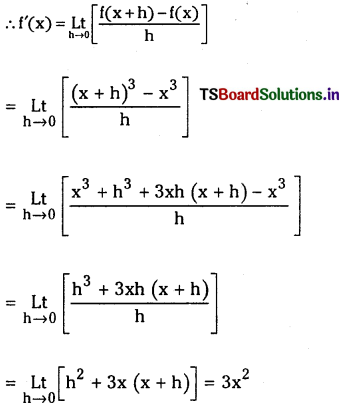
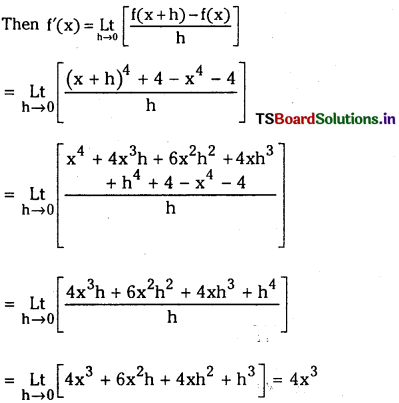
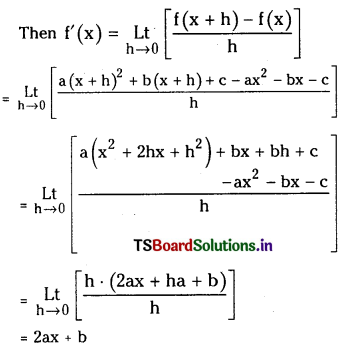
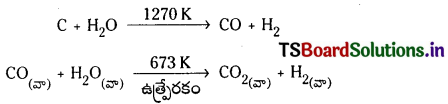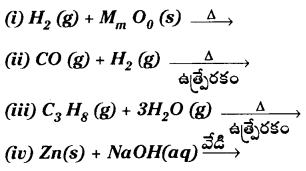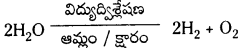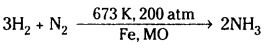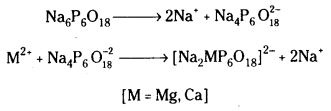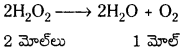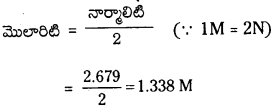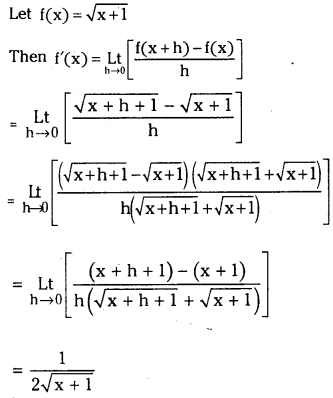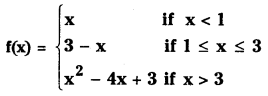Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material 8th Lesson హైడ్రోజన్ – దాని సమ్మేళనాలు Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material 8th Lesson హైడ్రోజన్ – దాని సమ్మేళనాలు
అత్యంత లఘు సమాధాన ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 1.
హైడ్రోజన్ ఐసోటోపులు మూడు వాటి చర్యావేగాల్లో భేదపడతాయి. కారణాలు తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
- హైడ్రోజన్ మూడు రకాల ఐసోటోపులు కలిగి ఉంటుంది. అవి
- ప్రోటియమ్ (1H1)
- డ్యుటీరియమ్ (2H1)
- ట్రైటియమ్ (3H1).
- ఈ మూడు ఐసోటోపులలో వరుసగా 0, 1, 2 న్యూట్రాన్లు ఉంటాయి. ట్రిటియం రేడియోధార్మికత కలిగి ఉంటుంది. ఈ హైడ్రోజన్ ఐసోటోపులు వాటి చర్యావేగాల్లో విభేదిస్తాయి. వీటి చర్యాశీలత క్రింది క్రమంలో ఉంటుంది.
H > D > T. - ఈ ఐసోటోపులు ఒకే ఎలక్ట్రాన్ విన్యాసం కలిగి ఉండటం వల్ల వాటికి సారూప్యరసాయన ధర్మాలు ఉంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 2.
అధిక ద్రవీభవన స్థానాలున్న లోహాలను వెల్డింగ్ చేయడానికి డైహైడ్రోజను ఎందుకు వాడతారు ?
జవాబు:
డ్రైహైడ్రోజన్ వియోగం చెంది పరమాణు హైడ్రోజన్ను ఇస్తుంది. ఈ పరమాణు హైడ్రోజన్ మండి 4000K ఉష్ణోగ్రతను ఇస్తుంది. కావున ఈ ఉష్ణోగ్రత జ్వాల సహాయంతో అధిక ద్రవీభవన స్థానాలున్న లోహాలను వెల్డింగ్ చేయటానికి డై హైడ్రోజను వాడతారు.

ప్రశ్న 3.
అత్యంత శుద్ధమైన డైహైడ్రోజనన్ను తయారుచేయడానికి ఒక పద్ధతిని వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
నికెల్ ఎలక్ట్రోడ్లతో వెచ్చని సజల బేరియమ్ హైడ్రాక్సైడ్ (Ba(OH)2]ను విద్యుద్విశ్లేషణ చేసి అత్యంత శుద్ధమయిన హైడ్రోజన్ ను పొందవచ్చు. ఈ ప్రక్రియలో 99.95% శుద్ధమైన H2, ఏర్పడును.
ప్రశ్న 4.
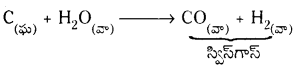
“సినా గ్యాస్” పదాన్ని వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
CO, H2 ల మిశ్రమాన్ని వాటర్ గ్యాస్ లేదా సిన్ గ్యాస్ అని అంటారు. దీనిని మిథనోల్ మరియు ఇతర హైడ్రోకార్బన్లను సంశ్లేషణం చేయటానికి వాడతారు.
తయారీ :
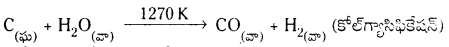
ప్రశ్న 5.
“కోల్ గాసిఫికేషన్” అంటే ఏమిటి ? దానిని సరైన తుల్య సమీకరణంతో వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
కోలన్ను ఉపయోగించి 1270K ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద నుంచి సిన్ గ్యాస్ ను తయారు చేయటాన్ని కోల్ గాసిఫికేషన్ అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 6.
హైడ్రైడ్ అంటే నిర్వచనం చెప్పండి. ఎన్ని రకాల హైడ్రేడ్లున్నాయి ? వాటి పేర్లను చెప్పండి.
జవాబు:
హైడ్రోజన్ ఇతర మూలకాలతో ఏర్పరచే ద్విగుణాత్మక సమ్మేళనాలను హైడ్రైడ్లు అంటారు. ఇవి మూడు రకాలు.
- అయానిక లేదా సెలైన్ లేదా ఆవరణ సదృశ హైడ్రైడ్లు. ఉదా || NaH, CaH2 మొ||
- కోవలెంట్ లేదా అణు హైడ్రైడ్లు. ఉదా || B2H6, CH4 మొ||వి.
- లోహ లేదా నాన్ – స్టాయికియోమెట్రిక్ హైడ్రైడ్లు. ఉదా || PdH
ప్రశ్న 7.
ద్రవీకృత ప్రావస్థలో నీటికి అసాధారణ లక్షణం ఉంటుంది. అది నీటి అధిక భాష్పీభవనోష్టానికి దారితీస్తుంది. ఆ ధర్మం ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
నీటి అణువుల మధ్య అంతరణుక హైడ్రోజన్ బంధాలు ఉండటం వలన ద్రవీకృత ప్రావస్థలో నీటికి అసాధారణ లక్షణం ఉంటుంది. దీని వలన నీటికి అధిక భాష్పీభవన స్థానం ఉంటుంది.

ప్రశ్న 8.
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరుగుతున్నప్పుడు నీరు గా ఆక్సీకరణం చెందుతుంది. అయితే ఏ మూలకం క్షయకరణం చెందుతుంది ?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియను ఈ విధంగా వ్రాస్తారు. 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
ఈ చర్యలో నీరు, O2 గా ఆక్సీకరణం చెందుతుంది. కార్బన్ క్షయకరణం చెందుతుంది. (కార్బన్ యొక్క ఆక్సీకరణ స్థితి +4 నుంచి ‘0’ కు తగ్గుతుంది.)
ప్రశ్న 9.
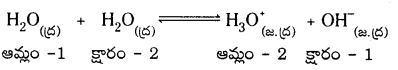
“స్వయం ప్రోటోలసిస్” అంటే మీకేమి తెలుస్తుంది ? నీటి స్వయం ప్రోటోలసిసికి సమీకరణాన్ని రాయండి.
జవాబు:
నీరు ఆమ్లంగాను, క్షారంగాను పనిచేయగల ద్విస్వభావ పదార్థంగా పనిచేస్తుంది. ఈ విధంగా నీరు స్వయం అయనీకరణం చెందే ధర్మాన్ని ‘స్వయం ప్రొటోలసిస్’ అంటారు. నీటి స్వయం ప్రొటోలసిస్ చర్యను క్రింది విధంగా వ్రాయవచ్చు.

ప్రశ్న 10.
బ్రాన్ స్టెడ్ సిద్ధాంతపరంగా నీరు ద్విస్వభావం గల పదార్థం. దానిని మీరు ఎట్లా వివరిస్తారు ?
జవాబు:
బ్రానెడ్ సిద్ధాంతం ప్రకారం ప్రోటాన్ దాత ఆమ్లంగాను, ప్రోటాన్ స్వీకర్త క్షారంగాను పనిచేస్తాయి. నీరు NH3 కు ప్రోటాను దానం చేసి ఆమ్లంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.

నీరు H2S నుంచి ప్రోటాన్ ను స్వీకరించి క్షారంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.

కావున నీరు ద్విస్వభావం గల పదార్ధం.
లఘు సమాధాన ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 11.
NH3, H2O, HF ల బాష్పీభవన స్థానాలు, ఆయా గ్రూపుల్లో వాటి తరవాత మూలకాల హైడ్రైడ్ల బాష్పీభవన స్థానాలకంటే ఎక్కువగా ఉంటాయి. మీ కారణాలు చెప్పండి.
జవాబు:
NH3, H2O, HF ల బాష్పీభవన స్థానాలు, అయా గ్రూపుల్లో వాటి తరువాత మూలకాల హైడ్రైడ్ల బాష్పీభవన స్థానాలకంటే ఎక్కువగా ఉంటాయి. కారణం,
- NH3, H2O, HF లలో హైడ్రోజన్ అధిక ఋణ విద్యుదాత్మకత గల N, O, F లతో బంధించబడి ఉంటుంది.
- అందువలన ఈ హైడ్రేడ్లలో హైడ్రోజన్ బంధాలు ఏర్పడతాయి.
- ఈ హైడ్రోజన్ బంధాలు ఏర్పడుట వలన ఈ హైడ్రైడ్లకు అధిక భాష్పీభవన స్థానాలుంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 12.
ఆవర్తన పట్టికలో హైడ్రోజన్ స్థానాన్ని దాని ఎలక్ట్రాన్ విన్యాసపరంగా చర్చించండి.
జవాబు:
ఆవర్తన పట్టికలో హైడ్రోజన్ యొక్క స్థానం చర్చనీయాంశం. హైడ్రోజన్ IA గ్రూపులోని క్షార లోహాలతోను, VIIA గ్రూపులోని హాలోజన్లతోను పోలికలు కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
హైడ్రోజన్ను IA గ్రూపు మూలకాలతో చేర్చుటకు కారణాలు
- హైడ్రోజన్ యొక్క ఎలక్ట్రాన్ విన్యాసం (1s1) క్షార లోహాల బాహ్య ఎలక్ట్రాన్ విన్యాసంను (ns1) పోలి ఉంటుంది.
- క్షార లోహలవలె హైడ్రోజన్ ఒక ఎలక్ట్రాన్ను పోగొట్టుకొని ఏకమాత్ర ధనావేశిత అయాన్ ను ఏర్పచగలదు. (H+)
హైడ్రోజన్ ను VII A గ్రూపు మూలకాలతో చేర్చుటకు కారణాలు :
- హైడ్రోజన్ హాలోజన్లవలె ద్విపరమాణుక అణువులను ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
- హైడ్రోజన్ హాలోజన్లవలె ఒక ఎలక్ట్రాన్ను పొంది ఏకమాత్ర ఋణావేశిత అయాన్లను ఏర్పరుస్తుంది. (H–) హైడ్రోజన్ యొక్క స్థానాన్ని దాని ఎలక్ట్రాన్ విన్యాసాన్ని 1s1 మాత్రమే పరిగణలోనికి తీసికుని 1A గ్రూపు మూలకాలతో కలిపారు.

ప్రశ్న 13.
హైడ్రోజన్ ఎలక్ట్రాన్ విన్యాసం దాని రసాయన ధర్మాలకు ఎట్లా అనువుగా ఉంటుంది ?
జవాబు:
హైడ్రోజన్ యొక్క ఎలక్ట్రాన్ విన్యాసం 1s1. కావున
- హైడ్రోజన్ ఒక ఎలక్ట్రాను కోల్పోయి చర్యలలో పాల్గొని H+ ను ఏర్పరచును.
ఉదా : HF + H2O → H3O+ + F– - హైడ్రోజన్ ఒక ఎలక్ట్రాను గ్రహించి చర్యలలో పాల్గొని HP ను ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
ఉదా : 2Na + H2 → 2NaH [Na+ H–] - హైడ్రోజన్ ఒక ఎలక్ట్రాను పంచుకొని సమయోజనీయ బంధాలను ఏర్పరచును.
ఉదా : H : Cl.
ప్రశ్న 14.
(a) క్లోరిన్ (b) సోడియం లోహంతో డైహైడ్రోజన్ చర్య జరిపితే ఏమవుతుంది ? వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
a) క్లోరిన్తో డైహైడ్రోజన్ చర్య : డై హైడ్రోజన్ క్లోరిన్తో చర్య జరిపి హైడ్రోజన్ క్లోరైడ్ను ఏర్పరచును.
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCI.
b) డై హైడ్రోజన్ Na లోహంతో చర్య : డై హైడ్రోజన్ Na లోహంతో చర్య జరిపి సోడియం హైడ్రైడన్ను ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
2Na + H2 → 2NaH
ప్రశ్న 15.
భారజలం పై ఒక వ్యాఖ్యను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
డ్యుటీరియం ఆక్సైడ్ (D2O) ను భారజలం అంటారు. \(\frac{\mathrm{N}}{2}\) NaOH ద్రావణంతో క్షారయుతం చేసిన నీటిని ఎక్కువ కాలం పాటు విద్యుద్విశ్లేషణ జరిపి భారజలాన్ని తయారుచేస్తారు.
(1) న్యూక్లియర్ రియాక్టర్లలో మోడరేటర్గాను,
(2) చర్యా విధానాల అధ్యయనంలో వినిమయ కారకంగాను భారజలాన్ని ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
ఇతర డ్యుటీరియమ్ సమ్మేళనాలను తయారుచేయటానికి D2O ను ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
CaC2 + 2D2O → C2D2 + Ca(OD)2
SO3 + D2O → D2SO4
Al4 C3 + 12D2O → 3 CD4 + 4 Al(OD)3
ఈ చర్యలను డ్యుటిరాలసిస్ చర్యలు అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 16.
హైడ్రోజన్ ఐసోటోపుల పేర్లను తెలపండి. ఈ ఐసోటోపుల ద్రవ్యరాశుల నిష్పత్తి ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
హైడ్రోజన్కు మూడు ఐసోటోపులున్నాయి.
- హైడ్రోజన్ \({ }_1^1 \mathrm{H}\)
- డ్యుటీరియమ్ \({ }_1^2 \mathrm{H}\) లేదా \({ }_1^2 \mathrm{D}\)
- ట్రైటియమ్ \({ }_1^3 \mathrm{H}\) లేదా \({ }_1^3 \mathrm{~T}\)
ఈ ఐసోటోపుల ద్రవ్యరాశుల నిష్పత్తి
H : D : T = 1 : 2 : 3
ప్రశ్న 17.
“వాటర్ గ్యాస్ షిఫ్ట్” చర్య అంటే ఏమిటి ? ఈ చర్యతో హైడ్రోజన్ తయారీని ఎట్లా పెంచగలరు ?
జవాబు:
CO, H2 ల మిశ్రమాన్ని వాటర్గా గ్యాస్ లేదా సిన్ గ్యాస్ అంటారు.
వాటర్గాస్ షిప్ట్ చర్య : H2 యొక్క ఉత్పత్తి పెంచటానికి సిన్గ్యాస్ మిశ్రమంలోని కార్బన్ మోనాక్సైడ్ను ఐరన్ క్రోమోట్ ఉత్ప్రేరకం సమక్షంలో నీటి ఆవిరితో చర్యనొందిస్తారు. ఈ చర్యను “వాటర్ గ్యాస్ షిఫ్ట్ చర్య” అంటారు.
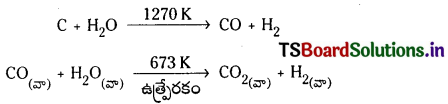
సోడియం ఆర్మినైట్ ద్రావణంలో మార్జనం చేసి CO2 ను తొలగించవచ్చు.

ప్రశ్న 18.
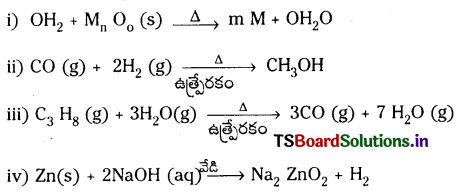
కింది చర్యలను పూర్తిచేసి, తుల్యం చేయండి.
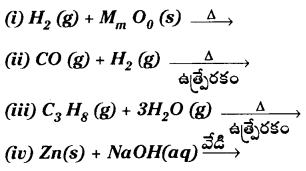
జవాబు:
ప్రశ్న 19.
13వ గ్రూపు మూలకాలు ఏర్పరచే హైడ్రైడ్ల స్వభావం ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
13వ గ్రూపు మూలకాలు p – బ్లాకు చెందుతాయి. ఇవి కోవలెంట్ హైడ్రైడ్లను ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. ఈ హైడ్రైడ్లు మూడు రకాలు
- ఎలక్ట్రాన్ న్యూనతగల సమ్మేళనాలు.
- ఎలక్ట్రాన్ ఖచ్చిత హైడ్రైడ్లు
- ఎలక్ట్రాన్ అధిక హైడ్రైడ్లు. ఇవి లూయీ ఆమ్లాలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి. ఉదా : B2H6
బోరాన్ ఏర్పరచే హైడ్రైడ్లను బోరేన్లు అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 20.
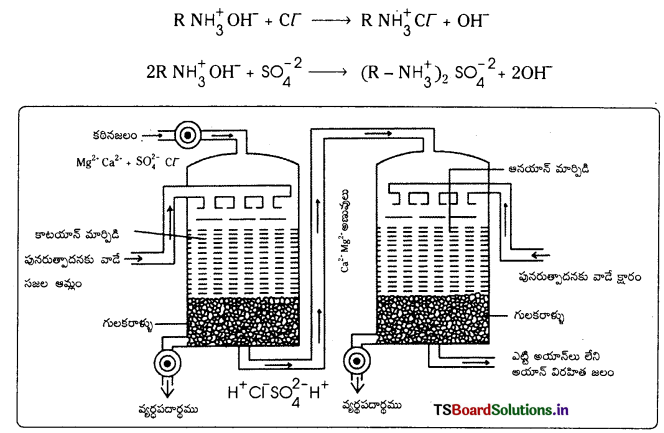
సంశ్లేషిత రెజిన్ పద్ధతి, అయాన్ వినిమయ రెజిన్ పద్ధతుల్లో జలకాఠిన్యతను తొలగించడానికి ఉపయోగించే సూత్రాన్ని, పద్ధతిని చర్చించండి.
జవాబు:
i) సంశ్లేషిత రెజిన్ల పద్దతి : ఈ పద్దతిలో అయాన్లను తొలగించడం రెండు రకాలుగా జరుగుతుంది. అన్ని రకాల లవణాలు తొలగించబడిన నీటిని అయాన్ విరహిత జలం అంటారు.
1. కాటయాను తొలగించుట : కాటయాన్ వినిమయ రెజిన్ ను కలిగి ఉన్న ట్యాంక్ గుండా కఠినజలాన్ని పంపుతారు. అపుడు Ca+2 మరియు Mg+2 అయాన్లు H+ అయాన్లతో స్థానభ్రంశం చెందించబడతాయి.
2RCOOH + Ca+2 → (R COO)2 + 2H+
2. ఆనయాన్లను తొలగించుట : ఆ తర్వాత నీటిని ఆనయాన్ వినిమయ రెజిన్ ట్యాంక్ ద్వారా పంపుతారు. అపుడు నీటిలోని ఆనయాన్లు రెజిన్లోని OH– అయాన్లతో స్థానభ్రంశం చెందించబడతాయి.
H+ మరియు OH– అయాన్లు ఏకమై అయాన్ విరహిత జలాన్ని ఏర్పరుస్తాయి.
కొంత కాలానికి రెజిన్లు తమ వినిమయ సామర్థ్యాన్ని కోల్పోతాయి. అందువలన వాటిని మరల ఉద్ధరించాలి. `కాటయాన్ రెజిన్ గుండా విలీన H2SO4 ప్రసరింపచేయడం ద్వారా పునరుద్ధరిస్తారు. ఆనయాన్ రెజిన్ గుండా కాస్టిక్ సోడా ప్రసరింపచేయడం ద్వారా పునరుద్ధరిస్తారు.
ii) అయాన్ వినిమయ పద్ధతి: ఈ పద్ధతిని జియొలైట్ లేదా పెరుటిట్ ప్రక్రియ అని కూడా అంటారు. ఆర్థ సోడియమ్ అల్యూమినియమ్ సిలికేట్ (Na A/SiO4) ను జియొలైట్ లేదా పెరుటిట్ అంటారు. దీనిని కఠిన జలానికి కలిపినపుడు వినిమయ చర్యలు జరుగుతాయి.
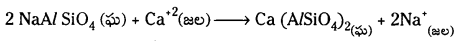
జియొలైట్లో ఉన్న సోడియమ్ అంతా ఖర్చు అయిపోయినపుడు అది వ్యయమైపోయింది అని అంటారు. దాన్ని సజల NaCl ద్రావణంతో అభిచర్యని జరిపి పునరుత్పత్తి చేస్తారు.
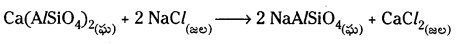
ప్రశ్న 21.
ఇంధనంగా హైడ్రోజన్ ఉపయోగాన్ని గురించి కొన్ని వాక్యాలు రాయండి. (March 2013)
జవాబు:
హైడ్రోజన్ అధిక మండు ఉష్ణోగ్రతలను కలిగి ఉంటుంది. అందువలననే, దీనిని పారిశ్రామిక ఇంధనంగా విరివిగా ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
- ఆక్సీ హైడ్రోజన్ బ్లోటార్చ్ : పరిశుద్ధ H2 మరియు O2 వాయువుల మిశ్రమాన్ని అత్యధిక ఉష్ణోగ్రత (3000°C సుమారుగా) వద్ద మండిస్తే ఆక్సీ హైడ్రోజన్ బ్లోటార్చ్ ఏర్పడుతుంది. ఈ జ్యాలను వెల్డింగ్ మరియు కరిగించే ప్రక్రియలలో ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
- వాటర్ గ్యాస్ : CO మరియు H2 ల మిశ్రమాన్ని వాటర్ గ్యాస్ అంటారు. వేడిగా ఉన్న ఎర్రని కోక్ మీదుగా నీటి ఆవిరిని పంపి దీనిని తయారుచేస్తారు. దీనిని పారిశ్రామిక ఇంధనంగా వాడతారు.
- సెమివాటర్ గ్యాస్ : హైడ్రోజన్, కార్బన్ మోనాక్సైడ్, కార్బన్ డై ఆక్స్డ్, నైట్రోజన్ మరియు మిథేన్ల మిశ్రమాన్ని సెమివాటర్ గ్యాస్ అంటారు. స్టీల్ పరిశ్రమలలో దీనిని ఇంధనంగా ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
- హైడ్రోజన్ ను, ఇంధన ఘటాలలో విద్యుత్ శక్తిని ఉత్పత్తి చేయుటకు ఉపయోగిస్తారు.

ప్రశ్న 22.
1% H2O2 ద్రావణాన్ని మీకు ఇచ్చాం. దాని నుంచి శుద్ధ H2O2 ని తయారుచేయడానికి మీరు ఏమి చర్యలను తీసుకుంటారు ?
జవాబు:
ఇవ్వబడిన 1% H2O2 నుండి శుద్ధ H2O2 ను క్రింది విధంగా పొందవచ్చు.
- 1% H2O2 ద్రావణాన్ని మొదట నీటితో నిష్కర్షించి. దానిని తగ్గించిన పీడనం వద్ద స్వేదనానికి గురిచేస్తారు. అప్పుడు H2O2 ఏర్పడుతుంది.
- 30% గాఢత గల H2O2 ద్రావణాన్ని అల్ప పీడనాల వద్ద జాగ్రత్తగా స్వేదనం చేస్తే గాఢత ఇంకా పెరిగి 85% అవుతుంది.
- పై దశలోని H2O2 ను ఘనీభవనంచేస్తే శుద్ధ H2O2 ఏర్పడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 23.
ఆధునిక కాలంలో H2O2 వలన కలిగే ఏవైనా మూడు ఉపయోగాలను చెప్పండి.
జవాబు:
- గృహ పారిశ్రామిక వ్యర్థ పదార్థాల కాలుష్య నివారణ అభిచర్యలో వాడతారు.
- సయనైడ్ల ఆక్సీకరణలో వాడతారు.
- మురుగు కాల్వల వ్యర్థాలకు ఏరోబిక్ స్థితులను పునర్వవస్థీకరించడానికి దీనిని వాడతారు.
దీర్ఘ సమాధాన ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 24.
వ్యాపార సరళిలో డైహైడ్రోజనిని తయారుచేయడంపై ఒక వ్యాసం రాయండి. తుల్య సమీకరణాలను ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
వ్యాపార సరళిలో డైహైడ్రోజన్ ను ఈ క్రింది పద్ధతులలో తయారు చేస్తారు.
i) ప్లాటినమ్ ఎలక్ట్రోడ్లను ఉపయోగించి ఆమ్లీకృత లేదా క్షారయుత జలాన్ని విద్యుద్విశ్లేషణ చేస్తే డై హైడ్రోజన్ ఏర్పడుతుంది.
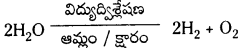
ii) నెల్సన్ పద్దతిలో బ్రైన్ ద్రావణాన్ని విద్యుత్ విశ్లేషణ చేసి డై హైడ్రోజన్ ను తయారు చేస్తారు.
Nacl → Na+ + Cl–
H2O → H+ + OH–
ఆనోడ్ వద్ద 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
కాథోడ్ వద్ద 2H+ + 2e– → H2
2Na+ + 20H– → 2NaOH
iii) ఉత్ప్రేరకం సమక్షంలో, అధిక ఉష్ణోగ్రతల వద్ద హైడ్రోకార్బన్ల పై నీటి ఆవిరి చర్య ఫలితంగా డై హైడ్రోజన్
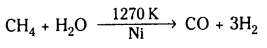
iv)ఎర్రగా కాల్చిన కోక్ మీదుగా నీటి ఆవిరిని పంపినపుడు డై హైడ్రోజన్ ఏర్పడుతుంది.

CO, H2 మిశ్రమాన్ని సిన్గ్యాస్ అంటారు. దీనిలోని CO ను ఐరన్ క్రోమేట్ ఉత్ప్రేరకం సమక్షంలో నీటి ఆవిరితో చర్యనొందించి H2 ను అధికంగా ఉత్పత్తి చేస్తారు. దీనినే వాటర్ గ్యాస్ షిఫ్ట్ చర్య అంటారు.
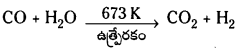
సోడియం ఆర్శినైట్ ద్రావణంతో మార్జనం చేసి CO2 ను తొలగిస్తారు.
ప్రశ్న 25.
i) N2
ii) లోహ అయాన్లు, లోహ ఆక్సైడ్లు
iii) కర్బన సమ్మేళనాలు.
వీటితో చర్యలను బట్టి డైహైడ్రోజన్ రసాయనశాస్త్రాన్ని వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
i) నైట్రోజన్ చర్య: నైట్రోజన్ హైడ్రోజన్ చర్య జరిపి అమ్మోనియాను ఇస్తుంది.
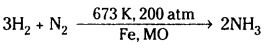
అమ్మోనియాను భారీగా తయారుచేయటానికి హాబర్ విధానంలో ఈ చర్యనే వాడతారు.
ii) a) లోహ అయాన్లతో చర్య : హైడ్రోజన్, లోహ అయానులను జల ద్రావణంలో లోహాలుగా క్షయకరణం చెందించును.

b) లోహ ఆక్సైడ్లతో చర్య : హైడ్రోజన్ లోహ ఆక్సైడ్ ను లోహాలుగా క్షయకరణం చెందించును.
H2 + CuO → Cu + H2O
iii) కర్బన సమ్మేళనాలతో చర్య ఉత్ప్రేరకాల సమక్షంలో హైడ్రోజన్ వివిధ రకాల కర్బన సమ్మేళనాలతో చర్య
జరుపుతుంది.
a) వృక్షజనితమయిన నూనెలను నికెల్ ఉత్ప్రేరక సమక్షంలో హైడ్రోజనీకరణం చేస్తే తినే కొవ్వును ఇస్తుంది.
b) ఓలిఫిన్లతో హైడ్రో ఫార్మైలేషన్ జరిపితే ఆల్డిహైడ్లు వస్తాయి. అవి మళ్ళీ క్షయకరణం చెంది ఆల్కహల్లను ఇస్తాయి.
H2C = CH2 + CO + H2 → CH3 CH2 CHO
CH3 CH2 CHO + H2 → CH3 CH2 CH2 OH
ప్రశ్న 26.
కింది వాటిని సరైన ఉదాహరణలతో వివరించండి.
i) ఎలక్ట్రాన్ కొరత గల హైడ్రైడ్లు
ii) ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు కచ్చితంగా ఉన్న హైడ్రైడ్లు
iii) ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు అధికంగాగల హైడ్రైడ్లు
జవాబు:
i) ఎలక్ట్రాన్ కొరత గల హైడ్రైడ్లు : 13వ గ్రూపు మూలకాలన్ని ఎలక్ట్రాన్ కొరత గల హైడ్రైడ్లను ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. లూయీ నిర్మాణాన్ని సాంప్రదాయ పద్దతిలో రాయటానికి కావలసిన ఎలక్ట్రాన్ల కన్నా తక్కువ ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు ఉంటాయి. ఇవి లూయీ ఆమ్లాలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి. ఉదా : B2H6
ii) ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు కచ్చితంగా ఉన్న హైడ్రైడ్లు: 14వ గ్రూపు మూలకాలు ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు కచ్చితంగా ఉన్న హైడ్రైడ్లను ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. లూయీ నిర్మాణాన్ని సాంప్రదాయక పద్ధతిలో రాయటానికి కావలసిన ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు ఉంటాయి.
ఉదా : CH4, SiH4
iii) ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు అధికంగా గల హైడ్రైడ్లు: 15 – 17 గ్రూపు మూలకాలు ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు అధికంగాగల హైడ్రైడ్లను ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. లూయీ నిర్మాణాన్ని సాంప్రదాయక పద్దతిలో రాయటానికి కావలసిన ఎలక్ట్రాన్ల కన్నా ఎక్కువ ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు ఉంటాయి. ఎక్కువయిన ఈ ఎలక్ట్రాన్లు ఒంటరి జంటలుగా ఉంటాయి. ఇవి లూయీ క్షారాలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి.
ఉదా : NH3, H2O
ప్రశ్న 27.
i) అయానిక హైడ్రైడ్లు
ii) అల్పాంతరాళ హైడ్రైడ్ల గూర్చి క్లుప్తంగా రాయండి.
జవాబు:
i) అయానిక హైడ్రైడ్లు లేదా సెలైన్ హైడ్రైడ్లు :
– అధిక ధన విద్యుదాత్మకత కల s – బ్లాక్ మూలకాలు అయానిక హైడ్రేడ్లను ఏర్పరుస్తాయి.
– LiH, BeHz, MgH, వంటి హైడ్రైడ్లలో కొంత సమయోజనీయ లక్షణం కనిపిస్తుంది.
– తయారీ : లోహాన్ని నేరుగా H2 తో సంయోగం ద్వారా వీటిని పొందవచ్చు.
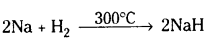
– ఘన స్థితిలో అయానిక హైడ్రైడ్లు స్పటిక, అభాష్పశీల, అవాహక పదార్థాలు. అయినా వీటి ద్రవాలు విద్యుత్ వాహకాలు. వాటి విద్యుత్ విశ్లేషణలో ఆనోడ్ వద్ద హైడ్రోజన్ వాయువు ఏర్పడుతుంది. దీనిని బట్టి H– అయాన్ ఉంటుందని నిర్ధారణ అవుతుంది.
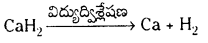
– సెలైన్ హైడ్రైడ్లు నీటితో చర్య జరిపి H2 వాయువును ఇస్తాయి.
NaH + H2O → NaOH + H2
ii) అల్పాంతరాళ హైడ్రైడ్లు: d – బ్లాకు, f బ్లాకు మూలకాలు హైడ్రోజన్తో సంయోగం చెంది అల్పాంతర లేదా నాన్-స్టాయికియోమెట్రిక్ హైడ్రైడ్లను ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. ఉదా : CrH, CrH2, ZnH2
అయితే 7, 8, 9 గ్రూపు లోహలు హైడ్రైడ్లను ఇవ్వవు. ఇవి నాన్-స్టాయికియోమెట్రిక్ సమ్మేళనాలు.
ఇంతకు ముందు కాలంలో, ఈ హైడ్రైడ్లలోని హైడ్రోజన్ లోహ జాలకంలోని అల్పాంతరాళాల్లో ఆక్రమించుకొని, జాలక రకంలో మార్పు లేకుండా దానిని వికృతి చెందిస్తుందని భావించారు. అయితే ఇటీవల అధ్యయనాలు Ni, Pd, Ce, AC హైడ్రైడ్లు మినహా మిగిలిన ఈ తరగతి హైడ్రైడ్లన్నింటి జాలకాలు వాటి మాతృ లోహల జాలకాల కంటే భిన్నంగా ఉంటాయని చూపాయి.
pd, pt వంటి లోహాలు చాలా ఎక్కువ ఘనపరిమాణంలో హైడ్రోజనన్ను తమలో ఇముడ్చుకోగలవు. అందుకని హైడ్రోజనన్ను నిల్వచేసే మాధ్యమాలుగా వాటిని ఉపయోగిస్తారు.

ప్రశ్న 28.
నీటి రసాయన ధర్మాలను ఏ నాలుగింటినైనా విశదీకరించండి.
జవాబు:
i) ద్విస్వభావ ప్రవృత్తి : నీరు ఆమ్లంగాను, క్షారంగాను పనిచేయగల సామర్థ్యాన్ని చూపుతుంది. అంటే ద్విస్వభావ పదార్థంగా పనిచేస్తుంది. బ్రాన్టెడ్ సిద్ధాంతపరంగా అది NH3 తో ఆమ్లంగా పనిచేస్తుంది. H2S తో నీరు క్షారంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
H2O + NH3 ⇌ OH– + \(\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}\)
H2O + H2S ⇌ H3O+ + HS–
ii) లోహలతో చర్య : అధిక ధనవిద్యుదాత్మకత గల లోహాలు నీటిని క్షయీకరించి డై హైడ్రోజన్గా మార్చగలవు.
2H2O + 2Na → 2NaOH + H2
iii) జలవిశ్లేషణ చర్య : కొన్ని సమయోజనీయ పదార్థాలు, కొన్ని అయానిక పదార్థాలు నీటిలో జలవిశ్లేషణ చెందుతాయి.
P4O10 + 6H2O → 4 H3PO4
SiCl4 + 2H2O → SiO2 + 4HCl
iv) ఆర్ద్ర లవణాలు ఏర్పడడం : జల ద్రావణాల నుంచి చాలా లవణాలు ఆర్ధ లవణాలుగా స్ఫటికీకరణం చెందగలవు.
a) సమన్వయ సమయోజనీయ జలం : ఉదా : [Cr(H2O)6]3+ 3Cl–
b) అల్పాంతరాళ జలం : ఉదా : BaCl2. 2H2O
c) హైడ్రోజన్ బంధిత జలం : ఉదా : [Cu (H2O)4]2+ \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\) . H2O ఇది CuSO4 . 5H2O లో ఉంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 29.
కఠినజలం, మృదుజలం అంటే వివరించండి.
i) `అయాన్ – వినిమయ పద్ధతి
ii) కాల్గన్ పద్ధతులను నీటి కఠినత్వాన్ని తొలగించడానికి వాడకంపై వ్యాఖ్యను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
కఠిన జలం : సబ్బుతో త్వరగా నురుగును ఇవ్వని నీటిని కఠిన జలం అంటారు.
- నీటిలో Ca మరియు Mg లవణాల వలన కఠినత్వం వస్తుంది.
- Ca, Mg బై కార్బోనేట్ల వల్ల అశాశ్వత కాఠిన్యత వస్తుంది.
- Ca, Mg క్లోరైడ్ లు, సల్ఫేట్ల వల్ల శాశ్వత కాఠిన్యత వస్తుంది.
మృదుజలం : సబ్బుతో త్వరగా నురుగును ఏర్పరచే నీటిని మృదుజలం అంటారు.
i) అయాన్ – వినిమయ పద్ధతి : ఈ పద్ధతిని జియొలైట్ లేదా పెరుటిట్ ప్రక్రియ అని కూడా అంటారు. ఆర్థ సోడియమ్ అల్యూమినియమ్ సిలికేట్ (Na AlSiO4) ను జియొలైట్ లేదా పెరుటిట్ అంటారు. దీనిని కఠిన జలానికి కలిపినపుడు వినిమయ చర్యలు జరుగుతాయి.
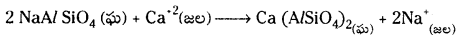
జియొలైట్లో ఉన్న సోడియమ్ అంతా ఖర్చు అయిపోయినపుడు అది వ్యయమైపోయింది అని అంటారు. దాన్ని సజల NaCl ద్రావణంతో అభిచర్యని జరిపి పునరుత్పత్తి చేస్తారు.
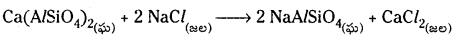
ii) కాల్గన్ పద్ధతి : సోడియమ్ హెక్సా మెటాఫాస్ఫేట్ (Na6P6O18) ని వ్యాపార సరళిలో కాల్గన్ అంటారు. దీనిని కఠిన జలానికి కలిపినపుడు కింది చర్యలు జరుగుతాయి.
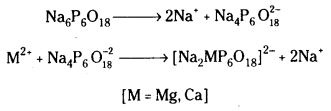
సంక్లిష్ట Mg+2, Ca+2 అయాన్లు ద్రావణంలో ఉంటాయి. ఇవి సబ్బుతో చర్య నొందవు. కావున ఈ నీరు సబ్బుతో నురగను ఇస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 30.
హైడ్రోజన్ పెరాక్సైడ్ ఆక్సీకరణిగాను, క్షయకరణిగాను పనిచేయగలదు అనడానికి రసాయన చర్యలను రాసి సమర్ధించండి.
జవాబు:
ఆమ్ల, క్షార యానకాలు రెండింటిలోను హైడ్రోజన్ పెరాక్సైడ్ ఆక్సీకరణిగాను, క్షయకరణిగాను పనిచేస్తుంది.
i) ఆమ్ల యానకంలో ఆక్సీకరణ చర్య :
2Fe+2 + 2H+ + H2O → 2Fe+3 + 2H2O
Pbs + 4H2O2 → PbSO4 + 4H2O
ii) ఆమ్ల యానకంలో క్షయకరణ చర్య :
2 Mn\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) + 6H+ + 5H2O2 → 2Mn+2 + 8H2O + O2
HOCl + H2O2 → H3O+ + O2
iii) క్షార యానకంలో ఆక్సీకరణ చర్య :
2Fe+2 + H2O2 → 2Fe+3 + 2OH–
Mn+2 + H2O2 → Mn+4 + 2OH–
iv) క్షార యానకంలో క్షయకరణ చర్య :
I2 + H2O2 + 2OH– → 2I– + 2H2O + O2
2 Mn\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) + 3H2O2 → 2MnO2 + 3O2 + 2H2O + 20H–
ప్రశ్న 31.
క్రింది రసాయన చర్యలను పూర్తి చేసి తుల్యం చేయండి.
i) Pbs (ఘ) + H2O2 (జల) →
ii) Mn\(O_4^{-}\) (జల) + H2O2 (జల) →
iii) CaO (ఘ) + H2O (వా) →
iv) Ca3N2 (ఘ) + H2O (ద్ర) →
పై చర్యలను
a) జలవిశ్లేషణ,
b) ఆక్సీకరణ-క్షయకరణ,
c) హైడ్రేషన్ చర్యలుగా వర్గీకరించండి.
జవాబు:
- Pbs + 4H2O2 → PbSO4 + 4H2O
ఈ చర్య రిడాక్స్ చర్య Pbs ఆక్సీకరణం చెందుతుంది. H2O2 క్షయకరణం చెందుతుంది. - 2 Mn\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) + 6H+ + 5H2O2 → 2Mn+2 + 8H2O + 5O2
ఈ చర్య రిడాక్స్ చర్య. Mn\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) క్షయకరణం చెందుతుంది. H2O2 ఆక్సీకరణం చెందుతుంది. - CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
ఈ చర్య హైడ్రేషన్ చర్య - Ca3N2 + H2O → 3 Ca(OH)2 + 2NH3
ఈ చర్య జలవిశ్లేషణ చర్య.

ప్రశ్న 32.
హైడ్రోజన్ పెరాక్సైడిని తయారుచేయడానికి వివిధ పద్ధతులను వాటికి అనువైన రసాయన సమీకరణాలతో చర్చించండి. వీటిలో ఏ పద్ధతి H2O2 ని తయారుచేయడానికి ఉపయోగపడుతుంది ?
జవాబు:
- బెరీయం పెరాక్సైడు చల్లని విలీన H2SO4 ను కలపడం ద్వారా H2O2 ను తయారుచేయవచ్చు.
BaO2. 8H2O (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 + H2O2 (aq) 8H2O - 50% H2SO4 ద్రావణాన్ని విద్యుద్విశ్లేషణ చేయడం ద్వారా పెరాక్సో డై సల్ఫ్యూరిక్ ఆమ్లాన్ని తయారుచేస్తారు. దీనిని జలవిశ్లేషణ చేస్తే H2O2 ఏర్పడుతుంది.
2HS\(\mathrm{O}_4^{-}\) → H2 S2 O8 + 2e–
H2S2O8 + 2H2O → 2H2SO4 + H2O2 - పారిశ్రామికంగా H2O2 ను 2 – ఆల్మెన్ ఆంత్రా క్వినోల్ను స్వయం ఆక్సీకరణం చేసి తయారుచేస్తారు.
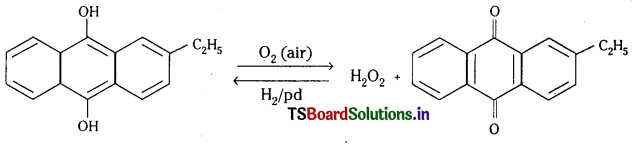
ప్రశ్న 33.
H2O2 గాఢతని ఎన్ని రకాలుగా మీరు చెప్పగలరు ? 15 ఘనపరిమాణ H2O2 గాఢతని gL-1 లలో లెక్కగట్టండి. ఈ గాఢతను నార్మాలిటీ, మొలారిటీలలో తెలియజేయండి.
జవాబు:
i) H2O2 ద్రావణ గాఢతను ఘనపరిమాణాలలో సూచిస్తారు.
ఉదా : 10 ఘ.ప H2O2, 20 ఘ.ప H2O2 మరియు 100 ఘ.ప H2O2
20 ఘ.ప H2O2 అనగా 1 మి.లీ ద్రావణం STP వద్ద 20 మి.లీ. O2 ను విడుదలచేస్తుంది.
∵ 10 మి.లీ 20 ఘ.ప H2O2 STP వద్ద 200 మి.లీ. O2 విడుదల చేస్తుంది.
10 ఘ.ప H2O2 ద్రావణం అనగా 1 మి.లీ. ద్రావణం STP వద్ద 10 మి.లీ. O2 వాయువును విడుదలచేస్తుంది.
ii) H2O2 గాఢతను భారశాతంలో చెప్పడం : H2O2 ఈ క్రింది విధంగా విఘటనం చెందుతుంది.
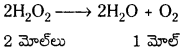
2 మోల్ల H2O2 నుండి 1 మోల్ O2 వాయువు వెలువడుతుంది. ∴ 2 × 34 గ్రా. H2O2 నుండి 22.4 లీ O2 వెలువడుతుంది.
STP వద్ద 10 లీ O2 వాయువును ఇచ్చే H2O2 భారం
1 లీ|| ద్రావణంలో H2O2 భారం = \(\frac{2 \times 34 \times 10}{22.4}\) = 30.36 %
30.36%(W/V) 100 మి.లీ ద్రావణం H2O భారాన్ని సూచిస్తుంది.
∵ H2O2 శక్తి = 30.36 (W/V)
∵ H2O2 మొలారిటి : ∵ H2O2 ద్రావణపు మొలారిటి = \(\frac{30.36}{34}\) = 0.893 M
H2O2 నార్మాలిటి : నార్మాలిటి అనగా 1లీ ద్రావణంలో గల ద్రావితపు తుల్యభారాల సంఖ్య.
∴ నార్మాలిటి = \(\frac{30.36}{17}\) = 1.786 N
15 ఘ.ప H2O2 శక్తి :
10 ఘ.ప H2O2 అనగా 3% W/V
15 ఘ.ప H2O2 అనగా \(\frac{15 \times 3}{10}\) = 4.5 gm / 100 మి.లీ.
1 litre H2O2 భారం = 45 gm/Litre
10 ఘ.ప H2O2 నార్మాలిటి – 1.786
15 ఘ.ప H2O2 నార్మాలిటి = \(\frac{15 \times 1.786}{10}\) = 2.679 N
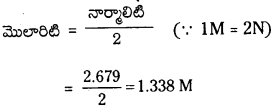
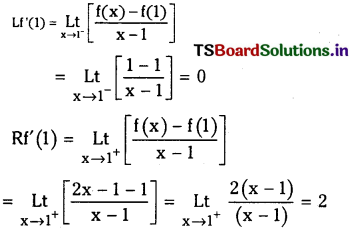
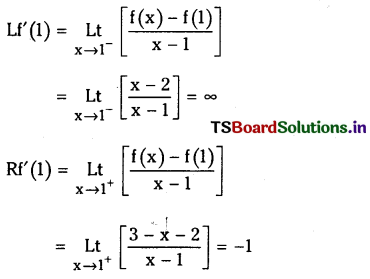
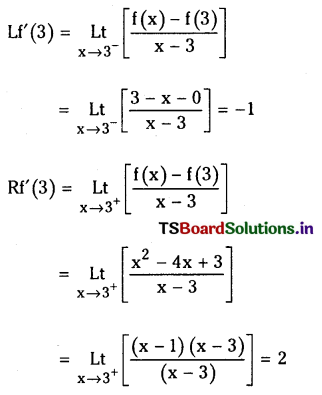
![]()
![]()