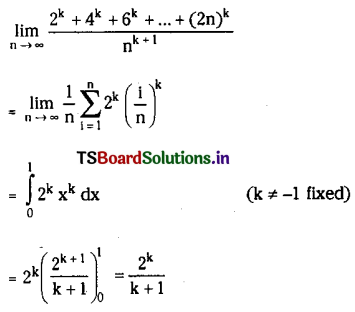
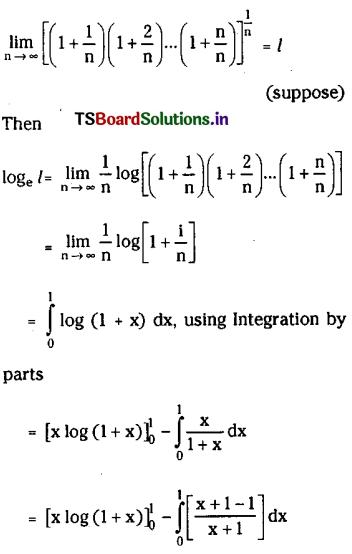
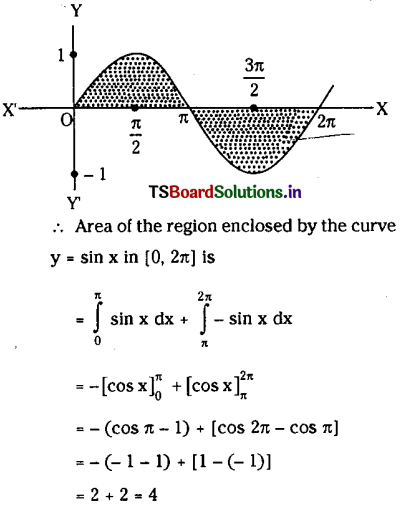
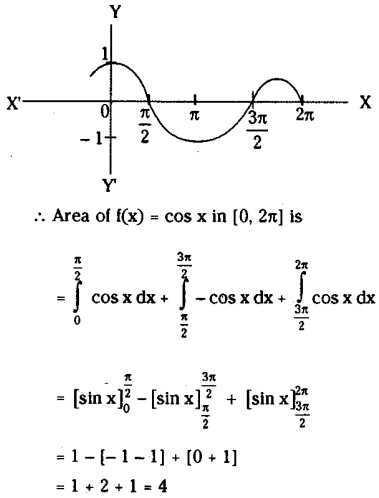
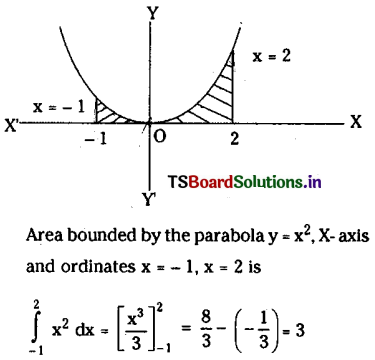
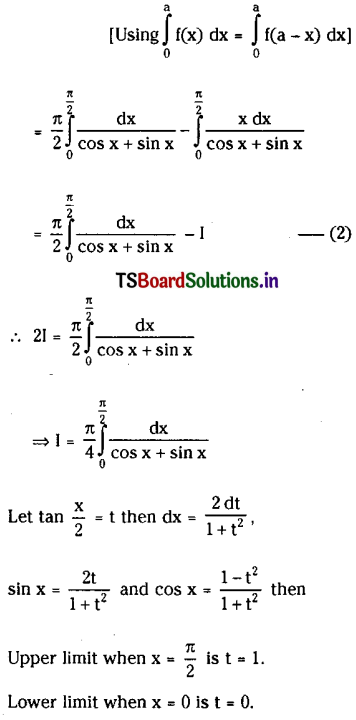
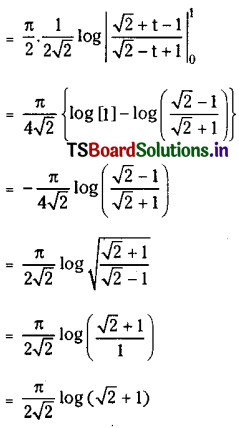
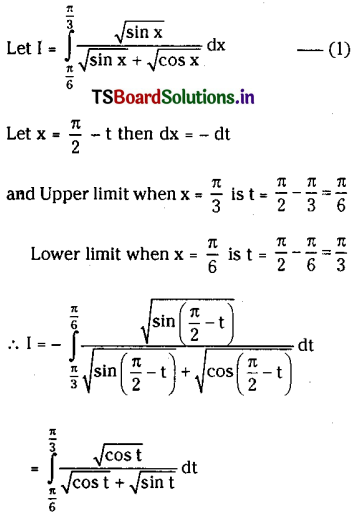
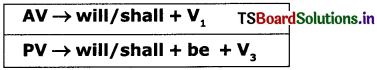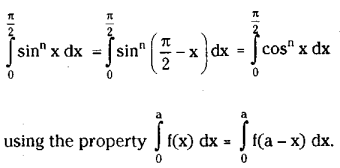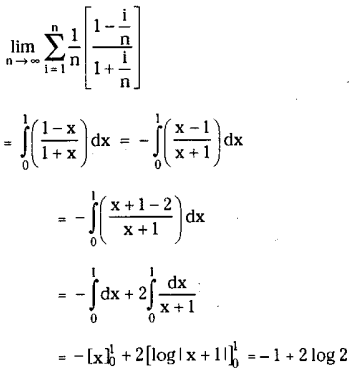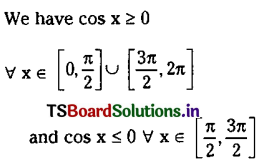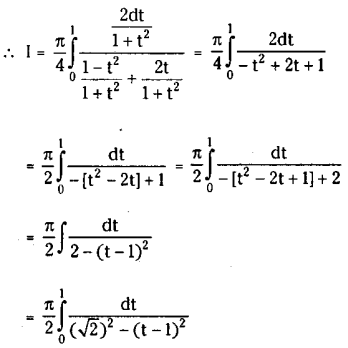Telangana SCERT TS 10th Class English Guide Pdf Unit 7A My Childhood Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 10th Class English Guide Unit 7A My Childhood
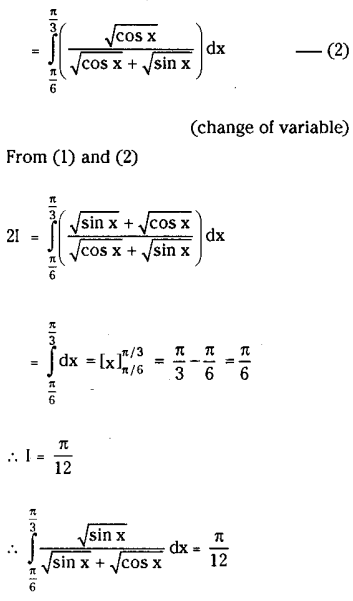
Nation and Diversity:
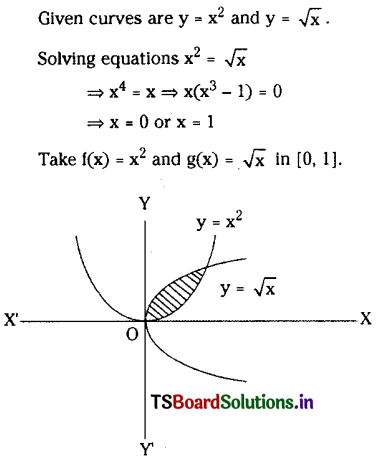
Look at the picture and answer the questions that follow :
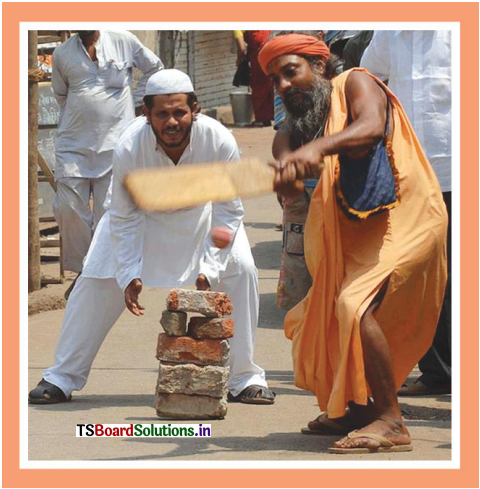

Question 1.
What does the picture signify ?
Answer:
The picture signifies religious harmony and the unity in diversity. In this picture, we see some Hindus and Muslims playing cricket together. We witness such kind of scenes everywhere in India. People in India have been living with the feelings of fraternity and integrity for ages. They forget their religions and cultural differences and live together peacefully.
Question 2.
Do you experience the theme reflected in the picture in your real life ? If not, what may be the possible reason for this ?
Answer:
I do experience the theme of religious harmony, as reflected in the picture. In our school, we all play and study together.

Oral Discourse:
Question.
Talk on – “Unity in diversity is the spirit of our nation.”
Answer:
Geographically, it is a land of contracts in numerous ways. It provides almost every type of climate, from extreme heat to extreme cold all the year round. The hilly regions in the North and elsewhere are as cold as some of the coldest parts of Europe. Certain areas in South are the hottest in the world. In Mumbai and Malwa, the climate is temperate though West Bengal is more humid.
India is a plural society. It is repository of multiplicity of cultures. Indian civilization, stretching over five thousand years, provides the most distinctive feature in the coexistence of unity in diversity.
India is said to be a synthesis of diverse social and cultural elements. A grand synthesis of cultures, religions and language of the people belonging to different castes and communities has upheld its unity and cohesiveness despite foreign invasions, and the Mughal and British rule.
National unity and integrity have been maintained even though sharp economic and social inequalities have obstructed the emergence of equalitarian social relations. It is this synthesis which has made India a unique mosaic of cultures. India is, in fact, a panorama of its own types without a parallel in other continents. Foreign invasions, immigration from other parts of the world and the existence of diverse languages, cultures and religions have made India’s culture tolerant, on the one hand, and a unique continuing and living culture with its specificity and historicity on the other.
Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, Islam, Sikhism and Christianity are the major religions Besides twenty two Constitutionally recognized languages, there are several hundred dialects There is diversity not only in regard to racial compositions, religious and linguistic distinctions but also in patterns of living, life styles, occupational pursuits, inheritance and succession of law and practices and rites related to birth, marriage, death etc.
The idea of unity of India is inherent in all its historical and socio-cultural facts as well as in its cultural heritage. India has one Constitution providing guarantees for people belonging to diverse religious, cultures and languages. It covers people belonging to all socio-economic strata.
India possesses varieties of social, economic, geographical conditions. In India there is unity in apparent diversities of race, religion, language, custom etc. The distinctive feature of India in its unity and diversity is also reflected in the social ethos.

Comprehension:
I. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What were the disadvantages faced by Kalam in his childhood ?
Answer:
Abdul Kalam was born in a middle class family. His home town was the island town of Rameswaram. His parents were neither much educated nor wealthy.
Question 2.
“…………………. that forced Samsuddin to look for helping hand” What does ‘that’ refers to ?
Answer:
Kalam’s cousin Samsuddin was the distributer of the daily ‘Dinamani’ in Rameswaram. During the Second World War, the halt for the train at Rameswaram station was suspended. The News Paper bundles had to be used to come in the train thrown from the train, at the station. So, Samsuddin wanted someone’s help to catch the bundles. Here, ‘that’ refers to the necessity of a person to help Samsuddin catch the bundles of newspapers.
Question 3.
“I filled the slot”. What does the sentence mean ?
Answer:
The sentence means that Kalam helped his cousin Samsuddin in catching the news paper bundles thrown from the moving train, at the Rameswaram Railway station. During the second World War the emergency was declared. The first casualty came in the form of the suspension of the train halt at Rameswaram station. The newspapers were to be bundled and thrown out from the moving train on the Rameswaram Road between Rameswaram and Dhanuskodi. Samsuddin, the cousin of Kalam needed a helping hand to catch the bundles of newspapers. Then Kalam came forward to do that job.
Question 4.
If one wants to bring a change in the social system, what qualities should one possess?
Answer:
If one wants to bring a change in the social system, one should possess the qualities such as courage, patience, determination, equanimity, grit, perseverance etc. One should be optimistic and should dare to face the problems which could arise.
Question 5.
Events from the Ramayana and from the life of the Prophet were the bedtime stories my mother and grandmother would tell the children in our family.
Choose the most appropriate meaning for the underlined word from the options given below.
a) stories told by the bed side
b) stories told on the bed
c) stories told before getting sleep
Answer:
c) stories told before getting sleep

Question 6.
“Your Children are not your children ” What does it mean ? Do you agree with the statement or disagree ? Give reasons.
Answer:
The expression, “Your children are not your children” means that the children develop their own ideas as they are growing. These words were spoken by Kalam’s father, Jainulabdeen in the context of his wife’s hesitation to send Kalam to Ramanathapuram. I totally agree with the statement as the children themselves develop their own thoughts naturally. The children have to be separated from their parents at some stage in life. They have to be let free so that they can realize their thoughts and set their goals.
Question 7.
As children, none of us ever felt any difference amongst ourselves because of our religious differences and upbringing. Choose the most appropriate meaning for the underlined word from the optious given below.
a) education
b) cared and trained
c) food and shelter
Answer:
b) cared and trained
Question 8.
Read the text and attribute the characteristics given in the box to the following women, conservative, sociable, kind, secular, generous, simple, tolerant, adamant, orthodox
a) Subramania Iyer’s wife
b) Ashiamma
Answer:
(a) Subramania Iyer’s wife – conservative, adament, orthodox
- conservative – She could not invite Kalam to her house.
- adamant – She refused to serve meal to Kalam.
- orthodox – She remained in the kitchen when Kalam was served meal by Subramania Iyer.
(b) Ashiamma – sociable, kind, secular, generous, simple, tolerant.
- sociable – She was friendly with all the people who visited her house.
- kind – She was kind with all the guests and family members.
- secular – Irrespective of the religious differences, Ashiamma fed all the people who came to her house.
- generous – She gave a secured emotional and material comforts to her children.
- simple – Ashiamma was a good partner to her husband and led a simple and happy life with him.
- tolerant – She was tolerant towards the visitors and her children.
Question 9.
Identify the features of the text “My childhood”
a) What type of a text is it ?
b) Reflections on the text
c) Anecdotes in the text.
Answer:
(a) The text is an autobiography.
(b) It mirrors the realities of life i.e., the divisions in the society and the reactions of various people to it and the pain it causes to the innocent ones. It shows that love, affection and kindness are above the false religious pride.
(c) (i) The situation in which Kalam earned money by selling tamarind seeds and catching
paper bundles from the running train.
(ii) Kalam’s friendship with Brahmin boys.
(iii) The ill-treatment of the new teacher towards Kalam and the warning given by Lakshmana Sastry to the new teacher not to show any discrimination that would spoil the minds of innocent children.
(iv) The hospitality of Sivasubramania Iyer.

Vocabulary:
I. Fill in the blanks with suitable words often confused given in brackets.
Question 1.
Samsuddin helped me earn my first __________ (wages / income).
Answer:
wages
Question 2.
He received a proportion of his __________ (wages / income) from selling tamarind seeds.
Answer:
income
Question 3.
He is __________ (innocent / ignorant) about technology.
Answer:
ignorant
Question 4.
However he was found __________ (innocent / ignorant) of any crime.
Answer:
innocent
Question 5.
He lost all the wealth he had __________ (inherited /acquired) from his father because he __________ (inherited / acquired) bad habits.
Answer:
inherited, acquired

Question 6.
People from different backgrounds could __________ (mix /mingle) easily. __________ (mixed /mingled) group people do not come to an agreement.
Answer:
mingle, mixed
Question 7.
People in Rameswaram were very __________ (rigid / adamant) in terms of segregation of different social groups . Subramania Iyer __________ (rigidly / adamantly) opposed it.
Answer:
rigid, adamantly
Question 8.
The car collided with a __________ (stationary / stationery) vehicle when we went to buy some __________ (stationary / stationery) from the book stall.
Answer:
stationary, stationery
Question 9.
She was __________ (envelop /enveloped) in a huge white towel.
Answer:
enveloped
Question 10.
We sent an airmail __________ (envelop / envelope) abroad.
Answer:
envelope
Question 11.
The floor was __________ (laid / lied) with a newspaper.
Answer:
laid
Question 12.
He __________ (laid / lied) many times.
Answer:
lied

II. Tick (✓) the appropriate meaning of the underlined word in each sentence below.
Question 1.
Kalam’s father possessed great innate wisdom and a true generosity of sprit.
(a) hospitality
(b) nobility
(c) kindness
Answer:
(b) nobility
Question 2.
A sudden demand for tamarind seeds erupted in the market.
(a) started
(b) came up
(c) appeared suddenly
Answer:
(b) came up
Question 3.
Our family arranged boats for carrying idols of the Lord from the temple to the marriage site, situated in the middle of the pond.
(a) place
(b) ceremony
(c) feast
Answer:
(a) place
Question 4.
The new teacher could not stomach a Hindu priest’s son sitting with a Muslim boy.
(a) imagine
(b) permit
(c) tolerate
Answer:
(c) tolerate
Question 5.
He looked utterly downcast as I shifted to my seat in the last row.
(a) lonely
(b) sad
(c) disappointed
Answer:
(b) sad
Question 6.
Sastry bluntly asked the teacher to either apologise or quit the school.
(a) immediately
(b) angrily
(c) plainly
Answer:
(b) angrily
Question 7.
The small society of Rameswaram was very rigid in terms of the segregation of different soical groups.
(a) strict
(b) firm
(c) strong
Answer:
(a) strict
Question 8.
Sivasubramania Iyer was not perturbed, nor did he get angry with his wife.
(a) disturbed
(b) disappointed
(c) pleased
Answer:
(a) disturbed
Question 9.
India’s freedom was imminent.
(a) expected
(b) necessary
(c) certain
Answer:
(c) certain

Grammar:
I. Read the following paragraph and note the underlined words.
. . .On the whole, the small society of Rameswaram was very rigid in terms of the segregation of different social groups. However, my science teacher Sivasubramania Iyer, though an orthodox Brahmin with a very conservative wife, was something of a rebel. He did his best to break social barriers so that people from varying backgrounds could mingle easily.
Notice the underlined words or phrases in the above paragraph. They are called linkers or discourse markers. Noticing and understanding discourse markers help learners to understand the logical structure of what they read and listen to, the order of events and the attitude of the speaker or writer and what they refer to.
Think of the following:
- What makes the writer use the linker ‘on the whole’ in the above paragraph ? Give reasons.
- What purpose does the linker ‘however’ serve in the paragraph?
- What does the wirter emphasize by using the linker ‘though’?
- Why did the writer use the linkers?
Answer:
- The writer used the linker’on the whole’ in order to summarise the previous incidents. When Kalam was separated from his close friend and orderd to sit in the last row by the new teacher, Lakshmana Sastry, the priest of the temple told the teacher that he should not spread the poison of social inequality and religious intolerance in the minds of innocent children. He bluntly asked the teacher to either apologize or quit the school and the island.
- ‘However’ serves as a linker indicating the result of an action. The science teacher was a broadminded Brahmin while his wife was conventional and adamant of the beliefs.
- The linker ‘though’ was used to indicate the inheritance of family culture in Iyer on par with his ideas of breaking social barriers inspite of different backgrounds.
- The writer used the linkers to show the relationship between ideas. He used them to maintain the unity of the text and make it an effective one. The linkers were used to maintain logical sequence of the text.
Some useful information about “Linkers”.
Linkers are words that combine senteces and show the relationship between ideas. Linkers are used to tell the reasons and results, contrasts, comparisons, purposes, consequences, additions, exemplifications, successions, results, orders, conclusions, explanations, sequences etc.
| Function | Linkers |
| (i) contrast | inspite of, despite, although, though, however, nevertheless, still, yet, even so, on the contrary, in contrast, on one hand, on the other hand, whereas, anyhow, rather than, otherwise, while, all the same. |
| (ii) reasons and cause | because, as, since, seeing that, because of, on account of, owing to, due to, in order to, so as to, to. |
| (iii) purpose | in order to, so as to, in oder that, so that. |
| (iv) consequence | as a consequence, consequently, as a result, therefore, as a result of, so |
| (v) addition | moreover, furthermore, in addition, besides, what’s more, as well as, for example, for instance, such as, apart from, except for |
| (vi) exemplification | for example, for instance, such as |
| (vii) adding information | for example, for instance, such as, moreover, further more, besides, in addtion to, apart from except for, what’s more, on the top of that, on one hand, on the other hand. |
| (viii) succession | first of all, firstly, to begin with, first, second, secondly, then, third, thirdly, after that, the next stage, finally, in short, to sum up, in conclusion, lastly, last but, not least. |
| (ix) result | as a result of, therefore, as a result, consequently, for this reason, that’s why, becasue of |
| (x) order | at first sight, first, first of all, in the first place, to start with, in the second place, second, secondly, third, thirdly, finally,in conclusion, lastly, eventually. |
| (xi) expressing facts | actually, as a matter of fact, infact, really. |
| (xii) expressing a personal opinion | as far as I am concerned, from my point of view, I agree, I disagree, in my opinion, in my view, I think that, it is true that, personally, to be honest, to tell the truth. |
| (xiii) explanation | that is, in other words, in short, above all, all in all, at least basically, especially, essentially, in general, in particular, on the whole, more or less, to a certain extent. |
| (xiv) exemplification | such as, for instance, for example, and so on |
| (xv) summarizing | in brief, all in all, in conclusion, in short, to sum up, on the whole. |
| (xvi) sequencing | next, suddenly, while, then, meanwhile, in the mean time, in the end, first of all, finally all of a sudden, after that etc. |

(A) Here is a list of linkers, which is not exhaustive. Some of them can be used synonymously. Refer to a dictionary and group them in the following table according to the function they perform in a sentence or discourse.
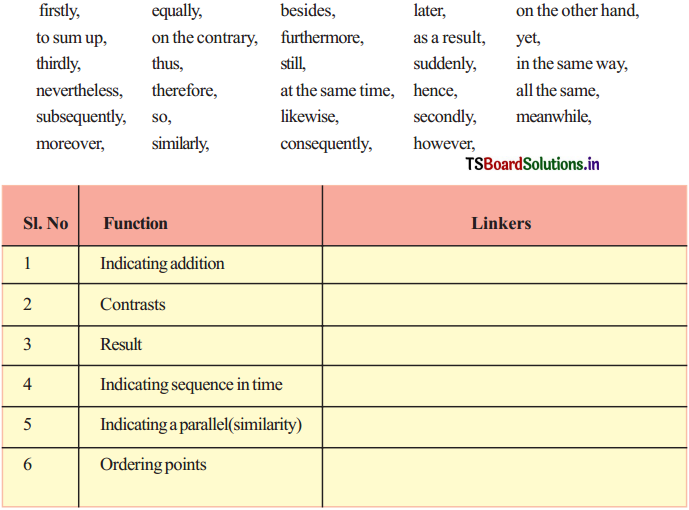
Answer:
| Function | Linkers |
| 1. Indicating additon | besides, furthermore, moreover. |
| 2. Contrasts | on the other hand, on the contrary, yet, still nevertheless, all the same, however. |
| 3. Result | as a result, thus, therefore, hence, so, consequently. |
| Indicating sequence in time | later, suddenly, at the same time, meanwhile, subsequently. |
| 5. Indicating a parallel (similarity) | equally, in the same way, likewise, similarly. |
| 6. Ordering points | firstly, to sum up, thirdly, secondly. |

B. Fill in the blanks appropriate choices given in brackets.
Question 1.
I don’t want to go to a restaurant; __________ (besides / as a result), we can’t afford it.
Answer:
besides
Question 2.
A career in IT field is lucrative; __________ (similarly / at the same time), it is stressful and it can even be harmful to one’s health.
Answer:
at the same time
Question 3.
I understand your problems; __________ (although / however), I can’t help you.
Answer:
however
Question 4.
Transportation has developed a lot in India; __________ (likewise / whereas), the trade too has improved.
Answer:
likewise
Question 5.
Some of the students scored low ranks in the exams; __________ (so that/ consequently), the teacher arranged remedial classes.
Answer:
consequently

C. Complete the following paragraph by choosing the appropriate linking word.

Answer:
Linking words help us in many ways in writing. For example, they help us in presenting our ideas in a meaningful way. Secondly, they help us to introduce and develop the main idea of the paragraph. Thirdly, they help us to illustrate and add supporting details. Next, they help us in moving from one idea to another by binding one sentence with another. Finally, they help us to understand the ideas presented in the paragraph. However, using too many linking words ruins the structure and coherence of the paragraph.
D. Join the following sentences using the linkers given in brackets.
Question 1.
There were freezing temperatures. They trekked for hours. (in spite of)
Answer:
Inspite of the freezing temperatures, they trekked for hours.
Question 2.
It’s an interesting city. We’re going to visit it again. (such …. that)
Answer:
It is such an interesting city that we are going to visit it again.
Question 3.
We booked a holiday. We had very little money. (although)
Answer:
Although we had very little money, we booked a holiday.
Question 4.
The tour guide was informative. We didn’t need to read our guidebook, (so … that)
Answer:
The tour guide was so informative that we didn’t need to read our guidebook.
Question 5.
He didn’t like water. He booked a cruise. (In spite of the fact that)
Answer:
Inspite of the fact that he didn’t like water, he booked a cruise.
Question 6.
Preachers preach many good things. Many of them do not practise what they preach, though/eventhough.
Answer:
Preachers preach many good things, however many of them do not practise what they preach, though/eventhough
Question 7.
Jainulabdeen had no formal education and no wealth, (neither…nor)
Answer:
Jainulabdeen had neither formal education nor wealth.
Question 8.
The continental dimensions of the country account for the variations and diversities. There are several religious sects and beliefs, (besides)
Answer:
Besides there being several religious sects and beliefs, the continental dimensions of the country account for the variations and diversities.

II. Passive Voice without agent:
Observe the following sentences taken from the text.
I was born.
Emergency was declared.
I was asked to go and sit on the back bench
You might have learnt in your previous classes about active and passive voice constructions. Though the above sentences are in the passive the agent is not mentioned.
The agents are not mentioned in the following situations.
- When the agent is obvious
- When the agent is not known
- When it is not desirable to reveal the identity of the agent.
Pick out from the text some more passive constructions without agents and give reasons why the agent is not mentioned.

Answer:
- All necessities were provided for (Agent is obvious)
- The Newspapers now had to be bundled and thrown out from the moving train (Agent is unknown)
- I was asked to go and sit on the back bench. (Agent is obvious)
- Soon India was forced to join the Allied Forces. (Agent is not known)
- Every child is born. (Agent is obvious)
- Sivasubramaniya Iyer was not perturbed. (Agent is not known)
- The house was built in the middle of the nineteenth century. (Agent in not known).
Some useful Notes on Passive Voice :
Verbs are either active or passive in voice. In the active voice, the subject and verb relationship is straightforward. Here the subject is a ‘doer’. In the passive voice, the subject of ‘the sentence is not a doer’. It is shown with by + doer or is not shown in the sentence. Passive voice is used when the focus is on action but not on the subject. It is not important who does the action here.
Active voice :
It describes a sentence where the subject (doer) performs the action stated by the verb.
Eg : (1) Raju sells bangles.
(2) Rama kills Ravana
(3) They make kites.
Passive Voice :
It describes a sentence where the subject (receiver or sufferer) is acted upon by the verb.
Eg : (1) Bangles are sold by Raju.
(2) Ravana is killed by Rama.
(3) Kites are made by them.
Rules we follow when we change the sentence from the Active Voice to the Passive Voice :
(i) Only a transitive verb (the verb with an object after it) has active and passive forms. Intransitive verbs don’t have passive forms. So we can’t change a sentence with an intransitive verb in to passive voice.
(ii) When we change the voice, the subject becomes the object and the object becomes the subject.
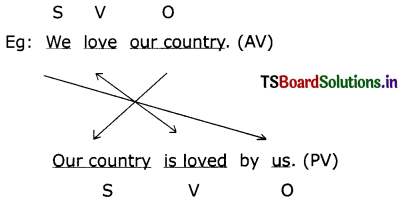
(iii) The subject (agent) of the active verb is made a ‘by + object’ in the possive sentence.
Eg: The CM inaugurated the exhibition (AV)
The exhibition was inaugurated by the CM. (PV)
| Tense | Active verb | Passive verb (be + V3) |
| Present simple | write, writes | is/are written |
| present continuous | is/are/am + writing | is/are/am + being + written |
| present perfect | has/have + written | has/have + been + written |
| Present perfect continuous | has/have + been + writing | No passive voice |
| Past simple | wrote | was/were written |
| Past continuous | was/were + writing | was/were + being + written |
| Past perfect | had + written | had + been + written |

(iv) The passive voice is mainly expressed by using ‘be’ verb along with a past participle of the main verb. The following table provides passive forms of the verb ‘write’.
| Tense | Active verb | Passive verb (be + V3) |
| Past perfect continuous | had + been + writing | No Passive voice |
| Future simple | will / shall + write | will/shall + be + written |
| Future continous | will/shall + be + writing | No passive voice |
| Future perfect | will/shall + have + written | will/shall + have + been + written |
| Future perfect continous | will/shall + be + writing | No passive voice |
| Modal auxiliaries | can/may/could/might/should/would/must/write | can/may/could/might/should/would/must + be + written |
(v) Changes of Pronouns :
| Active voice | Passive voice |
| I | me |
| we | us |
| he | him |
| she | her |
| they | them |
(vi) There is no passive form for the following tenses.
(a) present perfect continuous tense
(b) past perfect continous tense
(c) Future continuous tense
(d) Future perfect continuous tense
(e) Sentence contains Intransitive verb

EXAMPLES:
1. Simple Present Tense :

1. He sings a song. (AV)
A song is sung buy him. (PV)
2. They speak English. (AV)
English is spoken by them. (PV)
3. He loves me. (AV)
I am loved by him. (PV)
2. Present Continuous Tense :
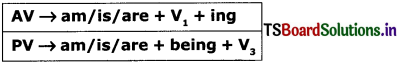
1. I am writing a letter. (AV)
A letter is being written by me. (PV)
2. He is painting walls. (AV)
Walls are being painted by him. (PV)
3. She is helping them. (AV)
They are being helped by her. (PV)
3. Present Perfect Tense:
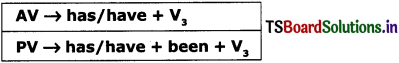
1. She has written a story. (AV)
A story has been written by her. (PV)
2. He has drawn pictures. (AV)
Pictures have been drawn by him. (PV)

4. Simple Past Tense:
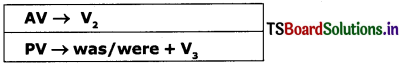
1. She killed a snake. (AV)
A snake was killed by her. (PV)
2. He wrote poems. (AV)
Poems were written by him. (PV)
5. Past continuous Tense:
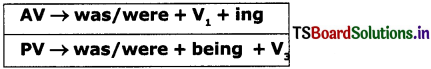
1. He was driving a car. (AV)
A car was being driven by him. (PV)
2. She was making kites. (AV)
Kites were being made by her. (PV)
6. Past Perfect Tense:
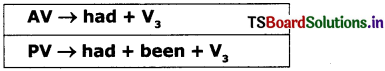
1. She had completed the task. (AV)
The task had been completed by her. (PV)

7. Simple Future Tense:
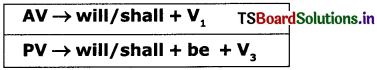
1. She will buy a car. (AV)
A car will be bought by her. (PV)
8. Future Perfect Tense :

1. You will have completed the course. (AV)
The course will have been completed by you. (PV)
(vii) . Demonstrative verbs have two objects (direct and indirect objects) after them. In that case, both objects can be moved to the subject position. So we can form two passive sentences from a sentence with a distransitive verb : in one sentence the direct object moves to the subject position and in the other indirect object moves to the subject position.

1. 
We were taught English by Mr. Srinivas. (PV) (or)
English was taught to us by Mr. Srinivas. (PV)
2. 
Nice presents were given to them. (By us). (PV) (or)
They were given nice presents. (By us) (PV)
(viii) Passive form for an imperative sentence.
Eg: Post the letter.
Let the letter be posted.
It is usually thought that the second sentence (beginning with ‘let’) is the passive form of the first one (an imperative sentence). In fact even the second sentence is an imperative sentence. The first sentence has only one main verb : Post. But the second sentence has two main verbs (‘let’ and ‘be’) and so it has two clauses – one imperative (let) and the other non finite clause (the letter be posted). A possible active sentence for the second sentence is : Let him post the letter.
(ix) Questions in Passive form :
Eg : (1) Are you writing a letter ? (AV)
Is a letter being written by you ? (PV)
(2) Have you played cricket ? (AV)
Has cricket been played by you ? (PV)
(3) Does she speak Telugu ? (AV)
Is Telugu spoken by her ? (PV)
(4) Who wrote the letter ? (AV)
By whom was the letter written ? (PV)
(5) Did you write the story ? (AV)
Was the story written by you ? (PV)

Passive Voice without agent:
(a) When the agent is unknown or unimportant, it is not used in the passive voice.
Eg: (1) Ram’s car has been stolen. (Unknown agent)
(2) She was advised to apply for a visa in advance. (Unimportant agent)
(b) When the subject of the active sentence is you, one, we, people etc. we use the passive voice with a generalised agent.
Eg: Internet is used for many different things.
(AV → we/people use Internet for many different things)
(c) When the agent is obvious, we don’t use the agent.
Eg: The thief has been arrested.
(AV → The police has arrested the thief)
(d) If we want to avoid naming the specific person responsible for the action, we don’t + use the agent.
Eg: It is decided to postpone the exams.
(e) If the emphasis is on the action and not on the pople who perform it, the agent is usually omitted.
Eg: The work has been completed with in a few days only.
Some more examples:
1. The purse was stolen. (Unknown agent)
2. Our army has been defeated. (Obvious agent)
3. Letters are delivered twice a week. (Obvious agent)
4. The rules should be obeyed. (Generalised agent)
5. He was dismissed from service. (Obvious agent)

III. Edit the following paragraph. It has some errors in the following areas like punctuation, spelling, tense, prepositions, articles.
he told me as if thinking aloud abul i know you have to go away to grow did the seagull not fly toward the son alone without a nest he quotes khalil gibran to my hesitant mother your children are not your children they are sons and daughters of lifes longing to itself they come to you but not from you may give them love but not your thoughts for they have there own thoughts
Answer:
He told me ‘as if thinking’ aloud, “Abul! I know you have to go away to grow. Does the seagull not fly across the sun, alone and without a nest?”. He quoted Khalil Gibran to my hesitant mother, “Your children are not your children. They are the sons and daughters of life’s longing for itself. They come through you but not from you. You may give them your love but not your thoughts. For they have their own thoughts.”
Writing:
I. Diary entry
Imagine that you were one of the students who witnessed the humiliation done to Kalam in the classroom. Reflect on the incident and write your emotions in your diary.
Answer:
…………… day, …………date ……………year.
Time : 8:00 pm
As usual, it was a fine day to start with but for the lone incident, which had shook the whole class. The new teacher had asked Abdul, our Muslim friend, to go back and sit there. As usual he was sitting along with Ramanathe Sastry, a brahmin boy, his best friend. But the teacher, who seems to be an orthodox brahmin, couldn’t bear it. Both the boys were crying. Almost so was I. It was a shock. We couldn’t even accept him as a teacher. No, a teacher shouldn’t have done so. It was really very cruel.
Ramesh.
II. In the lesson, Kalam gave a brief description of his heritage.
Kalam says, “I don’t recall the exact number of people she (his mother) fed every day, but I am quite certain that far more outsiders ate with us than all the members of our family put together
This shows the heritage of hospitality and kindness.
Kalam says, “events from the Ramayana and from the life of the Prophet were the bedtime stories my mother and grandmother would tell the children in our family”.
This shows the heritage of secular spirit.

Read the entire text and identify aspects related to the heritage of Kalam and his village.
Answer:
1. I had three close friends in my childhood – Ramanadha Sastry, Aravindan and Siva-
prakasan.
– This shows the heritage of universal brotherhood.
2. As children, none of us ever felt any difference amongst ourselves because of our religious differences and upbringing.
– This shows the heritage of unity in diversity.
3. During the annual Shri Sita Rama Kalyanam ceremony, our family used to arrange boats with a special platform for carrying idols of the Lord from the temple to the marriage site.
– This shows the heritage of communal equality.
4. Ramanadha Sastry looked utterly downcast as I shifted to my seat in the last row according to the instructions of new teacher.
– This shows the heritage of communal brotherhood.
5. Not only did the teacher regret his behaviour but the strong sense of convicton Lakshmana Sastry conveyed ultimately reformed this young teacher.
– This indicates the heritage of social equality and communal tolerance.
6. Sivasubramania Iyer did his best to break social barriers so that people from varying
backgrounds could mingle easily.
– This shows the heritage of social and economic equality and unity in diversity.
III. Here is a letter that Moses writes to his friend Ravi from the United States of America. Imagine yourself as Ravi and give a reply.
Answer:
Reply Letter,
10 – 12, Nidamanure,
Vijayawada Road,
India,
506 001
Dt: 27th January, 2015.
Hi, Moses Bridge,
It’s really great to hear from you that you plan to visit our country and the time to that you have selected for that also is the apt one – October, November.
Of course, we have a lot of festivals, whose roots running deep into our mythology, celebrated through out the year. But the month of October starts with a special celebration, Dussehara. It is immediately followed by Diwali, the festival of lights. Both these are celebrated with great pomp and glory. These two festivals are celebrated to comemmorate the success of goodness over evil, the ultimate success.
Dussehara is more religious in nature. The formal gathering, visit to temple, prayer, feast, and all. But Diwali, known as the festival of lights, is all about the entertainment with all the houses and walls decorated with lights and all are busy with a lot of crackers. I am sure, it could give you an unforgettable experience, forever. I hope that you will come to know more about the Indian rich cultural heritage, the people and their habits, their way of dressing, food they like, music and dance they like etc. during your visit to India.
Anyway, I’m not to go through all as the words couldn’t make it up all. Better be here to experience it all, the best! Expecting the confirmation of Dates of your visit, all the earliest.
Convey my regards to all,
Yours lovingly,
K.Ravi.
To
Moses Bridge,
St. Johns Enclave.
5 – 7/9, St. Pauls Avenue,
Washington D.C,
USA.

Listening:
A Speech by A.P.J Abdul Kalam
Dear friends,
“I have three visions for India. In 3000 years of our history, people from all over the world have come and invaded us, captured our lands, conquered our minds. From Alexander onwards, the Greeks, the Turks, the Moguls, the Portuguese, the British, the French, the Dutch, all of them came and looted us, took over what was ours. Yet we have not done this to any other nation. We have not conquered anyone. We have not grabbed their land, their culture, their history and tried to enforce our way of life on them. Why? Because we respect the freedom of others.
The is why my first vision is that of freedom. I believe that India got its first vision of this in 1857, when we started the war of independence. It is this freedom that we must protect and nurture and build on. If we are not free, no one will respect us. My second vision for India is development, for fifty years we have been a developing nation. It is time we saw ourselves as a developed nation. We are among top 5 nations of the world in terms of GDP. We have 10 percent growth rate in most areas. Our poverty levels are falling. Our achievements are being globally recognized today. Yet we lack the self confidence to see ourselves as a developed nation, self-reliant and self-assured. Isn’t this incorrect?.
I have a third vision. India must stand up to the world because I believe that unless India stands up to the world, no one will respect us. Only strength respects strength. We must be strong not only as a military power but also as an economic power. Both must go hand-in-hand. My good fortune was to have worked with three great minds. Dr. Vikram Sarabhai of the Dept, of Space, Prof. Satish Dhawan, who succeeded him and Dr. Brahm Prakash, father of nuclear material. I was lucky to have worked with all the three of them closely and consider this was the great opportunity of my life….
Why is the media here so negative? Why are we in India so embarrassed to recognize our own strengths, our achievements? We are such a great nation. We have so many amazing success stories but we refuse to acknowledge them. Why? We are the first in milk production. We are number one in Remote sensing satellites. We are the second largest producer of wheat and rice. Look at Dr. Sudharshan, he has transferred the tribal village into a self- sustaining, self driving unit. There are millions of such achievements but our media is only obsessed with failures and disasters…
Listen to an extract from speech by A.P.J. Abdul Kalam at IIIT Hyderabad on 27th September 2011, carefully and answer the following questions.

I. Now answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Who were the three great minds with whom the speaker worked ?
Answer:
Dr. Vikram Sara Bhai, Prof. Sathish Dhavan, Dr. Brahm Prakash were the three great minds with whom the speaker worked.
Question 2.
What dreams did Kalam talk about?
Answer:
Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam talks about dreams with freedom and development, which could make India a developed nation.
Question 3.
India realised its first vision of freedom in 1857 (True / False)
Answer:
True
Question 4.
We must be strong not only as A __________ but also as an __________.
Answer:
military power, economic power
Question 5.
Who is the father of nuclear material?
Answer:
Dr. Brahm Prakash is the father of nuclear material.

Oral Activity:
I. Role play
Read the episode of ill-treatment meted out to Kalam In paragraphs 6 and 7. Understand the character involved in the episode. Take the roles of the new teacher, Kalam, Ramanandha Shastry, Jainulabdeen and Laksmana Sastry. Picturize the episode In your mind and create appropriate dialogues and role play it.
Puplis : Good morning, sir!
New teacher : Very good morning, pupils. Sit down.
Puplis : Thank you sir!
New teacher : Now, introduce yourselves.
Kalam : I am APJ Kalam, sir,
Ramanatha Sastry : My name is Ramanatha Sastry, sir.
New teacher : Kalam, you have a cap on your head. Ithink you are a Muslim boy, but why do you sit beside that Brahmin boy, Ramanatha Sastry.
Kalam : Ramanatha Sastry is my close friend, sir, we daily sit here together in this front row, sir.
New teacher : No, no. You must follow social ranking. You should not sit beside a Brahmin as you are a Muslim. Go and sit on the back bench.
Ramanatha Sastry : Sir, sir, sir, … Please; don’t ask Kalam to sit in the last row. He is my best friend. Don’t separate us, sir.
(Kalam goes and sits in the last row. Both Kalam and Ramanatha Sastry are very sorrowful. They go home and tell their parents about the incident)
Lakashmana Sastry : Why are you so sad, my son?
Ramanatha Sastry : A new teacher has come to our school. When he has come to our V class, he has separated my best friend Kalam from me telling that it is the social ranking, dad.
Lakshmana Sastry : Is it? Don’t take it to your heart. I will come to your school and talk to your teacher.
Ramanatha Sastry : O.K. dad.
(The next day Lakshmana Sastry goes to the school).
Lakshmana Sastry : Good morning sir, are you the new teacher?
New teacher : Yes, I am.
Lakshmana Sastry : I am the father of Ramanatha Sastry.
New teacher : What can I do for you, sir?
Lakshmana Sastry : Yester day, you made Kalam sit in the last row. May I know why you did this?
New teacher : Kalam ¡s a Muslim boy; according to social hierarchy …
Lakshmana Sastry : Don’t think like that. You should not spread the poison of social inequality and communal intolerance in the minds of innocent childf€n. We, the villagers, don’t like these things at all. You should either apologize or quit the school immediately.
New teacher : I am sorry sir. I won’t repeat it under any circumstances. Forgive me.
Lakshmana Sastry : It’s allright. I hope you won’t do such mistakes in future.

II) Group discussion
Conduct a group discussion on how ‘National festivals’ promote natonal integrity.
You may use the following points for discussion.
a) kind of festival
b) nature of celebration
c) secular aspect of celebration
Points to remember:
i Each group will have a moderator to monitor / regulate the discussion.
i Each member of a group should take his / her turn and speak clearly, briefly and pinpointedly and use polite language.
i While speaking make an eye contact with others. i Give time to the others and listen to them.
i If a member wants to say or add a point, he/she has to raise his/her hand and politely seek permission of the moderator.
i The moderator has to connect the ideas expressed by the members and finally sum up.
Member of Group 1:
Answer:
I am very glad to start today’s group discussion about how ‘National festivals’ promote national integrity. I would go for ‘Independence Day’.
Member of Group 2:
‘Independence Day’ acts as an important unifying force. It is celebrated by all Indians and in all parts of the country, regardless of language, religion or culture.
Member of Group 3 :
Our country is secular one. This means that each citizen of our country has the right to practise his or her religion. The government can’t show preference to one religion at the expense of another.
Member of Group 4:
National integration is the awareness of a common identity amongst the citizens of a country. Though we belong to different castes, religions and regions and speak different languages, we recognize the fact that we are all one – Are are Indians.

Member of Group 1:
National integrity is very important in building up of a strong and prosperous nation.
Member of Group 3:
On the occasioin of ‘Independence Day’, we recall the sacrifices made by our freedom fighters which we remember forever. When we recall their heroic deeds, the feeling of oneness occupies all our thoughts.
Member of Group 1:
‘Independence Day’ rewinds us of our common nationality. People belong to different races, communities, castes and regions gather at one place and celebrate the national festival with great enthusiasm.
National integration indicates the feeling of common identity amongst the people of country even after being from different races, cultures, religions or regions in order to build a strong and developed nation. It promotes the unity in diversity and feeling of oneness amongst people to a great level. It brings a type of racial and cultural similarity among people of different community. Along with other factors, National Festivals act as an important unifying force. Independence Day is the festival that is celebrated by all Indians and in all parts of the country, regardless of language, religion or culture. It is celebrated all over India with great pomp and enthusiasm.

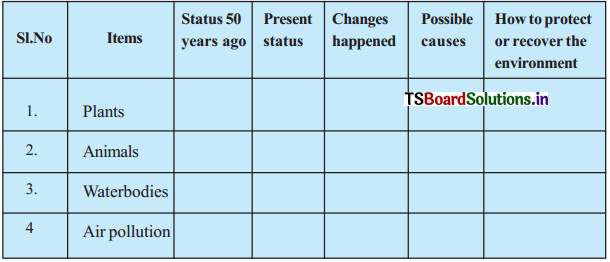
Study Skills:
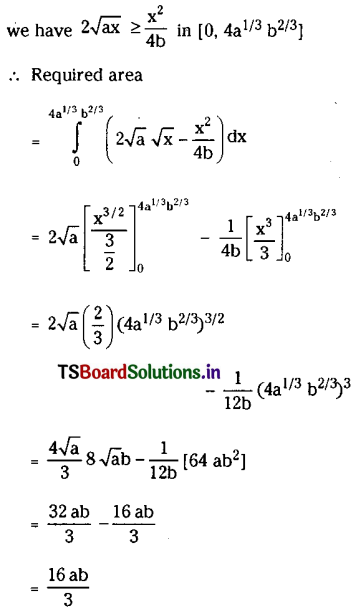
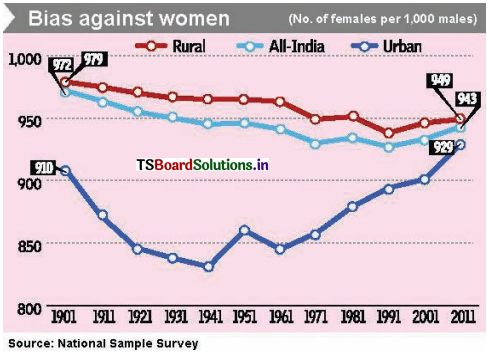
The following graph shows the female-male sex ratio in rural and urban areas comparing with the national average. Read the following graph and write a paragraph comparing the female-male sex ratio in rural and urban areas in India comparing with the national average. Comment on the reasons and its consequences.
Answer:
Sex ratio is a term used to define number of females per 1000 males. It is a great source to find the equality of males and females in a society at a given period of time. According to the graph given above, it is revealed that the population ratio in India is 943 femals per 1000 males in 2011. When we have a look at rural area, the population ratio is 949 females per 1000 males in 2011. In urban area, the population ratio is 929 femals per 1000 males in 2011. Indian sex ratio has shown some improvement in the last 10 years. The number of women in rural area, for every thousand males has decreased gradually from 1901 to 1991.
In the same way, sex ratio in India has decreased gradually from 1901 to 1991. In the above two cases, the sex ratio has gradually increased from 1991 to 2011. When we observe urban area, it is known that the sex ratio declined regularly from 1901 to 1941 and then raised up to 1951 and again decreased till 1961. Then it was all increase up to 2011.
The major cause of the decrease of the female birth ratio in India is considered to be the violent treatements meted out to the girl child at the time of the birth. The main cause of the decline of the sex ratio in India is due to the biased attitude which is meted out to the women. The main cause of this gender bias is inadequate education. Lack of education and poverty in rural area as leads to gender bias.

My Childhood Summary in English
In this lesson, Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam recalls some of his boyhood days and incidents. He was born in a middle class family in the island town of Rameswaram. His father was Jainulabdeen and mother Ashiamma. His childhood was a calm and peaceful one.
During the Second World War, (1939-1945) he used to collect tamarind seeds which had much demand and sold them. He helped his cousin Samsuddin to catch the bundles of The Dinamani daily, which were thrown from the train, at the Rameswaram Railway station. Thus he carried his memorable first wages.
Like his three brothers and sister, he had inherited the qualities like honesty, self-discipline etc from his father and goodness and kindness from his mother. His close friends were Ramanadha Sastry, Aravindan and Sivaprakasan. They never had any religious difference felt among them.
The stories from Ramayana and the life of Prophet were well told to the children. During the annual Shri Sita Rama Kalyanam ceremony, his family used to arrange boats with special platform, for carrying the idols of the Lord from the temple to the marriage site in the middle of the pond, called Rama Tirtha.

When he was studying in fifth class in Rameswaram Elementary School, a new teacher couldn’t tolerate a muslim boy sitting beside a Brahmin boy. He asked Kalam to go back and sit. Being hurt, both the boys complained the same to their parents. Laksmana Sastry, father of Ramanadha Sastry, summoned the teacher and boldly made him to render his apology for spreading the poision of communal intolerance.
Sivasubrammania Iyer, the science teacher, though he was an orthodox Brahmin, he was against class/religious oased social discrimination. He wanted Kalam to develop himself that he would be on par with highly educated people of the big cities. Once he invited Kalam for meals. But his wife was not willing to serve him the food. Iyer himself served Kalam the food. Kalam was again invited to have dinner at Iyer’s house. Kalam hesitated but Iyer insisted saying that one should face such situation if one wants to change the situations. But this time Iyer’s wife served him the food.
After the Second World War, India’s freedom was imminent and Gandhiji had declared that Indians would build their own India. Kalam asked his father the permission for higher studies in Ramanathapuram, which was granted. When his mother was hesitant, his father quoted Khalil Gibran to her convincing that nobody’s children were their own children. They were the sons and daughters of Life’s longing for itself. They come through their parents but not from them. They may give them their love, but not their thoughts as the children have their own thoughts.
About the Author:
Dr. Avul Pakir Jainulabdeen Abdul Kalam, was born on 15th October 1931 at Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu. He was responsible for the evolution of ISRO’s launch vehicle programme, particularly the PSLV configuration and for the development and operationalisation of AGNI and PRITHVI missiles and for building indigenous capability in critical technologies through networking of multiple institutions.
In his literary pursuit four of Dr. Kalam’s books – “Wings of Fire”, “India 2020 – A Vision for the New Millennium”, “My Journey” and “Ignited Minds – Unleashing the power within India” have become household names in India and among the Indian nationals abroad. Dr. Kalam received honorary doctorates from 30 universities and institutions. He was awarded the coveted civilian awards – Padma Bhushan (1981) and Padma Vibhushan (1990) and the highest civilian award Bharat Ratna (1997). Dr. Kalam became the 11th President of India on 25th July 2002.

Glossary:
erstwhile (adj) = former; .
innate (adj) = existing in one from birth ;
generosity (n) = noble mindedness;
undistinguished (adj) = not very interesting, successful or attractive ;
ancestral (adj) = belongs to forefathers ;
austere (adj) = severely simple and plain ;
isolated (adj) = separated from others ;
Allied Forces (n) = The combined forces of Great Britain, France, Soviet Union and the United States of America, in the second World war.;
casualty (n) = A misfortune as a result of an event;
slot (n) = a niche, a gap ;
surge (n) = sudden increase ;
inherit (v) = to recieve by succession ;
Orthodox (adj) = following closely the traditional beliefs and practices of a religion;
downcast (adj) = dejected/depressed ;
summon (v) = to order somebody to come to you ;
intolerance (n) = inability of tolerate (to allow/exist) ;
bluntly (adv) = honestly and directly in a rough way ;
regret (v) = to feel sorrow about for a fault ;
conviction (n) = the act of finding somebody guilty of crime ;
segregation (n) = the policy/ act of separating people ;
conservative (adj) = Opposed to great / sudden social change ;
rituals (n) = a series of actions, specially as a part of religious ceremony ;
perturb (v) = to make worried / anxious ;
confront (v) = to deal with a problem / situation ;
imminent (adj) = unavoidable;

optimism (n) = a feeling that good thing will happen ;
hesitant (adj) = holding back doubtful ;
formal (adj) = strict, proper;
possessed (v) = owned
ideal (adj) = perfect, suitable
spirit (n) = character, strength
rather (adv) = slightly
limestone (n) = a type of white stone
inessential (adj) = not necessary
secure (adj) = safe
materially (adj) = related to money and possessions
princely (adj) = not very large
erupted (v) = raised suddenly
suspension (n) = temporary halt
priest (n) = a person who performs religious duties and ceremonies
idol (n) = a statue that is worshipped as a god.
lasting (adj) = durable, to have an effect for a long time
rigid (adj) = firm
rebel (n) = a person who does not obey but fights against established authority. –
barriers (n) = hurdle, obstruction
varying (adj) = different
mingle (v) = mix, combine
on par with = equal to
horrified (v) = greatly feared
dine (v) = eat
pure (adj) = sacred
unprecedented (adj) = never known before
seagull (n) = a bird which lives at seacoast (a web footed sea bird)
longing (n) = an eager desire
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()