Students must practice these TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Important Questions Chapter 5 Products of Vectors to help strengthen their preparations for exams.
TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Products of Vectors Important Questions
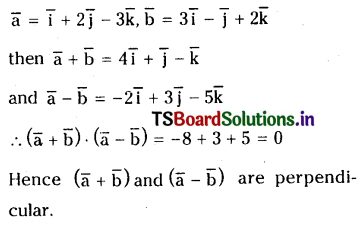
Question 1.
If \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}+2 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-3 \overline{\mathbf{k}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}=3 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{j}}+2 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\) then show that \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}+\overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{a}}-\overline{\mathbf{b}}\) are perpendicular.
Solution:
Question 2.
If the Vectors \(\lambda \overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{3} \overline{\mathbf{j}}+5 \overline{\mathrm{k}}, 2 \lambda \overline{\mathrm{i}}-\lambda \overline{\mathbf{j}}-\overline{\mathrm{k}}\) are perpendicular to each other find λ.
Solution:

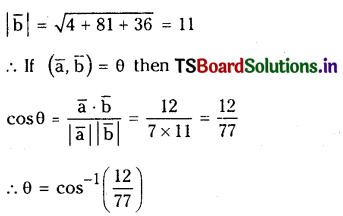
Question 3.
If \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}\) =6 \(\overline{\mathrm{i}}+2 \overline{\mathrm{j}}+3 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}=2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-9 \overline{\mathrm{j}}+6 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\) then find \(\overline{\mathrm{a}}, \overline{\mathrm{b}}\) and the angle between \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}\).
Solution:
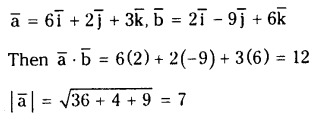
Question 4.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+4 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-5 \overline{\mathrm{k}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathrm{k}}\) and \( \overline{\mathbf{c}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}+2 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\). Find unit vector in the opposite direction of \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}+\overline{\mathbf{b}}+\overline{\mathbf{c}}\)
Solution:
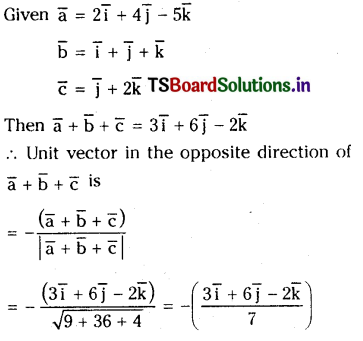
Question 5.
Let \(\bar{a}\) and \(\bar{b}\) be non zero, non collinear vectors. If \(|\overline{\mathbf{a}}+\bar{b}|=|\overline{\mathbf{a}}-\bar{b}|\) then find the angle between \(\bar{a}\) and \(\bar{b}\).
Solution:

