Students can practice TS 6th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Whole Numbers InText Questions to get the best methods of solving problems.
TS 6th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Whole Numbers InText Questions
Do This
Question 1.
Which is the smallest whole number ?
Answer:
‘0’ is the smallest whole
Think, Discuss And Write
Question 1.
Are all natural numbers whole numbers ?
Answer:
Yes, all natural numbers are whole numbers.
Question 2.
Are all whole numbers natural numbers ?
Answer:
No, all whole numbers are not natural numbers. Since 0 ∉ N.
![]()
Do This
Question 1.
Show these on number line :
1) 5 + 3
Answer:
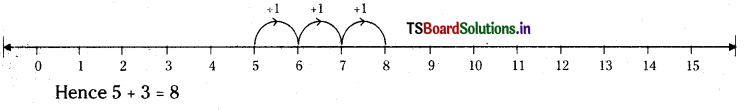
2) 5 – 3
Answer:
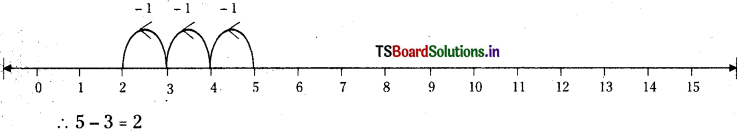
3) 5 + 3
Answer:
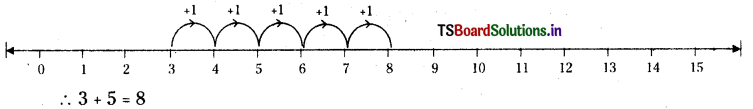
4) 10 + 1
Answer:

Try These
Find the following by using the number line.
Question 1.
What number should be deducted from 8 to get 5 ?
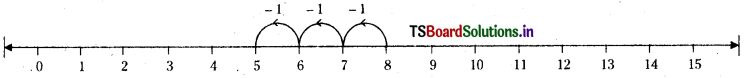
Answer:
3 should be deducted from 8 to get 5.
Question 2.
What number should be deducted from 6 to get 1 ?

5 should be deducted from 6 to get 1.
Question 3.
What number should be added to 6 to get 8 ?
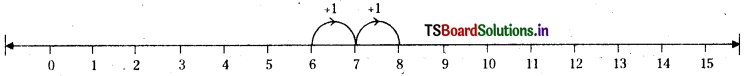
Answer:
2 should be added to 6 to get 8.
Question 4.
How many 6 are needed to get 30 ?
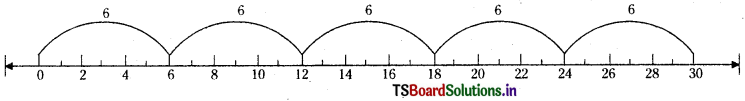
Answer:
The first leap takes you to 6.
From there, the second leap takes you to 12.
From there, the third leap takes you to 18.
From there, the fourth leap takes you to 24.
From there, the fifth leap takes you to 30.
∴ Five 6 are needed to get 30.
![]()
Think, Discuss And Write
Question 1.
Are the whole numbers closed under subtraction ?
Answer:
7 – 5 = 2, is a whole number.
5 – 7 = – 2, is not a whole number.
10 – 4 = 6, is a whole number.
4 – 10 = – 6, is not a whole number.
∴ The whole numbers are not closed under subtraction.
Question 2.
Are the whole numbers closed under division ?
Answer:
6 + 3 = 2, is a whole number,
5 ÷ 2 = \(\frac{5}{2}\), is not a whole number
14 ÷ 2 = 7, is a whole number.
19 ÷ 2 = \(\frac{19}{2}\), is not a whole number.
∴ The whole numbers are not closed under division.
Do This
Question 1.
Find out 12 ÷ 3 and 42 ÷ 7.
Answer:
12 ÷ 3 = 4 and 42 ÷ 7 = 6
Question 2.
What would 6 ÷ 0 and 9 ÷ 0 be equal to?
Answer:
6 ÷ 0 is not defined
9 ÷ 0 is also not defined.
Try These
Take a few examples and check whether.
Question 1.
Subtraction is commutative for whole numbers or not ?
Answer:
Observe the following:
i) 4 – 3 = 1; 3 – 4 = – 1
ii) 5 – 2 = 3; 2 – 5 = -3
1 and – 1 are not equal. 3 and – 3 are also not equal.
∴ Subtraction is not commutative for whole numbers.
Question 2.
Division is commutative for whole numbers or not ?
Answer:
Observe the following:
i) 6 ÷ 2 = 3; 2 ÷ 6 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
ii) 11 ÷ 3 = \(\frac{11}{3}\); 3 ÷ 11 = \(\frac{3}{11}\)
3 and \(\frac{1}{3}\) are not equal; \(\frac{11}{3}\) and \(\frac{3}{11}\) are not equal.
