్పరచే కేటయాన్లు (ఉదా : Na+, K+, Ca++, Ba++) బలమైన ఆమ్లాలు ఏర్పరచే ఏనయాన్లు (ఉదా : Cl–, Br–, N\(\mathrm{O}_3^{-}\), Cl\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\)) ఆర్ద్రీకరణం చెందుతాయి. కాని జలవిశ్లేషణం చెందవు. కాబట్టి బలమైన ఆమ్లాలు, బలమైన క్షారాలు చర్య జరిపి ఏర్పరచిన లవణాల జలద్రావణాలు తటస్థ స్వభావంతో ఉంటాయి. pH విలువ 7. బలహీన ఆమ్ల, క్షారాలు ఏర్పరచే లవణాలు జలవిశ్లేషణ చెందుతాయి.
i) బలహీన ఆమ్లాలు, బలమైన క్షారాలు ఏర్పరచిన లవణాలు ఉదా : CH3COONa
ii) బలమైన ఆమ్లాలు, బలహీన క్షారాలు ఏర్పరచిన లవణాలు. ఉదా : NH4 Cl
iii) బలహీన ఆమ్లాలు, బలహీన క్షారాలు ఏర్పరచిన లవణాలు. ఉదా : CH3COONH4
మొదటి రకం లవణాలలో ఏనయాన్ జలవిశ్లేషణ చెందుతుంది. OH– అయాన్లు ఏర్పడతాయి. అందువల్ల జలద్రావణం క్షార స్వభావాన్ని కలిగి ఉంటుంది. pH > 7. ఉదా : సోడియం ఎసిటేట్.
సోడియం ఎసిటేటు జలద్రావణంలో పూర్తిగా అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది.
CH3COONa (జల) → CH3COO– (జల) + Na+ (జల)
CH3COOH (జల) → H2O (ద్ర) ⇌ CH3COOH (జల) + OH– (జల)
బలమైన ఆమ్లం, బలహీన క్షారం వల్ల ఏర్పడిన రెండోరకం లవణాలలో కేటయాన్ జలవిశ్లేషణ చెంది H3O+ అయానును ఇస్తుంది. అందువల్ల ద్రావణం ఆమ్ల స్వభావాన్ని చూపుతుంది.
ఉదా : NH4 Cl.
NH4 Clపూర్తిగా జలద్రావణంలో అయనీకరణం చెందుతుంది.
NH4Cl (జల) → N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) (జల) + Cl– (జల)
N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) అయాన్లు నీటితో చర్య పొందుతాయి.
N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) (జల) + H2O (ద్ర) → NH4OH (జల) + H3O+ (జల)
దీని ఫలితంగా H+ అయాన్ల గాఢత పెరుగుతుంది. కాబట్టి NH4Cl జలద్రావణం pH 7 కంటే తక్కువగా వుంటుంది.
బలహీన ఆమ్లం, బలహీన క్షారం చర్య జరిపి ఏర్పరిచిన లవణానికి ఉదాహరణ CH3COONH4. ఇటువంటి లవణాలలో ఏనయాన్, కేటయాన్ కూడా చర్యల్లో పాల్గొంటాయి.
CH3COO– + N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\) + H2O ⇌ CH3COOH + NH4OH
CH3COOH, NH4OH లు రెండూ కూడా పాక్షికంగా అయనీకరణం చెందిన రూపాలలో ఉంటాయి.
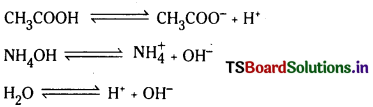
అట్టి ద్రావణాల pH విలువలు వాటి ఆమ్ల క్షారాల pK విలువల మీద ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది.
pH = 7 + 1/2 (pKa – pkb)
pKa, pKb ల భేదం విలువ ధనసంఖ్య కలిగి ఉంటే pH 7 కంటే ఎక్కువగా వుంటుంది. భేదం విలువ రుణసంఖ్య కలిగి ఉంటే pH 7 కంటే ఎక్కువగా ఉంటుంది.
గమనిక :
1) బలహీన ఆమ్లం, బలమైన క్షారం వల్ల ఏర్పడిన లవణాల జల ద్రావణాల pH ను లెక్కించుటకు సూత్రం
pH = \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{pK}_{\mathrm{w}}\) + \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{pK}_{\mathrm{a}}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)logC
pKw విలువ 25°C వద్ద 14.
pka బలహీన ఆమ్లం యొక్క విలువ. pKa = – log Ka
Ka అనునది ఆమ్ల విఘటన స్థిరాంకం.
C ఆమ్ల గాఢత.
2) బలమైన ఆమ్లం, బలహీన క్షారం వల్ల ఏర్పడిన లవణాల జలద్రావణాలు pH ను లెక్కించుటకు సూత్రం
pH = \(\frac{1}{2}\)pKw – \(\frac{1}{2}\)pKb – \(\frac{-1}{2}\)logC
Kb = క్షార విఘటన స్థిరాంకం. PKb = – log Kb