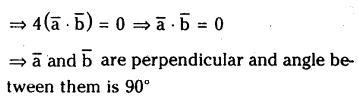
Question 6.
If \(|\overline{\mathbf{a}}|=11,|\bar{b}|=23 \text { and }|\overline{\mathbf{a}}-\overline{\mathbf{b}}|\) = 30 then find the angle between the vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}\), and also find \(|\overline{\mathbf{a}}+\overline{\mathbf{b}}|\)
Solution:
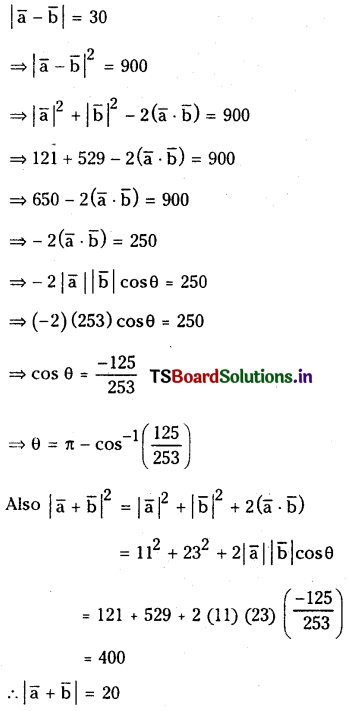
Question 7.
If \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{j}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}=2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-3 \overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}}\) then find the projection vector of \(\overline{\mathbf{b}} \text { on } \bar{a}\) and its magnitude.
Solution:
Projection vector of \(\overline{\mathbf{b}} \text { on } \bar{a}\) is
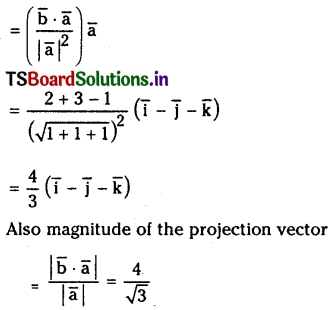
Question 8.
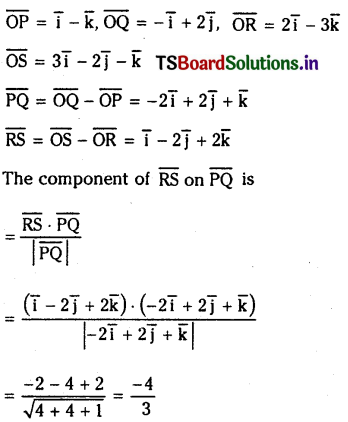
If P, Q, R, S are points whose position vectors are \(\overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}},-\overline{\mathbf{i}}+\mathbf{2} \overline{\mathbf{j}}, 2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-3 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\) and 3 \(\overline{\mathbf{i}}-2 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}}\) respectively, then find the component of \(\overline{\mathbf{R S}}\) on \(\overline{\mathbf{P Q}}\).
Solution:
Let O be the origin.
Question 9.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+3 \overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}=4 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}\) and \(\bar{c}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}-3 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-7 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\). Find the vector \(\overline{\mathbf{r}}\) such that \(\overline{\mathbf{r}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{a}}=9, \overline{\mathbf{r}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{b}}=7 \text { and } \overline{\mathbf{r}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{c}}=6\)
Solution:
Let \(\bar{r}=x \bar{i}+y \bar{j}+z \bar{k}\)
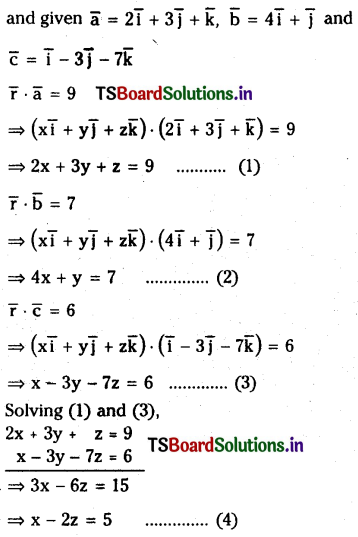
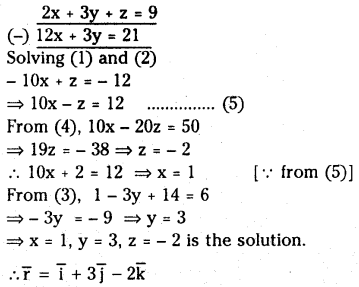
Question 10.
Show that the points \(2 \bar{i}-\bar{j}+\bar{k}, \bar{i}-3 \bar{j}-5 \bar{k}\) and \( 3 \bar{i}-4 \bar{j}-4 \bar{k}\) are the vertices of a right angled triangle. Also find the other angles.
Solution:
Let O be the origin and A,B,C be the given points, then
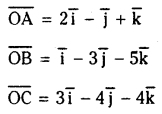
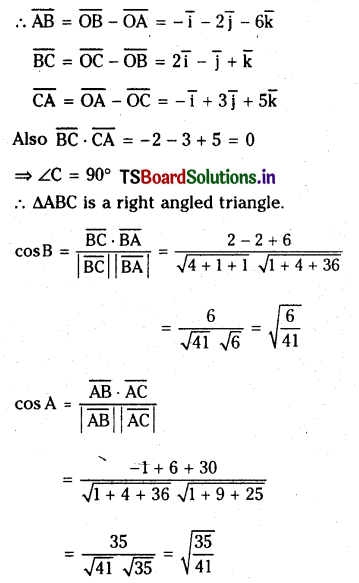
Question 11.
Prove that the smaller angle O between any two diagonals of a cube is given by \(\cos ^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)\)
Solution:
Consider a unit cube with its vertices as shown in the figure
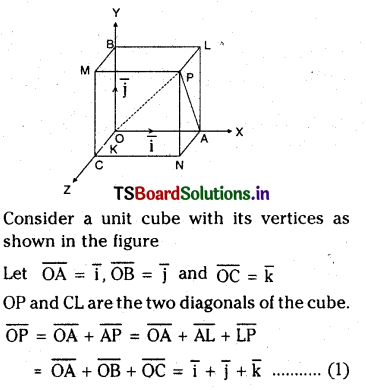
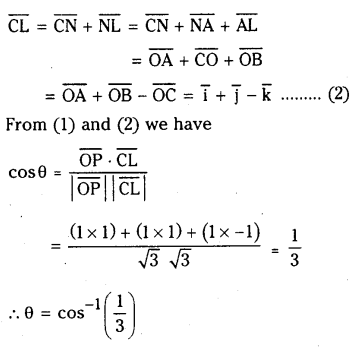
Similarly we can show the result for any other two diagonals of the cube.
Question 12.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) be non zero mutually orthogonal
vectors if \(\mathbf{x} \overline{\mathbf{a}}+\mathbf{y} \overline{\mathbf{b}}+\mathbf{z} \overline{\mathbf{c}}=\overline{\mathbf{0}}\) then x = y = z = 0
Solution:
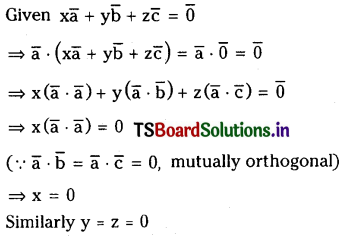
Question 13.
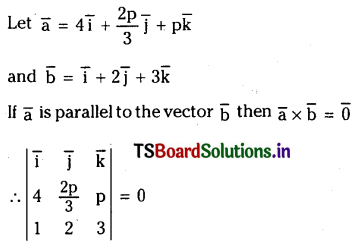
If \(4 \bar{i}+\frac{2 p}{3} \bar{j}+p \bar{k}\) is parallel to the vector \(\overline{\mathbf{i}}+2 \overline{\mathbf{j}}+3 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\). find p.
Solution:
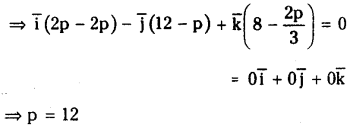
Question 14.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{b}} \) be vectors satisfying \(|\overline{\mathbf{a}}|=|\bar{b}|=5\) and \((\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}})=45^{\circ}\)
Solution:

Question 15.
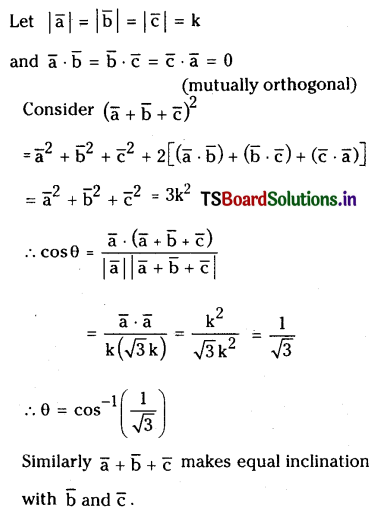
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) be mutually orthogonal vectors of equal magnitudes. Prove that the vector \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}+\overline{\mathbf{b}}+\overline{\mathbf{c}}\) is equally inclined to each of \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{c}}\), the angle of inclination being \(\cos ^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right)\)
Solution:
Similarly we can show the result for any other two diagonals of the cube.
Question 16.
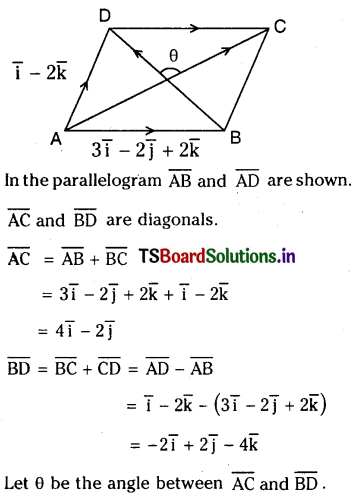
The vectors \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}=3 \overline{\mathrm{i}}-2 \overline{\mathrm{j}}+2 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{AD}}=\overline{\mathrm{i}}-2 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\) represent the adjacent sides of a parallelogram A B C D. Find the angle between the diagonals.
Solution:
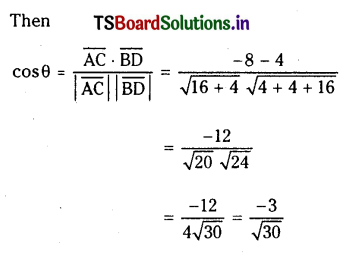
Question 17.
For any two vectors \(\bar{a}\) and \(\bar{b}\) show that
(i) \(|\overline{\mathbf{a}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{b}}| \leq|\overline{\mathbf{a}}||\overline{\mathbf{b}}|\) (Cauchy – Schawartz in equality)
(ii) \(|\overline{\mathbf{a}}+\overline{\mathbf{b}}| \leq|\overline{\mathbf{a}}|+|\overline{\mathbf{b}}|\)(Triangle inequality)
Solution:
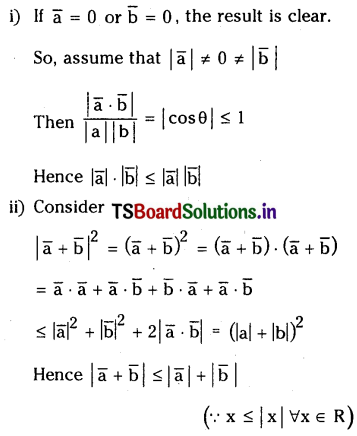
Question 18.
Find the area of parallelogram for which the vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-3 \overline{\mathbf{j}} \text { and } \overline{\mathbf{b}}=3 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}}\) are adjacent sides.
Solution:
The vector area of the parallelogram
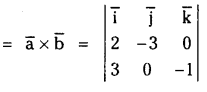

Question 19.
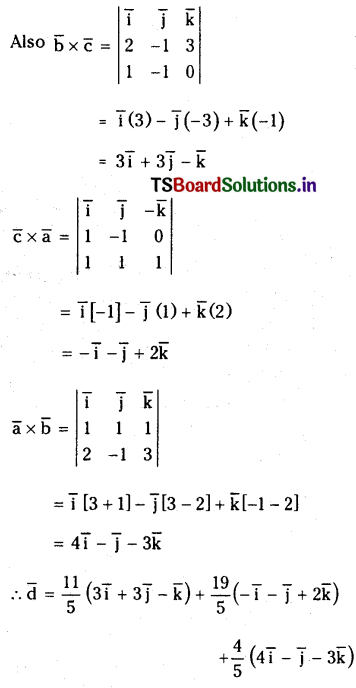
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}=\mathbf{2} \overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\mathbf{3} \overline{\mathbf{k}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{j}}\) and \(\bar{d}=6 \bar{i}+2 \bar{j}+3 \bar{k}\). Express \(\bar{d}\) interms of \(\overline{\mathbf{b}} \times \overline{\mathbf{c}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}} \times \overline{\mathbf{a}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}\).
Solution:
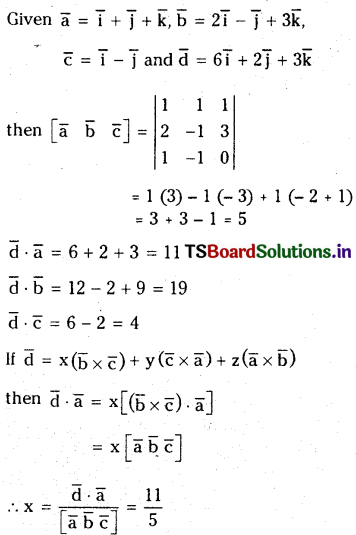
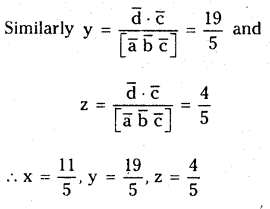
Question 20.
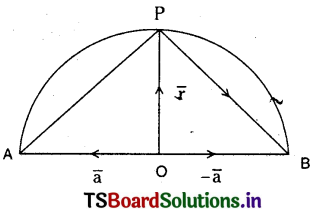
Show that the angle in a semicircle is a right angle.
Solution:
Let O be the centre and AOB be the diameter of the given semicircle. Let P be any point on it. Let the position vectors of A and P be taken as \(\overline{\mathrm{a}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{p}}\)

