Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 5th Lesson Cash Book Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 5th Lesson Cash Book
Essay Questions:
Question 1.
Explain the importance of Cash book.
Answer:
Cash book is essential to record all cash receipts and cash payments of organization to reveal the cash balance of organization on a particular date.
Cash book provides all information regarding cash position of the business organization for a particular period. So, that effective policy for cash control can be formulated by the management.
The following advantages, regarded as an importance of Cash Book :
- It helps to record all cash receipts and payments of organization on daily basis.
- It gives the cash and Bank balances of organization at any given period of time.
- It helps to verify the actual cash balance with the balance shown by the cash book. If any variation, mistakes and frauds can be detected easily.
- It helps to reconcile the bank balance as per the pass book with the balance shown by bank column of cash book.
- As cash book acts as Cash account, Preparation of separate cash account is not required. So, it will save the time and efforts.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the different types of Cash book.
Answer:
The form of the cash book depends on the need, nature and scope of activities of a business firm. Normally, the cash book is of the following types.
- Simple cash book.
- Double column cash book.
i) Containing cash and discount columns.
ii) Containing Bank and discount columns. - Triple column cash book (cash, bank and discount columns)
- Petty cash book.
1. Simple Cash Book :
The simple cash book is maintained, usually, by newly started business firms, where trade activities are limited. Only cash transactions are recorded in this book. So, it is called “Single column cash book”. The balance of the account must be found out as done in other accounts. This book is balanced everyday.
2. Double column cash book :
i) Cash book with cash and discount columns :
The transactions pertaining to cash and cash discounts are also recorded. That is why, it is called “Double column cash book”. Cash discount is the discount allowed by a debtor to creditor as an incentives for prompt payment. When the trader receives some rebate in the form of cash from the creditor. This is treated as cash discount received. In the same way, the rebate given by the creditor is treated as discount allowed. Along with cash column, discount column is maintained on both the debit side and credit side of the cash book.
ii) Cash book with bank and discount columns :
The transactions are usually carried out through banks. The payments and receipts are usually made through cheques. When cash of cheques deposited in the bank are recorded on the debit side and the cheques are drawn are shown on the credit side. The discount received is shown on the credit side and discount allowed is recorded the debit side.
3. Triple column cash book:
All business firms deals largely with the banks, they prepare a cash book containing cash, bank and discount columns. So, this book is called “Triple column cash book”.
4. Petty cash book :
It is a cash book where all petty expenses are recorded. It is maintained by the petty cashier. Petty cashier receives a voucher for every payment be makes. The serial number to all the vouchers are preserve by him for future reference.
![]()
Question 3.
Draw the format of Triple column cash book and explain the various important points to be noted in preparation of Triple colum cash book.
Answer:
Formate of Triple column cash book :
As the business firms largely deals with the banks, they prepare a cash book containing cash, bank and discount columns. So, this book is called “Triple column cash book”.
The modern organisations, in which the cash transactions are made amounts deal with the banks. The three column cash book is useful to the big trading organisations in the follows ways.
- It helps to record cash receipts and receipts through cheques.
- It is useful to record cash payments and payments by cheques.
- It helps to record large number of cash and bank transactions of different nature.
- Interest can be earned by deposting the cash balance in the bank.
Important points to be noted in preparation of three column cash book :
Points to be followed in the preparation of three column cash book are given below.
- Opening cash and bank balances are recorded on the debit side of the cash and bank columns. The opening balances to be written as To Balance b/’d in the particular column.
- All cash receipts are entered on the debit side of the cash book in the cash column and payments in cash on the credit side of the cash book in cash column.
- Amount paid into bank are recorded on the debit side in the bank column and on the credit side of the cash column. This is a contra entry side of the cash column. This is a contra entry.
- All payments made by cheques are entered in the bank column of the cash book credit side.
- When the cash is withdrawn from the bank for office use, it is recorded in the cash column on the debit side and bank column on the credit side. This is also a contra entry.
- All cheques received are entered first entered in the cash column on the debit side, because cheques received are treated as cash received. Subsequently when these cheques are sent to the bank for collection, they are treated similar to cash deposited in the bank.
- If the cheque is received from the customer is sent to the bank for collection on the same day, it is entered in the bank column on the debit side.
- If discounts are involved either in cash or bank transactions the amount of discount allowed received are recorded on the debit side or credit side of the discount column in the cash book.
![]()
Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Explain the advantages of Cash book.
Answer:
The following are the advantages of cash book :
- It helps to know the amount of cash received and the amount of cash paid by the business firm.
- It helps to know the cash and bank balance of the business at any time.
- Mistakes and frauds can be detected by verifying the closing balance of the cash book with the actual amount of cash in hand.
- Cash books serves as a journal as well as ledger. No separate cash account is needed.
Question 2.
State the characteristics of Cash book.
Answer:
The following are the characteristics of cash book :
- The cash book can also be treated as subsidiary book.
- Only cash transactions are recorded.
- It serves as a cash account.
- It records all cash receipts on the debit side and cash payments on the credit s ide.
- Cash book will show debit balance only.
![]()
Question 3.
Distinguish between trade discount and cash discount.
Answer:
The differences between the Trade discount and Cash discount are given below :
Differences between Trade Discount and Cash Discount:
| Trade Discount | Cash Discount |
| 1. It is allowed by seller to the buyer at the time of selling the goods. | 1. It is allowed by the creditor to the debtor at the settlement of due. |
| 2. It is shown in the Invoice or bill. | 2. It is not shown in the Invoice or bill. |
| 3. It is given to increase the sales volume. | 3. It is given to get early and prompt payment from the debtor. |
| 4. It is given on the catalogue price of the product. | 4. It is given on the due amount of the debtor. |
| 5. It is deducted from the catalogue price only. It is not recorded specially in the books of accounts. | 5. It is specially shown in the books of the accounts. |
Question 4.
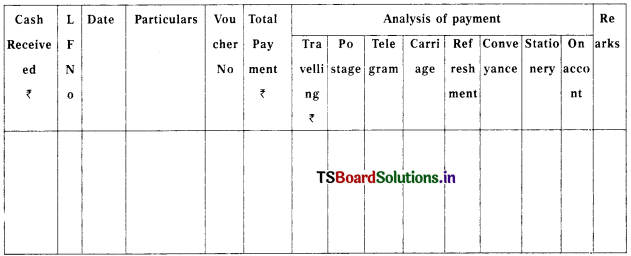
Draw the format of petty cash book.
Answer:
Format of Analytical Petty Cash Book :
Analytical Petty Cash
![]()
Very Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Cash Discount.
Answer:
- If a debtor clears his debit before or on the date specified he may receive some rebate in the form of cash from the creditor.
- This is treated as cash discount received by the debtor. In the same way, the rebate given by the creditor is treated as discount allowed. The discount column is maintained on both sides of the cash book.
Question 2.
Discount Allowed.
Answer:
- Discount given or allowed by the trader for settlement of due from his debtors is known as discount allowed.
- It is recorded on the debit side in discount column of the cash book.
Question 3.
Discount received.
Answer:
- If a debtor pays the amount before or on the due date, he may receive rebate in the form of cash. This is known as discount received.
- It is recorded on the credit side discount column of the cash book.
![]()
Question 4.
Contra Entry.
Answer:
- The entry which effects the both sides of Triple column cash book is known as Contra Entry.
- Contra Entry is denoted with “C” in L.F column against the entry. Generally, it is indicated with Red ink.
- In following cases, Contra Entries will arise, when the cash is deposited or paid into bank, When the cash is withdrawn from the bank for office use, When the cheque is received on one day and deposited on another day.
Question 5.
Imprest System.
Answer:
- Under this system, the petty cashier receives from the head cashier at the begining of the month sum money called petty cash imprest.
- The petty cashier makes petty cash payments and enters these transactions in the petty cash book.
- At the end of the month, the balances in the book is checked by the head cashier and advance the exact amount which is spent by the petty cashier.
![]()
Problems:
Question 1.
Prepare Single column cash book of “M/s. MANASVI” Traders from the following particulars.
2019 Jan.
Jan. 1st Business commenced with – ₹ 20,000
Jan. 3rd Sales – ₹ 5,000
Jan. 6th Cash paid into bank – ₹ 2,000
Jan. 10th Purchased machinery – ₹ 1,800
Jan. 14th Advertisement expenses paid – ₹ 600
Jan. 17th Drawings – ₹ 300
Jan. 19th Cash purchases – ₹ 5,000
Jan. 21st Sold goods to Naresh on credit – ₹ 3,000
Jan. 23rd Commission received – ₹ 800
Jan. 25th Paid to Shyam – ₹ 3,500
Jan. 28th Received rent – ₹ 1,200
Solution:
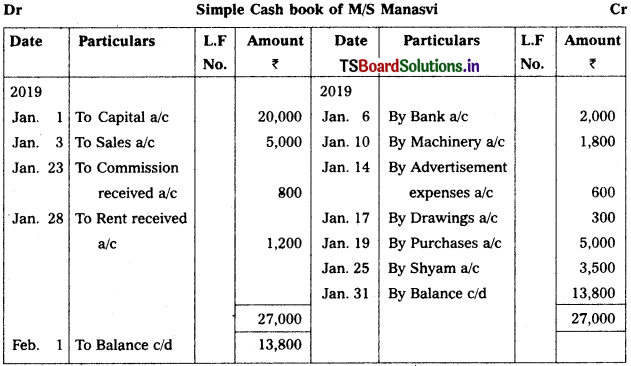
Note : On 21st 2019 is a credit transaction which is not recorded in cashbook.
Question 2.
Enter the following transactions in Single column cash book of Praveen traders.
2019 April
April 1st Cash balance – ₹ 12,000
April 2nd Purchased goods or cash – ₹ 3,000
April 4th Purchased furniture – ₹ 10,000
April 8th Cash received from Ajay – ₹ 5,500
April 12th Telephone bill – ₹ 600
April 14th Sold goods to Nikhil – ₹ 2,500
April 16th Interest paid – ₹ 300
April 18th Purchased stationery – ₹ 1,200
April 21st Cash sales – ₹ 4,000
April 25th Postage – ₹ 400
April 28th Paid to Tarun – ₹ 3,000
Answer:
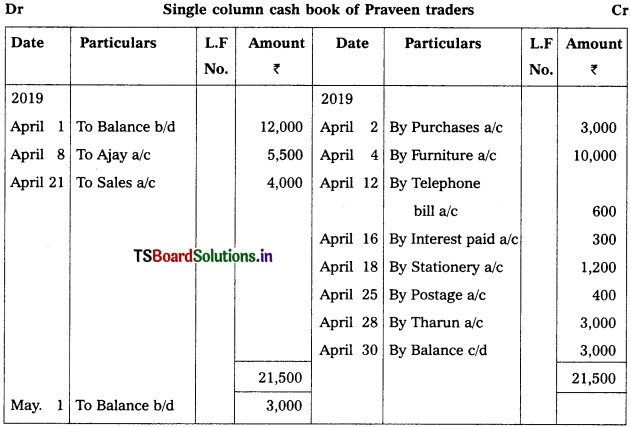
Note:
On April 14th it is a credit transaction which is not recorded in cash book.
![]()
Question 3.
Prepare Simple cash book as on 31.03.2019.
2019 Mar.
Mar. 1st Brought cash into business – ₹ 14,000
Mar. 3rd Cash Sales – ₹ 2,000
Mar. 6th Cash paid into bank – ₹ 5,000
Mar. 8th Purchased goods from Varun for cash – ₹ 1,500
Mar. 12th Xerox charges – ₹ 500
Mar. 15th Salaries – ₹ 1,400
Mar. 17th Interest received – ₹ 200
Mar. 21st Office expenses – ₹ 400
Mar. 25th Travelling expenses – ₹ 800
Mar. 27th Sold furniture – ₹ 8,500
Mar. 28th Drawings – ₹ 700
Mar. 30th Credit purchases from Raghu – ₹ 4,000
Mar. 31st Purchases – ₹ 3,000
Solution:
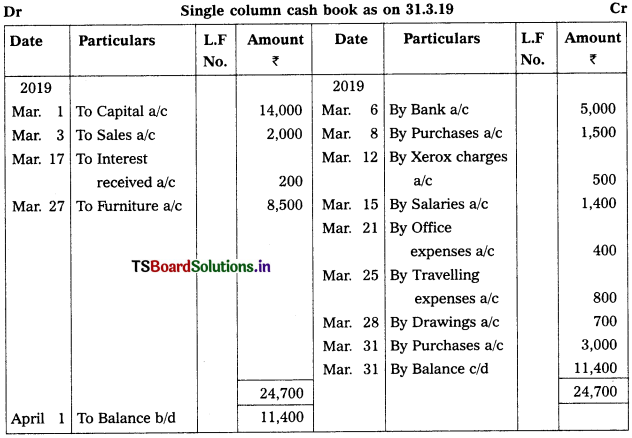
Note:
On 30th March 2019, its a credit transaction. It should not be recorded in cash book.
Question 4.
Record the following transactions in Itoo column cash book.
2018 Aug.
Aug. 1st Cash balance – ₹ 11,000
Aug. 2nd Purchases – ₹ 1,500
Aug. 4th Cash received from Prabhakar – ₹ 1,250
Discount allowed – ₹ 50
Aug. 7th Cash sales – ₹ 2,000
Aug. 10th Sundry expenses – ₹ 800
Aug. 12th Paid to Vamshi – ₹ 1,400
Discount received – ₹ 100
Aug. 14th Sold old machinery – ₹ 5,000
Aug. 16th Received from Anil – ₹ 425
Discount allowed – ₹ 75
Aug. 21st Commission paid – ₹ 300
Aug. 23rd Travelling expenses – ₹ 250
Aug. 25th Received interest – ₹ 125
Solution:
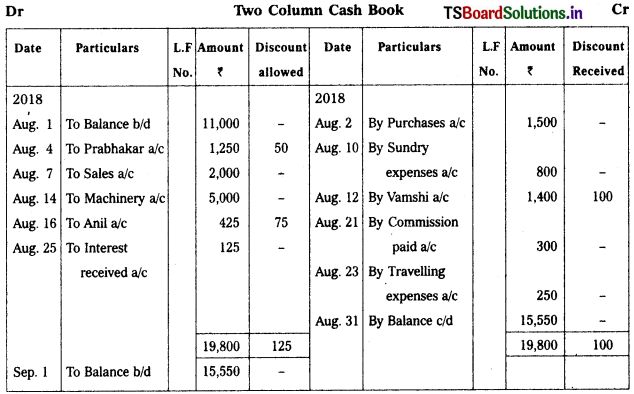
![]()
Question 5.
Prepare Double column cash book as on 31.03.2018. 4
2018 Mar.
Mar. 1st Cash in hand – ₹ 7,500
Mar. 3rd Drawings – ₹ 1,250
Mar. 6th Cash Sales – ₹ 6,000
Mar. 7th Paid cash to Swathi – ₹ 1,850
Discount Received – ₹ 150
Mar. 9th Sold goods to Ram on credit – ₹ 3,000
Mar. 10th Cash withdrawn from Bank – ₹ 1,400
Mar. 12th Paid for postage – ₹ 200
Mar. 14th Received cash from Anitha – ₹ 600
Discount allowed – ₹ 100
Mar. 16th Received commission – ₹ 450
Mar. 18th Cash paid to Neeraja – ₹ 2,850
Discount received – ₹ 150
Mar. 20th Paid interest – ₹ 1,200
Mar. 21st Salaries – ₹ 600
Solution:
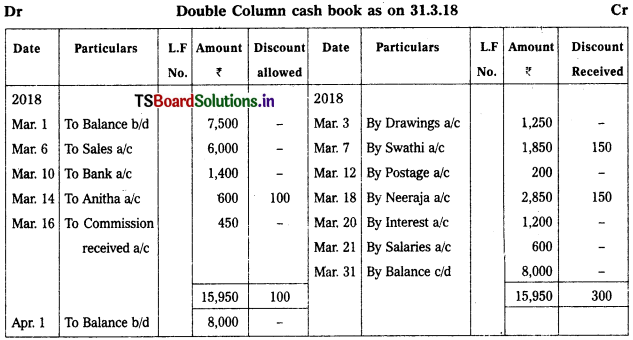
Note:
On 2018, March 9th is the credit transaction which is not be recorded in cash book.
Question 6.
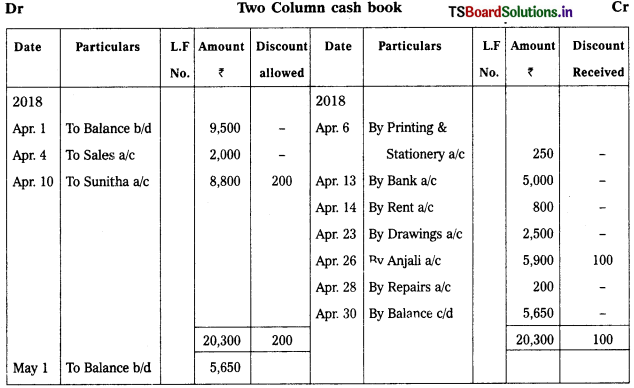
Prepare Two column cash book from the following.
2018 April
April 1st Opening balance – ₹ 9,500
April 4th Cash sales – ₹ 2,000
April 6th Printing & Stationery – ₹ 250
April 10th Cash received from Sunitha – ₹ 8,800
Discount allowed – ₹ 200
April 13th Cash deposited into bank – ₹ 5,000
April 14th Paid rent to land lord – ₹ 800
April 19th Bought furniture from Anjali – ₹ 6,000
April 23rd Cash drawn form personal use – ₹ 2,500
April 26th Cash paid to Anjali – ₹ 5,900
In full settlement of her account ₹ 6,000
April 28th Paid for repairs – ₹ 200
Solution:
Note :
On 19th april 2018, it is a credit transaction which is not be recorded in cash book.
![]()
Question 7.
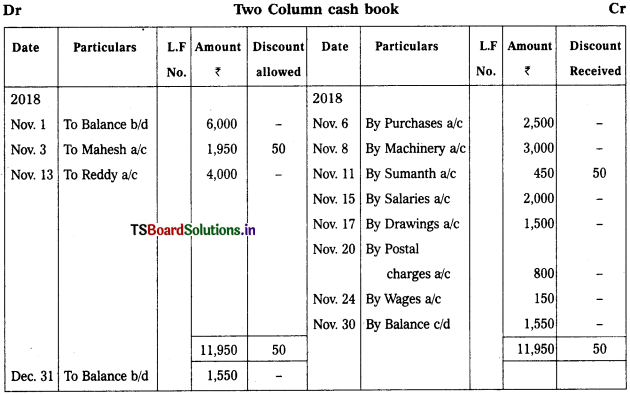
Prepare Two column cash books with bank and discount column from the following. Assume that all the cash receipts are deposited in the bank and all payments are made through cheques.
2018 Nov.
Nov. 1st Opening balance – ₹ 6,000
Nov. 3rd Cheque received from Mahesh – ₹ 1,950
Discount allowed – ₹ 50
Nov. 6th Purchases – ₹ 2,500
Nov. 8th Purchased machinery and payment made by cheque – ₹ 3,000
Nov. 11th Paid to Sumanth by Cheque – ₹ 450
In full settlement of his account – ₹ 500
Nov. 13th Sold goods to Reddy and received cheque – ₹ 4,000
Nov. 15th Paid salaries by cheque – ₹ 2,000
Nov. 17th Withdrawn from bank for personal use – ₹ 1,500
Nov. 20th Postal charges – ₹ 800
Nov. 24th Wages paid – ₹ 150
Solution:
Question 8.
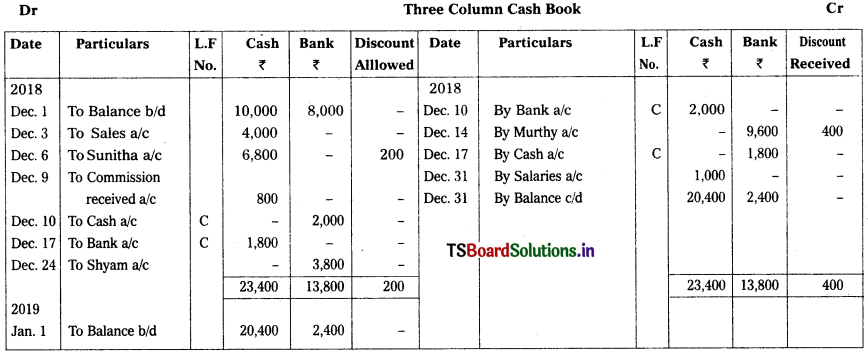
Prepare Triple column cash book.
2018 Dec.
Dec. 1st Cash In hand – ₹ 10,000
Cash at bank – ₹ 8,000
Dec. 3rd Sales – ₹ 4,000
Dec. 6th Cash received from Sunitha – ₹ 6,800
Discount allowed – ₹ 200
Dec. 9th Commission received – ₹ 800
Dec. 10th Cash deposited into bank – ₹ 2,000
Dec. 14th Cheque issued to Murthy – ₹ 9,600
Discount received – ₹ 400
Dec. 17th Withdrawn cash from bank for office use – ₹ 1,800
Dec. 20th Goods purchased from Rohith – ₹ 3,500
Dec. 24th Received cheque from Shyam (Deposited in the bank) – ₹ 3,800
Dec. 31st Salaries – ₹ 1,000
Solution:
![]()
Question 9.
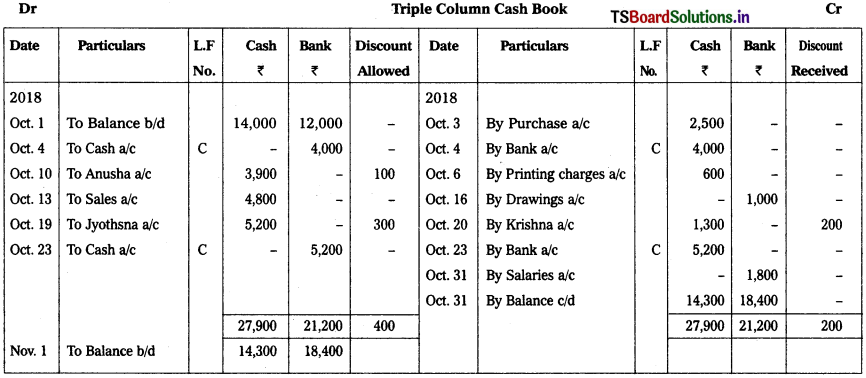
Prepare Triple column cash book from the following particulars.
2018 Oct.
Oct. 1st Cash balance – ₹ 14,000
Bank balance – ₹ 12,000
Oct. 3 Purchases – ₹ 2,500
Oct. 4th Paid into bank – ₹ 4,000
Oct. 6th Printing charges – ₹ 600
Oct. 10th Received from Anusha – ₹ 3,900
Discount allowed – ₹ 100
Oct. 13th Cash sales – ₹ 4,800
Oct. 16th Cash drawn from bank for personal use – ₹ 1,000
Oct. 19th Cheque received from Jyothsna – ₹ 5,200
Discount allowed – ₹ 300
Oct. 20th Paid cash to Krishna – ₹ 1,300
Discount received – ₹ 200
Oct. 23rd Jyothsna’s cheque deposited into bank
Oct. 31st Salaries paid by cheque – ₹ 1,800
Solution:
Question 10.
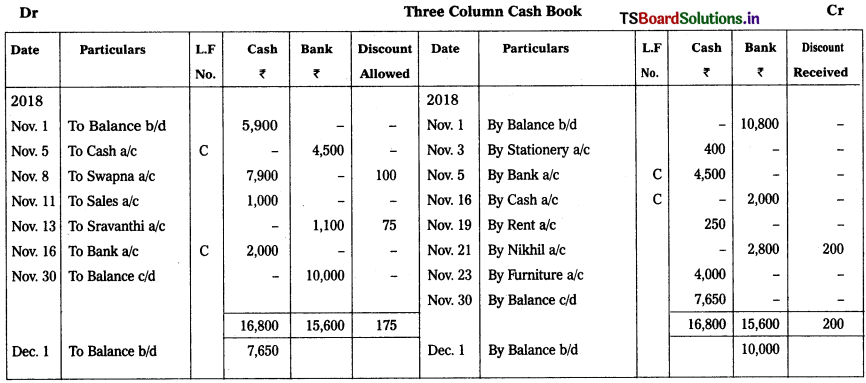
Prepare cash book with Cash Bank and Discount Columns from the following:
2018 Nov.
Nov. 1st Cash in hand – ₹ 5,900
Bank overdraft – ₹ 10,800
Nov. 3rd Paid for Stationery – ₹ 400
Nov. 5th Deposited into bank – ₹ 4,500
Nov. 8th Received cash from Swapna – ₹ 7,900
Discount allowed – ₹ 100
Nov. 11th Goods sold for cash – ₹ 1,000
Nov. 13th Received cheque from Sravanthi – ₹ 1,100
Discount allowed – ₹ 75 (Deposited into bank)
Nov. 16th Cash withdrawn from bank – ₹ 2,000
Nov. 19th Paid rent – ₹ 250
Nov. 21st Issued cheque to Nikhil – ₹ 2,800
Discount received – ₹ 200
Nov. 23rd Purchased furniture – ₹ 4,000
Solution:
![]()
Question 11.
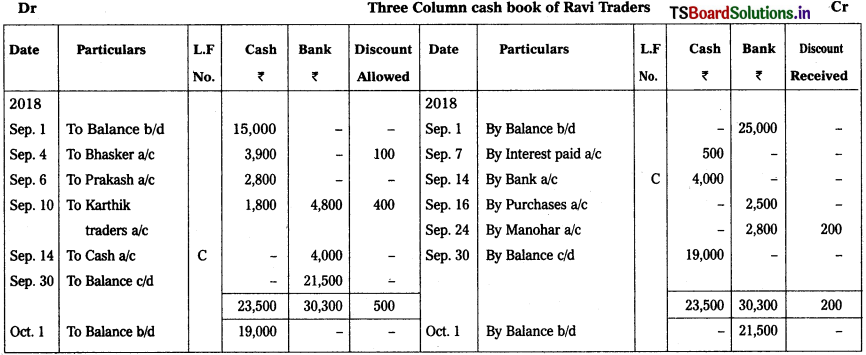
Prepare Three column cash book of Ravi fladers from the following particulars.
2018 Sep.
Sep. 1st Cash balance – ₹ 15,000
Bank balance (Cr.) – ₹ 25,000
Sep. 4th Received cash from Bhasker – ₹ 3,900
In full settlement of his account – ₹ 4,000
Sep. 6th Goods sold to Prakash for cash – ₹ 2,800
Sep. 7th Interest paid – ₹ 500
Sep. 10th Received from Karthik traders
Cash – ₹ 1,800
Cheque – ₹ 4,800
Discount allowed (Cheque sent to bank) – ₹ 400
Sep. 14th Cash deposited into bank – ₹ 4,000
Sep. 16th Purchased goods from Chaitanya and payment made through ‘paytm’ – ₹ 2,500
Sep. 24th Issued cheque to Manohar – ₹ 2,800
Discount received – ₹ 200
Solution:
Question 12.
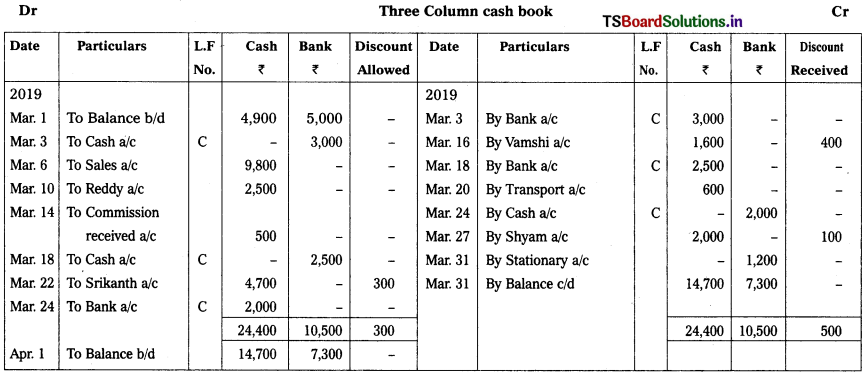
2019 Mar.
Mar. 1st Cash in hand – ₹ 4,900
Cash at bank – ₹ 5,000
Mar. 3rd Deposited cash into bank – ₹ 3,000
Mar. 6th Sales – ₹ 9,800
Mar. 10th Received a cheque from Reddy – ₹ 2,500
Mar. 14th Commission received – ₹ 500
Mar. 16th Paid to Vamshi – ₹ 1,600
Discount received – ₹ 400
Mar. 18th Reddy’s cheque deposited into bank
Mar. 20th Paid for transport – ₹ 600
Mar. 22nd Received cash from Srikanth – ₹ 4,700
Discount allowed 300
Mar. 24th Cash Withdrawn from Bank for office use – ₹ 2,000
Mar. 27th Paid to Shyam – ₹ 2,000
Discount received – ₹ 100
Mar. 31st Purchased stationery and paid through ‘debit card – ₹ 1,200
Solution:
![]()
Question 13.
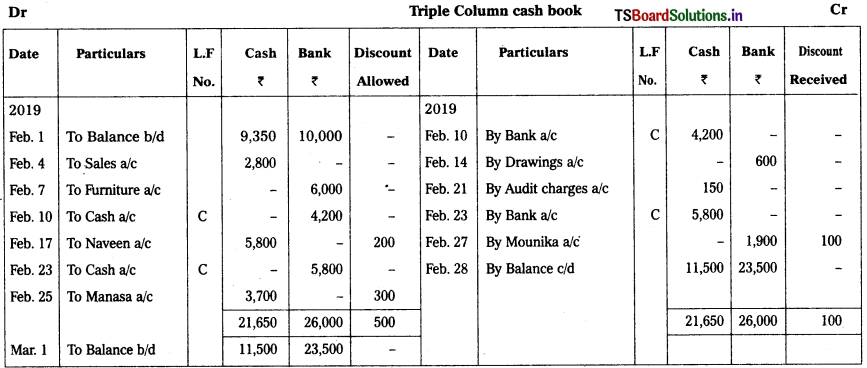
Prepare Triple column cash book from the following transactions.
2019 Feb.
Feb. 1st Cash – ₹ 9,350
Bank – ₹ 10,000
Feb. 4th Cash sales – ₹ 2,800
Feb. 7th Sold furniture and received amount through google pay – ₹ 6,000
Feb. 10th Cash deposited into bank – ₹ 4,200
Feb. 14th Cash withdrawn from bank for personal use – ₹ 600
Feb. 17th Cheque Received from Naveen – ₹ 5,800
Discount allowed – ₹ 200
Feb. 21st Audit charges – ₹ 150
Feb. 23rd Naveen’s cheque deposited into bank
Feb. 25th Received cash from Manasa – ₹ 3,700
Discount allowed – ₹ 300
Feb. 27th Paid to Mounika through cheque – ₹ 1,900
In full settlement of her account – ₹ 2,000
Solution:
Question 14.
Record the following transactions in cash book with Cash, Bank and Discount columns.
2019 April
April 1st Cash balance – ₹ 8,000
Bank balance – ₹ 14,000
April 3rd Issued cheque to Rahul – ₹ 1,450
Discount received – ₹ 50
April 6th Sales through Net banking – ₹ 2,800
April 9th Withdrawn cash from bank – ₹ 2,900
April 11th Received a cheque from Raju – ₹ 1,450
In full settlement of his account – ₹ 1,500 (Cheques sent to bank)
April 16th Purchases through ‘Debit Card’ – ₹ 2,400
April 19th Paid cash into bank – ₹ 800
April 24th Purchased machinery – ₹ 4,000
April 26th Received cash from Shekar – ₹ 350
Discount allowed – ₹ 50
April 28th Salaries – ₹ 650
April 30th Cash withdrawn from bank for personal use – ₹ 2,300
Solution:
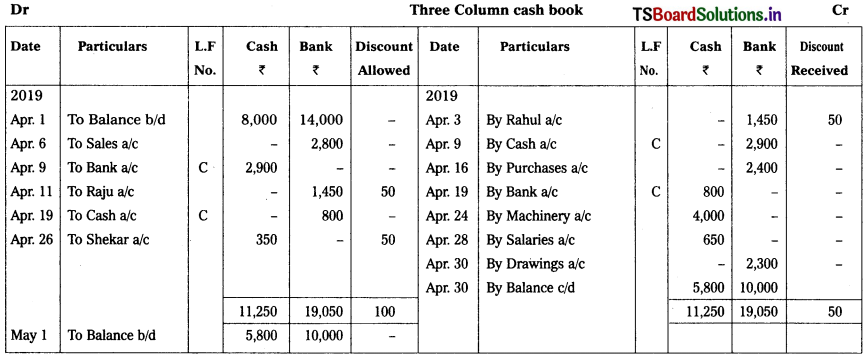
![]()
Question 15.
Prepare Triple column cash book from the following transactions.
2018 June
June 1st Cash in hand – ₹ 12,500
Cash at bank – ₹ 14,800
June 3rd Cash sales – ₹ 3,000
June 7th Purchased goods from Ashok and paid by cheque – ₹ 5,000
June 10th Cash paid into bank – ₹ 1,800
June 12th Cash paid to Laxmi – ₹ 1,850
Discount received – ₹ 240
June 16th Cash withdrawn from bank for office use – ₹ 2,000
June 19th Sold machinery and amount received through ‘paytm’ – ₹ 2,400
June 25th Advertisement expenses – ₹ 150
June 28th Received cheque from Vishnus – ₹ 1,980
Discount allowed – ₹ 120 (Vishnu’s cheque deposited to bank)
June 30th Salaries paid by cheque – ₹ 3,280
Solution:
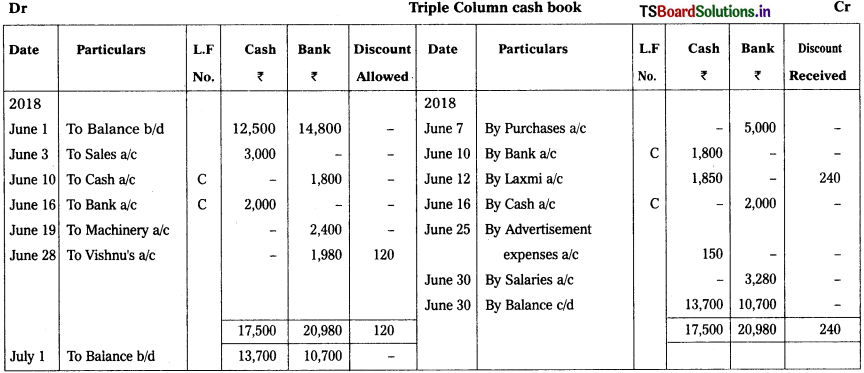
Question 16.
Prepare Three column cash book from the following particulars.
2018 July
July 1st Cash in hand – ₹ 6,000
Cash at bank – ₹ 10,000
July 5th Cash sales – ₹ 1,900
July 7th Issued cheque to D-Mart – ₹ 1,800
Discount received – ₹ 200
July 8th Received cash from Sai Traders – ₹ 1,850
July 14th Cash withdrawn from bank for office use – ₹ 550
July 22nd Cash purchases – ₹ 600
July 29th Paid into bank – ₹ 800
July 30th Salaries paid by cheque – ₹ 2,400
July 31st Bank charges as per bank Pass Book – ₹ 50
Discount allowed – ₹ 150
Solution:
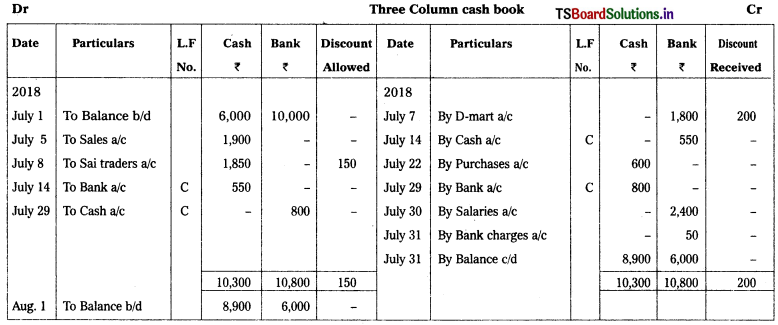
![]()
Question 17.
Prepare Triple column cash book.
2019 Feb.
Feb. 1st Cash balance – ₹ 12,000
Bank balance – ₹ 8,ooo
Feb. 3rd Issued cheque to Rama – ₹ 3,950
Discount – ₹ 50 (Cheque deposited with bank)
Feb. 6 Cash sales – ₹ 4,500
Feb. 10th Cash deposited into bank – ₹ 2,500
Feb. 18’s Received cash from Moban – ₹ 2,800
Cheque – ₹ 5,800
Discount – ₹ 400
Feb. 20’s’ Purchases – ₹ 3,400
Feb. 23 Mohans cheque dishonored
Feb. 24th Rent paid by cheque – ₹ 1,000
Feb. 28th Drew from bank for office use – ₹ 1,600
Solution:
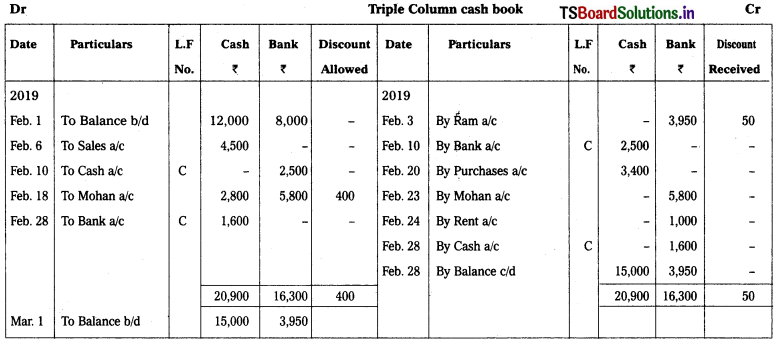
Question 18.
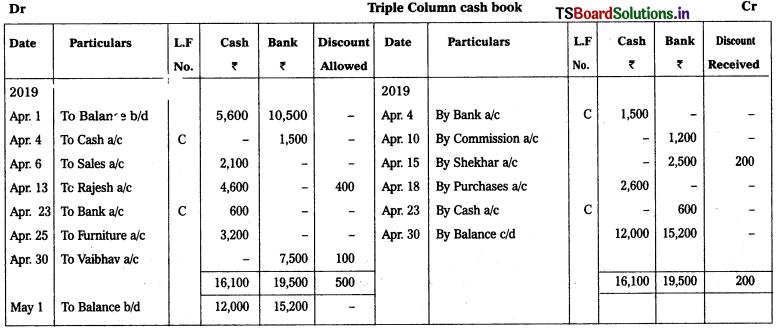
Prepare Triple column cash book.
2019 April
April 1 Cash in hand – ₹ 5,600
Cash at bank (Dr) – ₹ 10,500
April 4th Cash deposited into bank – ₹ 1,500
April 6th Cash sales – ₹ 2,100
April 10th Commission paid through ‘paytm’ – ₹ 1,200
April 13th Received cash from Rajesh – ₹ 4,600
Discount allowed – ₹ 400
April 15th Issued cheque to Shekar – ₹ 2,500
Discount received – ₹ 200
April 18th Purchases – ₹ 2,600
April 23rd Cash withdrawn from hank for office use – ₹ 600
April 25th Sold furniture – ₹ 3,200
April 30th Cheque received from Vaibhav – ₹ 7,500
Discount allowed – ₹ 100
(Cheque deposited Into bank)
Solution:
![]()
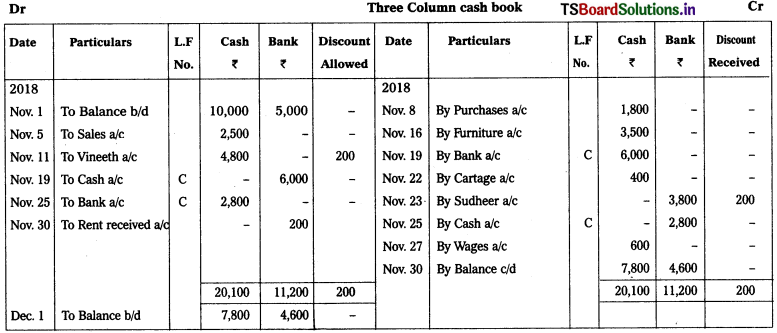
Question 19.
Prepare Triple column cash book.
2018 Nov.
Nov. 1st Cash in hand – ₹ 10,000
Cash at bank (Dr) – ₹ 5,000
Nov. 5th Sales – ₹ 2,500
Nov. 8th Purchases – ₹ 1,800
Nov. 11th Received from Vineeth – ₹ 4,800
Discount allowed – ₹ 200
Nov. 16th Purchased furnitUre for cash – ₹ 3,500
Nov. 19th Deposited into bank – ₹ 6,000
Nov. 22nd Paid cartage – ₹ 400
Nov. 23rd Cheque Issued to Sudheer – ₹ 3,800
In full settlement of his account – ₹ 4000
Nov. 25th Cash withdrawn from bank for office use – ₹ 2,800
Nov. 27th Wages – ₹ 600
Nov. 30th Received rent through ‘paytm’ – ₹ 200
Solution:
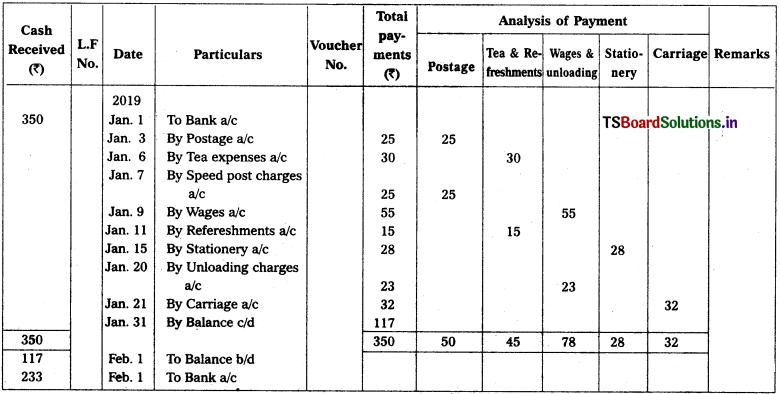
Question 20.
2019 Jan.
Jan. 1st Cheque received from Head Cashier – ₹ 350
Jan. 3rd Postal charges – ₹ 25
Jan. 6th Tea expenses – ₹ 30
Jan. 7th Speed post charges – ₹ 25
Jan. 9th Wages – ₹ 55
Jan. 11th Refreshments – ₹ 15
Jan. 15th Paid for stationery – ₹ 28
Jan. 20th Unloading charges – ₹ 23
Jan. 21st Carnage – ₹ 32
Solution:
Analytical petty cash book
![]()
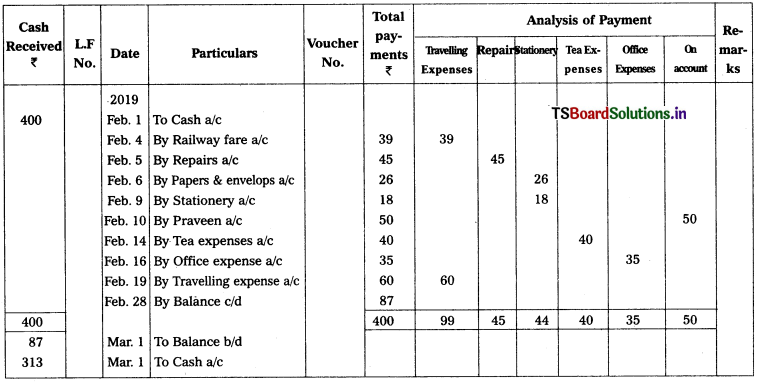
Question 21.
Prepare Analytical petty cash book.
2019 Feb.
Feb. 1st Advance received from Head cashier – ₹ 400
Feb. 4th Paid railway fare – ₹ 39
Feb. 5th Paid repairs – ₹ 45
Feb. 6th Paid for papers and envelops – ₹ 26
Feb. 9th Stationery paid – ₹ 18
Feb. 10 Paid to Praveen on account – ₹ 50
Feb. 14th Tea expenses – ₹ 40
Feb. 16th Paid for office expenses – ₹ 35
Feb. 19th Paid travelling expenses – ₹ 60
Solution:
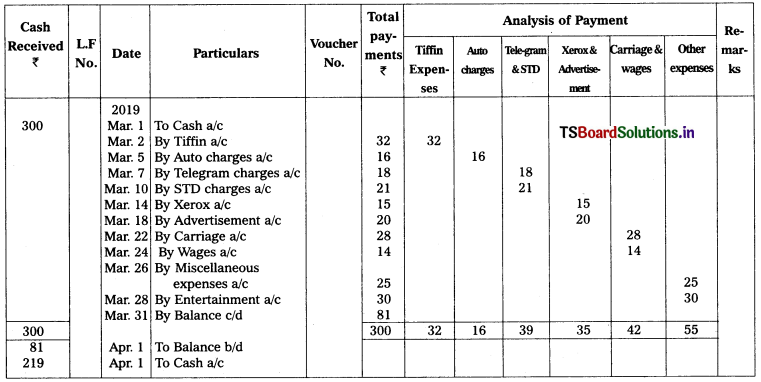
Question 22.
From the following particulars, prepare analytical petty cash bank.
2019 Mar.
Mar. 1st Received from head cashier – ₹ 300
Mar. 2nd Tiffin expenses – ₹ 32
Mar. 5th Auto charges – ₹ 16
Mar. 7th Telegram charges – ₹ 18
Mar. 10th STD Charges – ₹ 21
Mar. 14th Paid for xerox – ₹ 15
Mar. 18th Paid for Advertisement – ₹ 20
Mar. 22nd Carriage paid – ₹ 28
Mar. 24th Wages to office cleaner – ₹ 14
Mar. 26th Paid Miscellaneous expanses – ₹ 25
Mar. 28th Paid for entertainment – ₹ 30
Solution:
![]()
Textual Examples:
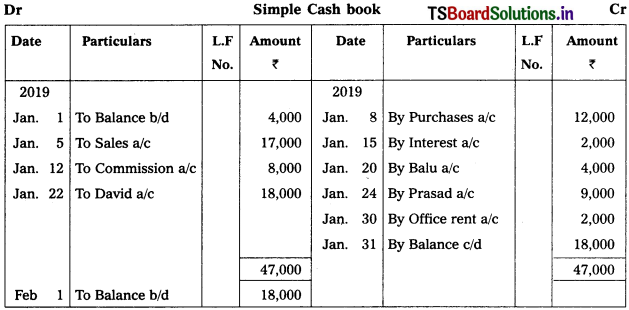
Question 1.
From the following transactions, prepare a simple cash book in the books of Sampath Traders.
2019
Jan. 1 Balance of cash – ₹ 4,000
Jan. 5 Cash sales – ₹ 17,000
Jan. 8 Cash purchases – ₹ 12,000
Jan. 12 Received commission – ₹ 8,000
Jan. 15 Paid interest – ₹ 2,000
Jan. 20 Paid to Balu – ₹ 4,000
Jan. 22 Received from David – ₹ 18,000
Jan. 24 Paid to Prasad – ₹ 9,000
Jan. 30 Paid office rent – ₹ 2,000
Solution:
In the books of Sampath Traders.
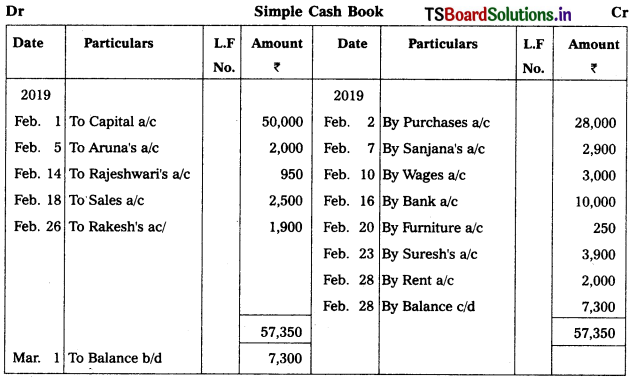
Question 2.
Enter the following transactions in simple cash book.
2019
Feb. 1 Commenced business with a cash – ₹ 50,000
Feb. 2 Purchased goods – ₹ 28,000
Feb. 5 Received cash from Aruna – ₹ 2,000
Feb. 7 Paid cash to Sanjana – ₹ 2,900
Feb. 10 Paid wages – ₹ 3,000
Feb. 14 Received from Rajeshwari – ₹ 950
Feb. 16 Deposited cash into bank – ₹ 10,000
Feb. 18 Cash sales – ₹ 2,500
Feb. 20 Purchased furniture for cash – ₹ 250
Feb. 23 Paid to Suresh – ₹ 3,900
Feb. 26 Received from Rakesh – ₹ 1,900
Feb. 28 Paid rent – ₹ 2,000
Solution:
![]()
Question 3.
Prepare simple cash book from the following transactions.
2019
Feb. 1 Balance of cash – ₹ 7,000
Feb. 10 Bought goods – ₹ 2,500
Feb. 11 Bought goods on credit from Srinu – ₹ 3,000
Feb. 15 Sold goods for cash – ₹ 4,700
Feb. 17 Paid rent – ₹ 1,000
Feb. 18 Withdrawn cash personal use – ₹ 500
Solution:
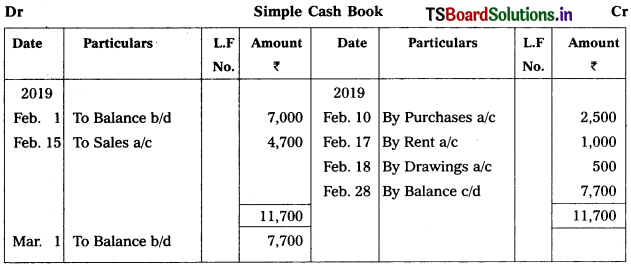
Note :
Transactions dated on 11th Feb. is a credit transaction. It should not be recorded in cash book.