ప్రశ్న98.
ద్రావణీయతా అంటే ఏమిటి ? అయానిక లవణాల ద్రావణీయతపై ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాన్ ప్రభావం వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
ఒక లవణ సంతృప్త ద్రావణంలో కేటయాన్, యానయాన్ గాఢతల లబ్ధాన్ని ద్రావణీయత లబ్ధం అంటారు. దీనిని తో సూచిస్తారు.
Kspకి ప్రమాణాలు (mole/lit)n
n = ఒక అణువు అయనీకరణంలో విడుదలయ్యే మొత్తం అయాన్ల సంఖ్య.
అద్రావణీయంగా ఉండే ఘనపదార్థం, దాని సంతృప్త ద్రావణంలో గల ఘనపదార్థం ఏర్పరచిన అయానుల మధ్య గల సమతాస్థితిని కింది సమీకరణం ద్వారా సూచించవచ్చు.
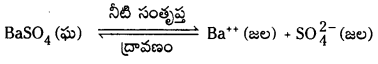
K = [Ba++][S\(\mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\)]/[BaSO4]
ఘనస్థితిలో గల శుద్ధ పదార్థానికి గాఢత స్థిరంగా వుంటుంది.
Ksp = K [BaSO4] = [Ba++] [S\(\mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\)]
Ksp ను ద్రావణీయతా లబ్ధ స్థిరాంకం అంటారు.
298 K వద్ద BaSO4 ద్రావణీయత లబ్ధం 1.1 × 10-10
ఉమ్మడి అయాను ప్రభావం : ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాను సమక్షంలో లవణం యొక్క ద్రావణీయత తగ్గుతుంది.
లీచాట్లీయర్ సూత్రాన్ని అనుసరించి ఒక అయాన్ గాఢతను పెంచినట్లైతే అది దాని ఆవేశానికి వ్యతిరేక ఆవేశం గల అయాన్తో సంయోగం చెంది Ksp = Qsp అయ్యే విధంగా కొంత లవణాన్ని అవక్షేపణం చెందిస్తుంది. ఇదే విధంగా ఒక అయాను గాఢతను తగ్గిస్తే, Ksp = Qsp అయ్యే విధంగా రెండు అయాన్ల గాఢతలు పెరిగే విధంగా లవణం అధిక పరిమాణంలో కరుగుతుంది. ఈ విషయం అధిక ద్రావణీయతను ప్రదర్శించే సోడియం క్లోరైడ్ వంటి లవణాలకు కూడా వర్తిస్తుంది. సోడియం క్లోరైడ్ సంతృప్త ద్రావణం తీసుకొని దానిలోని HCl వాయువును పంపినట్లైతే HCl విఘటనం ద్వారా ఏర్పడిన క్లోరైడ్ల గాఢత పెరగడం వల్ల సోడియం క్లోరైడ్ అవక్షేపణం చెందుతుంది. ఈ విధంగా లభ్యం అయిన సోడియం క్లోరైడ్ చాలా శుద్ధంగా ఉంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 99.
కింది వాటి గురించి లఘు వ్యాఖ్యలు రాయండి.
i) ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాన్ ఫలితం
ii) అల్ప ద్రావణీయత లవణం BaSO4 కు సంబంధించి Ksp కు, ద్రావణీయత (S) కు గల సంబంధం
జవాబు:
ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం వియోజనం చర్య సమతాస్థితి
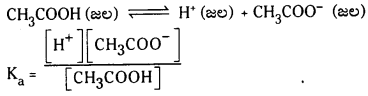
ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల ద్రావణానికి, ఎసిటేట్ అయాన్లను కలిపితే హైడ్రోజన్ అయాన్ల గాఢత [H+] తగ్గుతుంది. అలాగే, బాహ్యస్థానం నుంచి H+ అయానులను ద్రావణానికి చేర్చితే, వియోజనం చెందని ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం దిశవైపుగా సమతాస్థితి పయనిస్తుంది.
వియోజన సమతాస్థితిలో అప్పటికే ఏర్పడిన అయానిక రసాయన జాతి పరిమాణాన్ని పెంచే పదార్థాన్ని ద్రావణానికి కలిపితే సమతాస్థితిలో ప్రాప్తించే స్థానభ్రంశాన్ని ఉభయ సామాన్య అయాన్ ప్రభావం అంటారు.
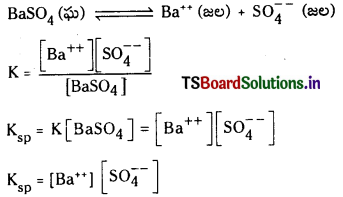
ఈ రెండు అయానుల వ్యక్తిగత గాఢతలు, బేరియం సల్ఫేటు మోలార్ ద్రావణీయతకు సమానంగా ఉంటాయి. మోలార్ ద్రావణీయత ‘S’ అయితే
Ksp = [S] [S] = S2
సంఖ్యాత్మక సమస్యలు
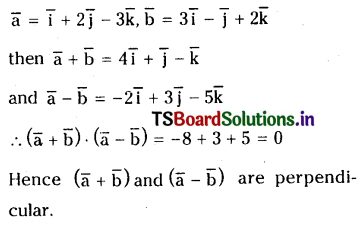
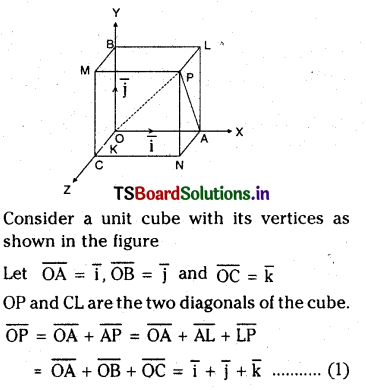
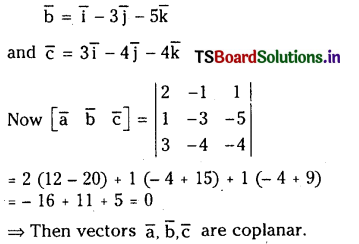
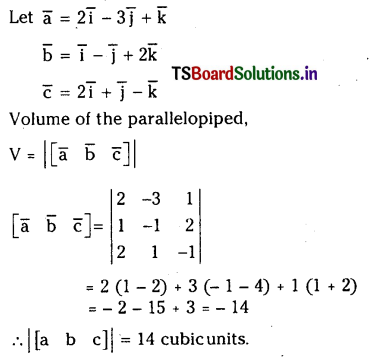
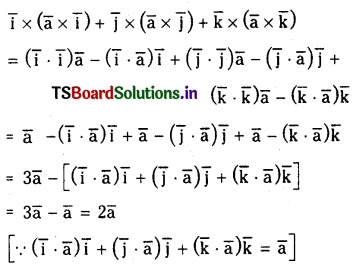
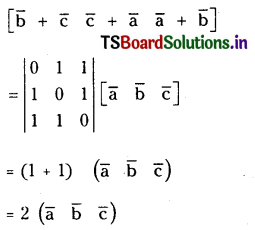
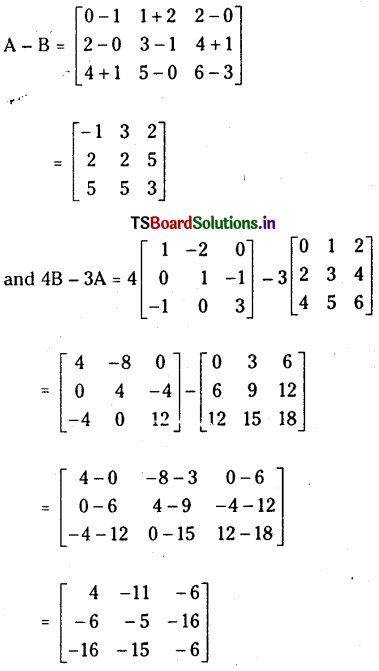
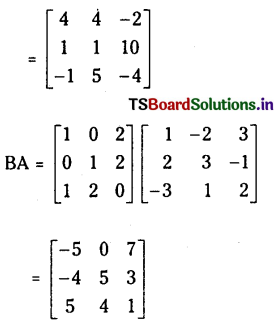
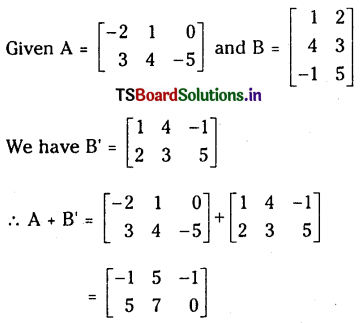
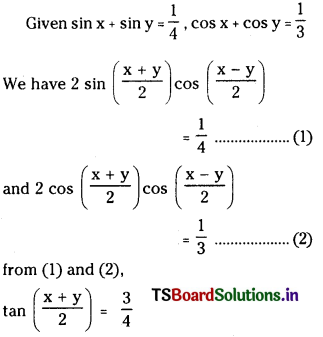
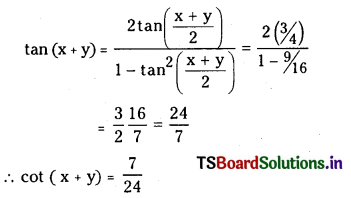
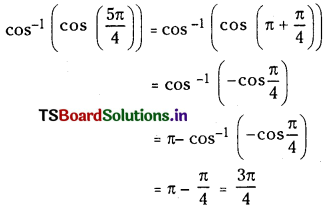
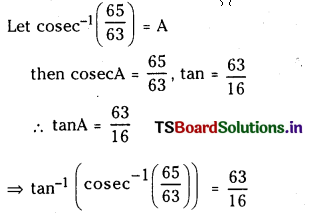
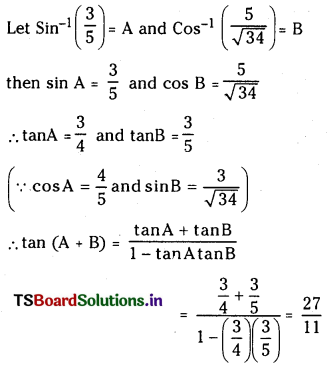
ప్రశ్న 1.
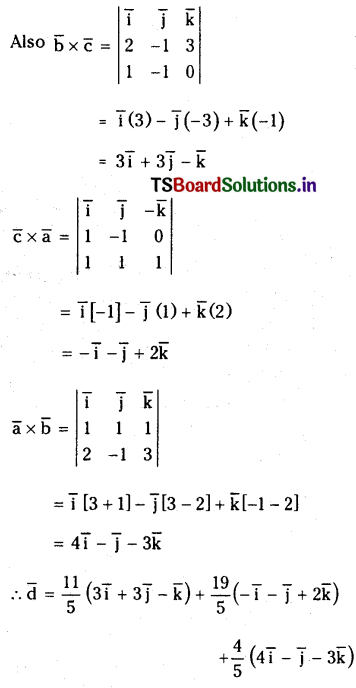
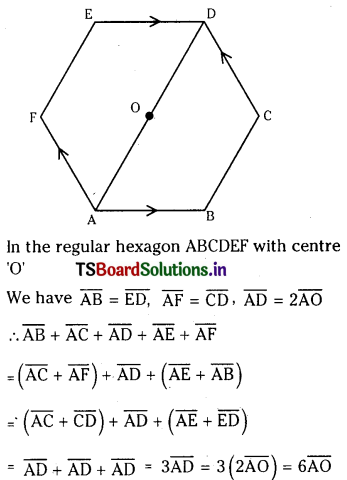
1 లీటరు ఘనపరిమాణం గల మూసిన పాత్రలో 1 మోల్ PCl5 ను వేడిచేస్తే సమతాస్థితి వద్ద 0.4 మోల్లు క్లోరిన్ ఏర్పడింది. సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాన్ని లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
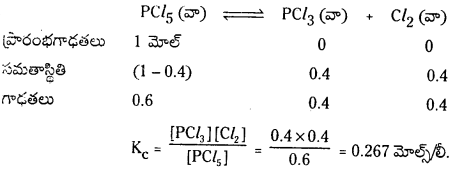
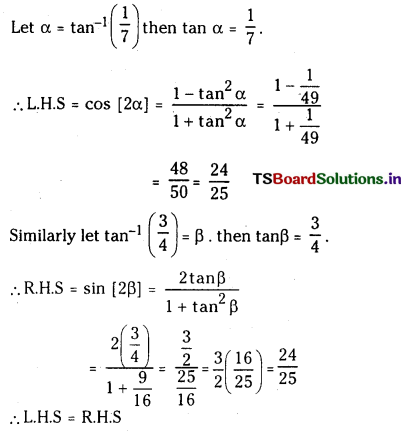
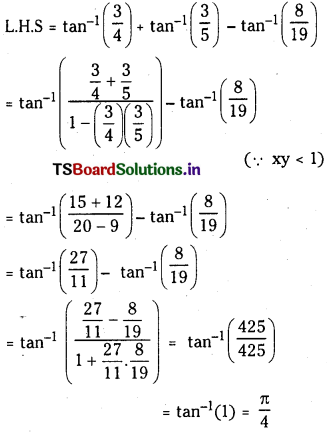
ప్రశ్న 2.
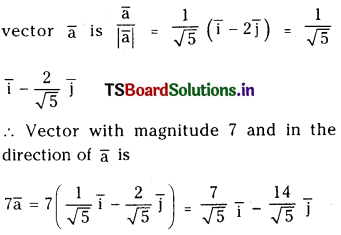
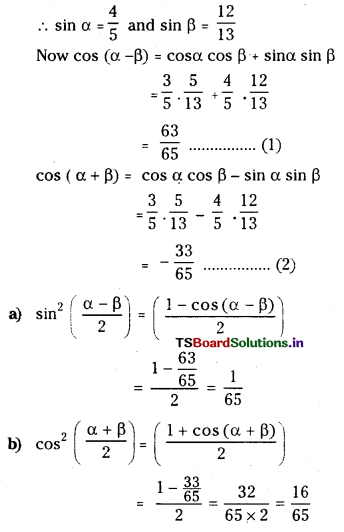
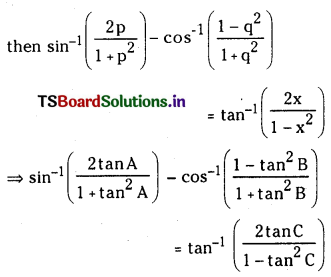
2NO2 (వా) ⇌ N2O4 (వా) అనే సమీకరణం అనుసరించి నైట్రోజన్ డై ఆక్సైడు, డై నైట్రోజన్ టెట్రాక్సైడును ఏర్పరుస్తుంది. 0.1 mole NO 2 ను 1 లీటరు ఘనపరిమాణం గల ఫ్లాసుకు 25°C కలిపినప్పుడు గాఢత మార్పు చెంది సమతాస్థితి వద్ద [NO2] = 0.016M, [N2O4] = 0.042 M గాను ఉన్నాయి.
a) ఏ చర్యా జరగక ముందు చర్య భాగఫలం Q విలువ ఎంత ?
b) చర్య సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
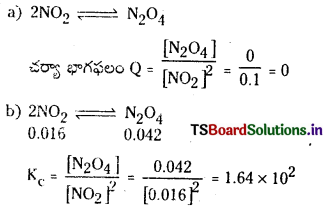
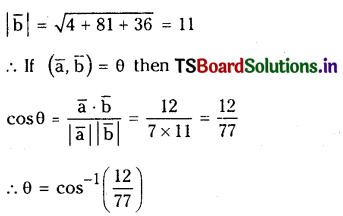
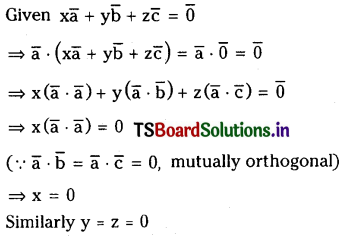
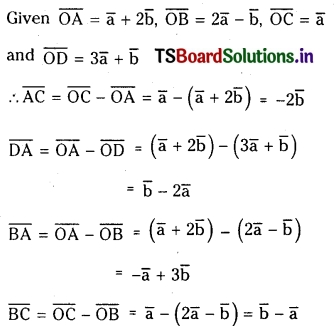
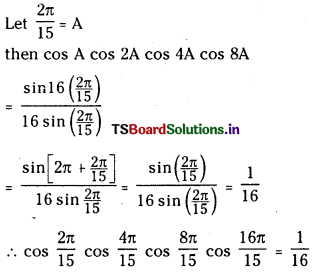
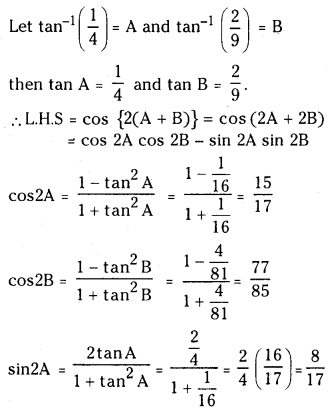
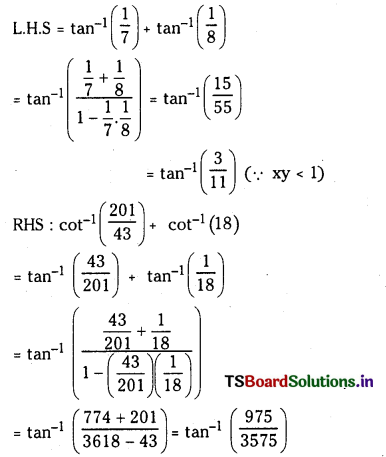
ప్రశ్న 3.
725 K వద్ద N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ⇌ 2 NH3 (వా) చర్య సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ 6.0 × 10–2. సమతాస్థితి వద్ద [H2] = 0.25 mol L−1, [NO3] = 0.06 mol L-1. N2 సమతాస్థితి గాఢతను లెక్కించండి.
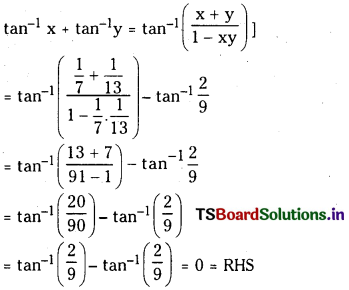
సాధన:
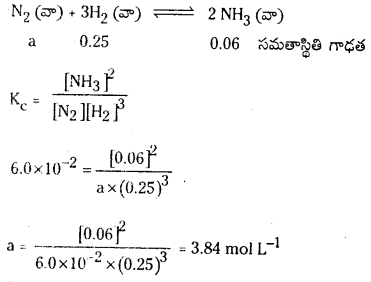
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద N2 గాఢత = 3.84 mol.L−1

