These TS 6th Class Science Important Questions 3rd Lesson Rain: Where Does it Come From? serves as a valuable tool for students to prioritize their studying and revision efforts.
TS 6th Class Science Important Questions 3rd Lesson Rain: Where Does it Come From?
I. Conceptual Understanding :
Question 1.
What are the three forms of the water ?
Answer:
Water on the earth can exist in 3 forms :
Ice (solid form), water (liquid form) and water vapour (gaseous form).
Question 2.
Define the following. Give suitable examples.
1) Evaporation
2) Condensation
(Or)
What is the process in which water changes to water vapour ?
Answer:
1) Evaporation: The process of changing of water into water vapour is called evaporation.
Eg : Cloud formation.
2) Condensation : The process of conversion of water vapour into water is called condensation.
Eg : Formation of rain.
Question 3.
What causes rain on the earth ?
Answer:
The cycle of evaporation and condensation of water, present on the earth’s surface, causes rain.
![]()
Question 4.
What is water cycle ?
Answer:
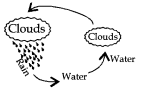
The conversion of water into water vapour, water vapour to clouds, clouds to rain is known as water cycle.
Question 5.
Write a few lines about the cause of floods or droughts.
Answer:
- Deforestation and pollution from factories are now causing global warming.
- So, the atmospheric conditions are not favourable for clouds to get cooled.
- Consequently, there is a decrease in the rainfall. This leads to disturbance of water cycle and causes either floods or droughts.
Question 6.
Write the changes that take place in the following blank. Ice water ?
Answer:
Ice \(\rightleftharpoons\) water \(\rightleftharpoons\) ………………?
Ice \(\rightleftharpoons\) water \(\rightleftharpoons\) water vapour.
Question 7.
In our state rains occur normally from June to September. What is the name of this monsoon ?
Answer:
- In our state rains occur normally from June to September.
- During that season we observe in the sky that clouds move along with the winds blowing from western directions.
- These winds are called “south – west monsoon”.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain north east monsoon and south east monsoon.
(Or)
What is meant by north – east monsoon ? In which season the rain occurs due to north east monsoon ?
- Generally, we get rains in some particular months during the year.
- In our state, rains occur normally from June to September .
- During that season you might have observed in the sky that clouds are moving along with the winds blowing from western direction (south west side).
- These winds are called “south west monsoon”.
- Similarly, we observe in the months of November and December rains occur due to movements of clouds in the direction of winds blowing from eastern side (north – east side).
- These winds are called “north – east monsoon”.
Question 9.
Explain various forms of water with suitable examples.
(Or)
In how many forms water exists on the earth ? How does water convert from one form to another ?
Answer:
Water is available in 3 forms
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gaseous
1. Solid form of water:
Solid form of water is ice. The lowest temperature below 0°C converts water into ice.
Eg : Ice cubes in fridge
2. Liquid form of water:
When ice melts it will change into water, normal temperature converts the ice into liquid. :
Eg : Water in rivers, lakes, oceans
3. Gaseous form of water:
The gaseous form of water is water vapour which is present in the air around us.
Eg: Water vapour releasing from boiling vessel.
![]()
Question 10.
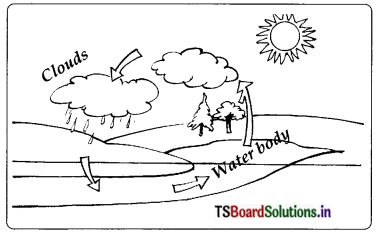
Describe the various stages of water cycle ? Explain what changes will occur in water cycle due to deforestation.
Answer:
Definition: The circulation of water into water vapour by evaporation, water vapour to clouds and clouds to rain by condensation is known as water cycle.
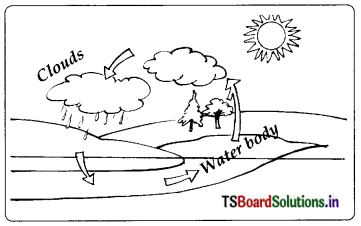
When it rains water bodies are filled with water. Some of this rain water seeps into the ground and becomes ground water. As it is very hot during summer, large quantity of water evaporates from water bodies and converts into water vapour.
This goes up into the air to form clouds. These clouds again cool and produce rain. Deforestation and pollution from factories cause global warming. Therefore atmospheric conditions become unfavourable for cooling of clouds. Consequently there will be decrease in rainfall. This disturbs the water cycle and causes either floods or droughts
![]()
Question 11.
Suppose you heard that there is raining in some area, but at the same time there may not be raining in other area. Why is it so ? (Conceptual Understanding)
Answer:
- Often we see that there may be rain in some area, where it may not be in its adjacent areas.
- This is because of condensation of clouds due to cool air which affects them in the specific area.
- Occurrence of winds won’t be same in all the areas. Pressure influences the presence of air.
- Clouds along with winds move from high pressure area to low pressure area at which cool air occurs.
- That’s why rain is seen only in some areas, where we can’t see it in its adjacent areas.
Question 12.
If there is no evaporation and condensation (or) in the nature what would happen. What are the consequences of decrease in rainfall ?
Answer:
Absence of evaporation and condensation in the nature causes lack of rainfall. Consequences that occur due to lack of rains or less rain fall.
- Fertile lands become unfit for harvestation.
- Water scarcity occurs.
- Rain based agriculture will face many problems. As a result, crops and plants will not grow.
- Global warming will affect the earth.
- Plants will die in every region.
Question 13.
What questions do you ask a meteorologist to know about clouds ?
Answer:
- Why are clouds formed only in the sky ?
- How are clouds formed ?
- Why do we have rains only in some seasons ?
- Why don’t we have rains in summer ?
![]()
Question 14.
In winter mornings we observe small dew drops on grass leaves. What is this process ?
Answer:
Especially during winter water vapour present in the air cools down due to cold weather. Therefore condensation occurs and as a result water vapour appears in the form of dew on the leaves.
Question 15.
Though it is rainy season, we are not getting enough rains. To find out the reason, what questions do you ask your teacher ?
Answer:
- Why do not we have sufficient rains ?
- What are the reasons for less rains ?
- Who are responsible for having less rains ?
- What should we do to have good rains ?
Question 16.
What changes are seen if there is no occurrence of condensation in the water cycle ?
(Or)
What happens if evaporated water does not condense ?
Answer:
If there is no occurrence of condensation in the water, water cycle stops due to lack of rains. If there are no rains water sources will not be filled with water. Even ground water level decreases. Low percentage of water levels in the natural water bodies cause damage to the living kingdom, thus it finally leads to destruction of nature. Hence condensation process is very essential in the water cycle.
Question 17.
“Clouds lead to falling of rains.” There are some other concepts like above in the lesson. Find out and write them.
Answer:
Some important concepts :
- Three forms of water are interchangeable.
- Evaporation is the process of water into water vapour.
- Condensation is the process of water vapour into water.
- The circulation of water in three forms in the nature is called water cycle.
![]()
Question 18.
Frame three innovative questions on the following.
(1) Evaporation
(2) Condensation
Answer:
- Evaporation:
- What is the importance of evaporation ?
- How do we get clouds due to evaporation ?
- Where do you find evaporation ?
- Condensation :
- Where do we see condensation ?
- Define condensation.
- What are the uses of condensation ?
- What is the relation between rains and condensation ?
Question 19.
What happens if size of the evaporated water molecules increases in the cloud ?
Answer:
If size of the water molecules in the cloud increases, they convert into water droplets and condense to form rains.
III. Experimentation and field Investigation :
Question 20.
Explain the procedure to prove the conversion of water vapour into water.
(OR)
What is condensation ? How do you prove the process by condensation ?
Answer:
Definition : The process of conversion of water vapour into water is called condensation.
Procedure:
- A vessel is taken and filled with water.
- It is kept on a stove and heated slowly.
- It is observed for sometime. Now the vessel is covered with a plate.
- The plate is removed after a couple of minutes.
Observation : The water vapour that lied beneath the lower suface of plate converts into water.
Inference : This proves how water vapour condenses into water.
![]()
Question 21.
Explain the procedure to be followed in the experiment condensation.
(OR)
When we poured cool (water) drink in a glass, we observed water droplets on the outer surface of the glass. Why ?
Answer:
- Ice cold water in the glass cools its surface.
- Air around the glass contains water vapour which is warmer than the surface of the glass.
- Due to the cold glass, air close to its surface will also become cooler.
- This changes the water vapour in the air around the surface of the glass into water and forms small drops on the outer surface of glass. It occurs if there is only either ice or cold water.
Question 22.
You feel happy while raining. Ask any two questions to your teacher to clarify your doubts on raining.
Answer:
- How do rains fall ?
- Why don’t we see rains in all the seasons ?
- Rain falling in one place is not seen in other place. Why ?
- How does rain start in the sky ?
IV. Information Skills and Projects :
Question 23.
Read the information given below and answer the questions.
We call solid form of water ice. Snow occurs naturally. If we heat ice, it will change into water. Water in liquid form is present in oceans, seas, lakes, rivers and even underground. The gaseous form of water is water vapour which is present in the air around us. We know that when ice is heated, it converts into water and if water is heated it turns into water vapour. Similarly when water vapour is cooled we can get back water. If water is cooled further we get ice.
1. Name few sources of water in liquid form.
Answer:
Oceans, seas, rivers etc.
2. How do you interchange the three states of water ?
Answer:
Solid form of water (ice) is heated to convert into liquid state. Liquid form of water is further heated to convert into water vapour. Ice <— Water <— Water vapour
3. Name the process which converts water into water vapour.
Answer:
Evaporation
4. Where do you find solid ice in nature ?
Answer:
Polar regions and glaciers
![]()
Question 24.
Visit your school library or internet, collect information about (Kashmir) Dal Lake. In which season water in the lake becomes ice and snow fall is very high and why the place attracts more tourists ?
Answer:
- Project Work on Dal Lake
- Dal Lake is the beautiful, naturally formed resource in the Kashmir valley.
- To obtain information about it, I collected necessary points by visiting internet.
- Dal Lake premises are the famous tourism hub for so many visitors all over the world.
- During winter (between December and February) Dal Lake freezes due to freezing atmosphere with minus
- degree Celsius.
- It forms like solidified ice snow area due to freezing conditions.
- It looks like a playground during freezing winter season.
- During summer, it shows beauty of the nature of Kashmir in the name of
V. Communication through Drawing and Model Making :
Question 25.
In the given diagram you can observe droplets of water on the surface of ice containing glass.
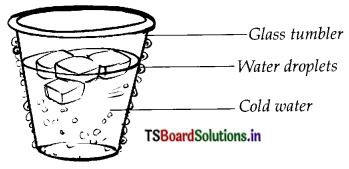
1) Why are those drops formed ?
2) Do they form if there is no ice in the glass ?
Answer:
- Ice cold water in the glass cools its surface.
- Air around the glass contains water vapour which is warmer than the surface of the glass.
- Due to the cold glass, air close to its surface will also become cooler.
- This changes the water vapour in the air around the surface of the glass into water and forms small drops on the outer surface of glass. It will occur if there is only either ice or cold water. Draw the diagram of showing water cycle on the earth and label it.
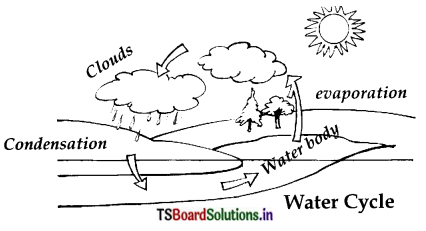
Question 26.
Draw the diagram of showing water cycle on the earth and label it.
Answer:
Question 27.
Draw the diagram of water cycle and write a note on it.
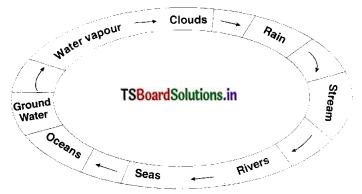
Answer:
Definition : The circulation of water into water vapour by evaporation, water vapour to clouds and clouds to rain by condensation is known as water cycle.
When it rains water bodies are filled with water. Some of this rain water seeps into the ground and becomes ground water. As it is very hot during summer, large quantity of water evaporates from water bodies and converts into water vapour. This goes up into the air to form clouds. These clouds again cool and produce rain.
VI. Aesthetic Sence. Values and Application to Daily Life and Concern to Bio-diversity:
Question 28.
Harsha appreciated that the nature is a great gift of giving rain. How can you appreciate it ?
Answer:
Nature is the great gift of giving rain.
- Hills stop the clouds and cool them and give sufficient rains.
- Forests in the nature stop the clouds and convert them into rains.
- The entire nature is like heaven to sustain our life by giving rains seasonally. Therefore we should protect this precious environment.
![]()
Question 29.
How do you appreciate the contribution of water cycle in making the water available for various needs of plants and animals ?
Answer:
- When it rains ponds, lakes etc., are filled with water.
- Water from rainfall runs down as small streams.
- These small streams join together and make bigger streams. These bigger streams join the rivers.
- The rivers flow down to seas and oceAnswer:Some of this rain water seeps into the ground and becomes ground water.
- The plants and animals depend on water bodies such as ponds filled with rain water.
- The water bodies are ponds, lakes, streams, rivers, seas and oceans.
- All the living things sustain their life by utilizing water resources.