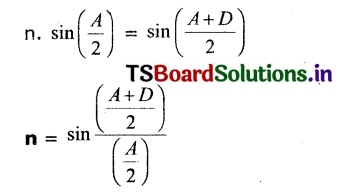
Solving these TS 10th Class Maths Bits with Answers Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Bits for 10th Class will help students to build their problem-solving skills.
Coordinate Geometry Bits for 10th Class
Question 1.
The scientist who introduced co-ordinate Geometry is
A) J.J. Sylvester
B) Crames
C) Rene Descartes
D) Newton
Answer:
C) Rene Descartes
Question 2.
The distance between the points (x, 1) and (1, y)is
A) \(\sqrt{(x+1)^2+(y+1)^2}\)
B) \(\sqrt{(1-x)^2+(y-1)^2}\)
C) \(\sqrt{(x-1)^2+(y+1)^2}\)
D) \(\sqrt{(x+1)^2+(y-1)^2}\)
Answer:
B) \(\sqrt{(1-x)^2+(y-1)^2}\)
Question 3.
A point on Y – axis is
A) (3, 0)
B) (1, 2)
C) (0, 0)
D) (0, 3)
Answer:
D) (0, 3)

Question 4.
The points (0, 3) (0, 0) (4, 0) form a
A) Isosceles triangle
B) Equilateral triangle
C) Right angle triangle
D) Scalene triangle
Answer:
C) Right angle triangle
Question 5.
The slope of the line joining (4, 6) and (2, -5) is
A) \(\frac{11}{2}\)
B) \(\frac{2}{11}\)
C) \(\frac{-2}{11}\)
D) \(\frac{-11}{2}\)
Answer:
A) \(\frac{11}{2}\)
Question 6.
The distance between (7, 0) and (4, k) is 5 units then k =
A) – 4
B) + 4
C) + 4
D) none
Answer:
B) + 4
Question 7.
A straight line make an angle 8 with the X-axis then the slope is
A) – sin θ
B) cos θ
C) tan θ
D) sec θ
Answer:
C) tan θ

Question 8.
Mid-point of the line joining points (-4, 2) and (2, 8) is
A) (-1, 5)
B) (-3, -3)
C) (-2, 10)
D) (-6, -6)
Answer:
A) (-1, 5)
Question 9.
(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4) are vertices of a triangle then its centroid is
A) (6, 9)
B) (0, -1)
C) (2, 3)
D) (-2, -3)
Answer:
C) (2, 3)
Question 10.
(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1) are the midpoints of the sides of a triangle then the area of the triangle is (in.sq.units)
A) 7
B) \(\frac{5}{2}\)
C) 14
D) 6
Answer:
D) 6
Question 11.
The co-ordinates of the mid point of the line joining points (3,-1) and (5, 3) is
A) (8, 4)
B) (\(\frac{8}{3}\), \(\frac{4}{3}\))
C) (4, 2)
D) (4, 1)
Answer:
D) (4, 1)

Question 12.
The equation of the line passing through origin having slope
A) 2x – 3y = 0
B) 2y = x
C) 3x – 2y = 0
D) 3y – 2x
Answer:
D) 3y – 2x
Question 13.
If a line make an angle 150° with +ve X – axis then the slope of the line
A) \(\sqrt{3}\)
B) –\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
C) –\(\sqrt{3}\)
D) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
Answer:
B) –\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
Question 14.
Slope of the line 3x – 4y + 12 = 0
A) \(\frac{3}{4}\)
B) \(\frac{-4}{3}\)
C) 4
D) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
Answer:
A) \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 15.
Slope of the line joining points (2, -3) (1, 4)
A) – 7
B) 7
C) -1
D) – \(\frac{3}{7}\)
Answer:
A) – 7

Question 16.
The angle made by the line y = x with +ve direction of Y-axis
A) 30°
B) 60°
C) 90°
D) 45°
Answer:
D) 45°
Question 17.
The slope of the line \(\frac{x}{a}\) + \(\frac{y}{b}\) = 1
A) –\(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{b}}\)
B) \(\frac{\mathrm{-b}}{\mathrm{a}}\)
C) 1
D) \(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{b}}\)
Answer:
B) –\(\frac{\mathrm{-b}}{\mathrm{a}}\)
Question 18.
The line y = mx + c cut the Y – axis at the point
A) (0, 0)
B) (0, c)
C) (c, 0)
D) (0, m)
Answer:
B) (0, c)
Question 19.
The distance of the point (a, b) from the origin
A) \(\sqrt{a+b}\)
B) \(\sqrt{a^2-b^2}\)
C) \(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
D) \(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\)
Answer:
C) \(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)

Question 20.
The centriod of the triangle made by the vertices (-2, 3), B(4, 1), C(1, 2) is
A) (1, 2)
B) (\(\frac{3}{2}\), 0)
C) (0, 0)
D) (\(\frac{7}{3}\), 2)
Answer:
A) (1, 2)
Question 21.
The slope of the line is \(\frac{2}{5}\) then the slope of the parallel of that line.
A) \(\frac{5}{2}\)
B) \(\frac{2}{5}\)
C) \(\frac{-5}{2}\)
D) 1
Answer:
B) \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Question 22.
If the line y = mx + c passing through the points (0, 3) (4, 0) then intercept is
A) 4
B) – 3
C) -4
D) 3
Answer:
A) 4
Question 23.
The line ax + by + c = 0 intersects X – axis at
A) (\(\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{a}}\), 0)
B) (0, \(\frac{-\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{b}}\))
C) (0, 0)
D) (\(\frac{-\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{a}}\), 0)
Answer:
D) (\(\frac{-\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{a}}\), 0)