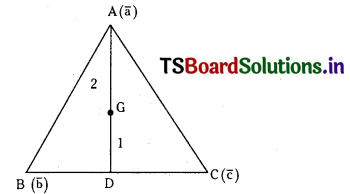
ప్రశ్న 4.
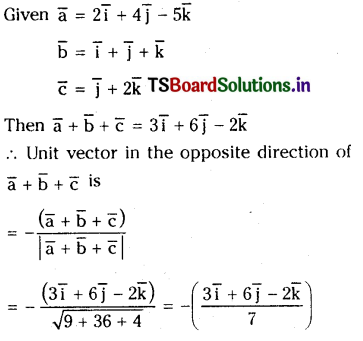
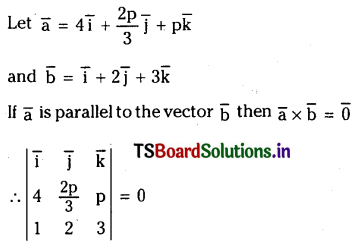
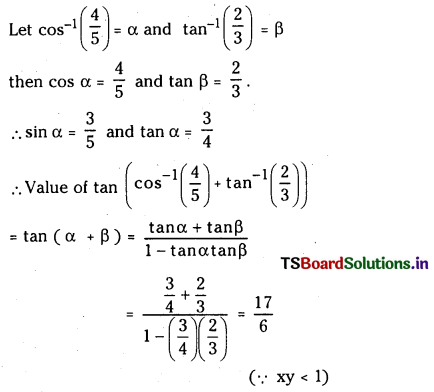
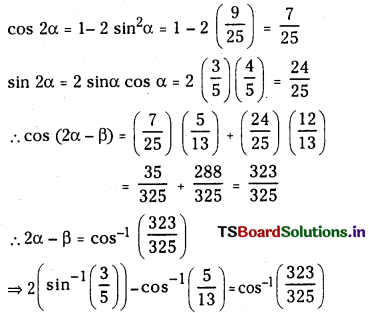
SO2 (వా) + NO2 (వా) ⇌ SO3 (వా) + NO (వా) చర్యకు K విలువ నిర్దిష్ట ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద 16. ఒక లీటరు పాత్రలో ఆరంభంలో నాలుగు వాయువులను ఒక్కొక్క మోల్ పరిమాణంలో తీసుకొన్నాం. NO, NÓ2 ల సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలు ఏమిటి ?
సాధన:
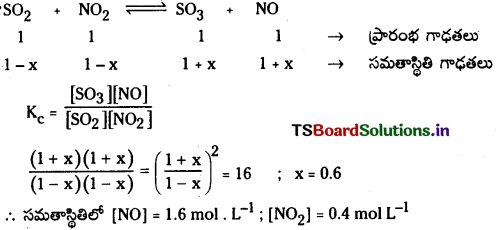
ప్రశ్న 5.
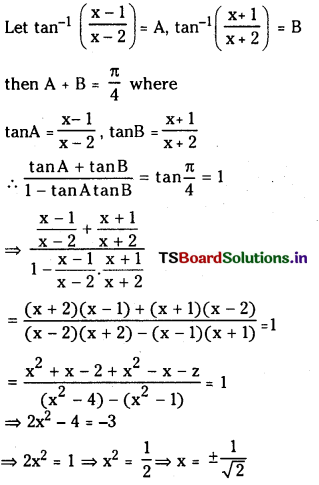
నిర్దిష్ట ప్రయోగ పరిస్థితులలో PCl5 (వా), PCl3 (వా), Cl2(వా) గా విఘటనం చెందే చర్య సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం విలువ 0.0211 mol L -1 .PCl5 ఆరంభ గాఢత 1.00 M అయితే సమతాస్థితి వద్ద PCl5, PCl3, PCl2 ల సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలను లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
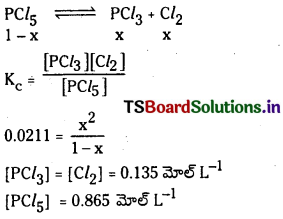
ప్రశ్న 6.
A + B ⇌ 3C చర్యకు సంబంధించి, 25°C వద్ద 3 లీటర్ల పాత్రలో A, B, C లు వరుసగా 1, 2, 4 మోల్లలో ఉన్నాయి. కింది పరిస్థితులలో చర్య జరిగే దిశను ఊహించండి.
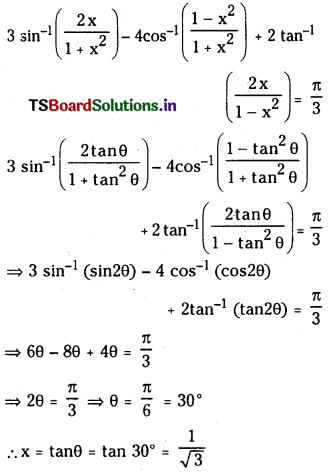
a) చర్యకు Kc విలువ 10
b) చర్యకు Kc విలువ 10
c) చర్యకు Kc విలువ 10.66
సాధన:
A + B ⇌ 3C.
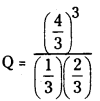
Q = 10.66
a) Kc = 10
Q > Kc కనుక తిరోగామి చర్య జరుగుతుంది.
b) Kc = 15
Q < Kc కనుక పురోగామి చర్య జరుగుతుంది.
c) Kc = 10.66
Q = Kc సమతాస్థితి ఏర్పడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 7.
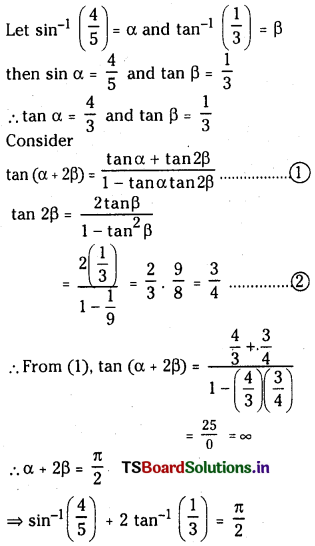
5.0 × 10-3 mol L-1, 4.0 × 10-3 mol L-1, 2.0 × 10-3 mol L-1 గాఢతలలో వరుసగా H2, N2, NH3 గల మిశ్రమాన్ని తయారుచేసి, 500K ఉష్ణోగ్రతకు వేడిచేస్తారు. 3H2 (వా) + N2 (వా) ⇌ 2NH3 (వా) చర్యకు ఈ ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం 60. ఈ గాఢత వద్ద అమ్మోనియా ఏర్పడుతుందా ? లేదా ? ఏర్పడిన అమ్మోనియా విఘటనం చెందుతుందా ?
సాధన:
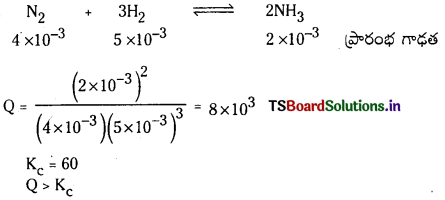
Q విలువ Kc కన్న ఎక్కువగా ఉంది కావున తిరోగామి చర్య జరుగుతుంది. అనగా అమ్మోనియా విఘటనం చెందుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 8.
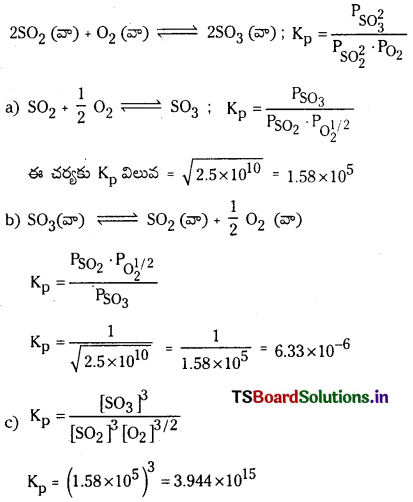
2 SO2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2SO3 (వా) చర్యకు 500 K వద్ద Kp విలువ 2.5 × 1010. అదే ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద కింది చర్యలకు K, విలువలను లెక్కించండి.
a) SO2 (వా) + 1/2 O2 (వా) ⇌ SO3 (వా)
b) SO3 (వా) ⇌ SO2 (వా) + 1/2 O2 (వా)
c) 3SO2 (వా) + 3/2 O2 (వా) ⇌ 3 SO3 (వా)
సాధన:

ప్రశ్న 9.
25°C 3 N2O4 (వా) ⇌ 2NO2 (వా) చర్యకు K విలువ 4.63 × 10-3.
a) ఇదే ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద Kp విలువ ఎంత ?
b) 25°C వద్ద ఉండే సమతాస్థితిలో N2O4 (వా) పాక్షిక పీడనం 0.2 atm, NO2(వా) సమతాస్థితి పీడనం
లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
a) Kp = Kc [RT]Δn
N2O4 (వా) ⇌ 2NO2 (వా)
Δn = 2 – 1 = 1
∴ Kp = 4.63 × 10−3 × 0.0821 × 298
= 0.1132 atm.
b)
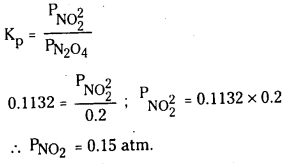
ప్రశ్న 10.
27°C వద్ద PCl5 (వా) ⇌ PCl3 (వా) + Cl2 (వా) ద్విగత చర్యకు Kp విలువ 0.65. Kcను లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
Kp = Kc [RT]Δn
ఇవ్వబడిన చర్యలో Δn = 2 – 1 = 1;
∴ Kp = Kc. RT = Kc
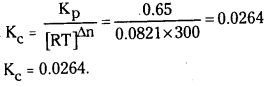
ప్రశ్న 11.
N2 (వా) + 3H2 (వా) ⇌ 2NH3 (వా) కు 400K వద్ద K విలువ 0.5 అయిన Kp విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
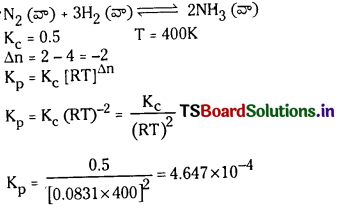
ప్రశ్న 12.
A + B ⇌ C + D సమతాస్థితి చర్యలో ఆరంభంలో 1 మోల్ A ను, 1 మోల్ B ను 5 లీటర్ల ఫ్లాస్కులో తీసుకొన్నాం. సమతాస్థితి వద్ద 0.5 మోల్ C ఏర్పడింది. ఇదే చర్యను 2 మోల్ ల A, 1 మోల్ B తో 5 లీటర్ల ఫ్లాస్క్ అదే ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద జరిపించినట్లైతే ప్రతిజాతి మోలార్ గాఢతలను లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
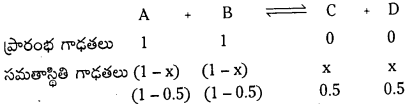

ప్రశ్న 13.
PCl5(వా) ⇌ PCl3 (వా) + Cl2 (వా) 0.4 మోల్ లు PCl3, 0.6 355 Cl2 తీసుకొన్నాం. K విలువ 0.2 అయితే చర్య ఏ దిశలో జరుగుతుంది ? ఊహించండి.
సాధన:
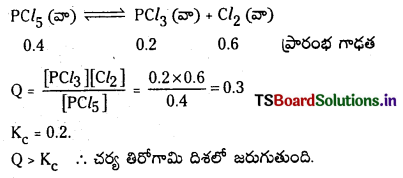
ప్రశ్న 14.
A + B ⇌ C + D సమతాస్థితిలో, T ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద A, B లను ఒక పాత్రలో తీసుకొన్నారు. A ఆరంభ గాఢత, B ఆరంభ గాఢతకు రెండు రెట్లు సమతాస్థితిని చేరుకొన్న తరువాత ‘C’ గాఢత B గాఢతకు మూడురెట్లు Kr విలువను లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
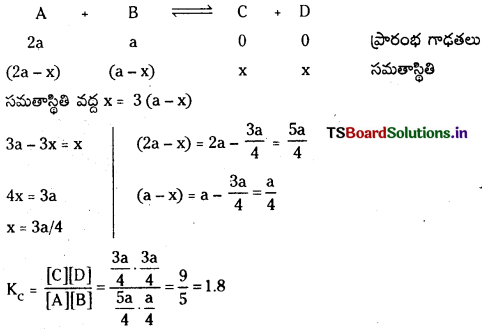

ప్రశ్న 15.
2SO2 (వా) + O2 (వా) ⇌ 2SO3 (వా) చర్యకు K విలువ 100 గ్రా. ఉండే ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద SO2, SO3, O2 వాయువులను 10 లీటర్ల ఫ్లాస్క్ లో తీసుకొన్నారు. సమతాస్థితి వద్ద
a) SO3, SO2 వాయువుల మోల్ల సంఖ్య ప్లాస్కులో సమానంగా ఉన్నాయి. O2 మోల్లల సంఖ్య ఎంత ?
b) ప్లాస్క్ SO3 మోల్ల సంఖ్య, SO2 మోల్ల సంఖ్యకు రెట్టింపు అయితే, O2 ఎన్ని మోల్లు ఉంది ?
సాధన:
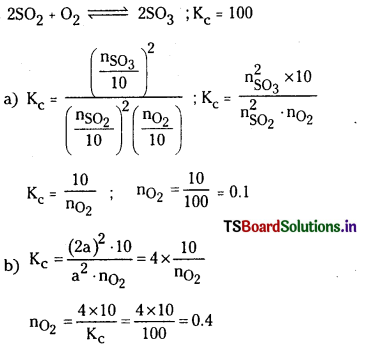
ప్రశ్న 16.
ఒక ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద A + B ⇌ C సమతాస్థితి చర్యలో A, B ల సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలు 15 మోల్ L-1 గా ఉన్నాయి. ఘనపరిమాణాన్ని రెండు రెట్లు గావించినపుడు A సమతాస్థితి గాఢత 10 మోల్-1 గా ఉంది. కింది వాటిని లెక్కించండి.
a) Kc
b) మూల సమతాస్థితిలో C గాఢత
సాధన:
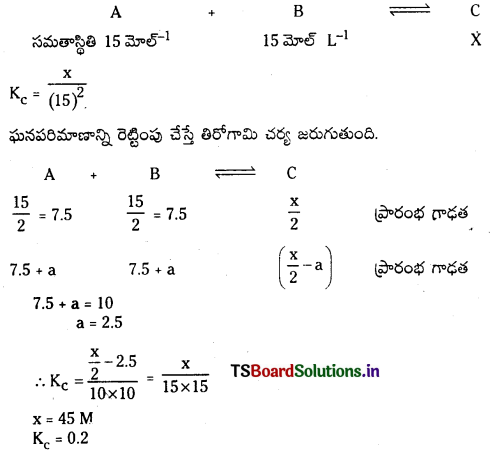
ప్రశ్న 17.
100K వద్ద ఒక పాత్రలో CO2 వాయువు 0.5 atm పీడనం వద్ద ఉంది. గ్రాఫైటును కలిపినప్పుడు CO2 లో కొంత భాగం CO గా మారింది. సమతాస్థితి వద్ద పీడనం 0.8 atm అయితే K విలువ లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
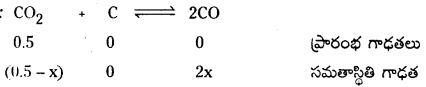
మొత్తం పీడనం = 0.8 atm
సమతాస్థితి మిశ్రమంలో CO మరియు CO2 ఉంటాయి.
(0.5 + x) atm = 0.8 atm.
x = 0.3 atm
Kp = \(\frac{(0.6)^2}{0.2}\) = 1.8 atm.
ప్రశ్న 18.
460°C వద్ద H2(వా) + I2 (వా) ⇌ 2HI(వా) చర్యకు Kp విలువ 49. H2, I2 ల ఆరంభ గాఢతలు వరసగా 0.5 atm అయితే సమతాస్థితి వద్ద ప్రతీ వాయువు పాక్షిక పీడనాన్ని లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
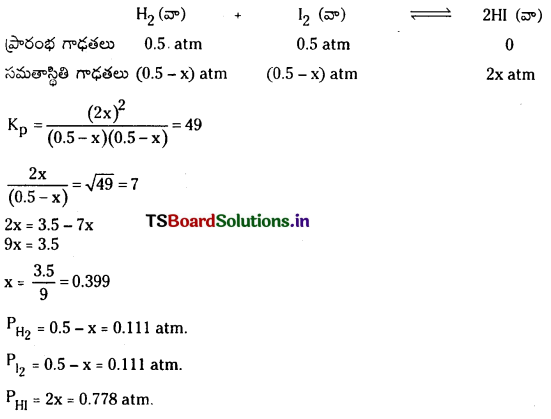
ప్రశ్న 19.
448°C వద్ద 10 లీటర్ల ఫ్లాస్క్ లో 0.5 మోల్ H2, 0.5 మోల్ 12 చర్య జరిపాయి. H2 (వా) + I2 (వా) ⇌ 2HI(వా) చర్యకు సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం Kc విలువ 50.
a) Kp విలువ ఎంత ?
b) సమతాస్థితి వద్ద I2 మోల్ల సంఖ్య ఎంత ?
సాధన:
a) Kp = Kc [RT]Δn.
H2 (వా) + I2 (వా) ⇌ 2HI (వా)
ΔN = 0
Kp = Kc = 50
b)
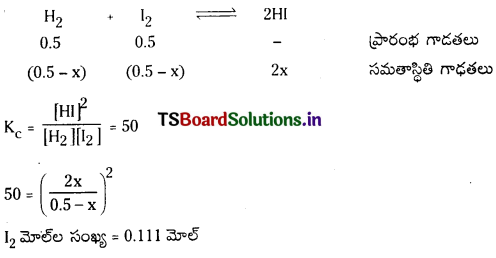
ప్రశ్న 20.
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద 0.1 మోల్ Cl2 రాబట్టాలి అంటే 250°C వద్ద ఒక లీటరు పాత్రలో ఎంత PCl5 తీసుకోవాలి?
PCl5(వా) ⇌ PCl3(వా) + Cl2(వా)
సాధన:
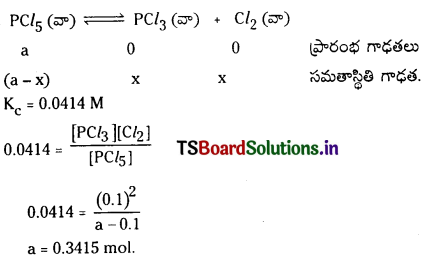
0.3415 మోల్ల PCl5 ను 1 లీ. ప్లాస్కు కలిపితే 0.1 మోల్ క్లోరిన్ సమతాస్థితి వద్ద లభిస్తుంది.

ప్రశ్న 21.
400°C N2(వా) + 3H2(వా) ⇌ 2NH3(వా) చర్యకు Kp Dev3 1.64 × 10-4.
a) Kc ను లెక్కించండి.
b) Kc విలువ ఉపయోగించి ΔG° విలువ లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
a) N2(వా) + 3H2(వా) ⇌ 2NH3(వా) Kp = 1.64 × 10-4 Kp = Kc [RT]Δn
Δn = 2 – 4 = -2
Kp = Kc [RT]-2
1.64 × 10-4/(RT)-2 = 1.64 × 10-4 × (RT)2
Kc = 1.64 × 10-4 × (0.0821 × 673)2
= 0.5129
b) ΔG° = -2.303 RT log K
= -2.303 × 0.0821 × 673 log 0.5129
= 3873 J
ప్రశ్న 22.
కింది ద్రావణాల pH విలువలను లెక్కించండి.
a) 10-3 M HCl
b) 10−3 MH2 HO4
c) 10-6 M HNO3
d) 0.02 MH2SO4
సాధన:
a) pH = – log [H+]
= -log [1 × 10-3]
b) H2SO4 → 2H+ + S\(\mathrm{O}_4^{2-}\)
1 మోల్ H2SO4 నుండి 2 మోల్ల H+ విడుదలవుతుంది.
[H+] = 2 × 10-3 M
pH = -log 2 × 10-3 = 3 – log 2
= 2.699
c) 10-6 M HNO3
pH = -log 10-6 = 6
d) 0.02 M H2SO4
[H+] = 2 × 0.02 = 2 × 2 × 10-2 = 4 × 10-2
pH = – log 10-6 = 6
pH = -log 4 × 10-2 = 2 – log 4
= 2 – 0.6021 = 1.4
ప్రశ్న 23.
కింది ద్రావణాల pH విలువలను లెక్కించండి.
a) 0.001 M NaOH
b) 0.01 M Ca(OH)2
c) 0.0008M Ba(OH)2
d) 0.004 M NaOH
సాధన:
ప్రశ్న 24.
ఒక ద్రావణం pH 3.6. దీని H3O+ అయాన్ గాఢత లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
pH = 3.6
– log [H+] = 3.6
log [H+] = -3.6 = \(\overline{4} .4\)
[H+] = anti log \(\overline{4} .4\) = 2.5 × 10-4 మోల్/లీ
ప్రశ్న 25.
ఒక ద్రావణం pH విలువలు గల ద్రావణాలలో OH– గాఢత ఎంత ?
సాధన:
pH = 8.6
РОН = 5.4
– log [OH–] = 5.4
log [OH–] = – 5.4 = \(\overline{6} .6\)
[OH–] = anti log \(\overline{6} .6\)
[OH–] = 3.98 × 10-6 M.
ప్రశ్న 26.
కింది pH విలువలు గల ద్రావణాలలో [H+] గాఢత ఎంత ?
a) pH = 3
సాధన:
a) pH = 3
[H+] = 10-3 M
b) pH = 4.75
– log [H+] = 4.75
– log [H+] = 4.75
log [H+] = -4.75 = \(\overline{5} .25\)
[H+] = anti log \(\overline{5} .25\)
= 1.778 × 10-5 M.
c) pH = 4.4
– log [H+] = 4.4
log [H+] = – 4.4 = \(\overline{5} .6\)
log [H+] = 10-5 × anti log 0.6
= 3.981 × 10-6 M.
ప్రశ్న 27.
0.005 M2 HSO4 ద్రావణాన్ని 100 రెట్లు విలీనం చేసినప్పుడు విలీన ద్రావణం pH లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
H2SO4 = 0.005 M
[H+] = 2 × 0.005 M = 0.01 M
pH = -log 0.01 = – log 10-2 = 2
100 రెట్లు విలీనం చేస్తే pH విలువ 2 యూనిట్లు పెరుగుతుంది. pH = 4

ప్రశ్న 28.
HCl ద్రావణం pH = 3. ఈ ద్రావణం 1 mL ను 1 లీటరుకు విలీనం చేస్తే ఫలిత ద్రావణం pH విలువ ఎంత?
సాధన:
1 mL ను 1 లీకు (1000 ml) విలీనం చేస్తే 1000 రెట్లు విలీనం చేసినట్లు భావించాలి.
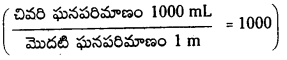
(10 రెట్లు విలీనం చేస్తే pH విలువ 1 యూనిట్ పెరుగుతుంది
100 రెట్లు విలీనం చేస్తే pH విలువ 2 యూనిట్లు పెరుగుతుంది
1000 రెట్లు విలీనం చేస్తే pH విలువ 3 యూనిట్లు పెరుగుతుంది.)
∴ ఫలిత ద్రావణం pH = 3 + 3 = 6
ప్రశ్న 29.
10-8 M HCl pH విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
HCl గాఢత = 10-8 m.
ఈ సందర్భంలో నీటి అయనీకరణం వల్ల లభించిన H+ గాఢతను కూడా లెక్కించాలి.
మొత్తం H+ గాఢత = HCl అయనీకరణం వల్ల [H+] + నీటి అయనీకరణం వల్ల CH+]
[H+] = 10-8 + 10-7
= \(\frac{10^{-7}}{10}\) + 10-7
= 10-7(\(\frac{1}{10}\) + 1)
= 1.1 × 10-7 = 7 – log 1.1
= 7 – 0.04 = 6.96
ప్రశ్న30.
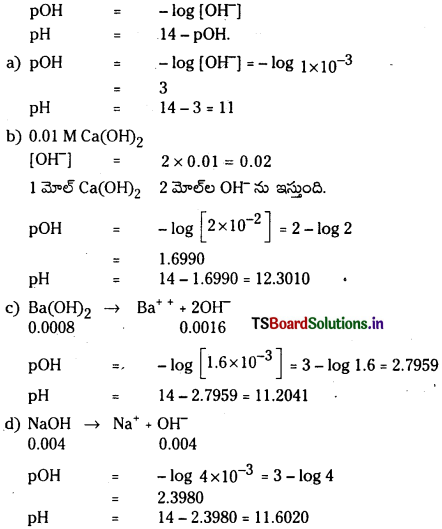
కింది క్షార ద్రావణాల pH విలువలను లెక్కించండి. (March 2013)
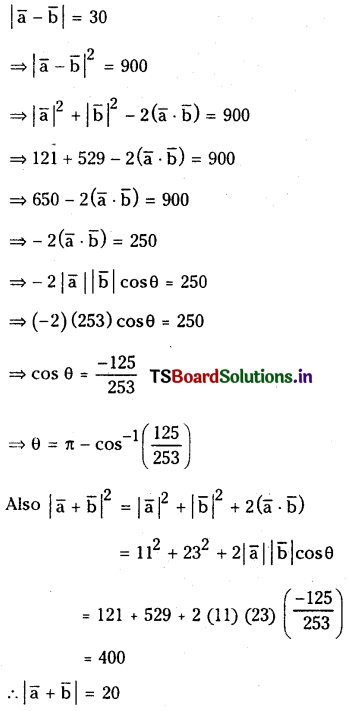
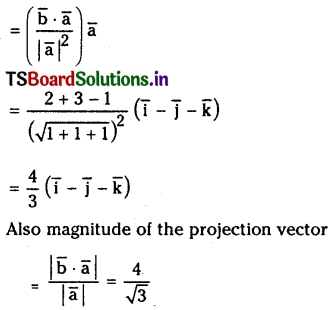
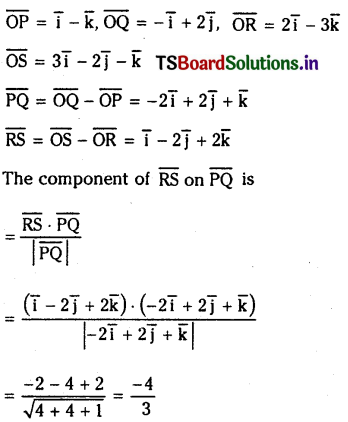
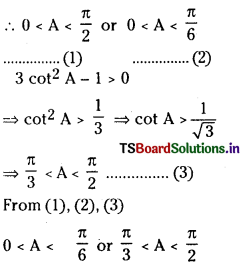
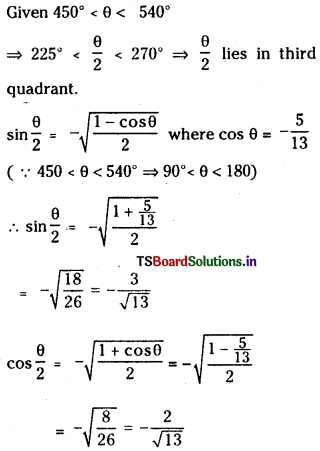
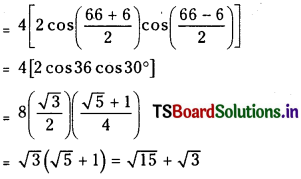
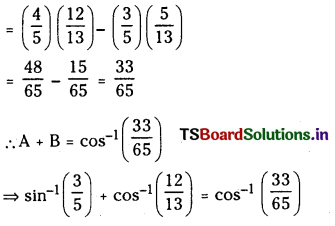
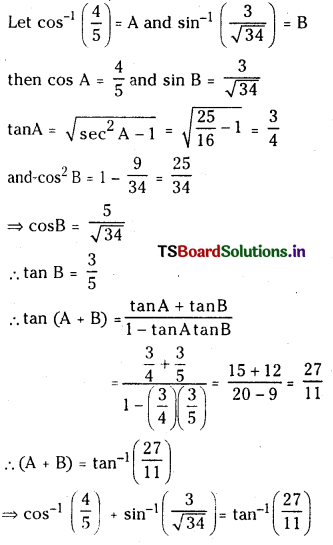
a) [OH–] = 0.05 M
b) [OH–] = 2 × 10-4 M
సాధన:
a) [OH–] = 0.05 M
РОН = -log 5 × 10-2
pH = 14 – 1.3 = 12.7
b) [OH–] = 2 × 10-4 M
РОН = -log 2 × 10-4
= 4 – log 2 = 4 – 0.3010
= 3.7
pH = 14 – 3.7 = 10.3
ప్రశ్న31.
నీటిలో 2 గ్రా. NaOH ను కరిగించి ద్రావణాన్ని 1 లీటరుకు విలీనం చేస్తే, ద్రావణం pH విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
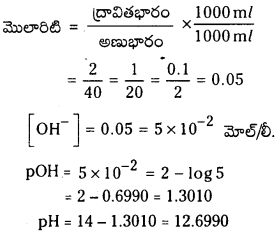
ప్రశ్న32.
కింది ద్రావణాల pH విలువలు లెక్కించండి.
a) 500 mL ద్రావణంలో 0.37 g of Ca(OH)2 కరిగి ఉంది.
b) 200 mL ద్రావణంలో 0.3 g NaOH కరిగి ఉంది.
c) 0.1825% HCl జల ద్రావణం.
d) 1 లీటరు ద్రావణానికి 1 mL 13.6 M HCI ను విలీనం చేసి ఏర్పరచిన ద్రావణం
సాధన:

ప్రశ్న33.
10 pH గల 100 mL NaOH ద్రావణంలో ఎన్ని గ్రాములు NaOH కరిగి ఉంది ?
సాధన:
PH = 10
[H+] = 10-PH = 10-10 మోల్స్/లీ.
[H+] = 10-PH = 10-10 మోల్స్/లీ.
ద్రావిత భారం = మొలారిటి × ఘనపరిమాణం × గ్రా. అణుభారం
= 10-4 × \(\frac{100}{1000}\) = 4 × 10-4.
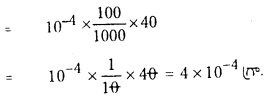

ప్రశ్న34.
ఒక ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద నీటి K విలువ 9.55 × 10-14 గా ఉంది. ఈ ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద నీటి pH విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:

ప్రశ్న35.
10-8 M NaOH, pH విలువ లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
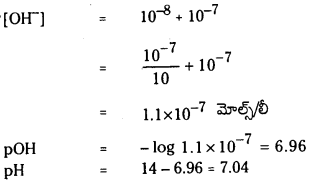
ప్రశ్న36.
150 mL 0.5 M HCl, 100 ml of 0.2 M HCl ద్రవణాలను కలిపి మిశ్రమం చేసారు. ఫలిత ద్రావణం ను లెక్కించండి pH ను లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
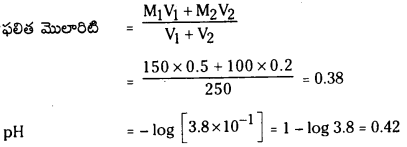
ప్రశ్న37.
100 mL 0.1 M HCl, 40 ml 0.2 M H2SO4 కలిపి మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం తయారు చేసారు. దీని pH విలువ లెక్కించండి.
లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
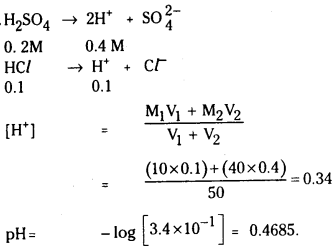
ప్రశ్న38.
100 mL pH = 4 ద్రావణం 100 mL pH = 6 ద్రావణం కలిపిన మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం ?
సాధన:
మొదటి ద్రావణం [H+] = 10-4
రెండవ ద్రావణం = [H+] = 10-6
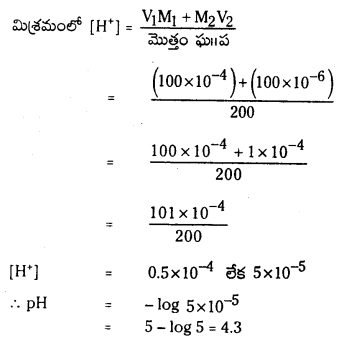
ప్రశ్న39.
0.5 M NaOH ద్రావణాన్ని, 0.3 M KOH ద్రావణాన్ని సమ ఘనపరిమాణాలలో కలిపారు. ఫలిత ద్రావణం pOH, pH విలువలను లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
NaOH మరియు KOH ద్రావణాల మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం
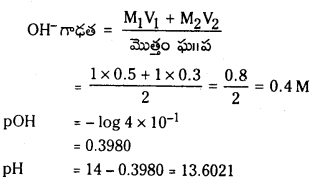
ప్రశ్న40.
60 mL 1 M HCI ద్రావణాన్ని, 40 mL 1M Na OH ద్రావణాన్ని కలిపారు. ఫలిత ద్రావణం pH విలువ ఎంత?
సాధన:
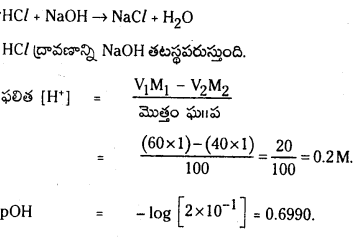
ప్రశ్న41.
100 mL 0.1 M HCI ద్రావణం, 9.9 ml 1.0 M NaOH ద్రావణం గల మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం pH విలువ లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
100 ml 0.1 M HC/ మిల్లీ తుల్యాంకాలు = 1000.1 = 10 meq
9.9 m l 1.0M NaOH
మిల్లీ తుల్యాంకాలు = 9.9 × 1 = 9.9 meq
HClను NaOH తటస్థపరిచినపుడు మిగిలిన ఆమ్ల మిల్లీ తుల్యాంకాలు = 10 – 9.9 = 0.1
ఆమ్ల నార్మాలిటి = \(\frac{0.1}{109.9}\) = 9 × 10-4
pH = – log 9 × 10-4
pH = 4 – log 9 = 3.0416
ప్రశ్న42.
200 mL pH = 2 గల HCI జల ద్రావణాన్ని 300 ml pH = 12 గల NaOH జల ద్రావణాన్ని కలిపినప్పుడు ఏర్పడిన మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం pH ఎంత ?
సాధన:
HCl pH = 2 ∴ [H+] = 10-2 M
NaOH pH = 12 pOH = 2
∴ [OH–] = 10-2
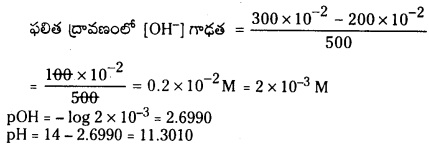
ప్రశ్న43.
0.2 M HCL ద్రావణం 50 mL, 0.1 M KOH ద్రావణం 30 mL కలిపి తయారుచేసిన మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం pH విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
ఫలిత ద్రావణం ఆమ్ల లక్షణం కలదు.
[H+] = \(\frac{(50 \times 0.2)-(30 \times 0.1)}{80}\) = \(\frac{(50 \times 0.2)-(30 \times 0.1)}{80}\)
= 0.0875
pH = – log [8.75 × 10-2]
= 1.0579
ప్రశ్న44.
40 mL 0.2 M HNO3 ద్రావణం, 60 mL 0.3 M NaOH ద్రావణంతో చర్య జరిపి మిశ్రమ ద్రావణాన్ని ఏర్పరచింది. ఫలిత ద్రావణం pH విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
NaOH మిల్లీ మోల్ సంఖ్య అధికంగా వుంది. ఫలిత ద్రావణం క్షారం.
ఫలిత మొలారిటి = \(\frac{60 \times 0.3-0.2 \times 40}{100}\)
= \(\frac{18-8}{100}\) = \(\frac{10}{100}\) = \(\frac{1}{10}\)
[OH–] = 0.1 = 10-1
РОН = 1
∴ pH = 14 – 1 = 13
ప్రశ్న45.
100mL 0.2 M HNO3 ద్రావణానికి 50 mL ల 0.1 MH2 SO4 ద్రావణం కలపబడింది. మిశ్రమ ద్రావణాన్ని 300 ml లకు విలీనం చేశారు. ఫలిత ద్రావణం pH విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
ఫలిత H+ గాఢత = \(\frac{100 \times 0.2+50 \times 0.2}{300}\)
\(\frac{20+10}{300}\) = \(\frac{30}{300}\) = \(\frac{1}{10}\) = 0.1
pH = -log 0.1 = -log 10-1 = 1
ప్రశ్న46.
pKw విలువ 13.725g గల జలద్రావణం Kw విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
pKw = 13.725
– log Kw = 13.725
log Kw = -13.725 = \(\overline{14} .275\)
Kw = anti log \(\overline{14} .275\) = 1.
= 1.884 × 10−14
ప్రశ్న47.
80°C వద్ద నీటి అయానిక లబ్ధం విలువ 2.44 × 10–13, 80°C వద్ద హైడ్రోనియం అయాన్, హైడ్రాక్సైడ్ అయాన్ల గాఢతలు శుద్ధ నీటిలో ఎంత ?
సాధన:
80°C వద్ద నీటి అయానిక లబ్ధం : 2.44 × 10-13
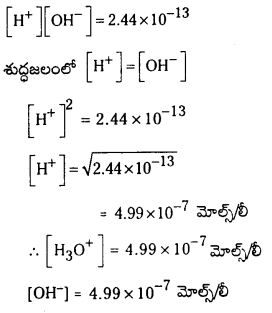
ప్రశ్న48.
40°C వద్ద నీటి అయనీకరణ స్థిరాంకం విలువ 2.9 × 10-14. 40°C వద్ద శుద్ధ నీటికి [H3O+], [OH], pH,
pOH లను లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
నీటి అయనీకరణ స్థిరాంకం విలువ 40°C = 2.9 × 10–14
Kw = [H+][OH–] = 2.9 × 10-14
[H+] = [OH–] = \(\sqrt{2.9 \times 10^{-14}}\) = 1.703 × 10-7
pH = − log [1.703 × 10-7] = 6.7689
POH = – log [1.703 × 10-7] = 6.7689
ప్రశ్న49.
కింది వాటి pH విలువలు లెక్కించండి.
a) 0.002 M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల ద్రావణం విఘటన శాతం 2.3%
b) 0.002 M NH4 OH ద్రావణం విఘటన శాతం 2.3%
సాధన:
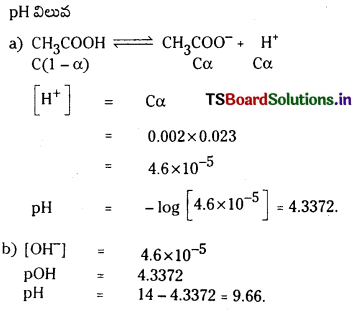

ప్రశ్న50.
కింద ఇచ్చిన సమతాస్థితి గాఢతల ఆధారంగా ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం Ka ను లెక్కించండి.
[H3O+] = [CH3COO–] = 1.34 × 10-3 M
[CH3COOH] = 9.866 × 10−2 M.
సాధన:
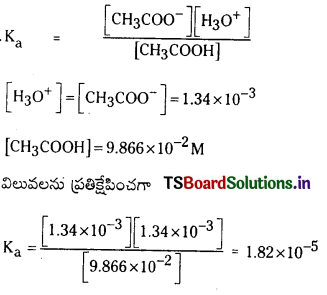
ప్రశ్న51.
Ka విలువ 1.8 × 10-5 g గల 0.1 M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం pH విలువ లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
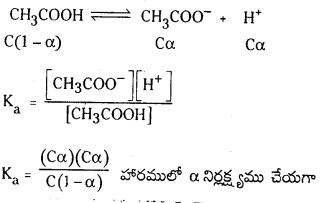
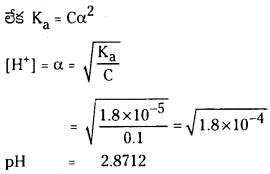
ప్రశ్న52.
0.1M గాఢత గల ఒక మోనోప్రోటిక్ ఆమ్లం pH విలువ 4.0 [H+], Ka లను లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
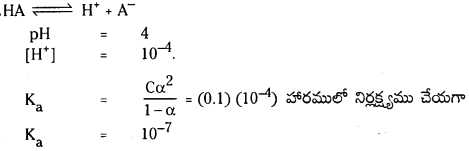
ప్రశ్న53.
0.02 M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం Ka విలువ 1.8 × 10-5. అయిన కింది వాటిని లెక్కించండి.
a) [H3O+]
b) pH
సాధన:

ప్రశ్న54.
298K వద్ద CH3COOH K విలువ 1.8 × 10-5 అయిన 0.01 M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల ద్రావణం pH విలువ ఎంత?
సాధన:
α2 = \(\frac{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{C}}\)
= \(\frac{1.8 \times 10^{-5}}{0.01}\)
= 180 × 10-5
α = 4.1 × 10-2
∴ [H3O+] = 0.01 × 4.1 × 10-2 = 4.1 × 10-4
pH = – log [H3O+]
= -log (4.1 × 10-4)
= 3.38.
ప్రశ్న55.
ఒక కర్బన పదార్థ ఆమ్లం 0.1 M ద్రావణం pH విలువ 4.0. ఆమ్లం విఘటన స్థిరాంకం విలువ లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
ద్రావణం యొక్క pH = 4
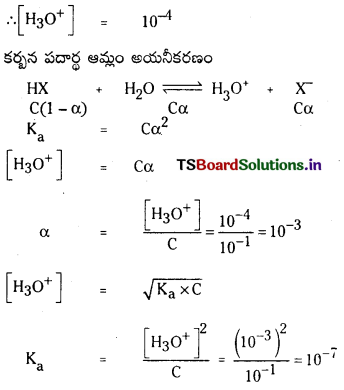
ప్రశ్న56.
298 K వద్ద HF, H COOH, HCN ల అయనీకరణ స్థిరాంకాల విలువలు వరుసగా 6.8 × 10-4, 1.8 x 104, 4.8 x 100 వాటి కాంజుగేటు
సాధన:
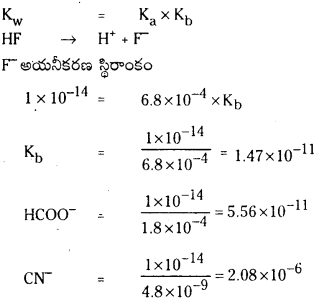
ప్రశ్న57.
బలహీన క్షారమైన ట్రై మిథైల్ ఏమీన్ 0.25 M ద్రావణంలో హైడ్రాక్సిల్ అయాన్ గాఢత లెక్కించండి.
(CH3)3 N + H2O ⇌ (CH3)3 N+H + OH,sup>- ; Kb = 7.4 × 10−5
సాధన:
బలహీన ఆమ్లం అయనీకరణ స్థిరాంకం Kb = 7.4 × 10-5. క్షారం యొక్క అయనీకరణ అవధి a౫ అనుకొనుము.
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద
[ట్రై మిథైల్ ఏమిన్] = 0.25 (1 – α) = 0.25 M.

ప్రశ్న 58.
ఒక మోల్ క్షారిత ఆమ్ల 0.005 M ద్రావణం pH = 5. దీని అయనీకరణ అవధి ఎంత ?
సాధన:
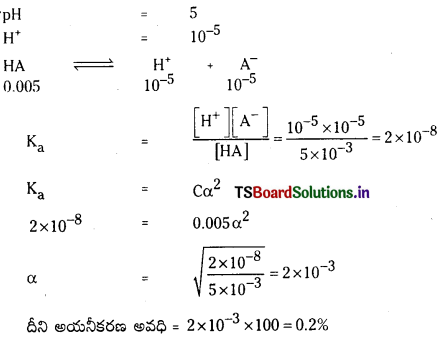
ప్రశ్న 59.
50 mL of 0.1 M NH4 OH, 25 mL 2 M NH4 Cl లను కలిపి బఫర్ ద్రావణం తయారుచేశారు. దీని pH ఎంత ? pKa = 4.8.
సాధన:
బఫర్ ద్రావణం
pОН = pKb + log \(\frac{M_1 V_1}{M_2 V_2}\)
M1 లవణం మొలాలిటీ = 2 M2 క్షారం మొలాలిటీ = 0.1
V1 = లవణం ఘనపరిమాణం = 25 ml V2 = క్షారం ఘనపరిమాణం = 50 ml
pОН = 4.8 + log \(\frac{2 \times 25}{0.1 \times 50}\)
= 4.8 + log 10 = 5.8
pH = 14 – 5.8 = 8.2
ప్రశ్న 60.
50 mL 0.2 M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం ద్రావణం, 25 mL సోడియం ఎసిటేట్ ద్రావణం కలిపి తయారుచేసిన బఫర్ ద్రావణం pH 4.8. దీని pKa విలువ 4.8. CH3COONa ద్రావణం గాఢత ఎంత ?
సాధన:
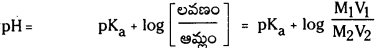
M1 = లవణం మొలారిటీ ?
M2 = క్షారం యొక్క మొలారిటీ = 0.2
V1 = క్షారం ఘనపరిమాణం = 25ml V2 = ఆమ్లం ఘనపరిమాణం = 50 ml
pH = 4.8
pKa = 4.8
లవణము గాఢత = ఆమ్లం గాఢత అయితే pH = pKa.
∴ M1 × 25 = 0.2 × 50
M1 = \(\frac{0.2 \times 50}{25}\) = 0.4 M.

ప్రశ్న 61.
50 mL 0.1 M సోడియం ఎసిటేట్ను 25 mL 0.1 M సోడియం ఎసిటేట్ను 25 mL 0.2 M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లాన్ని కలిపి బఫర్ ద్రావణం చేశారు. CH3COOH, pKa విలువ 4.8, బఫర్ ద్రావణం pH విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:

ప్రశ్న 62.
20 mL 0.1 M NH4 OH ద్రావణాన్ని 20 mL 1MNH4 Cl ద్రావణానికి కలిపారు. బఫర్ ద్రావణం pH 8.2.
NH4 OH, pKa ఎంత ?
సాధన:

ప్రశ్న 63.
1 లీటరు బఫర్ ద్రావణంలో 0.1 మోల్ ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం, 1 మోల్ సోడియం ఎసిటేట్ ఉన్నాయి. CH3COOH, pKa విలువ 4.8. అయిన బఫర్ ద్రావణం pH ఎంత ?
సాధన:
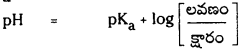
= 4.8 + log \(\frac{1}{0.1}\)
= 4.8 + log 10
= 4.8 + 1 = 5.8.
ప్రశ్న 64.
50 mL 1M CH3COOH ద్రావణం, 50 mL 0.5 M NaOH ద్రావణం కలిపి తయారుచేసిన మిశ్రమ ద్రావణం pH విలువ ‘X’. ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం pKa 4.8 అయితే ‘X’ విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
50 ml 0.5 M NaCH ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లాన్ని తటస్థీకరిస్తుంది.
V1N1 = V2N2
50 × 0.5 = V2 × 1
∴ V2 = \(\frac{50 \times 0.5}{1}\) = 50
కనుక ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం 50% తటస్థీకరించబడింది. కనుక ఫలిత ద్రావణంలో సమాన పరిమాణం గల ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లము మరియు సోడియం ఎసిటేటు ఉంటాయి. ∴ pH = pKa = 4.8
ప్రశ్న 65.
AgCl ద్రావణీయతా లబ్ధం విలువ 1.6 × 10-10 mol2 / L2. దీని ద్రావణీయత ఎంత ?
సాధన:
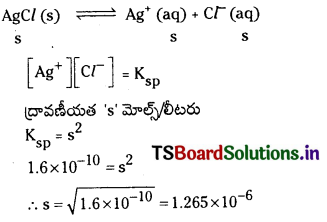
ప్రశ్న 66.
Zr (OH)2 యొక్క ద్రావణీయతా లబ్ధం విలువ 4.5 × 10-17 mol3 L-1. దీని ద్రావణీయత ఎంత ?
సాధన:
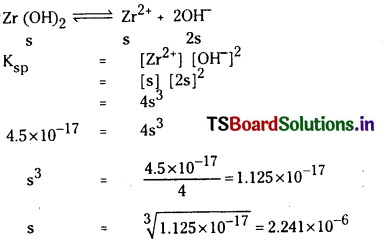
ప్రశ్న 67.
Ag2 CrO4 ద్రావణీయత 1.3 × 10-4 మోల్ L-1, దీని ద్రావణీయతా విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
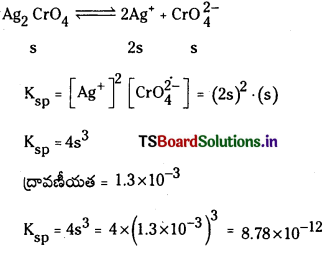
ప్రశ్న 68.
A2B = 2 × 10-3 mol L-1. దీని ద్రావణీయతా లబ్ధం విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
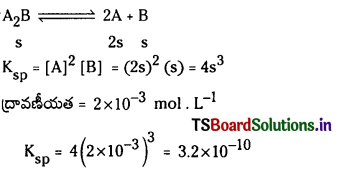
ప్రశ్న 69.
AB = 10-10 mol2 L-2. దీని ద్రావణీయతా లబ్ధం విలువ ఎంత ?
సాధన:
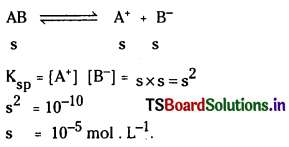
ప్రశ్న 70.
PQ, RS2లు అల్ప ద్రావణీయతా లవణాలు. వీటి ద్రావణీయతా లబ్ధం విలువలు సమానం. ప్రతీ దాని విలువ 4.0 × 10–18, ఏ లవణం వీటిలో అధిక ద్రావణీయత కలిగి ఉంది ?
సాధన:
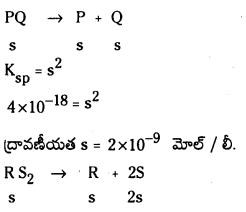
Ksp = [s] [2s]2 = 4s3
4s3 = 4 × 10-18
s3 = \(\frac{4 \times 10^{-18}}{4}\) = 1 × 10-18
s = 1 × 10-6 mole. L-1
RS2 కు అధిక ద్రావణీయత కలదు.

ప్రశ్న 71.
0.1M ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల ద్రావణంలో ఆమ్లం 1.34% అయనీకరణం చెందింది. అయిన [H+], [CH3COO–], [CH3COOH] లను లెక్కించండి. ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం Ka విలువ లెక్కించండి.
సాధన:
CH3⇌ COOH = CH3COO– + H+
అయనీకరణ అవధి = 1.34%
కనుక 0.1 M అయనీకరణం = \(\frac{1.34 \times 0.1}{100}\) = 1.34 × 10-3 M
.·. [H+] = [CH3COO−] = 1.34 × 10-3 M
[CH3COOH) = 1 – 1.34 × 10-3 M
Ka = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}^3\right]}\) = \(\frac{1.34 \times 10^{-3} \times 1.34 \times 10^{-3}}{0.1}\) = 1.8 × 10-5
అదనపు ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 1.
ద్రవ్యరాశి క్రియానియమాన్ని వ్రాయండి. సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంక సమీకరణాన్ని రాబట్టండి.
సాధన:
ద్రవ్యరాశి క్రియానియమం : ఏ క్షణమునందైనా నిర్దిష్ట ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద రసాయన చర్యావేగం ఆ క్షణం వద్ద ఉండే క్రియాజనకాల క్రియాశీల ద్రవ్యరాశుల అంకగణిత లబ్ధానికి అనులోమానుపాతంలో ఉంటుంది.
A + B ⇌ C + D చర్యకు
పురోగామి చర్యావేగం α [A][B]
= Kf [A][B]
Kf ను పురోగామి వేగస్థిరాంకం అంటారు.
తిరోగామి చర్యావేగం α [C] [D]
= Kb [C] [D]
సమతాస్థితి వద్ద, పురోగామి చర్యావేగం = తిరోగామి చర్యావేగం
Kf [A] [B] = Kb [C] [D]
∴ Kc ను సమతాస్థిరాంకం అంటారు.
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD చర్యకు
Kc = \(\frac{[C]^C[D]^d}{[A]^a[B]^b}\)
ప్రశ్న 2.
500 K వద్ద సమతాస్థితి ఉన్న N2, H2 ల ద్వారా NH3 ను ఏర్పరిచే చర్యకు కింద సూచించిన గాఢతలు ఉన్నాయి. [N2] = 1.5 × 10-2 M. [H2] = 3.0 × 10-2 M, [NH3] = 1.2 M × 10−2 M. దీని సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాన్ని లెక్కించండి.
జవాబు:
(N2 (వా) + 2H3 (వా) చర్యకు, సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకాన్ని కింద చూపిన విధంగా రాస్తాం.
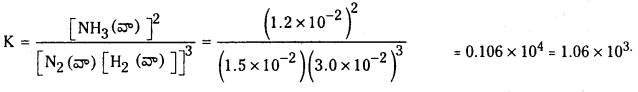
ప్రశ్న 3.
2A ⇌ B + C చర్యకు Kc విలువ 2 × 10-3. ఒక నిర్దేశిత కాలం వద్ద చర్యా మిశ్రమంలో [A] = [B] = [C] = 3 × 10-4 M. ఏ దిశలో చర్య పురోగమిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
చర్యకు భాగఫలం Qc విలువను కింది సమీకరణం తెలుపుతుంది.
Qc = [B] [C] / [A]2
కాని [A] = [B] = [C] = 3 × 10-4 M కాబట్టి
Qc = (3 × 10-4)(3 × 10-4)/(3 × 10-4)2 = 1
అంటే Qc > Kc. కాబట్టి చర్య తిరోగామి దిశగా ప్రయాణిస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 4.
సుక్రోజ్ జలవిశ్లేషణాన్ని కింది సమీకరణం సూచిస్తుంది.
సుక్రోజ్ + H2O ⇌ గ్లూకోజ్ + ఫ్రక్టోజు
చర్యకు సమతాస్థితి స్థిరాంకం K. విలువ 300 K వద్ద 2 × 1013, 300K వద్ద Δ\(\mathbf{G}^{\ominus}\) విలువ ఎంత ?
జవాబు:
Δ\(\mathbf{G}^{\ominus}\) = RTln Kc
Δ\(\mathbf{G}^{\ominus}\) = (-8.314 J mol-1 K-1) 300 K × ln (2 × 1013)
Δ\(\mathbf{G}^{\ominus}\) = −7.64 × 104 J mol-1

ప్రశ్న 5.
బ్రాన్టెస్టెడ్ ఆమ్లాలు : HF, H2SO4, HC\(\mathrm{O}_3^{-}\) లకు కాంజుగేటు క్షారాలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
కాంజుగేటు క్షారాలు ఒక ప్రోటాను తక్కువగా కలిగి ఉండాలి. కాబట్టి ఈ ఆమ్లాల కాంజుగేటు క్షారాలు వరుసగా F–,HS\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\), C\(\mathrm{O}_3^{2-}\) లు.
ప్రశ్న 6.
బ్రాన్టెస్టెడ్ క్షారాలు : N\(\mathrm{H}_2^{-}\), NH3, HCOO– లకు కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్లాలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్లంలో ఒక ప్రోటాను అధికంగా ఉండాలి. కాబట్టి కాంజుగేటు ఆమ్లాలు వరుసగా : NH3, N\(\mathrm{H}_4^{+}\), HCOOH లు.
ప్రశ్న 7.
ఒక మృదుపానీయం నమూనా ద్రావణంలో హైడ్రోజన్ అయాన్ గాఢత 3.8 × 10-3 = 3m. దీని pH విలువ ఎంత?
జవాబు:
pH = – log (3.8 × 10-3)
= {-log (3.8) + log (10-3)}
= -[(0.58) + (-3.0)] = -[−2.42] = 2.42
కాబట్టి మృదుపానీయం pH విలువ 2.42. దీనిని అనుసరించి ఇది ఆమ్లగుణం కలిగి ఉంది అని తెలుస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 8.
1.0 × 10-8 M గాఢత గల HCl ద్రావణం pH విలువ లెక్కించండి.
జవాబు:
2H2O (ద్ర) ⇌ H3O+ (జల) + OH (జల)
Kw = [OH–] [H3O+] = 10-14
నీటిలో x = [OH] = [H3O+] అనుకొందాం.
H3O+ అయాన్ల గాఢత
(i) ద్రావణం స్థితిలో ఉండే HCl అయనీకరణం ప్రక్రియ మీద అంటే
HCl (జల) + H2O (ద్ర) ⇌ H3O+ (జల) + CF– (జల)
(ii) H2O అయనీకరణం ప్రక్రియ మీద ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది. అతి విలీన ద్రావణాలలో H3O+ కు సంబంధించిన రెండు ఉత్పత్తి స్థానాలను పరిగణనలోకి తీసుకోవాలి.
[H3O+] = 10-8 + x
Kw = (10-8 + x) (x) = 10-14
లేక x2 + 10-8 x – 10-14 = 0
(OH–) = x = 9.5 × 10-8
pOH = 7.02, pH = 6.98.
ప్రశ్న 9.
ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్లం pKa అమ్మోనియా హైడ్రాక్సైడు pKb విలువ వరుసగా 4.76, 4.75. అమ్మోనియం ఎసిటేట్ జలద్రావణం pH కనుక్కోండి.
జవాబు:
pH = 7 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) = [pKa – pKb]
= 7 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)[4.76 – 4.75] = 7 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)[0.01] = 7 + 0.005 = 7.005.
ప్రశ్న 10.
శుద్ధ నీటిలో A2pX3 ద్రావణీయతను లెక్కించండి. దీనిలో ఏర్పడిన ఏ అయాన్ నీటితో చర్య జరపదు అని ఊహించండి. A2X3 ద్రావణీయతా లబ్ధం విలువ K = 1.1 × 10-23.
జవాబు:
A2X3 ⇌ 2A3+ + 3X2–
Ksp = [A3+]2 [X2–]3
S = A2X3 ద్రావణీయత అయితే
[A3+] = 2S [X2-] = 3S.
Ksp = (2S)2 (3S)3 = 108S5 = 1.1 × 10-23
S5 = 1 × 10-25
S = 1.0 × 10-5 మోల్ L-1.
ప్రశ్న 11.
2NOCl (వా) ⇌ 2NO (వా) Cl2 (వా) K్య విలువ 1069K వద్ద 3.75 × 10-6 లో అయిన ఈ ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద ఈ చర్యకు Kp విలువ లెక్కించండి.
జవాబు:
Kp = Kc (RT)Δn
Δn = (2 + 1) – 2 = 1
Kp = 3.75 × 10-6 (0.0831 × 1069) = 0.033