Question 21.
For any vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{c}}\) prove that \((\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}) \times \overline{\mathbf{c}}=(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{c}}) \overline{\mathbf{b}}-(\overline{\mathbf{b}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{c}}) \overline{\mathbf{a}}\)
Solution:

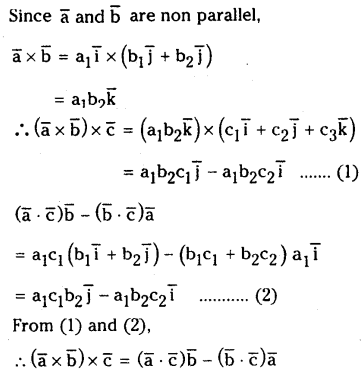
Question 22.
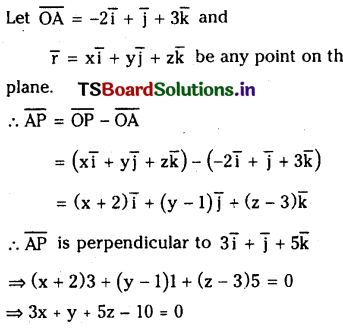
Find the cartesian equation of the plane passing through the point (-2,1,3) and perpendicular to the vector 3 \(\overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\mathbf{5} \overline{\mathbf{k}}\).
Solution :
Question 23.
Find the cartesian equation of the plane through the point A (2, – 1, -4) and parallel to the plane 4x – 12y – 3z – 7 = 0.
Solution:
The equation of the parallel plane is 4x- 12y-3z = p
11 passes through A (2, – 1, – 4) then
4(2)-12 (- 1)-3(-4) = p
⇒ 8 + 12 + 12 = p = p = 32
The equation of the required plane is
4x- 12y-3z = 32
Question 24.
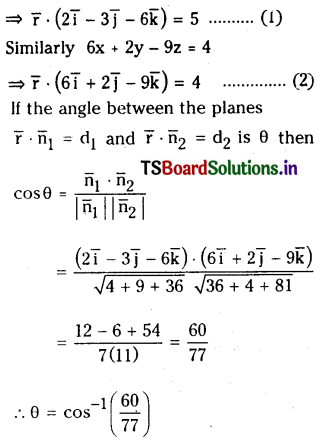
Find the angle between the planes
2x – 3y – 6z = 5 and 6x + 2y – 9z = 4.
Solution:
Equation of the plane is 2x – 3y – 6z = 5
Question 25.
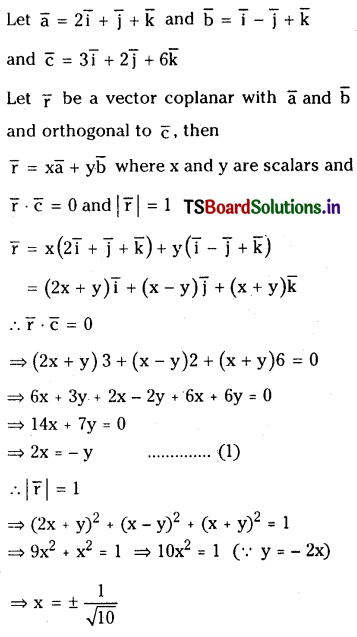
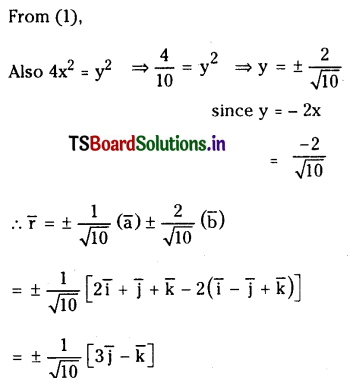
Find limit vector orthogonal to the vector \(3 \bar{i}+2 \bar{j}+6 \bar{k}\) and coplanar with the vectors
\(2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}} \text { and } \overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}}\)
Solution:
Question 26.
If \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-3 \overline{\mathbf{j}}+5 \overline{\mathbf{k}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}=-\overline{\mathbf{i}}+4 \overline{\mathbf{j}}+2 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\) then find \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}\) and unit vector perpendicular to both \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}\).
Solution:
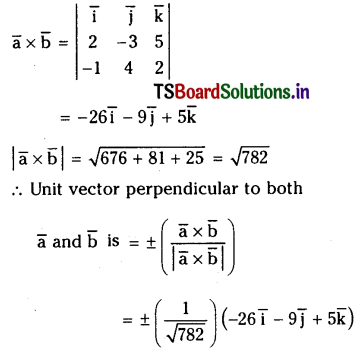
Question 27.
If \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=2 \overline{\mathrm{i}}-3 \overline{\mathrm{j}}+5 \overline{\mathrm{k}}, \overline{\mathrm{b}}=-\overline{\mathrm{i}}+4 \overline{\mathrm{j}}+2 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\) then find \((\bar{a}+\bar{b})_{\times}(\bar{a}-\bar{b})\) and unit vector perpendicular to both \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}+\overline{\mathbf{b}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}-\overline{\mathbf{b}}\).
Solution:

