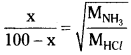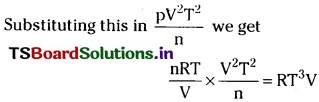Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 3rd Lesson Sole Proprietorship, Joint Hindu Family Business and Cooperative Societies Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 3rd Lesson Sole Proprietorship, Joint Hindu Family Business and Cooperative Societies
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Sole proprietorship and state its features.
Answer:
Sole proprietorship is the oldest form of business organisation in which a single individual introduces his / her own capital, skill and intelligence in the management of its affairs and is solely responsible for the results of its operations. It is also known as Individual Proprietorship or Single Entrepreneurship.
A sole proprietor contributes and organizes the resources in a systematic way and controls the activities with the objective of earning profit.
Definition:
J.L. Hanson: “A type of business unit where one person is solely responsible for providing the capital and bearing the risk of the enterprise, and for the management of the business”.
Features of Sole Proprietorship: The following are the important features of sole proprietorship business organisation.
a) Individual Initiative: The sole proprietorship business is started by the initiative of a single person who wishes to start the business. The profits or losses of the business are taken by the individual.
b) Single Ownership: The sole proprietorship form of business organisation has a single owner who himself / herself start the business by bringing together all the resources.
c) Less Legal Formalities: The formation and operation of a sole proprietorship involves less legal formalities. Thus, its formation and winding up is quite easy and simple.
d) Unlimited Liability: The liability of the sole proprietor is unlimited. In case of loss, if his / her business assets are not enough to pay the business liabilities, his personal property can also be utilised to pay off the liabilities of the business.
e) Ownership and Management Exist Together: The owner himself / herself manages the business as per his / her own skills and intelligence. There is no separation of ownership and management. The business is dissolved if the owner dies, becomes insolvent or removed from the business.
f) Motivation: The sole proprietorship enjoys all the profits and at the same time bears the losses, if any. No other person shares the profits and losses of the business. It he works more, he will earn more.
g) Secrecy: All the important decisions are taken by the sole proprietorship himself / herself. He / she keeps all the business secrets only with himself / herself.
h) No Separate Entity: The sole proprietor and the business enterprise are one and the same. The sole proprietor is responsible for everything that happens in his / her business unit.
i) One-Man Control: The management and controlling power of the sole proprietorship business always remains with the owner. He / she runs the business as per his / her own will.
j) Limited Area of Operations: As the sole proprietor has limited resources and managerial abilities, sole proprietorship business has usually limited areas of operations.
Question 2.
Write the advantages and disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship.
Answer:
Advantages of Sole Proprietorship: The following are the basic advantages of sole proprietorship business.
a) Easy to Form and Wind Up: It is very easy and simple to form a sole proprietorship form of business organization as it require less legal formalities and less time. Any person wishing to start a sole-trade business can start without loss” of time. The proprietor can be wind up business at any point of time.
b) Quick Decision and Prompt Action: Nobody interferes in the affairs of the sole proprietary business. Hence, he / she can take quick decisions on the various issues relating to business and accordingly prompt action can be taken.
c) Flexibility in Operations: A sole proprietorship concern generally runs on a small scale basis. If any change in operation he can adjust its production according to the changing demand patterns.
d) Direct Motivation: In sole proprietorship concern the entire profit of the business is enjoyed by the owner himself / herself. This motivates and encourages the proprietor to work hard and run the business effectively and efficiently.
![]()
e) Maintenance of Business Secrets: The business secrets are known only to the proprietor. He / she is not required to disclose any information to others.
f) Personal Contact with Customers: The proprietor maintain good personal contacts with the customers and employees. By knowing the likes, dislikes and tastes of the customers, the proprietor can adjust his operations accordingly.
g) Easy to Raise Finance: The sole proprietor is able to create goodwill for his business by his hardwork. This helps him / her to establish the creditworthiness in the market.
h) Socially Desirable: Large number of sole traders have entered different types of business which helps in avoiding concentration of wealth. The consumers will not depend on big businesses. Thus, sole-trader business is socially desirable.
i) Self Employment: The sole proprietorship form of business offers the means of self-employment. To earn livelihood, the individuals can easily start small scale business as a sole trader.
j) Inexpensive Management: As the sole proprietor is the owner, manager and controller of his business, there is no need to appoint specialized employees for various functions of business. Thus, management expenses can be saved to a larger extent.
Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship: Sole proprietorship business is suffering from the following disadvantages.
a) Limited Resources: The resources of a sole proprietor are always limited. Being the single owner, it is not always possible to arrange sufficient funds from his own sources. So, the proprietor has a limited capacity to raise funds for his business.
b) Unlimited Liability: The liability of a sole proprietor is unlimited. His / her private properties can also be used for meeting business losses and obligations.
c) Limited Managerial Ability: A sole proprietorship form of business organisation always suffers from lack of managerial expertise. A single person may not be an expert in all fields like purchasing, selling, financing etc.
d) Lack of Continuity: The sole trade business continues as long as sole proprietor lives. The continuity of the business is linked with the life of the proprietor. Illness, death or insolvency of the proprietor can lead to closure of the business.
e) Not suitable for Large Scale Operations: As the financial resources and the managerial abilities of a sole proprietor are limited, this kind of business organisation is not suitable for large-scale businesses.
f) Wrong Decisions: A sole proprietor has to take all the decisions by himself / herself. He cannot consult experts to have proper knowledge about various aspects of the business. So, there is a possibility of taking wrong decisions which may lead to loss.
Question 3.
“One man management is the best in the world provided one man is big enough to take care of everything”. Discuss.
Answer:
In his book “The organisation of modem business” William R. Basset said that, “one man control is the best in the world if that man is big enough to manage everything.” One man controlled business is the best provided. That man is able to manage all the activities efficiently and effectively.
The sole proprietor is motivated to work more as there is direct relationship between efforts and reward. He can take prompt decisions and implement them immediately to avail of business opportunities. This type business is easy to form because there are no legal formalities to be observed. The capital required to start this business is less. The sole proprietor has direct contact with the customers and caters to their individual tastes. The incidence of taxation is lowest on this type of business. The proprietor should avoid risky and speculative transactions because of his unlimited liability.
All the above advantages of sole proprietorship can be availed only if the sole proprietor is intelligent, capable of taking quick decisions, able to manage the business properly and dynamic in nature. The pre-condition is that the man should be big enough to control every thing. That is, the sole proprietor is outstanding and is able to cope up with the work.
The sole trading form of business is suitable in the following cases:
- Where the capital required is small.
- Where the risk is not heavy.
- Where the decisions are to be taken quickly.
- Where the customers require personal attention.
- Where market is local.
- Where business is of speculative nature.
- Where production of artistic goods to be carried on.
Question 4.
What is Joint Hindu Family Business? Discuss its main features.
Answer:
Meaning:
- “A business, which continues from one generation to another generation is known as “Joint Hindu Family Business”. This is special form of business organization, which now exists only in India. And the business is within the family.
- The head of the family is the head of the business also. He is also known as “Karta” and the members are known as “co-parceners”.
Features of Joint Hindu Family Business: The essential features of the Joint Hindu Family Business are as follows.
a) Formation: In Joint Hindu Family business there must be atleast two members in the family, having some ancestral property. It is not created by an agreement but by operation of law.
b) Governed by Hindu Law: The JHF business is a jointly owned business. The management and control of the JHF business is done according to Hindu Succession Act, 1956.
c) Membership: The membership of the family can be acquired only by birth. Unlike other business, outsiders are not allowed to become the coparceners in the JHF business. However, by adoption and Marriage with male member also confers membership.
d) Management: The business is managed by the senior most member of the family known as ‘Karta’ or ‘Manager’. Other members do not have the right to participate in the management. The Karta has the authority to manage the business as per his own will. His ways of managing cannot be questioned.
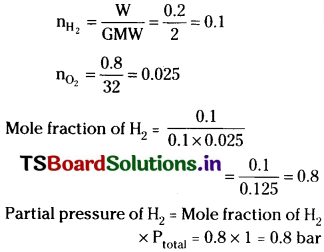
![]()
e) Profit Sharing: The Joint Hindu Family business is jointly owned by all the members. All the coparceners have equal share in the profits of the business.
f) Liability: All the members in a Joint Hindu Family have limited liability to the extent of property. The self acquired property of any member cannot be taken to pay the liabilities of the family. But the liability of the Karta is unlimited. His personal property can also be utilised to meet the business liability.
g) Continuity: Death of any coparceners does not affect the continuity of business. Even on the death of the Karta, it continues to exist as the eldest of the coparceners takes position of Karta.
h) Accounts: The accounts are maintained by Karta. Karta is not accountable to any member and no member is supposed to ask what are the profits and losses of business.
Question 5.
State the advantages and disadvantages of Joint Hindu Family Business Organisation.
Answer:
Advantages of Joint Hindu Family Business: The important advantages of a Joint Hindu Family business are as follows:
a) Centralized and Efficient Management: The management of Joint Hindu Family firm is vested in the hands of Karta only. This results in the unity command and disciplined management.
b) Continuity: It is not dissolved by the death of a coparcener. Even on the death of the Karta, it will be continued as the eldest of the family members assumes the charge of Karta.
c) Unlimited Membership: By birth every coparcener will automatically become a member in Hindu Undivided Family. Minors can also become members of the Joint Hindu Family. Hence there is no limit to membership.
d) Better Credit Facilities: The credit worthiness of the Joint Hindu Family business is better than that of the Sole Trader. There are more credit facilities are available to the JHF business.
e) Quick Decision: In Joint Hindu Family business, as Karta is the only decision maker, he can take very quick decisions.
f) Secrecy: As in Joint Hindu Family firm only Karta is to manage the affairs of busi-ness. He can keep business matters secret even from the members of the firm.
Disadvantages of Joint Hindu Family Business: The important disadvantages of a Joint Hindu Family business are as follows:
a) No Direct Reward for Efficiency: Karta alone looks after the business of Joint Hindu Undivided Family. But benefits are shared among all coparceners. The persons who work more efficiently and dedicatedly are not rewarded for their work.
b) Limited Managerial Ability: In Joint Hindu Family as an eldest of person only Karta has to manage business. The management and control of all the business affairs becomes difficult for Karta alone. Thus, expansion and growth of the business is difficult, as Karta has limited managerial ability.
c) Suspicion among Members: The Karta is empowered with vast power of secrecy and he / she can keep business affairs secret members. This leads to suspicion among the members themselves which even lead to disastrous for the Joint Hindu Family business.
d) Limited Capital and Financial Resources: The capital and financial resources of the Joint Hindu Family business are limited as compared with that of Partnership and Joint Stock Company.
Question 6.
Define the Co-operative Society. Explain its features.
Answer:
Meaning: The term “cooperation” is derived from the Latin word “co-operari”. The word “Co” means “with” and “operari” means “to work”. Thus the term cooperation means working together. Co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons who work together to promote their economic interest.
Definition: The Indian co-operative societies Act 1912, section (4) defines co-operative society as “a society, which has its objectives for the promotion of economic interests of its members in accordance with co-operative principles”.
Features:
1) Voluntary Association: A co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons. That means, persons can join and leave the society when they want.
2) Open Membership: The Membership is open to all persons having a common economic interest. Any person can become a member irrespective of his/her caste, creed, religion, colour, sex etc.
3) Number of Members: A Minimum of ’10’ members are required to form a co-operative Society. In case of multi-state co-operative societies, the minimum number of members should be ’50’ from each state.
4) Registration of the society: In India, co-operative societies are registered under the co-operative Societies Act, 1912 or, under the State co-operative Societies Act.
5) State control: Every co-operative society comes under the control and supervision of the Government. Every society has to get its accounts audited from the co-operative Department of the government.
6) Capital: The capital of the co-operative society is contributed by its members, it often depends on the loans and grants from state and central Government.
7) Democratic set up: The co-operative societies are managed in a democratic manner. The Management of a co-operative society is control by managing committee elected on the basis of “one-man one-vote” irrespective of the number of shares held by any member.
8) Service Motive: The primary objective of all co-operative societies is to provide services to its members, rather than to earn profits.
9) Return on capital Investment: The members of co-operative society get returns on their capital investment in the form of dividend. The multi cooperative societies registered under the state cooperative societies Act, 2000.
10) Distribution of surplus: After giving dividends to the members of the society, the surplus profit is distributed among the members in the form of bonus.
The multi co-operative societies registered under multi state co-opeerative societies Act, 200.
![]()
Question 7.
A co-operative society form of oganisation is a method of ‘Self Help’- Discuss.
Answer:
The co-operative movement has been necessiated to protect the interests of weaker sections of society. The primary objective of this movement is how to protect economically the weaker sections of the society from the oppression of economically strong segment of the society. In all forms of business organisations, be it a sole trade, partnership or joint stock company, the primary motive is to increase the profits. The businessman tries to promote his own interests through all positive means including exploitation of consumers. The cooperative form of organisation is a democratic set up run by its members for serving their own interests. It is self help through mutual help. The philosophy behind cooperative movement is all for each and each for all’.
In the words of Dr. H.N. Kunzen co-operative is self help as well as mutual help. It is a joint enterprise of those who are not financially strong and cannot stand on their legs and therefore, come together not with a view to get profits but to overcome disability arising out of the want of adequate financial resources.
Co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons who work together to pro-mote their economic interests. It works on the principle of self-help and mutual help. The primary objective is to provide support to the members. The motto of co-operative society is “Each for all and all for each”. People come forward as a group, pool their individual resources, utilise them in the best possible manner and derive some common benefits out of it.
Question 8.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of Co-operative Societies.
Answer:
Advantages of co-operative society:
1) Simple formation: It is easy to form a co-operative society as the legal formalities are not many. It is economical as it need not pay stamp duty, registration fees.
2) Democratic management: The management is done in a democratic way. Every member has one vote irrespective of the number of shares held by him. So, every one has an equal voice in the management.
3) Limited liability: The liability of the members is limited. He is not personally liable.
4) Stability and continuity: A co-operative society has perpetual existance. It need not be dissolved on the death, lunacy, insolvency of its members.
5) Economy in operation: Some of the members may voluntarily offer their free services. Therefore, some of the management expenses are saved.
6) Cheaper and better commodities: A co-operative society aims at service rather than profit. The consumers can get goods of better quality at reasonable price.
7) Priviliges state patronage: The government has granted several priviliges to cooperative societies. The government provide finance at concessional rates of interest.
8) Elimination of middlemen: A cooperative society purchases goods directly from the producers and sells directly to its members. Hence middlemen are eliminated.
9) Aim at mutual prosperity: Cooperates function on the principle of “Each for all and all for each” with the aim of mutual prosperity.
Disadvantages of Co-operative Society:
1) Inefficient management: The members of the managing committee are elected persons. Hence inexperience and unscrupulous persons may be elected. This leads to weak and inefficient management.
2) Limited financial resources: Restriction on dividend and the principle of one member, one vote discourage rich people from joining the society. Due to shortage of funds, there is limited scope for expansion and growth.
3) Lack of unity among members: The members are drawn from different sections of the society. There is lack of harmony among them.
4) Lack of incentive to work hard: Managing committee members do not take active part as they are not paid for their services. The loyalty of the members may not always assured.
5) Lack of secrecy: It is very difficult to maintain business secrets which are important for the success of the business unit.
6) Political interference: Government nominates members to the managing committee. Every government tries to send their own party members to these societies.
7) Government interference: Cooperative societies have to follow the rules and regulations of the cooperative societies act and government.
8) Cash trading: The members need credit facilities. But the societies sells goods only for cash. So, the members may go to private traders who extend credit facility.
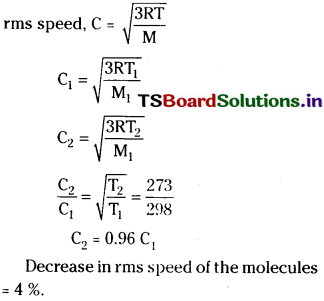
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the features of Sole Proprietor.
Answer:
Sole proprietorship is the oldest form of business organisation in which a single individual introduces his / her own capital, skill and intelligence in the management of its affairs and is solely responsible for the results of its operations. It is also known as Individual Proprietorship or Single Entrepreneurship.
A sole proprietor contributes and organizes the resources in a systematic way and controls the activities with the objective of earning profit.
Definition:
J.L. Hanson: “A type of business unit where one person is solely responsible for providing the capital and bearing the risk of the enterprise, and for the management of the business”.
Features of Sole Proprietorship: The following are the important features of sole proprietorship business organisation.
a) Individual Initiative: The sole proprietorship business is started by the initiative of a single person who wishes to start the business. The profits or losses of the business are taken by the individual.
b) Single Ownership: The sole proprietorship form of business organisation has a single owner who himself / herself start the business by bringing together all the resources.
c) Less Legal Formalities: The formation and operation of a sole proprietorship involves less legal formalities. Thus, its formation and winding up is quite easy and simple.
d) Unlimited Liability: The liability of the sole proprietor is unlimited. In case of loss, if his / her business assets are not enough to pay the business liabilities, his personal property can also be utilised to pay off the liabilities of the business.
e) Ownership and Management Exist Together: The owner himself / herself manages the business as per his / her own skills and intelligence. There is no separation of ownership and management. The business is dissolved if the owner dies, becomes insolvent or removed from the business.
f) Motivation: The sole proprietorship enjoys all the profits and at the same time bears the losses, if any. No other person shares the profits and losses of the business. It he works more, he will earn more.
Question 2.
Explain the limitations of, Sole Trader.
Answer:
The following are the limitations of sole trading business.
1. Limited resources: The resources of sole trader are limited. He has only two sources of securing capital, personal savings and borrowing on personal security. Hence, he can raise very limited amount of capital.
2. Instability: It has no separate legal status. The business and the owner are inseparable from one another. The business comes to an end on the death, insolvency, insanity of the owner.
3. Unlimited liability: The liability of the sole trader is unlimited. The creditors can recover the loan amounts not only from the business but also from his private property.
4. Not suitable for large scale operations: The resources are limited. Therefore, it is suitable only for small business and not large scale operations.
5. Limited managerial skill: The managerial ability is limited. A person may not be an expert in all matters. Sometimes wrong decisions may be taken.
6. Restricted growth: The limitations of capital and managerial ability will restrict the growth development and expansion of the business.
7. Dependence on paid employees: When the business expands, the sole trader has to depend on the paid employees. They may not work hard and show interest. Hence the efficiency suffers.
![]()
Question 3.
State the suitability of Sole Proprietorship.
Answer:
The sole trading form of business is suitable in the following cases:
- Where the capital required is small.
- Where the risk is not heavy.
- Where the decisions are to be taken quickly.
- Where the customers require personal attention.
- Where market is local.
- Where business is of speculative nature.
- Where production of artistic goods to be carried on.
Question 4.
What are the features of Joint Hindu Family Business?
Answer:
Meaning:
- “A business, which continues from one generation to another generation is known as “Joint Hindu Family Business”. This is special form of business organization, which now exists only inf India. And the business is within the family.
- The head of the family is the head of the business also. He is also known as “Karta” and the members are known as “co-parceners”.
Features of Joint Hindu Family Business: The essential features of the Joint Hindu Family Business are as follows.
a) Formation: In Joint Hindu Family business there must be atleast two members in the family having some ancestral property. It is not created by an agreement but by operation of law.
b) Governed by Hindu Law: The JHF business is a jointly owned business. The management and control of the JHF business is done according to Hindu Succession Act, 1956.
c) Membership: The membership of the family can be acquired only by birth. Unlike other business, outsiders are not allow become the coparceners in the JHF business. However, by adoption and Marriage with male member also confers membership.
d) Management: The business is managed by the senior most member of the family known as ‘Karta’ or ‘Manager’. Other members do not have the right to participate in the management. The Karta has the authority to manage the business as per his own will. His ways of managing cannot be questioned.
e) Profit Sharing: The Joint Hindu Family business is jointly owned by all the members. All the coparceners have equal share in the profits of the business.
Question 5.
Explain the features of Co-operative Societies.
Answer:
Meaning: The term “cooperation” is derived from the Latin word “co-operari”. The word “Co” means “with” and “operari” means “to work”. Thus the term cooperation means working together. Cooperative society is a voluntary association of persons who work together to promote their economic interest.
Definition: The Indian co-operative societies Act 1912, section (4) defines co-operative society as “a society, which has its objectives for the promotion of economic interests of its members in accordance with co-operative principles”.
Features:
1) Voluntary Association: A co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons. That means, persons can join and leave the society when they want.
2) Open Membership: The Membership is open to all persons having a common economic interest. Any person can become a member irrespective of his/her caste, creed, religion, colour, sex etc.
3) Number of Members: A Minimum of TO’ members are required to form a co-operative Society. In case of multi-state co-operative societies, the minimum number of members should be ’50’ from each state.
4) State control: Every co-operative society comes under the control and supervision of the Government. Every society has to get its accounts audited from the co-operative Department of the government.
5) Capital: The capital of the co-operative society is contributed by its members, it often depends on the loans and grants from state and central Government.
![]()
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is Business Organisation?
Answer:
1) In order to carry out any business and to achieve its objective of earning profit, it is required to bring together all the resources and put them into action in a systematic way, and to coordinate and control all these activities properly. This arrangement is known as business organisation.
2) Arrangement of ownership and management of business organisations is termed as ‘Form of Business Organisation’. Business organisations may be owned and managed by a single person (Sole Proprietorship) or a group of persons (Partnership) or in the form of a company Joint Stock Company.
Question 2.
Define Sole Proprietorship.
Answer:
1) Sole proprietorship is the oldest form of business organisation in which a single individual introduces his / her own capital, skill and intelligence in the management of its affairs and is solely responsible for the results of its operations. It is also known as Individual Proprietorship or Single Entrepreneurship.
2) A sole proprietor contributes and organizes the resources in a systematic way and controls the activities with the objective of earning profit.
Definition:
J.L. Hanson:
“A type of business unit where one person is solely responsible for providing the capital and bearing the risk of the enterprise, and for the management of the business”.
Question 3.
What is Joint Hindu Family Business?
Answer:
1) Meaning: “A business, which continues from one generation to another generation, is known as “Joint Hindu Family Business”. This is special form of business organization, which now exists only in India. And the business is within the family.
2) The head of the family is the head of the business also. He is known as “Karta” and the members are known as “Co-parceners”.
Question 4.
Define Co-operative Society.
Answer:
1) Cooperative society is a voluntary association of persons who work together to promote their economic interests. It works on the principle of self help and mutual help.
2) The motto of co-operative society is “Each for all and all for each”. People come forward as a group, pool their individual resources, utilise them in the best possible manner and derive some common benefits out of it.
![]()
Question 5.
Briefly explain the different types of co-operative societies.
Answer:
According to the needs of people different types of co-operative societies are started in India. They are:
1) Consumers Co-operative Society: These are started to help lower and middle class people. These societies protect weaker sections from the clutches of profit hungry businessmen. These societies make bulk purchases directly from producers and sells these goods to members on retail basis. The commission and profit of the middlemen are eliminated. The members contribute capital and membership is open to all irrespective of caste, creed, colour etc.
2) Producers Co-operative Society: Small producers find it difficult to collect various factors of production they also face marketing problem. The production of goods is undertaken by members in their houses or at common place. They are paid wages for their services. They are supplied raw material and equipment by the society. The output is collected and sold by the society. The profits are distributed among members after retaining some profit in the general pool.
Ex.: Appco, Co-Optex, Emniganur weavers co-operative society.
3) Marketing Co-operative Society: These societies are established by producers for selling their products at remunerative prices. These societies pool production from different members and undertake to sell these products by eliminating middlemen. The goods are sold when the market is favourable. The societies provide some advance money to the members for helping them in meeting their urgent needs. The sale proceeds are shared among members according to their contributions. These societies provide services like grading, warehousing, insurance, finance etc.
4) Co-operative Credit Society: The people with moderate means are formed with the object of extending short term credit to their members. They also develop thrift among the members. The funds are contributed by the members. These societies are divided into rural credit co-operative societies and urban credit co-operative societies.
5) Co-operative Housing Society: The low and middle income group of people are not able to construct their own house for want of money. Co-operative society arrange loans for their members from financial institutions and government agencies against security of the houses. These societies helps the members to become owners of house over a period of time. Ex.: Housing Board Colonies.
6) Co-operative Farming Societies: These societies are basically agricultural co-operatives. These are formed by the small land owners. They pool their resources to achieve the benefits of large scale farming and maximizing agricultural product. They solve the problems of finance, irrigation seeds, fertilizers etc.
Question 6.
Karta.
Answer:
1) The senior most male member of the family is Karta. All the affairs of the Joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person. He is known as Karta or Manager.
2) The liability of the Karta is unlimited. He acts on behalf of the other members of the family. He is not accountable to anyone. He is the great master of the grandshow.
Question 7.
Co-parcener.
Answer:
- The members of the Joint Hindu Family are called co-parceners.
- Co-parcener is a person who has a share in common property formed either through inheritance or conversion of assets by members. The liability of the co-parceners is limited to their share of interest in the common property.
Question 8.
Dayabhaga.
Answer:
- This school of Hindu prevails only in Assam and West Bengal.
- Under this the right of the property comes to a co-parcener by succession and not by birth.
- Share in a Joint Hindu Family does not fluctuates, on the basis of birth or death of a member.
![]()
Question 9.
Mitakshara.
Answer:
- This school of Hindu law prevails in the entire India except in Assam and West Bengal.
- Family members of the male line and their wives, and unmarried daughters are its members. By birth, a member gets a share in common property, it continues till his death.
- In this way shares in the property get fluctuate in accordance with the number of co-parceners.