![]()
Question 4.
Prepare cash book with cash and discount columns.
2019
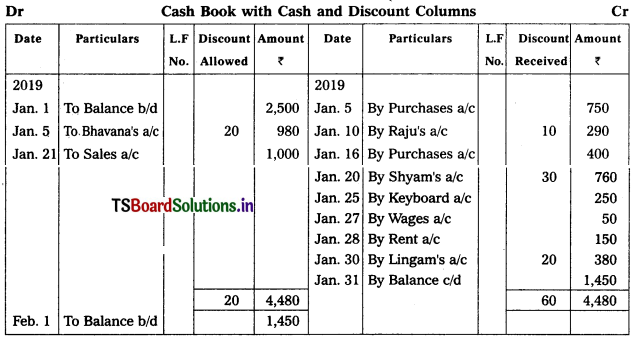
Jan. 1 Balance in hand – ₹ 2,500.
Jan. 5 Purchased goods from Saibabu for cash – ₹ 750.
Jan. 7 Received cash from Bhavana – ₹ 980/- after allowing her discount of ₹ 20/-
Jan. 10 Paid to Raju ? 290/- and received discount of – ₹ 10/-
Jan. 16 Purchased goods for – ₹ 400/-
Jan. 20 Paid to shyam – ₹ 760/- received discount ₹ 30/-
Jan. 21 Sales – ₹ 1,000/-
Jan. 25 Purchased key board for cash ₹ 250/-
Jan. 27 Paid wages – ₹ 50/-
Jan. 28 Paid rent – ₹ 150/-
Jan. 30 Paid to Lingam – ₹ 380/- and received a discount ₹ 20/-
Solution:
Question 5.
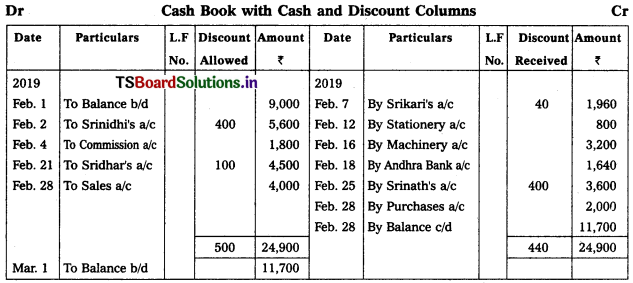
Prepare two column cash book from the following transactions.
2019
Feb. 1 Cash in Hand – ₹ 9,000
Feb. 2 Received cash from Srinidhi – ₹ 5,600
Discount allowed – ₹ 400
Feb. 4 Commission received – ₹ 1,800
Feb. 7 Cash paid to Srikari – ₹ 1,960
Discount allowed by her – ₹ 40
Feb. 12 Paid for stationery – ₹ 800
Feb. 16 Purchased machinery – ₹ 3,200
Feb. 18 Cash deposited in the Andhra Bank a/c – ₹ 1,640
Feb. 21 Received cash from Sridhar – ₹ 4,500
Allowed him discount – ₹ 100
Feb. 25 Paid cash to Srinath – ₹ 3,600
Discount received from him – ₹ 400
Feb. 28 Purchases – ₹ 2,000
Feb. 28 Sold goods for cash – ₹ 4,000
Solution:
![]()
Question 6.
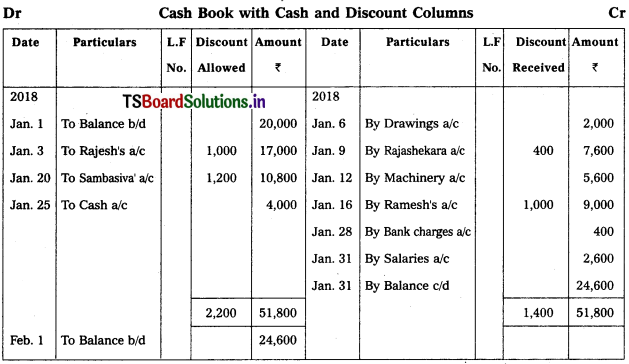
Prepare Cash book with Bank and Discount Columns.
2018
Jan. 1 Cash at bank – ₹ 20,000
Jan. 3 Received cheque from Rajesh – ₹ 17,000
Discount allowed – ₹ 1,000
Jan. 6 Cash withdrawn for personal use – ₹ 2,000
Jan. 9 Paid to Rajashekar by ‘paytm’ – ₹ 7,600
Discount received – ₹ 400
Jan. 12 Bought machinery by debit card – ₹ 5,600
Jan. 16 Cheque issued to Ramesh – ₹ 9,000
Discount received – ₹ 1,000
Jan. 20 Received from Sambasiva through ‘google pay1 10,800
Allowed discount – ₹ 1,200
Jan. 25 Paid in to bank – ₹ 4,000
Jan. 28 Bank charges as per pass book – ₹ 400
Jan. 31 Salaries paid by cheque – ₹ 2,500
Solution:
![]()
Question 7.
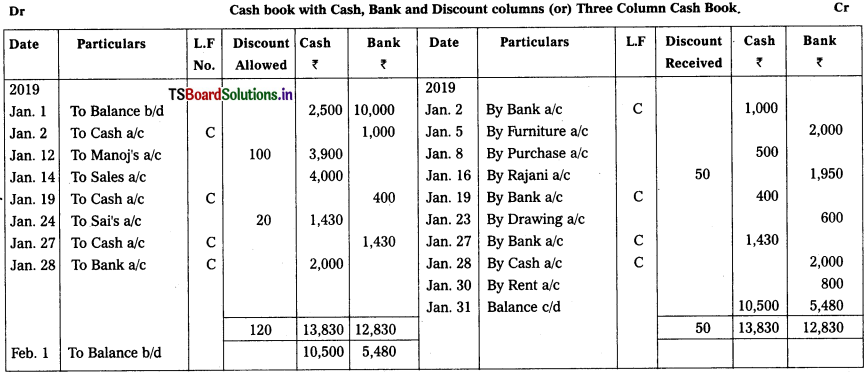
Prepare a cash book with Cash, Bank and Discount columns from the following transactions.
2019
Jan. 1 Cash in hand ₹2,500, Cash at bank ₹ 10,000.
Jan. 2 Paid into bank ₹ 1,000.
Jan. 5 Bought furniture and paid through cheque ₹ 2,000.
Jan. 8 Purchases ₹ 500.
Jan. 12 Received cash from Manoj ₹ 3,900 and
Discount allowed to him ₹ 100.
Jan. 14 Sales ₹ 4,000.
Jan. 16 Paid to Rajani by cheque ₹ 1,950 and discount received from her ₹ 50.
Jan. 19 Paid into Bank ₹ 400.
Jan. 23 withdrawn cash from bank for personal ₹ 600.
Jan. 24 Received cheque from Sal ₹ 1,430 and
allowed him discount ₹ 20.
Jan. 27 Deposited Sais cheque into bank.
Jan. 28 Withdraw cash from bank for office use ₹ 2,000.
Jan. 30 Rent paid cheque ₹ 800.
Solution:
![]()
Question 8.
Prepare Triple column cash book from the following transaction.
2019 Jan.
Jan. 1 Cash in hand ₹ 15,000 and Cash at bank ₹ 4,000.
Jan. 4 Purchased machinery and payment made by cheque ₹ 2,000.
Jan. 6 Deposited into bank ₹ 6,000.
Jan. 8 Bought goods for cash ₹ 2,500.
Jan. 10 Paid to Manoj ₹ 850 in full settlement of ₹ 900.
Jan. 14 Received ₹ 1,250 from David and allowed him discount ₹ 40.
Jan. 18 Paid through Debit Card to Satish for ₹ 1,750
Jan. 20 Paid for purchase of goods ₹ 355.
Jan. 25 Used ‘paytm’ for personal use ₹ 800.
Solution:
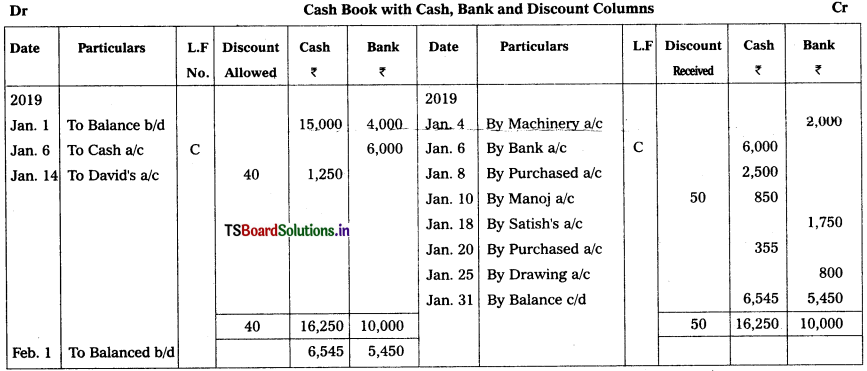
Question 9.
Prepare Triple column cash book from the following transactions.
2019
Mar. 1 Balance of cash ₹ 5,000 and Bank overdraft ₹ 10,000.
Mar. 3 Received amount through net banking from Mahesh for ₹ 1,000 and allowed him discount ₹ 130.
Mar. 5 Deposited cash into bank ₹ 6,000.
Mar. 10 Paid to Anil through Debit Card ₹ 320 in full settlement of his account ₹ 350.
Mar. 15 Received from cash sales : Cash ₹ 275 and Cheque ₹ 5,225 Deposited cheque on the same day.
Mar. 19 Purchased goods by Paytm ₹ 645.
Mar. 22 Paid by cheque to Kavya ₹ 725 in full settlement of ₹ 800.
Mar. 25 Cash withdrawn from bank for office use ₹ 1,900 and personal use ₹ 900.
Mar. 27 Paid for advertisement ₹ 245.
Mar. 28 Paid staff salary by crossed cheque ₹ 2,250.
Mar. 29 Paid office rent by cash 400 and house rent by cheque ₹ 375.
Mar. 30 Received crossed cheque of ₹ 580 from Srinivas in Settlement of ₹ 620.
Solution:
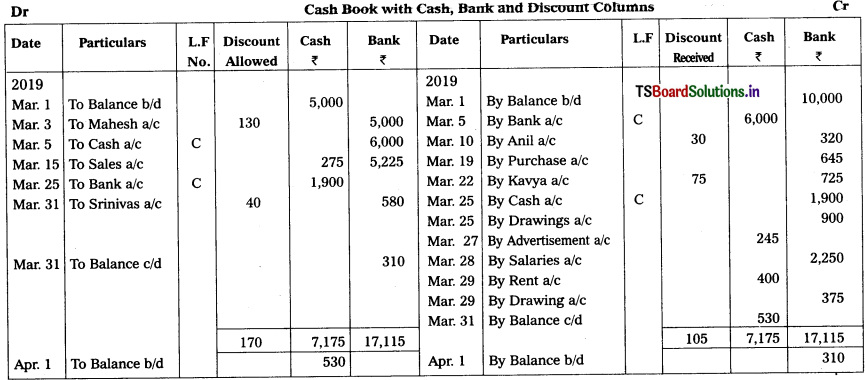
![]()
Question 10.
From the following transactions, prepare Three column cash book.
2019
Mar. 1 Commenced business with Cash ₹ 10,000 and bank balance ₹ 18,000.
Mar. 4 Received a cheque from Satish ₹ 3,000.
Mar. 6 Paid through ‘Net banking’ for personal ₹ 1,000.
Mar. 12 Satish’s cheque deposited into Bank.
Mar. 15 Satish’s cheque dishonored.
Mar. 28 Received fresh cheque ₹ 3,000 from Satish and deposited in the Bank on the same date.
Mar. 29 Received cash from Ravi ₹ 2,900 discount allowed ₹ 100.
Mar. 29 Salaries paid ₹ 3,900.
Mar. 31 Bank Charges as per pass book ₹ 250.
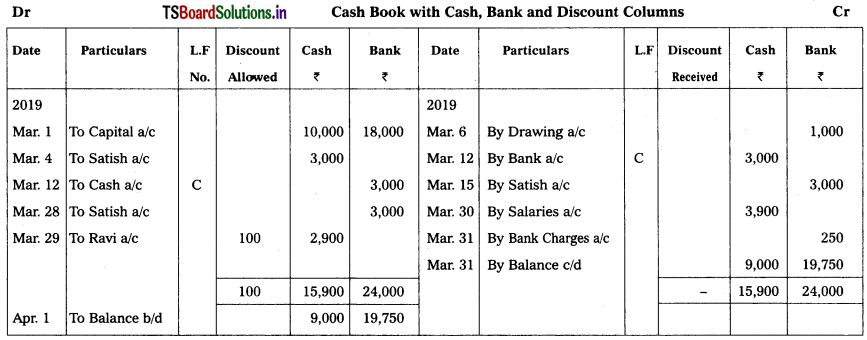
Question 11.
Prepare petty cash book from the following details.
2019
Jan. 1 Received cheque from Head Cashier – ₹ 200
Jan. 5 Paid postage – ₹ 15
Jan. 7 Paid carriage – ₹ 10
Jan. 10 PaId telegram – ₹ 12
Jan. 12 Repairs – ₹ 23
Jan. 14 Office cleaning – ₹ 10
Jan. 19 Stationery – ₹ 40
Jan. 20 Paid Manoj on account – ₹ 15
Jan. 24 Sundry expenses – ₹ 20
Jan. 28 Telegram – ₹ 10
Jan. 30 Xerox – ₹ 5
Solution:
Analytical Petty Cash Book
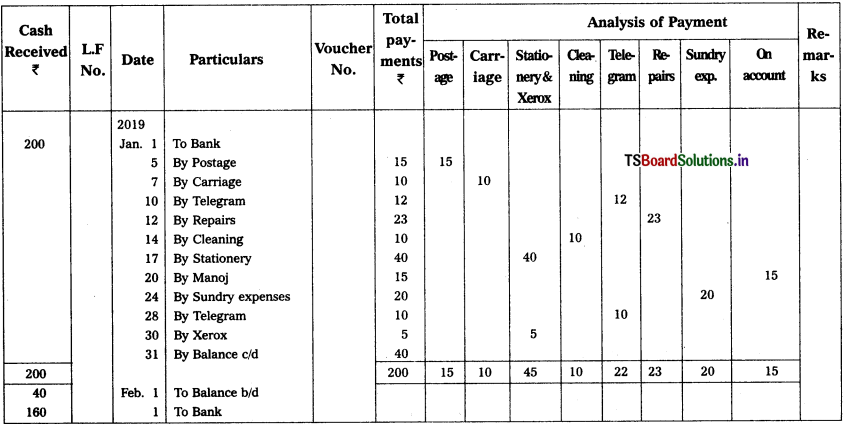
![]()
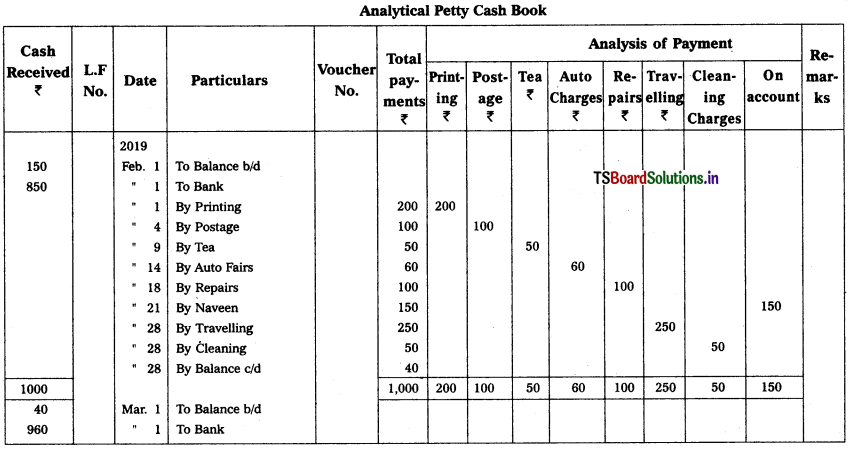
Question 12.
From the following transactions, prepare an analytical petty cash book on imprest methods, Impest amount ₹ 1,000. Balance of previous month ₹ 150.
2019
Feb. 1 Printing charges – ₹ 200
Feb. 4 Postage – ₹ 100
Feb. 9 Tea – ₹ 50
Feb. 14 Auto charges – ₹ 60
Feb. 18 RepaIr of Printer – ₹ 100
Feb. 21 Paid to Naveen on account – ₹ 150
Feb. 28 travelling expenses – ₹ 250
Feb. 28 Cleaning charges – ₹ 50
Solution:
Analytical Petty Cash Book