Question 28.
If \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}, \overline{\mathbf{d}}\) are vectors such that \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{c}} \times \overline{\mathbf{d}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{c}}=\overline{\mathbf{b}} \times \overline{\mathbf{d}}\) then show that the vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}-\overline{\mathbf{d}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}-\overline{\mathbf{c}}\) are parallel.
Solution:
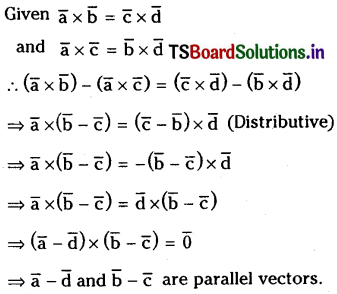
Question 29.
Find the area of the triangle formed by the two sides \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}+2 \overline{\mathbf{j}}+3 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}=3 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+5 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}}\).
Solution:
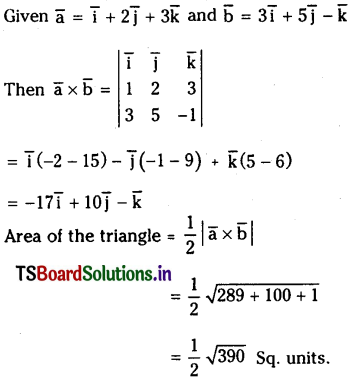
Question 30.
In a \(\triangle \mathrm{ABC}\) if \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}=\overline{\mathrm{a}}, \overline{\mathrm{CA}}=\overline{\mathrm{b}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}=\overline{\mathbf{c}}\) then show that \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{b}} \times \overline{\mathbf{c}}=\overline{\mathbf{c}} \times \overline{\mathbf{a}} \cdot\)
Solution:

Question 31.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=\mathbf{2} \overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}=3 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+4 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}}\). If ‘θ’ is the angle between \(\bar{a}\) and \(\bar{b}\) then find \(\sin \theta\)
Solution:
\(\bar{a}=2 \bar{i}-\bar{j}+\bar{k}, \bar{b}=3 \bar{i}+4 \bar{j}-\bar{k}\)
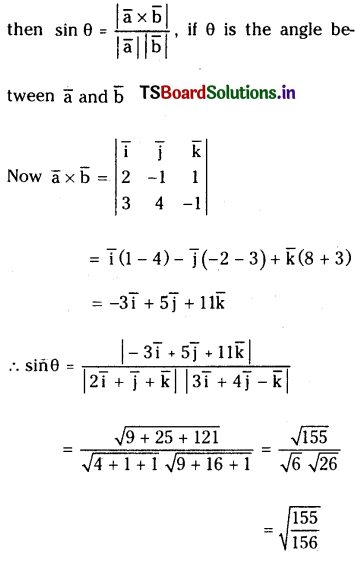
Question 32.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) be such that \(\overline{\mathbf{c}} \neq \overline{\mathbf{0}}, \overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{c}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}} \times \overline{\mathbf{c}}=\overline{\mathbf{a}}\). Show that \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) are pair wise orthogonal vectors and \(|\overline{\mathbf{b}}|=1,|\overline{\mathbf{c}}|=|\overline{\mathbf{a}}|\).
Solution:

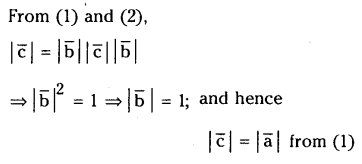
Question 33.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}-2 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\); \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}\). If \(\bar{c}\) is a vector such that \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{c}}=|\overline{\mathbf{c}}|,|\overline{\mathbf{c}}-\overline{\mathbf{a}}|=2 \sqrt{2}\) and the angle between \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathrm{b}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{c}}\) is 30° then find the value of \(|(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}) \times \overline{\mathbf{c}}|\).
Solution:
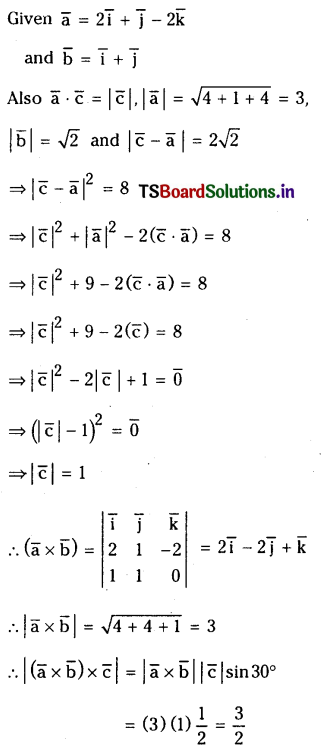
Question 34.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}\) be two non-collinear unit vectors if \(\bar{\alpha}=\overline{\mathbf{a}}-(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{b}}) \overline{\mathbf{b}}\) and \(\bar{\beta}=\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}\) then show that \(|\bar{\beta}|=|\bar{\alpha}|\).
Solution:

Question 35.
A non zero vector \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}\) is parallel to the line of intersection of the plane determined by the vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{i}}, \overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}\) and the plane determined by the vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{j}}, \overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}}\). Find the angle between \(\bar{a}\) and the vector \(\bar{i}-2 \bar{j}+2 \bar{k}\).
Solution:
Let l be the line of intersection of planes determined by the pairs \(\bar{i}, \bar{i}+\bar{j}\) and

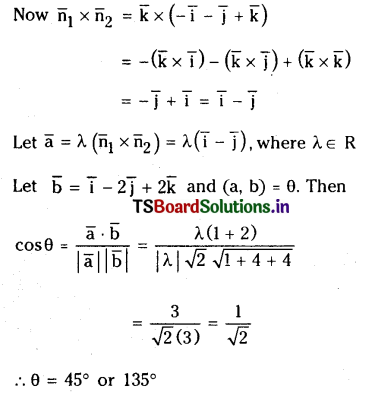
Question 36.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=4 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+5 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}}\), \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}-4 \overline{\mathbf{j}}+5 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{c}}=3 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}}\). Find the vector α which is perpendicular to both \(\bar{a}\) and \(\bar{b}\) and \(\alpha \cdot \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) = 21 \(\bar{\alpha}\) is perpendicular to both \(\bar{a}\) and \(\bar{b}\)
Solution:

Question 37.
For any vector \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}\) show that
\(|\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{i}}|^2+|\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{j}}|^2+|\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{k}}|^2=2|\overline{\mathbf{a}}|^2\)
Solution:
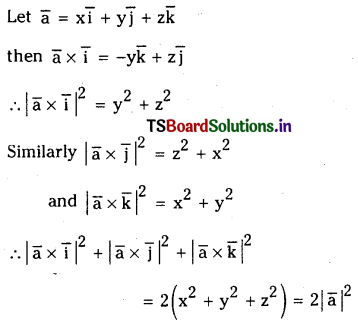
Question 38.
If \(\bar{a}\) is a non zero vector and \(\bar{b}\) and \(\bar{c}\) are two vectors such that \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{a}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) then prove that \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{c}}\)
Solution:
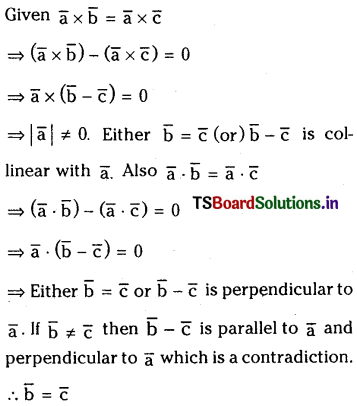
Question 39.
Prove that the vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}=2 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}=\overline{\mathbf{i}}-3 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-5 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{c}}=3 \overline{\mathbf{i}}-4 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-4 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\) are coplanar.
Solution:
\(\bar{a}=2 \bar{i}-\bar{j}+\bar{k}\)
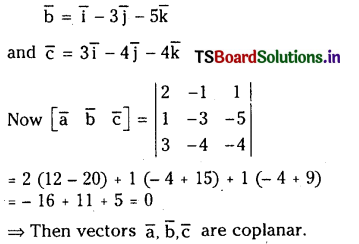
Question 40.
Find the volume of the parallelopiped whose coterminous edges are represented by the vectors \(2 \bar{i}-3 \bar{j}+\bar{k}, \bar{i}-\bar{j}+2 \bar{k}\) and \(\mathbf{2} \overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}-\overline{\mathbf{k}}\)
Solution:
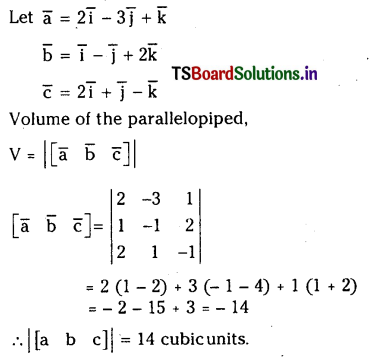
Question 41.
Show that
\(\overline{\mathbf{i}} \times(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{i}})+\overline{\mathbf{j}} \times(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{j}})+\overline{\mathbf{k}} \times(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{k}})=2 \overline{\mathbf{a}}\) For any vector \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}\).
Solution:
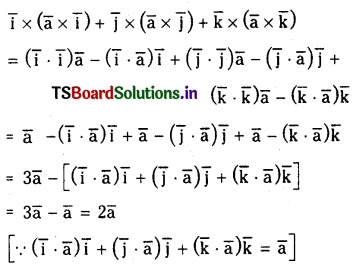
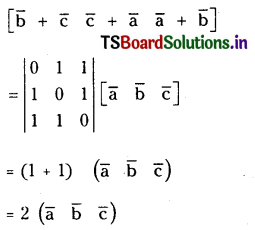
Question 42.
Prove that for any three vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}} \left[\begin{array}{lll}
\bar{b}+\bar{c} & \bar{c}+\overline{\mathbf{a}} & \overline{\mathbf{a}}+\bar{b}
\end{array}\right]=2\left[\begin{array}{lll}
\overline{\mathbf{a}} & \bar{b} & \overline{\mathbf{c}}
\end{array}\right]\)
Solution:
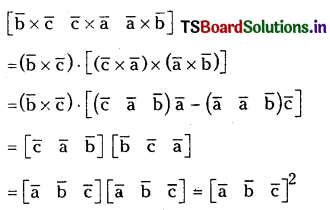
Question 43.
For any three vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) prove that
\(\left[\begin{array}{lll}
\overline{\mathbf{b}} \times \overline{\mathbf{c}} & \overline{\mathbf{c}} \times \overline{\mathbf{a}} & \overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}
\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{lll}
\overline{\mathbf{a}} & \overline{\mathbf{b}} & \overline{\mathbf{c}}
\end{array}\right]^2 \cdot(\mathbf)\)
Solution:
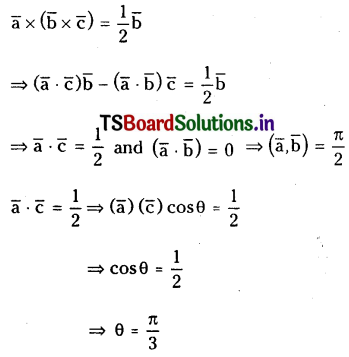
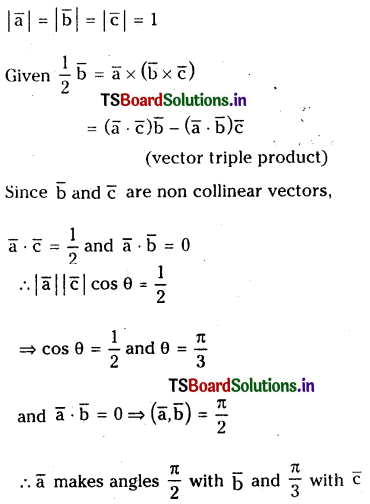
Question 44.
Let \(\bar{a}, \bar{b}\) and \(\bar{c}\) be unit vectors such that \(\bar{b}\) is not parallel to \(\overline{\mathbf{c}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times(\overline{\mathbf{b}} \times \overline{\mathbf{c}})=\frac{1}{2} \overline{\mathbf{b}}\). Find the angles made by \(\bar{a}\) with each of \(\overline{\mathbf{b}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{c}}\).
Solution:
Question 45.
For any four vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{d}}\).
Prove that \((\bar{b} \times \overline{\mathbf{c}}) \cdot(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{d}})+(\overline{\mathbf{c}} \times \overline{\mathbf{a}}) \cdot(\overline{\mathbf{b}} \times \overline{\mathrm{d}}) +(\overline{\mathbf{a}} \times \overline{\mathbf{b}}) \cdot(\overline{\mathbf{c}} \times \overline{\mathbf{d}})=0(\mathrm)\)
Solution:
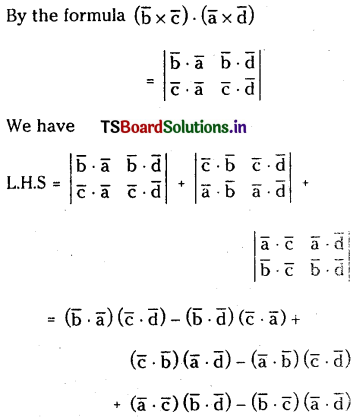
= 0
Question 46.
Find the equation of the plane passing through the points \(\mathrm{A}=(2,3,-1), \mathrm{B}=(4,5, 2)\) and C=(3,6,5).
Solution:
Let \(\overline{\mathrm{OA}}=2 \overline{\mathrm{i}}+3 \overline{\mathrm{j}}-\overline{\mathrm{k}}
\overline{\mathrm{OB}}=4 \overline{\mathrm{i}}+5 \overline{\mathrm{j}}+2 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\)
\(\overline{\mathrm{OC}}=3 \overline{\mathrm{i}}+6 \overline{\mathrm{j}}+5 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\) with respect to origin \(\mathrm{O}\).
Let P be any point on the plane passing through the points A,B,C
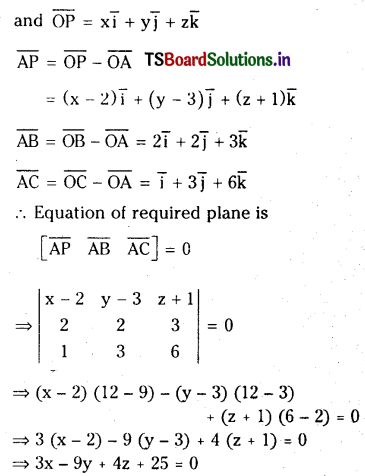
Question 47.
Find the equation of the plane passing through the point A(3,-2,-1) and parallel to the vectors \(\bar{b}=\bar{i}-2 \bar{j}+4 \bar{k}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{c}}=3 \overline{\mathbf{i}}+2 \overline{\mathbf{j}}-5 \overline{\mathbf{k}}\).
Solution:
The equation of the plane passing through A=(3,-2,-1) and parallel to the vectors

