Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 3rd Lesson Subsidiary Books Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Materia 3rd Lesson Subsidiary Books
Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Explain various types of Subsidiary Books.
Answer:
All day – to – day transactions are first recorded in the journal. In a small business unit, it is possible to record all business transactions in one book. But in a big organisation where the transactions are large in number, it is c ficult to record all business transactions in one place.
Hence, in big organisations, there is need to sub divide journal into special journals. Each journal is meant for recording the transactions of separate category and of repetitive nature. These special journals are called ‘Subsidiary Books’ or Day Books.
Types of Subsidiary Books:
Keep in view the nature and need of the business transactions, the subsidiary books are classified as follows.
1.Purchases Book :
Only credit purchases of goods are recorded in this book. Cash purchases and purchase of assets are not recorded in this book. The recording of entries in this book is based on the invoices and bills received by the firm from the suppliers.
2. Sales Book :
The credit sale of the goods are recorded in sales book. Cash sales and sale of assets are not recorded in this book. The recording of entries in this book is based on the outward invoices or bills prepared by the trader on the customer.
3. Purchase Returns Book :
Sometimes, goods purchased are returned to the suppliers for various reasons such as the goods are not of the required quality or defective, not matching to the specifications, price difference etc., such return of goods is recorded in the purchase returns book. For every return, a debit note is prepared and send it to the supplier.
4. Sales Return Book :
This book is used to record the return of the goods by the customers. Sometimes, customers return a part of the goods purchased from the trader. On receipt of goods from the customer, credit note is prepared.
5. Cash Book :
The cash book is maintained to record all cash transactions. All cash receipts are debited and all cash payments are credited in this book.
6. Bills Receivable Book :
The bill on which the amount is yet to be received and promissory note drawn by the seller or creditor are recorded in bills receivable book.
7. Bills Payable Book:
All bills and promissory note accepted by the buyer or debtor are recorded in the bills payable book.
8. Journal Proper:
This book is used to record only those transactions which cannot be recorded in any of the above mentioned subsidiary books.
![]()
Question 2.
State advantages of subsidiary books.
Answer:
The following are the advantages of subsidiary books.
- No need of writing journal entries. The transactions are entered directly into their respective journals.
- Ledger accounts can be prepared on the basis of subsidiary books.
- Recording of transactions is very fast and easy. .
- By entrusting different subsidiary books to different persons, division of work principle can be implemented.
- Accounting work will be done efficiently by allotting work to different experts who prepare the special books.
- Labour involved and time can be saved.
- Since separate books are maintained to record a particular set of transactions, errors can be easily detected.
- Information relating to similar types of transactions will be available at one place.
E.g. Relating to sales, purchases, cash etc.
Question 3.
Explain about purchases and sales book draw the formats.
Answer:
Purchases book :
In this book, all credit purchases of goods are recorded i.e. cash purchases of goods and purchase of assets are not recorded.
The recording of entries in this book is based on the invoices or bills received by the firm from the suppliers.
Proforma of purchases :

Sales Book:
The credit sale of the goods are recorded in sales book. Cash sales and sale of assets are not recorded in this book. The recording of entries in the book is based on the outward invoices or bills prepared by the trader on the customer.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Journal Proper ? Write any five items which are recorded in Journal Proper.
Answer:
All business transactions are recorded in different subsidiary books according to their nature. But there are certain transactions which occassionally happen and these are not recorded in any of the subsidiary books.
However, they are recorded in a special book known as ‘Journal Proper’. That is, the transactions which are not recorded is the respective subsidiary books are recorded in the journal proper.
The following transactions are recorded in the journal proper.
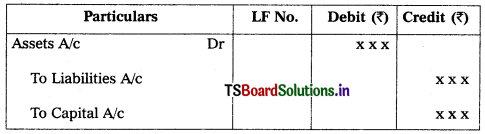
1. Opening entries :
Opening entries are used to record at the beginning of the financial year to open the books by recording assets, liabilities and capital appearing in the Balance Sheet.
2. Closing entries :
Closing entries are used at the end of the accounting year for closing all accounts relating to expenses and revenues. These accounts are closed by transfer-ring their balances to Trading account and Profit and Loss account.
3. Purchase and sale of assets on credit:
Every organisation purchase the assets or sell the assets either on cash basis or on credit basis. When they are purchased or sold on credit basis, they are recorded in journal proper.
4. Rectification entries :
While recording the transactions in the books of accounts, some errors may arise due to negligence of the clerk or due to ignorance of fundamental principle of accounts. In such cases profit or loss cannot be determined correctly. So, necessary rectification entries are passed in journal proper.
5. Adjustment entries :
There are certain incomes and expenses are not recorded even at the date of closing the accounts. If they are not taken into account, correct profit or loss cannot be ascertained. So, necessary adjustment entries with regarding to those expenses and incomes are recorded in journal proper.
6. Transfer entries :
These entries in the journal proper for transferring an item from one account to another account.
Ex : Transfer of profit to reserve fund, transfer of drawings a/c to capital a/c.
7. In addition to the above, some transactions like loss of goods due to fire, Dishonour of cheques or bills of exchange, Goods sent on consignment are recorded in journal proper.
Very Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What is Debit Note ?
Answer:
- It is a document sent to the supplier while returning the goods purchased on credit from him.
- It intimating that his account is debited to the extent of goods returned and the reasons for returning them. It is prepared by the purchaser.
Question 2.
What is Credit Note ?
Answer:
- It is a note (document)prepared and sent to the customer to inform that his account is credited with the amount of the goods returned by him.
- It is a common to make it in red ink. It contain name and address of customs, value of goods returned and reasons for return of goods.
Question 3.
What is Invoice ?
Answer:
- It is a statement sent by the supplier along with the goods or in advance, to the trader, stating that the goods are supplied along with the price, discount offered and other terms and conditions.
- The document is called ‘Inward Invoice”, as it is received by the trader from the supplier.
Question 4.
Trade Discount.
Answer:
- The rebate offered by the supplier on the catalogue price is known as trade discount.
- If trade discount is given, it is to be deducted from the purchase price and only net amount is to be recorded in the books.
Question 5.
Journal Proper.
Answer:
- Journal proper is also known as “Journal Residual” or “General Journal”.
- This book is used to record only those transactions which cannot recorded in purchase book or sales book or cash book, purchase returns or sales return book, Bills Receivable or Bills Payable book.
- E.g. When a firm purchased machinery on credit.