Question 24.
The line ax + by + c = 0 intersects Y-axis at
A) (0, \(\frac{-\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{b}}\))
B) (\(\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{b}}\), 0)
C) (\(\frac{-\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{b}}\), 0)
D) (0, -c)
Answer:
A) (0, \(\frac{-\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{b}}\))
Question 25.
Distance between the points (0, 0) (a cosθ, a sinθ)
A) 2
B) a2
C) a
D) \(\frac{\mathrm{a}^2}{2}\)
Answer:
C) a
Question 26.
If ‘C is the mid point of A (0, 0) B(4, 8). then the co-ordinates of the mid-points B and C is
A) (2, 4)
B) (3, 6)
C) (1, 2)
D) (4, 6)
Answer:
B) (3, 6)
Question 27.
The slope of the line y = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x is
A) 0
B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
C) –\(\frac{1}{2}\)
D) 1
Answer:
B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)

Question 28.
The equation of the X-axis is
A) y = 0
B) x = 0
C) x = y
D) xy = 0
Answer:
A) y = 0
Question 29.
The point of intersection of the lines x = 2 and y = 3 is
A) (0, 0)
B) (3, 0)
C) (0, 2)
D) (\(\frac{4}{3}\), 1)
Answer:
D) (\(\frac{4}{3}\), 1)
Question 30.
If the line 3x + 4y = k passing through the point (4, 2) then k
A) 10
B) – 20
C) 20
D) – 10
Answer:
C) 20
Question 31.
If the distance between two points (5, 2) (3, a) is \(\sqrt{8}\) units then a
A) – 2
B) 2
C) 8
D) 4
Answer:
D) 4

Question 32.
The ratio in which the Y-axis dividing line joining the points (5, 7) (-1, 3) is
A) 5 : 1
B) 3 : 7
C) 2 : 1
D) 4 : 3
Answer:
A) 5 : 1
Question 33.
The point on X – axis
A) (2, 3)
B) (2, 0)
C) (0, 4)
D) (0, -3)
Answer:
B) (2, 0)
Question 34.
The point on Y – axis
A) (0, 2)
B) (4, 0)
C) (-3, 4)
D) (2, -1)
Answer:
A) (0, 2)
Question 35.
The slope of the line x = 0
A) 0
B) 1
C) ∞
D) – 1
Answer:
C) ∞

Question 36.
The point (4, -7) in ……………….. quadrant
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q4
Answer:
D) Q4
Question 37.
The line ax – by + c = 0 of slope
A) \(\frac{-\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{b}}\)
B) \(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{b}}\)
C) \(\frac{-\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}\)
D) \(\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}\)
Answer:
B) \(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{b}}\)
Question 38.
The line y = 5 is
A) Parallel to x-axis
B) Parallel to y-axis
C) Perpendicular to x – axis
D) Perpendicular to y-axis
Answer:
A) Parallel to x-axis
Question 39.
If the line 2x – 3y = k passes through the origin then the value of k
A) – 1
B) 0
C) 1
D) –\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
D) –\(\frac{1}{2}\)

Question 40.
The centriod of the triangle made by the vertices A(-2, 3) (4, 1) (1, 2) is
A) (1, 2)
B) [\(\frac{3}{2}\), 2]
C) (0, 0)
D) [\(\frac{7}{3}\), 2]
Answer:
D) [\(\frac{7}{3}\), 2]
Question 41.
Area of the ∆ formed by the points A(0, 0), B (1, 0) and C(0, 1) is ……………….. sq. units. (A.P. Mar. ’15)
A) 0
B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
C) 1
D) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer:
B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 42.
Where do the points lie on co-ordinate axis (-4, 0), (2, 0), (6, 0), (8, 0) (A.P. Mar. ’15)
A) Q1
B) x-axis
C) y-axis
D)Q4
Answer:
B) x-axis
Question 43.
The distance between (0, 0) (x1, y1) points is ……………. units. (A.P. Mar. ’15)
A) \(\sqrt{x_1^2+y_1^2}\)
B) \(\sqrt{x_1+y_1}\)
C) \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)
D) \(\sqrt{x+y}\)
Answer:
A) \(\sqrt{x_1^2+y_1^2}\)

Question 44.
The distance between the points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) which are on the line parallel to Y-axis is ……………. (A.P. Mar.’15)
A) |Y1 – Y2| or |Y2 – Y1|
B) |y22 – y12| or |y12 – y22|
C) \(\sqrt{\left(x_2-x_1^2\right)+\left(y_2-y_1^2\right)}\)
D) |x2 – x1| or |x1 – x2|
Answer:
A) |Y1 – Y2| or |Y2 – Y1|
Question 45.
The mid point of line segment joined by (4, 5) and (-6, 3) is ……………… (A.P. June ’15)
A) (1, 4)
B) (-1, 4)
C) (1, -4)
D) (-1, -4)
Answer:
B) (-1, 4)
Question 46.
The distance to X-axis from the point (3, -4) is …………….. (A.P. June’15)
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 1
Answer:
B) 4
Question 47.
If the mid point of (-4, a) and (2, 8) is (-1, 5) then a = ………………. (A.P. June ’15)
A) -4
B) 2
C) 5
D) 8
Answer:
B) 2

Question 48.
The graph of y = 5 is ……………… (A.P. June ’15)
A) Parallel of X-axis
B) Perpendicular to X-axis
C) Parallel to Y-axis
D) Perpendicular to Y-axis
Answer:
A) Parallel of X-axis
Question 49.
The distance between (0, 7) and (-7, 0) is ………………… (A.P. Mar. ’16)
A) 2\(\sqrt{7}\)
B) 7\(\sqrt{2}\)
C) \(\sqrt{14}\)
D) +1
Answer:
B) 7\(\sqrt{2}\)
Question 50.
Slope of Y-axis is ……………… (A.P. Mar.’16)
A) not defined
B) 0
C) well defined
D) finite
Answer:
A) not defined
Question 51.
The distance from X-axis to (-4, 3) is ………………. units. (A.P. Mar.’16)
A) 2
B) 3
C) -4
D) -1
Answer:
B) 3

Question 52.
The distance from origin to (2, 3) is …………….. units. (A.P. Mar.’16)
A) \(\sqrt{6}\)
B) \(\sqrt{5}\)
C) \(\sqrt{1}\)
D) \(\sqrt{13}\)
Answer:
D) \(\sqrt{13}\)
Question 53.
The distance from Y-axis to (4, 0) is ……………… units. (A.P. Mar.’16)
A) 4 units
B) \(\sqrt{16}\) units
C) 16 units
D) 2\(\sqrt{2}\) units
Answer:
A) 4 units
Question 54.
The mid point of (2, 3) and (-2, 3) is ……………… (A.P. Mar.’16)
A) (0, 3)
B) (-2, 0)
C) (3, 0)
D) (-3, 2)
Answer:
A) (0, 3)
Question 55.
The centroid of the triangle formed by (0, 3); (3, 0) and (0, 0) is …………….. (A.P. Mar.’16)
A) (1, 1)
B) (0, 3)
C) (3, 3)
D) (3, 0)
Answer:
A) (1, 1)

Question 56.
Slope of the line that passes through the point P(x1, y1) and Q (x2, y2) and making an angle ‘θ’ with X-axis is ……………….. (A.P. Mar.’16)
A) \(\frac{\mathrm{y}_2+\mathrm{y}_1}{\mathrm{x}_2+\mathrm{x}_1}\)
B) θ
C) \(\frac{\mathrm{y}_2-\mathrm{y}_1}{\mathrm{x}_2-\mathrm{x}_1}\)
D) sin θ
Answer:
C) \(\frac{\mathrm{y}_2-\mathrm{y}_1}{\mathrm{x}_2-\mathrm{x}_1}\)
Question 57.
Slope of the line passing through the points (-1, 1) and (1, 1) is …………….. (A.P. Mar. ’16)
A) -1
B) 0
C) 1
D) not defined
Answer:
C) 1
Question 58.
A point on the Y-axis is of the form
A) (0, y)
B) (x, 0)
C) (x, y)
D) (y, y)
Answer:
A) (0, y)
Question 59.
A point on the X-axis is of the form
A) (0, y)
B) (x, 0)
C) (x, y)
D) (x, x)
Answer:
B) (x, 0)

Question 60.
The distance of the point (-8, 3) from the origin is ……………….
A) 5
B) 55
C) 73
D) 24
Answer:
C) 73
Question 61.
The distance of the point (-4, 3) from X-axis is ……………..
A) -4
B) -3
C) 4
D) 3
Answer:
D) 3
Question 62.
The distance of the point (-8, -7) from Y-axis is ………….
A) 8
B) -7
C) -8
D) 7
Answer:
A) 8
Question 63.
The points (-3,0), (0,5) and (3,0) are the vertices of a ……………… triangle.
A) scalene
B) isosceles
C) equilateral
D) right angled
Answer:
B) isosceles

Question 64.
The distance between the points (-2, 3) and (2, -3) is ……………..
A) 0
B) 52
C) \(\sqrt{52}\)
D) 16
Answer:
C) \(\sqrt{52}\)
Question 65.
If the distance between the points (4, y) and (1, 0) is 5, then y = …………
A) 0
B) 4
C) ±4
D) ±2
Answer:
C) ±4
Question 66.
The distance between the points (0, 7) and (-7, 0) is ……………….
A) \(\sqrt{14}\)
B) 49
C) 2\(\sqrt{7}\)
D) 7\(\sqrt{2}\)
Answer:
D) 7\(\sqrt{2}\)
Question 67.
A circle is drawn with origin as centre and passing through (2, 3), then its radius is ………………
A) 2
B) 3
C) 13
D) \(\sqrt{13}\)
Answer:
D) \(\sqrt{13}\)

Question 68.
The area of the triangle formed by (a, b + c), (b, c + a) and (c, a + b) is
A) 2(a + b + c)
B) abc
C) 0
D) a + b + c
Answer:
C) 0
Question 69.
If points (x, 0), (0, y) and (1, 1) are collinear, then \(\frac{1}{x}\) + \(\frac{1}{y}\) = …………….
A) 1
B) -1
C) 0
D) 2
Answer:
A) 1
Question 70.
The point which divides the line segment joining the points (3, 4) and (7, -6) internally in the ratio 1 : 2 lies in the ………….. quadrant.
A) Q1
B) Q2
C) Q3
D) Q4
Answer:
D) Q4
Question 71.
The points (a, 2a), (3a, 3a) and (3, 1) are collinear, then k = …………….
A) \(\frac{-1}{4}\)
B) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
C) \(\frac{-2}{3}\)
D) \(\frac{-1}{3}\)
Answer:
D) \(\frac{-1}{3}\)

Question 72.
A circle drawn with origin as centre passes through (\(\frac{13}{2}\), 0). The point which doesn’t lie in the interior of the circle is ………………..
A) (-6, 3)
B) (5, \(\frac{1}{2}\))
C) (2, \(\frac{7}{3}\))
D) (\(\frac{-3}{4}\), 1)
Answer:
A) (-6, 3)
Question 73.
The distance of the point (-9, 40) from the origin is ………….
A) 9
B) 40
C) 53
D) 41
Answer:
D) 41
Question 74.
If (-2, 8) and (6, -4) are the end points of the diameter of a circle, then the centre of the circle is ………………..
A) (3, 6)
B) (4, 2)
C) (2, 2)
D) (-3, 2)
Answer:
C) (2, 2)
Question 75.
The angle between X-axis and Y-axis is ………………
A) 0°
B) 180°
C) 360°
D) 90°
Answer:
D) 90°

Question 76.
The midpoint of the line joining of (2, 3) and (-2, -3) is ………………
A) (0, 0)
B) (2, 3)
C) (1, 1\(\frac{1}{2}\))
D) (-1, -1\(\frac{1}{2}\))
Answer:
A) (0, 0)
Question 77.
The slope of line join of (5, -1), (0, 8) is ……………….
A) \(\frac{7}{5}\)
B) \(\frac{9}{5}\)
C) –\(\frac{9}{5}\)
D) –\(\frac{5}{9}\)
Answer:
C) –\(\frac{9}{5}\)
Question 78.
Slope of X-axis is ……………………
A) 0
B) 1
C) -1
D) Not defined
Answer:
A) 0
Question 79.
The centroid of the triangle whose vertices are (2, -3), (4, 6), (-2, 8) is
A) \(\left(\frac{8}{3}, \frac{17}{3}\right)\)
B) (4, 11)
C) (-3, -8)
D) \(\left(\frac{4}{3}, \frac{11}{3}\right)\)
Answer:
D) \(\left(\frac{4}{3}, \frac{11}{3}\right)\)

Question 80.
Two vertices of a triangle are (3, 5) and (-4, -5). If the centroid of the triangle is (4,3), find the third vertex.
A) (13, 9)
B) (-9, -13)
C) (9, 13)
D) (13, -9)
Answer:
A) (13, 9)
Question 81.
The ratio in which the point (4, 8) divide the line segment joining the points (8, 6) and (0, 10) is ………………..
A) 2 : 1
B) 1 : 1
C) 1 : 2
D) 3 : 1
Answer:
B) 1 : 1
Question 82.
If (-2, -1), (a, 0), (4, b) and (1,2) are the vertices of a parallelogram then a = ……………….
A) 3
B) -1
C) 4
D) 1
Answer:
A) 3
Question 83.
In the above problem b = ……………
A) 3
B) 4
C) -5
D) none
Answer:
D) none

Question 84.
(-2, 8) ∈ ………………….
A) Q1
B) Q4
C) Q2
D) Q3
Answer:
D) Q3
Question 85.
If A, B, C are collinear then area of ∆ABC = ………………
A) 2
B) 1
C) 0
D) none
Answer:
C) 0
Question 86.
Area of triangle formed by (-4, 0), (0, 0) and (0, 5) is ……………. sq. units.
A) 12
B) 10
C) 13
D) 9
Answer:
B) 10
Question 87.
The value of p if the distance between (2, 3) and (p, 3) is 5 is ……………….
A) 7
B) 9
C) 12
D) 10
Answer:
A) 7

Question 88.
The value of k if the distance between (2, 8) and (2, k) is 3 is ……………….
A) 4.5
B) 10
C) 9
D) 5
Answer:
D) 5
Question 89.
A(0, -1), B(2,1) and C(0, 3) are the vertices of ∆ABC then median through B has a length …………… units.
A) 9.5
B) 10
C) 2
D) 9
Answer:
C) 2
Question 90.
The closed figure formed by the points (-2, 0), (2, 0), (2, 2), (0, 4) and (-2, -2) is a …………………
A) pentagon
B) triangle
C) circle
D) none
Answer:
A) pentagon
Question 91.
The co-ordinates of the midpoints joining P(x1, y1) and Q(x2, y2) is ……………
A) \(\left(\frac{x_1+x_2}{2}, \frac{y_1+y_2}{2}\right)\)
B) \(\left(\frac{x_1-x_2}{2}, \frac{y_1+y_2}{2}\right)\)
C) \(\left(\frac{x_1+y_1}{2}, 1\right)\)
D) none
Answer:
A) \(\left(\frac{x_1+x_2}{2}, \frac{y_1+y_2}{2}\right)\)

Question 92.
The centroid divides each median in the ……………… ratio.
A) 3 : 1
B) 1 : 3
C) 1 : 2
D) 2 : 1
Answer:
D) 2 : 1
Question 93.
If the distance between the points (3, k) and (4, 1) is \(\sqrt{10}\) then the value of k = ……………..
A) 8 or 10
B) 4 or -2
C) -1 or 2
D) none
Answer:
B) 4 or -2
Question 94.
If the points (1, 2) (-1, x) and (2, 3) are collinear then the value of x is ……………….
A) 9
B) 7
C) 0
D) -1
Answer:
C) 0
Question 95.
If the centroid of the triangle formed with (a, b), (b, c) and (c, a) is 0(0, 0) then a3 + b3 + c3 = ……………..
A) a + b + c
B) \(\frac{a+b+c}{3}\)
C) \(\frac{a b c}{3}\)
D) 3 abc
Answer:
D) 3 abc

Question 96.
The distance between the points (a cos θ, 0) and (0, a sin θ) is ……………….. units.
A) \(\frac{a}{3}\)
B) a
C) a2
D) \(\frac{a}{2}\)
Answer:
C) a2
Question 97.
Distance of (x, y) from X-axis is …………………
A) y
B) -x
C) -y
D) none
Answer:
A) y
Question 98.
Distance of (x, y) from Y-axis is …………………
A) -x
B) Y
C) x
D) none
Answer:
C) x
Question 99.
(x, 0) is a point on …………………..
A) X-axis
B) Y-axis
C) origin
D) none
Answer:
A) X-axis

Question 100.
(0, y) is a point on ………………..
A) (0, 0)
B) Y-axis
C) X-axis
D) none
Answer:
D) none
Question 101.
Distance of (x, y) from origin is ……………….
A) \(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\)
B) \(\sqrt{x+y}\)
C) \(\sqrt{xy}\)
D) \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)
Answer:
D) \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)
Question 102.
If a < 0 then (-a, -a) ∈ …………………..
A) Q2
B) Q1
C) Q4
D) Q3
Answer:
B) Q1
Question 103.
Slope of the line y = mx is …………………
A) y
B) x
C) m
D) none
Answer:
C) m

Question 104.
Slope of the line joining the points (2a, 3b) and (a, -b) is ……………….
A) \(\frac{-a}{b}\)
B) \(\frac{b}{a}\)
C) \(\frac{b}{4 a}\)
D) \(\frac{4 b}{a}\)
Answer:
D) \(\frac{4 b}{a}\)
Question 105.
Slope of the line joining the points A(-1.4, -3.7) and B(-2.4, 1.3) is ……………….
A) -5
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
Answer:
A) -5
Question 106.
(3, -5) ∈ …………………
A) Q4
B) Q3
C) Q1
D) Q2
Answer:
A) Q4
Question 107.
The angle between the lines x = 2 and y = 3 is …………………….
A) 60°
B) 70°
C) 90°
D) 80°
Answer:
C) 90°

Question 108.
Slope of vertical line is ……………………
A) 0
B) -1
C) 3
D) not defined
Answer:
D) not defined
Question 109.
Area of triangle formed with (-5, -1), (3, -5) and (5, 2) is ………………. sq. units.
A) 28
B) 20
C) 32
D) 16
Answer:
C) 32
Question 110.
If the points (k, k), (2, 3) and (4, -1) are collinear then k = ……………………..
A) \(\frac{-1}{7}\)
B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
C) \(\frac{3}{7}\)
D) \(\frac{7}{3}\)
Answer:
D) \(\frac{7}{3}\)
Question 111.
A(2, 0), B(1, 2), C(1, 6) then ∆ABC = …………………..
A) 10
B) 12
C) 0
D) 9
Answer:
C) 0

Question 112.
Identify collinear points.
A) (1, -6) (3, -4), (4, -3)
B) (1, -1) (2, 3), (2, 0)
C) (5, 2), (3, -5), (-5, -1)
D) all
Answer:
A) (1, -6) (3, -4), (4, -3)
Question 113.
The area of square formed with the vertices (0, -1), (2, 1), (0, 3) and (-2, 1) taken in order as vertices is ………………. sq. units.
A) 12
B) 6
C) 8
D) none
Answer:
D) none
Question 114.
The co-ordinates of centroid of the triangle formed with the vertices (-1, 3), (6, -3) and (-3, 6) is …………………….
A) (1, \(\frac{1}{2}\))
B) (\(\frac{2}{3}\), 2)
C) (8, \(\frac{-1}{2}\))
D) (0, 3)
Answer:
B) (\(\frac{2}{3}\), 2)
Question 115.
A(1, -1), B(0, 6) and C(-3, 0) then G = ………………..
A) (\(\frac{8}{9}\), \(\frac{1}{7}\))
B) (\(\frac{6}{7}\), \(\frac{1}{3}\))
C) (\(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{1}{3}\))
D) (\(\frac{-2}{3}\), \(\frac{5}{3}\))
Answer:
D) (\(\frac{-2}{3}\), \(\frac{5}{3}\))

Question 116.
The point of concurrence of medians of a triangle is called ……………….
A) centroid
B) orthocentre
C) centre
D) none
Answer:
A) centroid
Question 117.
Mid point of the line joining the points (1,1) and (0, 0) is ……………….
A) (0, 9)
B) (3, 7)
C) (\(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\))
D) (1, \(\frac{1}{2}\))
Answer:
C) (\(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\))
Question 118.
The radius of the circle whose centre is (3, 2) and passes through (-5, 6) is ………………. units.
A) 2\(\sqrt{5}\)
B) 4\(\sqrt{7}\)
C) 4\(\sqrt{3}\)
D) 4\(\sqrt{5}\)
Answer:
D) 4\(\sqrt{5}\)
Question 119.
Area of parallelogram = ……………….. sq.units.
A) \(\frac{1}{2}\)bh
B) bh
C) b2h2
D) none
Answer:
B) bh

Question 120.
A(4, 5), B{7, 6) then AB = …………………. units.
A) \(\sqrt{10}\)
B) 10
C) 8
D) \(\sqrt{19}\)
Answer:
A) \(\sqrt{10}\)
Question 121.
In quadrilateral ABCD, AB = BC = CD = AD and AC ≠ BD then it is a ……………
A) trapezium
B) square
C) parallelogram
D) none
Answer:
C) parallelogram
Question 122.
A(a, b) and B(-a, -b) then BA = …………………. units.
A) 2\(\sqrt{a}\)
B) 2\(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
C) 2\(\sqrt{b}\)
D) 2\(\sqrt{a^2+b}\)
Answer:
B) 2\(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
Question 123.
If θ is the angle made by a line with X-axis then slope m = …………………..
A) tan θ
B) sec θ
C) cosec θ
D) none θ
Answer:
A) tan θ

Question 124.
A(4, 0), B(8, 0) then AB = ………………. units.
A) 6
B) 10
C) 4
D) 12
Answer:
C) 4
Question 125.
Other name for X-Coordinate of a point is …………………..
A) abscissa
B) point
C) ordinate
D) none
Answer:
A) abscissa
Question 126.
(8, 10) ∈ …………………….
A) Q2
B) Q1
C) Q3
D) none
Answer:
B) Q1
Question 127.
Slope of horizontal line is ………………….
A) 3
B) -1
C) 0
D) none
Answer:
C) 0

Question 128.
ax + by + c = 0, represents a ………………..
A) straight line
B) circle
C) curve
D) none
Answer:
A) straight line
Question 129.
In Heron’s formula S = …………….
A) \(\frac{a-b-c}{2}\)
b) \(\frac{a+b-c}{2}\)
C) \(\frac{ab}{2}\) + c
D) \(\frac{a+b+c}{2}\)
Answer:
D) \(\frac{a+b+c}{2}\)
Question 130.
Coordinates of origin are ……………………
A) (a, b)
B) (3, 7)
C) (0, 0)
D) none
Answer:
C) (0, 0)
Question 131.
A(4, 3), B(8, 6) then AB = ………………. units.
A) 9
B) 5
C) 16
D) 12
Answer:
B) 5

Question 132.
Q1 ∩ Q2 = …………………..
A) Φ
B) {0}
C){8, 4}
D) none
Answer:
A) Φ
Question 133.
Slope of the line \(\frac{x}{a}\) + \(\frac{y}{b}\) = 1 is ………………..
A) \(\frac{-b}{a}\)
B) \(\frac{b}{a}\)
C) \(\frac{a}{b}\)
D) none
Answer:
A) \(\frac{-b}{a}\)
Question 134.
The midpoint of the line joining the points (1, 2) and (1, p) is (1, -1) then p = ……………………
A) -31
B) -3
C) -4
D) none
Answer:
C) -4
Question 135.
The centroid of the triangle formed with the line x + y = 6 with the co-ordinate axes is ………………..
A) (4, 0)
B) (1, 3)
C) (8, 1)
D) (2, 2)
Answer:
D) (2, 2)

Question 136.
Slope of the line joining the points (2, 5) and (k, 3) is 2 then k = ………………..
A) 4
B) 1
C) -1
D) none
Answer:
B) 1
Question 137.
A point on X-axis is …………………….
A) (9, 0)
B) (0, 3)
C) (9, 3)
D) (3, -1)
Answer:
A) (9, 0)
Question 138.
The slope of a line passing through (-2, 3) and (4, a) is \(\frac{-5}{3}\) then a = ……………….
A) 1
B) 7
C) -7
D) 2
Answer:
C) -7
Question 139.
If (1, x) is at \(\sqrt{10}\) units from origin then the value of x = ………………..
A) ±31
B) ±3
C) ±2
D) ±1
Answer:
B) ±3

Question 140.
A = (\(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{3}{2}\)), B = (\(\frac{3}{2}\), \(\frac{-1}{2}\)) then BA = ……………
A) \(\sqrt{5}\)
B) \(\sqrt{6}\)
C) \(\sqrt{19}\)
D) none
Answer:
A) \(\sqrt{5}\)
Question 141.
X and Y axes will intersect at …………………
A) (1, 1)
B) (2, 2)
C) (0, 0)
D) (8, 5)
Answer:
C) (0, 0)
Question 142.
In ∆ ABC, AB = AC = BC then it is ……………….. triangle.
A) scalene
B) equilateral
C) isosceles
D) none
Answer:
B) equilateral
Question 143.
Y-axis can be represented by ………………….
A) x = 0
B) y = 0
C) y = \(\frac{-1}{2}\)
D) all
Answer:
A) x = 0

Question 144.
y intercept of the line x – 2y + 1 = 0 is ……………..
A) \(\frac{-1}{2}\)
B) 1
C) -1
D) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
B) 1
Question 145.
In the figure AD : GD = ………………..

A) 3 : 1
B) 1 : 2
C) 2 : 1
D) none
Answer:
A) 3 : 1
Question 146.
Equation of X-axis is ………………..
A) x = 0
B) x = 7
C) x = 1
D) y = 0
Answer:
D) y = 0
Question 147.
If (p, 2p), (2p, 3p) and (3,1) are collinear then P = …………………
A) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
B) -1
C) \(\frac{-1}{3}\)
D) none
Answer:
A) \(\frac{1}{3}\)

Question 148.
In ∆ABC, all the sides are different then it is called ………………….. triangle.
A) isosceles
B) scalene
C) equilateral
D) none
Answer:
B) scalene
Question 149.
In ∆PQR, PQ = QR then it is called …………………… triangle.
A) isosceles
B) right triangle
C) equilateral
D) none
Answer:
A) isosceles
Question 150.
A(1, -1), B(2 1/2, 0), C(4, 1) then area of ∆ABC = ……………… sq. units.
A) 2
B) 9
C) 0
D) none
Answer:
C) 0
Question 151.
The point of concurrence of attitudes of a triangle is called its ……………….
A) orthocentre
B) centroid
C) isosceles
D) none
Answer:
A) orthocentre

Question 152.
Angle made by the line y = x with the positive direction of X-axis is ……………………
A) 45°
B) 60°
C) 90°
D) 70°
Answer:
A) 45°
Question 153.
Number of medians of a triangle is ……………..
A) 5
B) 4
C) 7
D) 3
Answer:
D) 3
Question 154.
Slope of line y = 7 is ……………….
A) 1
B) 7
C) 0
D) none
Answer:
C) 0
Question 155.
If A(p, q), B(m, n) and C(p – m, q – n) are collinear then pn = ………………….
A) q2m
B) qm
C) \(\frac{q}{m}\)
D) none
Answer:
B) qm

Question 156.
In the problem y = …………………
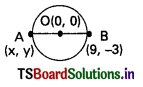
A) 3
B) 7
C) -3
D) 8
Answer:
A) 3
Question 157.
Area of trapezium = ……………….. sq. units.
A) ph
B) h(a + b)
C) \(\frac{1}{2}\) h(a + b)
D) \(\frac{1}{2}\)(a + b)
Answer:
C) \(\frac{1}{2}\) h(a + b)
Question 158.
P(cos θ, -cos θ), Q(sin θ, sin θ) then PQ = ……………….
A) cos θ
B) sin2 θ
C) 0
D) none
Answer:
D) none
Question 159.
A(t, 2t), B(-2, 6), C(3, 1) and ∆ABC = 5 sq. units then t = ………………..
A) 9
B) 4
C) -9
D) 2
Answer:
D) 2

Question 160.
The diagonals of a parallelogram whose vertices are (2, 3), (4, 5), (4, 9) and (2, 7) will intersect at ………………
A) (0, 0)
B) (5, 6)
C) (0, 9)
D) (3, 6)
Answer:
B) (5, 6)
Question 161.
Slope of the line 3x – 2 = 0 is …………………
A) 2
B) 3
C) 0
D) not defined
Answer:
D) not defined
Question 162.
Each angle is equilateral triangle is ………………….
A) 100°
B) 70°
C) 60°
D) 90°
Answer:
C) 60°
Question 163.
A(cot θ, 1), B(0, 0) then BA = ………………….
A) 5
B) 4
C) 1
D) none
Answer:
D) none

Question 164.
Slope of the line joining the points A(0, 0), B(\(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\)) is ……………………
A) 4
B) 1
C) 3
D) 7
Answer:
B) 1
Question 165.
(3, 0), (8, 0), (\(\frac{1}{2}\), 0) ……………….. points lie on ………………..
A) X-axis
B) Y-axis
C) (0, 0)
D) none
Answer:
A) X-axis
Question 166.
(x, y) ∈ Q4 then ……………….
A) x = 0, y = 0
B) x < 0, y > 0
C) x > 0, y < 0
D) none
Answer:
C) x > 0, y < 0
Question 167.
y intercept of the line y = mx + c is ……………….
A) y
B) m
C) 1
D) none
Answer:
D) none

Question 168.
The midpoint of a line segment divides it in the ratio
A) 1 : 1
B) 2 : 1
C) 1 : 2
D) 1 : 4
Answer:
A) 1 : 1
Question 169.
Diagonals in a parallelogram …………………
A) equal
B) trisect
C) bisect
D) none
Answer:
C) bisect
Question 170.
The line joining the mid point of one side of a triangle from opposite vertex in called ………………….
A) ortho centre
B) median
C) centroid
D) none
Answer:
B) median
Question 171.
x intercept of the line x – y + 1 = 0 is ………………
A) 1
B) 2
C) 7
D) -1
Answer:
A) 1

Question 172.
In rhombus all sides are ……………….
A) equal
B) not equal
C) 3 cm
D) 8 cm
Answer:
A) equal
Question 173.
If the point (4, -p) lie on X-axis then p2 + 2p – 1 = ………………….
A) 0
B) 1
C) -1
D) 4
Answer:
C) -1
Question 174.
If the point (a, 5) lie on Y-axis, the value of a …………………
A) a > 0
B) a < 0
C) a = 0
D) none
Answer:
C) a = 0

Question 175.
If the distance between the points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is |x1 – x2| then they are parallel to ……………….
A) X-axis
B) XY-axis
C) XY-axis
D) Y-axis
Answer:
A) X-axis
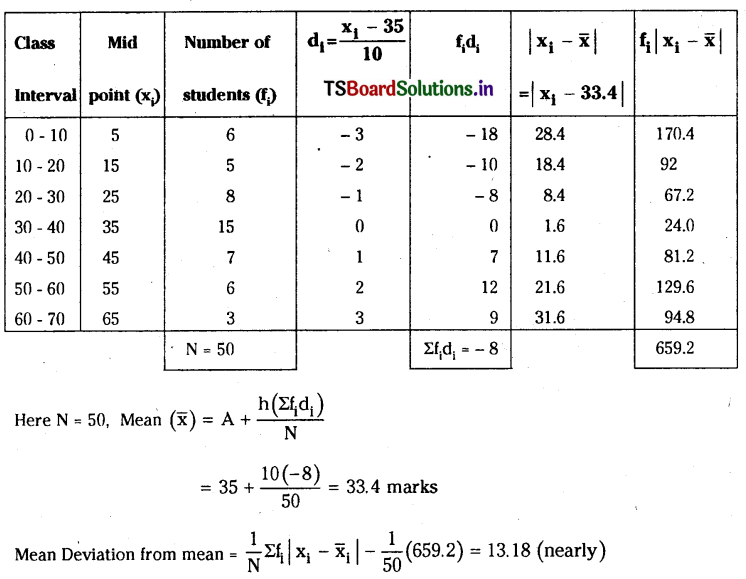
![]()
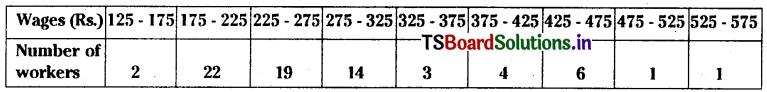
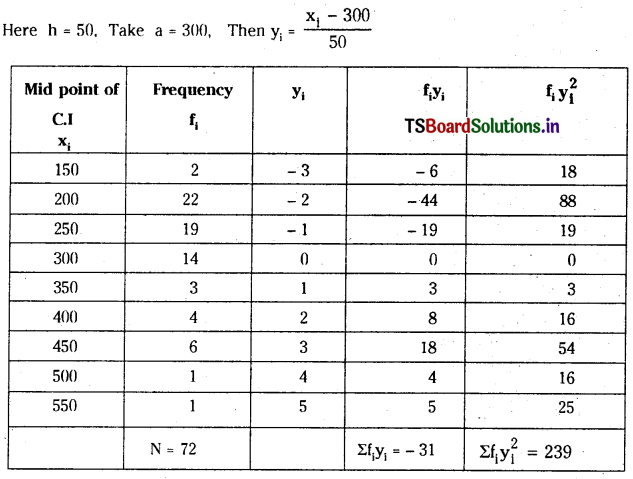
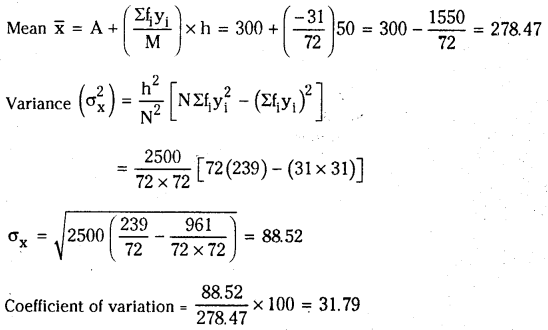
![]()
![]()

![]()



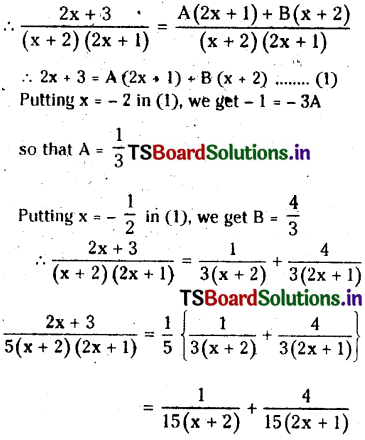
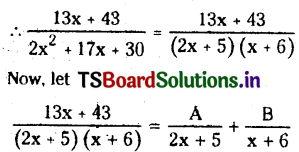
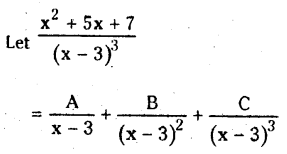
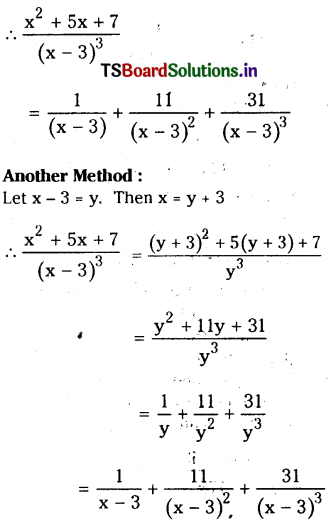

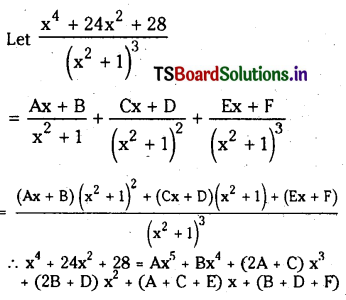
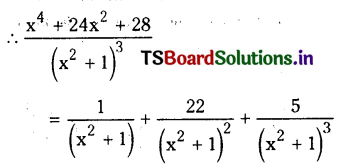
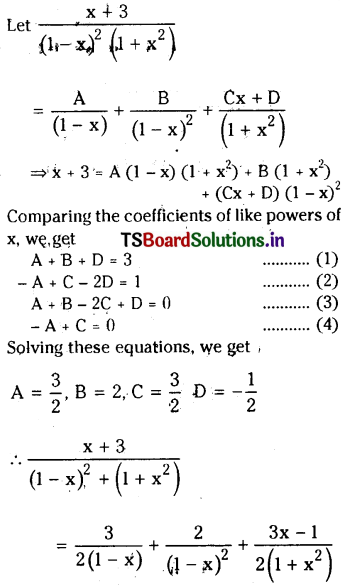
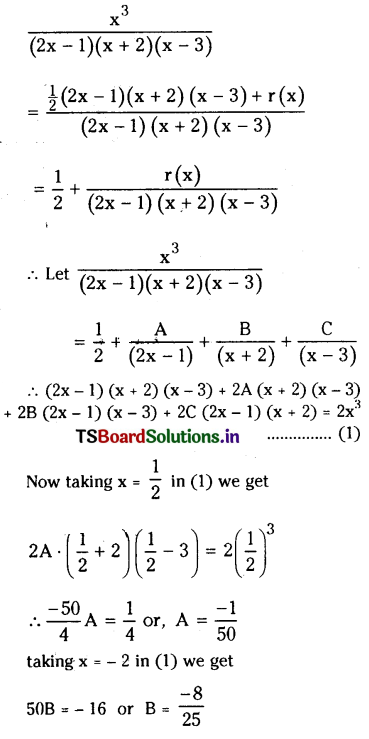
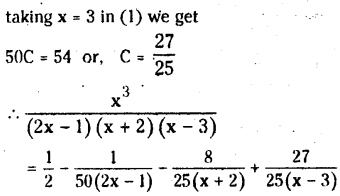
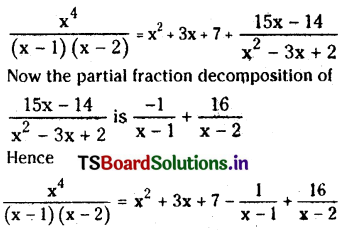
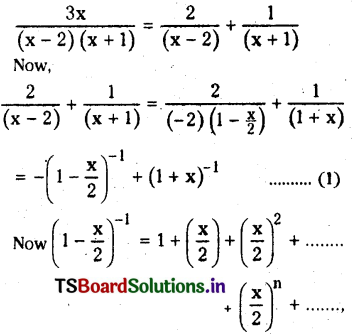

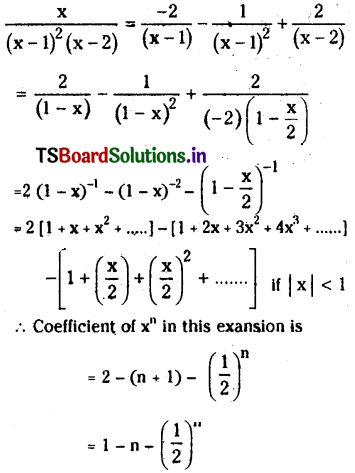
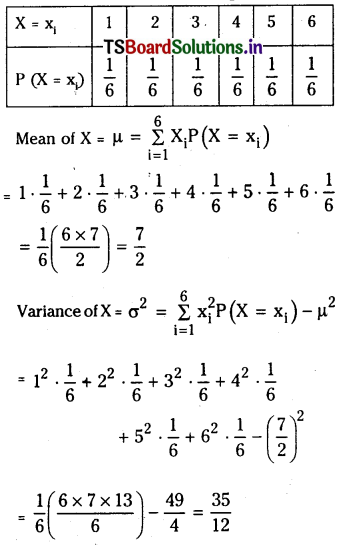
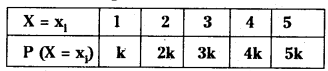
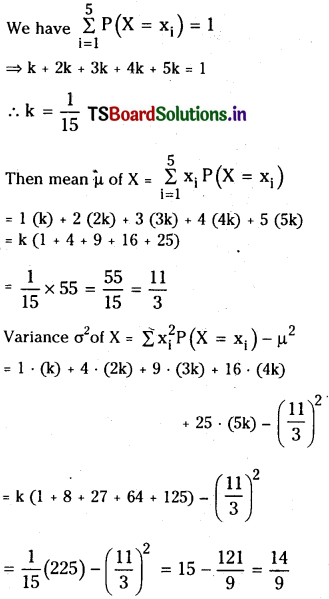
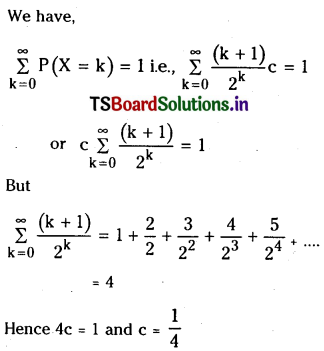
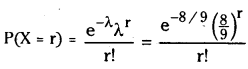
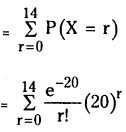
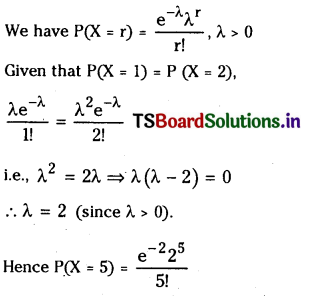



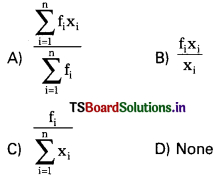


 from the equation 5?
from the equation 5?