Question 48.
Find the vector equation of the plane passing through the intersection of planes \(\overline{\mathbf{r}} \cdot(\overline{\mathbf{i}}+\overline{\mathbf{j}}+\overline{\mathbf{k}})=6\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{r}} \cdot(2 \bar{i}+3 \overline{\mathbf{j}}+4 \overline{\mathbf{k}})=-5\) and the point (1,1,1).
Solution:
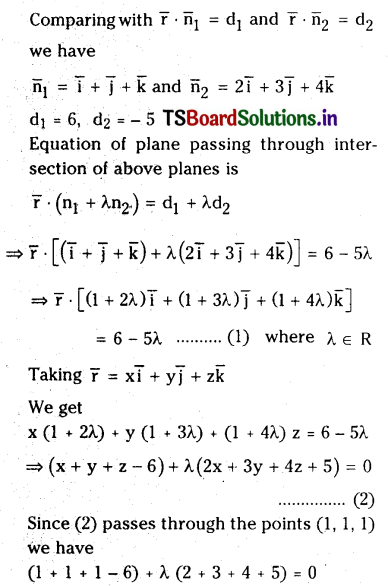
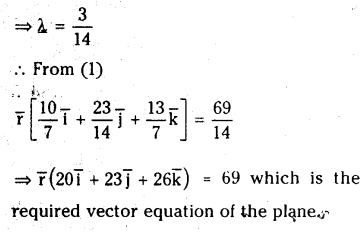
Question 49.
Find the distance of the point (2,5,-3) from the plane \(\overline{\mathbf{r}} \cdot(6 \bar{i}-3 \bar{j}+2 \bar{k})=4 \cdot\)
Solution:
Here \(\bar{a}=\bar{i}+5 \bar{j}-3 \bar{k}, \bar{n}=6 \bar{i}-3 \bar{j}+2 \bar{k}\) and d=4
Then \(\overline{\mathrm{r}} \cdot \overline{\mathbf{n}}=\overline{\mathrm{d}}\)
The distance of the point (2,5,-3) from the given plane is
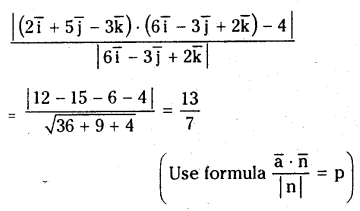
Question 50.
Find the angle between the line \(\frac{x+1}{2}=\frac{y}{3}=\frac{z-3}{6}\) and the plane 10 x+2 y-11 z=3
Solution:
Let φ be the angle between the given line and normal to the plane.
Concert the above equations to vector notation,
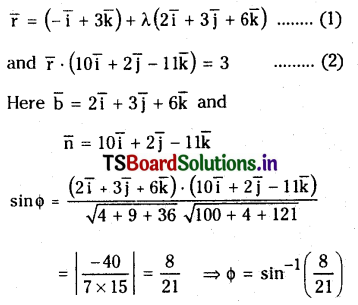
Question 51.
For any four vectors \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) and \(\overline{\mathbf{d}}\) show that
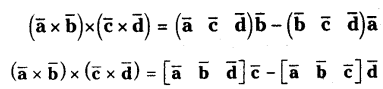
Solution:
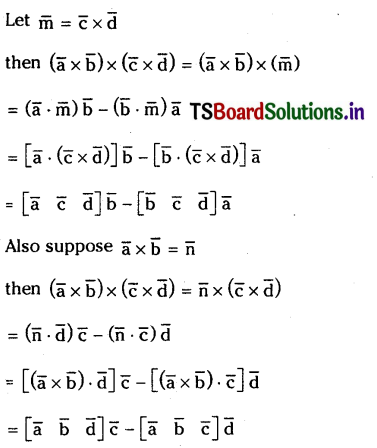
Question 52.
Find the shortest distance between the skew
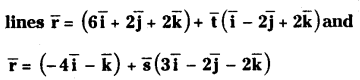
Solution:
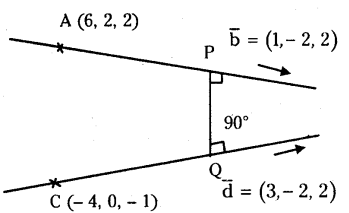
The first line passes through the point A(6,2,2) and parallel to the vector \(\overline{\mathrm{b}}=\overline{\mathrm{i}}-2 \overline{\mathrm{j}}+2 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\).
The second line passes through the point C(-4,0,-1) and parallel to the vector \(\overline{\mathrm{d}}=3 \overline{\mathrm{i}}-2 \overline{\mathrm{j}}-2 \overline{\mathrm{k}}\)
Shortest distance is =\(\frac{|[\overline{\overline{A C}} \bar{b} \bar{d}]|}{|\bar{b} \times \bar{d}|}\)
Question 53.
i) Show that the altitudes of a triangle are concurrent.
ii) The perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle are concurrent.
Solution:
(i)
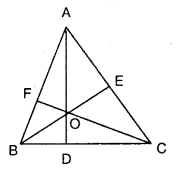
Consider ΔABC . O is point of intersection of altitudes.
To prove that the three altitudes are concurrent at ‘ O ‘. We have to prove that \(\overline{\mathrm{OC}}\) is perpendicular to \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)

∴ \(\overline{\mathrm{OC}}\) is the third altitude which passes through ‘ O ‘.
Hence the three altitudes of the triangle are concurrent.
(ii)
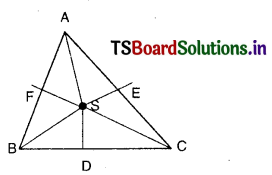

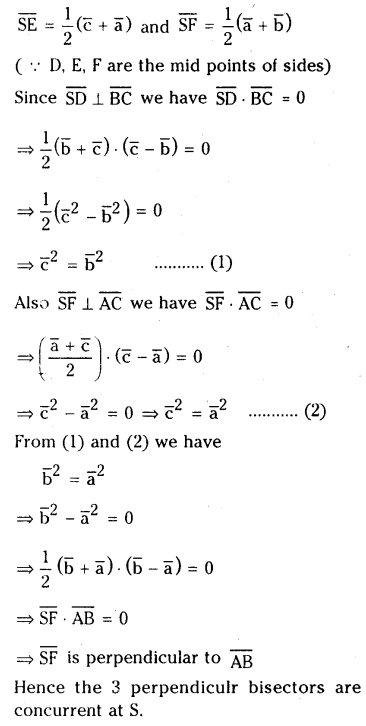
Question 54.
Show that the vector area of the quadrilateral ABCD having diagonals \(\overline{\mathrm{AC}}, \overline{\mathrm{BD}}\) is \(\frac{1}{2}(\overline{\mathrm{AC}} \times \overline{\mathrm{BD}})\)
Solution:
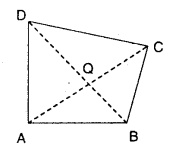
ABCD is a quadrilateral. \(\overline{\mathrm{AC}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{BD}}\) are diagonals of the quadrilateral. Q is the point of intersection of diagonals.
Vector area of quadrilateral ABCD = Sum of the vector area of ΔAQB, ΔBQC, ΔCQD and ΔDQA.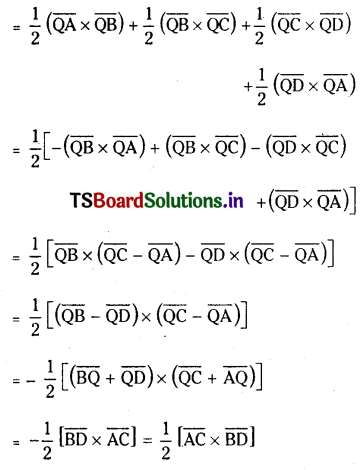
Question 55.
Let \(\overline{\mathbf{a}}, \overline{\mathbf{b}}, \overline{\mathbf{c}}\) be unit vectors such that \(\bar{b}\) is not parallel to \(\bar{c}\) and \(\bar{a} \times(\bar{b} \times \bar{c})=\frac{1}{2} \bar{b}\). Find the angle made by the vector \(\bar{a}\) with each of the vectors \(\bar{b}\) and \(\bar{c}\).
Solution: