Students must practice this TS Intermediate Maths 2A Solutions Chapter 1 Complex Numbers Ex 1(c) to find a better approach to solving the problems.
TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2A Solutions Chapter 1 Complex Numbers Exercise 1(c)
I.
Question 1.
Express the following complex numbers in modulus – amplitude form
i) 1 – i
ii) 1 + i√3
iii) – √3 + i
iv) – 1 – i√3
Solution:
i) (1 – i) = r cos θ + i r sin θ
r cos θ = 1, r sin θ = – 1
r2 (cos2 + sin2) = 2
r2 = 2
r = ± √2
tan θ = – 1
θ = \(-\frac{\pi}{4}\)
√2 [cos (\(-\frac{\pi}{4}\) ) + i sin (\(-\frac{\pi}{4}\) )]
ii) 1 + i√3 = r cos θ + r i sin θ
r cos θ = 1 r sin θ = √3
r2 (cos2 θ + sin2 θ) = 1 + 3
r2 = 4
r = ± 2
tan θ = √3
θ = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
2 (cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) + i sin \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)).
iii) – √3 + i = r cos θ + r i sin θ
r cos θ = – √3
r sin θ = 1
r2 (cos2 θ + sin2 θ) = 3 + 1
r = ± 2
tan θ = \(\frac{-1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\(2\left(\cos \left(\frac{5 \pi}{6}\right)+i \sin \left(\frac{5 \pi}{6}\right)\right)\)
\(2\left(\cos \frac{5 \pi}{6}+i \sin \frac{5 \pi}{6}\right)\)
iv) – 1 – √3i = r cos θ + r i sin θ
r cos θ = – 1
r sin θ = – √3
r2 (cos2 θ + sin2 θ) = 4
r = ± 2
tan θ = √3
θ = \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
Hence 2 (cos \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\) + i sin \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)).
![]()
Question 2.
Simplify – 2i (3 + i) (2 + 4i) (1 + i) and obtain the modulus of that complex number.
Solution:
z = – 2i (6 + 12i + 2i – 4) (1 + i)
= – 2i (2 + 14i) (1 + i)
= – 2i (2 + 2i + 14i – 14)
= – 2i (- 12 + 16i)
= 24i + 32 = 8 (4 + 3i)
| z |2 = 64.25
| z | = 8 × 5 = 40.
Question 3.
i) If z ≠ 0 find Arg z + Arg \(\overline{\mathbf{Z}}\).
ii) If z1 = – 1 and z2 = – i then find Arg(z1z2)
iii) If z1 = – 1 and z2 = i then find Arg \(\left(\frac{z_1}{z_2}\right)\).
Solution:
i) z = x + iy;
\(\overline{\mathbf{Z}}\) = x – iy
Arg z = tan-1 \(\frac{y}{x}\)
Arg \(\overline{\mathbf{Z}}\) = tan-1 \(\frac{-y}{x}\)
Arg z + Arg \(\overline{\mathbf{Z}}\)
tan-1 \(\frac{y}{x}\) – tan-1 \(\frac{-y}{x}\)
0 when Arg z ≠ n
2n when Arg z = n
ii) z1 = – 1 + 0i; z2 = – i
Arg (z1z2) = Arg z1 + Arg z2
= tan-1 \(\frac{0}{-1}\) + tan-1 \(\frac{(-1)}{0}\)
= π – \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) = \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
iii) z1 = – 1; z2 = i
Arg \(\left(\frac{z_1}{z_2}\right)\) = Arg z1 + Arg z2
tan-1 \(\frac{0}{-1}\) – tan-1 \(\frac{1}{0}\)
= π – \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) = \(\frac{\pi}{2}\).
![]()
Question 4.
i) (cos 2α + i sin 2α) (cos 2β + i sin 2β) = cos θ + i sin θ then find the value of θ.
ii) If √3 + i = r (cos θ + i sin θ) then find the value of θ in radian measure.
iu) If x + iy = cis α . cis β then find the value of x2 + y2.
iv) If \(\frac{z_2}{z_1}\); z1 ≠ 0 is an imaginary number then find the value of \(\left|\frac{2 z_1+z_2}{2 z_1-z_2}\right|\).
v) If (√3 + i)100 = 299 (a + ib) then show that a2 + b2 = 4.
Solution:
i) (cos 2α + i sin 2α) (cos 2β + i sin 2β) = cos θ + i sin θ
(cos 2α cos 2β – sin 2α sin 2β) + i(sin 2α cos 2β + sin 2β cos 2α) = cos θ + i sin θ
cos 2(α + β) + i sin 2(α + β) = cos θ + i sin θ
θ = 2 (α + β)
ii) √3 + i = r(cos θ + i sin θ)
r cos θ = √3
r sin θ = 1
r2 (sin2 θ + cos2 θ) = 4
r = ± 2
tan θ = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
θ = \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
iii) If x + iy = (cos α + i sin α) (cos β + i sin β)
(cos α cos β – sin α sin β) + i(cos α sin β . sinα cos β)
x + iy = cos(α + β) + i sin (α + β)
x = cos (α + β)
y = sin (α + β)
x2 + y2 = 1.
iv) \(\frac{z_2}{z_1}=k i\left|\frac{2+\frac{z_2}{z_1}}{2-\frac{z_2}{z_1}}\right|\)
\(\left|\frac{2+k i}{2-k i}\right|=\frac{\sqrt{4+k^2}}{\sqrt{4+k^2}}\) = 1
v) (√3 + i)100 = 299 (a + ib)
|√3 + i|100 = 299 |a + ib|
(√4)100 = 299 \(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
2100 = 299 \(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
4 = a2+ b2
![]()
Question 5.
i) If z = x + iy and |z| = 1, then find the locus of z.
ii) If Ihe amplitude of (z – 1) is \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) then find the locus of z.
iii) If the Arg \(\overline{\mathbf{z}}_1\) and Arg \(\overline{\mathbf{z}}_2\) are \(\frac{\pi}{5}\) and \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) respectively then find Arg z1 + Arg z2.
iv) If z = \(\frac{1+2 i}{1-(1-i)^2}\) then find Arg (z).
Solution:
i) z = x + iy
|z| = \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)
1 = x2 + y2
Locus is circle.
ii) z – 1 = (x – 1) + iy
\(\tan ^{-1} \frac{y}{x-1}=\frac{\pi}{2}\)
x – 1 = 0, y ≠ 0 also y > 0.
iii) Arg \(\overline{\mathrm{z}}_1\) = \(\frac{\pi}{5}\)
Arg z2 = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
Arg \(\overline{\mathrm{z}}_1\) = – Arg z1 = \(\frac{-\pi}{5}\)
Arg \(\overline{\mathrm{z}}_1\) + Arg z2 = \(\frac{\pi}{3}-\frac{\pi}{5}=\frac{2 \pi}{15}\).
iv) z = \(\frac{1+2 i}{1-(1-i)^2}\)
= \(\frac{1+2 i}{1-1+2 i-i^2}\)
= \(\frac{1+2 i}{2 i+1}\) = 1
Arg z = 0.
![]()
II.
Question 1.
Simplify the following complex nunibers and find their modulus.
i) \(\frac{(2+4 i)(-1+2 i)}{(-1-i)(3-i)}\)
ii) \(\frac{(1+i)^3}{(2+i)(1+2 i)}\)
Solution:
i) \(\frac{(2+4 i)(-1+2 i)}{(-1-i)(3-i)}\)
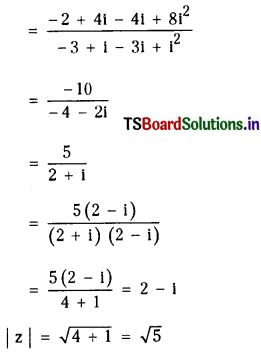
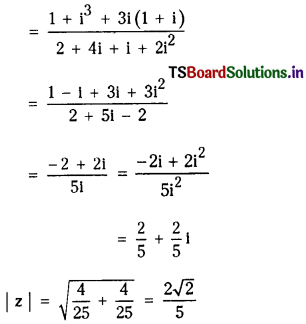
ii) z = \(\frac{(1+i)^3}{(2+i)(1+2 i)}\)
![]()
Question 2.
i) If(1 – i) (2 – i) (3 – i) …………. (1 – ni) = x – iy then prove that 2 . 5 . 10 ….. (1 + n2) = x2 + y2.
ii) If the real part of \(\frac{z+1}{z+i}\) is 1,then find the locus of z.
locus of z.
iii) If |z – 3 + i| = 4 determine the locus of z.
iv) If |z + ai| = |z – ai| then find the locus of z.
Solution:
i) (1 – i) (2 – i) (3 – i) ……….. (1 – ni) = x – iy
Taking modulus both sides
|(1 – i)| |(2 – i)| …………… |1 – ni| = |x – iy|
√2 . √5 ………….. \(\sqrt{1+n^2}=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)
2 . 5 . ………………… . (1 + n2) = x2 + y2
ii) \(\frac{z+1}{z+i}\)
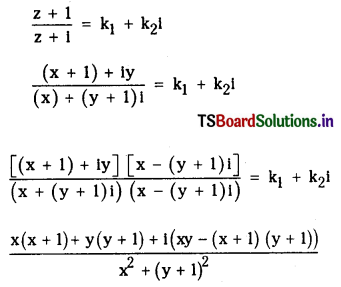
= k1 + k2i
Here k1 = 1
x2 + y2 + x + y = x2 + (y + 1)2
x2 + y2 + x + y – x2 + y2 + 2y + 1
x – y = 1
iii) |z – 3 + i| = 4
|(x – 3) + 1(y + 1)| = 4
(x – 3)2 +(y + 1)2 = 16
x2 + y2 – 6x + 2y + 10 = 16
x2 + y2 – 6x + 2y – 6 = 0
iv) If |z+ ai| = |z – ai|
|x + (y – a)i| = |x + (y – a)i|
x2 + (y + a)2 = x2.(y – a)2
y = 0.
![]()
Question 3.
lf z = x + iy and if the point P in the Argand plane represents z, then describe geometrically the locus of P satisfyIng the equations
i) |2z – 3| = 7
ii) |z|2 = 4 Re (z + 2)
iii) |z + i|2 – |z – i|2 = 2
iv) |z + 4i| + |z – 4| = 10
Solution:
i) |2z – 1| = 7
|2(x) – 3 + 2yi| = 7
\(\sqrt{(2 x-3)^2+4 y^2}\) = 7
4x2 – 12x + 9 + 4y = 49
4x2 + 4y2 – 12x – 40 = 0
x2 + y2 – 3x – 10 = 0.
Centre (\(\frac{3}{2}\), 0) radius = \(\frac{7}{2}\).
ii) |z|2 = 4 Re (z + 2)
x2 + y2 = 4 (x + 2)
x2 + y2 – 4x – 8 = 0
Circle centre (2, 0),
Radius = √12 = 2√3.
iii) |z + i|2 – |z – i|2 = 2
(x)2 + (y + 1)2 – x2 – (y – 1)2 = 2
4y = 2
2y = 1
⇒ 2y – 1 = 0.
Line parallel to x-axis.
iv) |z + 4i| + |z – 4i| = 10
|(x + (y + 4)i)| + |(x + (y – 4)i| = 10
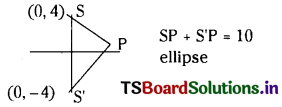
\(\sqrt{x^2+(y+4)^2}+\sqrt{x^2+(y-4)^2}\) = 10
x2 + (y + 4)2 = (10 – \(\sqrt{x^2+(y-4)^2}\))2
x2 + (y + 4)2 = 1oo + x2 + (y – 4)2 – 20\(\sqrt{x^2+(y-4)^2}\)
Solving we get
25x2 + 9y2 = 225 is ellipse
centre (0,0),
eccentricity = e = \(\sqrt{\frac{a^2-b^2}{a^2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{25-9}{25}}\)
e = \(\frac{4}{5}\).
![]()
Question 4.
If z1, z2 are two non-zero complex numbers satisfying
i) |z1 + z2| = |z1| + |z2| then show that Arg z1 – Arg z2 = 0.
ii) If z = x + iy and the point P represents z in the Argand plane and \(\left|\frac{\mathbf{z}-\mathbf{a}}{\mathbf{z}+\mathbf{a}}\right|\) = 1. Re(a) ≠ 0 then find the locus of P.
Solution:
i) |z1 + z2| = |z1| + |z2|
Squaring both sides
|z1 + z2|2 = (|z1| + |z2|)2
(z1 + z2) \(\left(\bar{z}_1+\bar{z}_2\right)\) = |z1|2 + |z2|2 + 2|z1| |z2|
z1\(\bar{z}_1\) + z2\(\bar{z}_2\) + z1\(\bar{z}_2\) + z2\(\bar{z}_1\) = |z1| + |z2| + 2|z1| |z2|
(x1 + iy1) (x2 – iy2) + (x2 + iy2) (x1 – iy1) = 2
2 (x1x2 + y1y2) + i (y1x2 – x1y2 + x1y2 – y1x2) = 2 \(\sqrt{\mathrm{x}_1^2+\mathrm{y}_1^2} \sqrt{\mathrm{x}_2^2+\mathrm{y}_2^2}\)
Squaring on both sides we get
(x1x2 + y1y2)2 = (x12 + y12) (x22 + y22)
(x1y2 – y1x2)2 = 0
\(\frac{\mathrm{y}_2}{\mathrm{x}_2}=\frac{\mathrm{y}_1}{\mathrm{x}_1}\)
∴ Arg z1 – Arg z2 = 0.
ii) |z – a| = |z + a|
Squaring on both sides (x – a)2 + y2 = (x + a)2 + y2
4xa = 0
x = 0
Parallel to y – axis.