These TS 6th Class Science Important Questions 9th Lesson Plants: Parts and Functions are crafted to align with the curriculum, ensuring students are well-prepared for assessments.
TS 6th Class Science Important Questions 9th Lesson Plants: Parts and Functions
Question 1.
What is venation ? What is its use?
Answer:
The arrangement of veins in the lamina of leaf is called venation. Venation acts as a skeleton of the leaf and gives it a shape and support.
Question 2.
What is transpiration?
Answer:
Plants release excess water in their body through stomata and some other parts as well. This water is released in the forms of vapour and this process is called transpiration.
Question 3.
What are the functions of root?
Answer:
Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and also help in anchoring the plant body to the soil.
![]()
Question 4.
Name the types of venations we see in the plants.
Answer:
There are two types of venations in different plants.
- Reticulate venation
- Parallel venation
Question 5.
How many types of roots are present in plants and name them.
Answer:
There are two types of root systems.
- Tap root system
- Fibrous root system
![]()
Question 6.
What happens when stomata are not present in leaf?
Answer:
If stomata are absent in leaf plants cannot take carbon dioxide which is useful for preparation of food.
Excess of water taken by plants cannot he expelled out. Exchange of gases will be stopped. As a result plant cannot perform its functions.
Question 7.
What would happen if there are no veins in the leaf?
Answer:
If veins are absent the leaves would lose their specific shape and support from the stem. The food that is prepared in the leaf cannot be supplied to the other parts of the plant. The water and minerals coming from the roots (via) stem cannot reach the leaves due to absence of veins.
Question 8.
Prove the experiment. “The excess water is evaporated from plants by the process by transpiration”. With the help of the procedure write the result.
(Or)
Write the procedure you followed for conducting an experiment on transpiration. Write the required material for experiment. What did you observe at last?
Answer:
Material required for transpiration experiment: Well watered potted plant, 2 polythene bags, twine thread.
Procedure: A well watered potted plant is picked up from the school garden. One of the leafy branches of the plant is enclosed in a polythene bag and tied up at its mouth. Another polythene bag is tied up at its mouth without keeping plant. The preparations are kept in the sun for few hours.
Observation : It is observed that tiny droplets of water appear on the inner side of leafy branch enclosed in polythene bag, whereas the other bag has no such droplets.
Question 9.
Collect any 5 plants and observe their paris. Write your observations in the table as it is given below.
Answer:
| S.No. | Name of the plant | Root Yes/No |
Stem Yes/No |
Leaves Yes/No |
Flowers Yes/No |
1. We have to observe the following.
- Presence or absence of flowers, roots, leaf, skin.
- Common parts in the collected plants.
I collected the following plants and tabulated as the following:
Answer:
| Name of the plant | Root | Stem | Leaves | Flower | Common parts in collected plants |
| 1. Tridax | Yes/No | Yes/No | Yes/No | Ye^No | All the parts |
| 2. Small neem | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Root, stem, leaves |
| 3. Datura | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | All the parts. |
| 4. Mango | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | All the parts |
| 5. Jasmine | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | All parts |
Question 10.
Collect the following plants, observe the roots. Classify the type of root system in them. (Tap root system and fibrous root system)
Tabulate the information as given below. Name of the plants :
(a) Grass
(b) Tulasi
(c) Ummetta
(d) Maize (Jonnalu)
(e) Beans.
| S.No. | Plant name | Root system |
| Tap root system / fibrous | ||
Answer:
I collected the given plants from the surroundings. I observed the root systems of the plants. They are tabulated as given below.
| S.No. | Plant name | Root system |
| Tap root system/fibrous root system | ||
| 1. | Grass | Fibrous root system |
| 2. | Tulasi | Tap root system |
| 3. | Datura (Ummetta) | Tap root system |
| 4. | Maize (Jonnalu) | Fibrous root system |
| 5. | Beans | Tap root system |
Question 11.
Teacher asked you to collect any 5 branches of 5 different plants. Observe the leaf modifications (Leaf base, Petiole, Lamina, shape and Edges of the leaves). Tabulate the information as shown. I was asked to find out the similarities among those collected leaves.
| S.No. | Plant name |
Leaf base Yes/No | Petiole Yes/No |
Lamina Yes/No |
Shape of leaf Yes/No | Edge of leaf Yes/No |
Answer:
Aim : To find out similarities among the collected plant leaves.
Procedure : I visited my surroundings. I collected the branches of 5 different plants. I observed their leaf modifications. All the information is tabulated as given below.
| Name of | Leaf base | Petiole | Lamina | Shape of | Edge of |
| the Plant | Yes/No | Yes/No | Yes/No | the leaf | the leaf |
| Tridax plant | Yes | Yes | Yes | Ovate and | Coarsely |
| Banyan | Yes | Yes | Yes | simple | edge |
| Mango | Yes | Yes | Yes | Simple | Smooth |
| Neem | Yes | Yes | Yes | Simple | Smooth |
| Rose | Yes | Yes | Yes | Compound | Serrated |
Question 12.
VI class boys brought stems of 5 differents plants. They are
1. Beans
2. Guava
3. Brinjal
4. Neem
5. Cucumber.
They were asked to find out their position of growth. They tabulated the information. How can you get the information with the following table ?
| SNo. | Plant name | Stem grows Vertically / Horizontally | Branches are Present/ Absent |
Answer:
| S.No. | Plant name | Stem grows Vertically / Horizontally |
Branches are Present/Absent |
| 1. | Beans | Vertically or horizontally | Creepers are seen |
| 2. | Guava | Vertically | Branches present |
| 3. | Brinjal | Vertically | Branches present |
| 4. | Neem | Vertically | Branches present |
| 5. | Cucumber | Horizontally | Creepers are seen |
Question 13.
Read the following information and answer the given questions.
The leaf lamina usually consists of a midrib/ veins and veinlets arranged in the form of a network. The long vein present in the middle of the lamina is called midrib. The branches arising from the midrib are called veins and the even finer divisions are veinlets. The arrangement of veins in the lamina is called venation. Venation acts as a skeleton of the leaf and give it a shape and support.
1. Which structures form a network in the leaf ?
Answer:
Midrib, veins and veinlets.
2. What is the use of venation to the leaf ?
Answer:
Venation acts as a skeleton of the leaf.
3. What are the veins ?
Answer:
The branches arising from the midrib of leaf are called veins.
4. Which is the long vein in lamina ?
Answer:
Midrib.
![]()
Question 14.
Draw the diagrams of tap root system and fibrous root system of plants.
Answer:

Question 15.
Draw any three storage roots (tubers). Write the definition of tubers.
Answer:

Definition of tubers : The roots which store the food material in storage tissue are called tubers.
Question 16.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of stomata in leaf. How is it useful to plant?

Use of stomata in plants : Stomata are useful in the exchange of gases between the plant and atmosphere.
Question 17.
Mention the indicated parts of the following and write any function of the leaf.
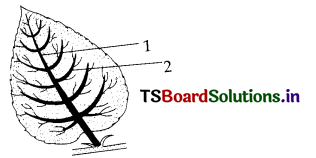
Answer:
- Mid rib of the leaf
- Leaf lamina
Function of leaf: Leaf prepares food by the process of photosynthesis.
Question 18.
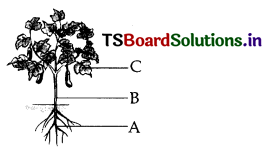
(a) Draw the following plant and identify the parts A, B, C.
Answer:
A – Roots B – Stem C – Leaf
(b) How do roots help the plant?
Answer:
Roots help in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil.