Here students can locate TS Inter 1st Year Economics Notes Chapter 2 Theories of Consumer Behaviour to prepare for their exam.
TS Inter 1st Year Economics Notes Chapter 2 Theories of Consumer Behaviour
→ Utility means wanting satisfying power of a thing, measurement of utility can be two types: 1. Cardinal utility 2. Ordinal utility.
→ Cardinal utility was developed by Alfred Marshall. According to the cardinal utility approach, a utility can be measured in terms of numbers like 1, 2, 3, 4 etc.
![]()
→ Ordinal utility approach was developed by R.J.D. Hicks & Allen. According to this approach, utility is subjective. So, it is not possible to measure in terms of numbers. They are ranked 1st, 2nd, 3rd etc.
→ The law of Diminishing marginal utility was developed by H.H. Gossen in 1854 and later it was popularised by Marshall. This law shows the relationship between the quantity of a thing consumed and its marginal utility. If a consumer goes on consuming a commodity then the satisfaction that derives from its additional units declines.
→ The law of Equi-Marginal Utility explains as to how a consumer distributes his limited income among various commodities to get maximum satisfaction. The consumer will be in equilibrium when the following condition is satisfied :
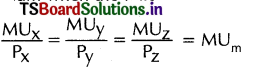
→ Indifference curve is a technique based on the ordinal utility approach. Ic represents the satisfaction of a consumer from two goods.
→ MRS is the rate at which an individual exchanges successive units of one commodity for another.
→ A set of indifference curves drawn for different income levels is called as an indifference map.
→ Consumer equilibrium is a point where the consumer gets maximum satisfaction from two goods.
TS Inter 1st Year Economics Notes Chapter 2 ప్రవర్తనా సిద్ధాంతాలు
→ ఒక వస్తువుకు ఉండే మానవుని కోరికను తీర్చగలిగే శక్తిని ప్రయోజనం అంటారు.
→ వివిధ వస్తువుల నుంచి పొందే ప్రయోజనాలను యుటిల్స్ అనే ఊహాత్మక యూనిట్ల ద్వారా కొలవడానికి వీలుంది. దీనిని అభివృద్ధిపరచినది మార్షల్. 1, 2, 3 మొదలగు సంఖ్యలను కార్డినల్ సంఖ్యలు అంటారు. వీటి ద్వారా వినియోగదారుని ప్రయోజనమును కొలవవచ్చు.
![]()
→ వస్తువు అన్ని యూనిట్ల వినియోగం ద్వారా పొందగలిగే మొత్తం తృప్తిని మొత్తం ప్రయోజనం అంటారు.
→ వినియోగదారుడు అదనంగా వస్తువు యూనిట్ను ఉపయోగించడం వల్ల మొత్తం ప్రయోజనంలో కలిగే మార్పు MO = ΔTU/ΔQ
→ క్షీణోపాంత ప్రయోజన సూత్రంను గాసెన్ మొదటి సూత్రం అంటారు. ఇది వస్తు పరిమాణానికి, ప్రయోజనానికి మధ్య ఉన్న సంబంధాన్ని గూర్చి తెలుపును. ఒకే రకమైన వస్తువును వినియోగదారుడు క్రమంగా ఎక్కువగా వినియోగిస్తూ ఉంటే, మొత్తం ప్రయోజనం ఒక దశ వరకు పెరిగి, ఆ తరువాత తగ్గుతుంది.
→ సమోపాంత ప్రయోజన సూత్రాన్ని గాసెన్ ద్వితీయ సూత్రం అని కూడా అంటారు. వినియోగదారుడు తన పరిమితమైన ఆదాయాన్ని ఖర్చుచేసి ఏ విధంగా గరిష్ట ప్రయోజనం పొందుతాడో తెలియజేసేది.
→ కార్డినల్ విశ్లేషణలో ప్రయోజనం అనేది మానసికపరమైంది. అందువల్ల దాన్ని సంఖ్యా రూపంలో కొలవడానికి సాధ్యం కాదు. అందువల్ల R.J.D. హిక్స్ మరియు అలెన్ ఆర్డినల్ విశ్లేషణ ద్వారా వినియోగదారుని ప్రవర్తనను తెలియజేశారు. ఈ విశ్లేషణలో వినియోదారు తనకు లభ్యమైన వివిధ వస్తు సముదాయాలకు ర్యాంకులు 1, 2, 3 మొదలైనవి ఇవ్వడం ద్వారా వాటన్నిటిని క్రమ పద్ధతిలో ఏర్పరచుకుంటారు.
![]()
→ వినియోగదారుడు కొనుగోలు చేసే రెండు వస్తువుల వివిధ సమ్మేళనాలను తెలియజేసే బిందువులను కలుపగా ఏర్పడే రేఖలను “ఉదాసీనతా వక్రరేఖ” అంటారు. దీని ద్వారా కూడా వినియోగదారుని ప్రయోజనాన్ని కొలవవచ్చు.