∴ Division is not commutative for whole numbers.
Do this
Question 1.
Verify the following.
(i) (5 × 6) × 2 = 5 × (6 × 2)
Answer:
(5 × 6) × 2 = 30 × 2 = 60 (∵ 5 × 6 = 30)
5 × (6 × 2) = 5 × 12 = 60 (∵ 6 × 2= 12)
(5 × 6) × 2 = 5 × (6 × 2)
(ii)(3 × 7) × 5 = 3 × (7 × 5)
Answer:
(3 × 7) × 5 = 21 × 5 = 105 (∵ 3 × 7 = 21)
3 × (7 × 5) = 3 × 35 = 105 (∵ 7 × 5 = 35)
(3 × 7) × 5 = 3 × (7 × 5)
We see that multiplication is associative over whole numbers.
Do This
Question 1.
Use the commutative and associative properties to simplify the following.
(i) 319 + 69 + 81
(ii) 431 + 37 + 69 + 63
(iii) 2 × (71 × 5)
(iv) 50 × 17 × 2
Answer:
| Commutative | Associative | |
| (i) 319 + 69 + 81 → | 319 + (81 + 69) → | (319 + 81) + 69 = 400 + 69 = 469 |
| (ii) 431 + 37 + 69 + 63 → | (431 + 69) + (37 + 63) = 500 + 100 = 600 | |
| (iii) 2 × (71 × 5) → | 2 (5 × 71) → | (2 × 5) × 71 → 10 × 71 = 710 |
| (iv) 50 × 17 × 2 → | 50 × (2 × 17) → | (50 × 2) × 17 → 100 × 17 = 1700 |
![]()
Think, Discuss And Write
Question 1.
Is (16 ÷ 4) + 2 = 16 ÷ (4 ÷ 2) ?
Does the associative property for division hold for the set of whole numbers? Check if the property holds for subtraction of whole numbers too.Give 5 examples each for substantiate your answer.
Answer:
(16 ÷ 4) ÷ 2 = 16 ÷ (4 ÷ 2)
⇒ 4 ÷ 2 = 16 ÷ (4 ÷ 2)
⇒ 4 ÷ 2 = 16 ÷ 2
⇒ 2 = 8 (False)
For division associative property doesn’t applicable.
Examples for Associative property for division
1) (54 ÷ 9) ÷ 3 = 18 ÷ (9 ÷ 3)
6 ÷ 3 = 18 ÷ 3
2 = 6 (false)
2) (64 ÷ 8) ÷ 4 = 64 ÷ (8 ÷ 4)
8 ÷ 4 = 64 ÷ 2
2 = 32(false)
3) (24 ÷ 6) ÷ 2 = 24 ÷ (6 ÷ 2)
4 ÷ 2 = 24 ÷ 3
2 = 8 (false)
4) (32 ÷ 8) ÷ 4 = 32 ÷ (8 ÷ 4)
4 ÷ 4 = 32 ÷ 2
1 = 16 (false)
5) (49 ÷ 7) ÷ 7 = 49 ÷ (7 ÷ 7)
7 ÷ 7 = 49 ÷ 1
1 = 49 (false)
Similarly, 3 – (2 – 1) = (3 – 2) – 1 ⇒ 3 – 1 = 1 – 1 ⇒ 2 = 0 (False)
∴ For subtraction also associative property doesn’t applicable.
Examples for associative property for subtraction :
1) 4 – (3 – 1) = (4 – 3) – 1
4 – 2 = 1 – 1
2 = 0 (false)
2) 8 – (4 – 3) = (8 – 4) – 3
8 – 1 = 4 – 3
7 = 1 (false)
3) 12 – (4 – 1) = (12 – 4) – 1
12 – 3 = 8 – 1
9 = 7 (false)
4) 13 – (8 – 7) = (13 – 8) – 7
13 – 1 = 5 – 7
12 = -2(false)
5) 15 – (12 – 3) = (15 – 12) – 3
15 – 9 = 3 – 3
6 = 0 (false)
Do This
Question 1.
Find the values of 25 × 78; 17 × 26; 49 × 68 + 32 × 49 using distributive property.
Answer:
(i) 25 × 78; a × (b + c) = a × b + a × c =>.25x 78 = 25 × (80 – 2) = 25 × 80 – 25 × 2 = 2000 – 50 = 1950
(ii) 17 × 26 = 17 × (30 – 4) = 17 × 30 – 17 × 4 = 510 – 68 = 442
(iii) 49 × 68 + 32 × 49 = 49 [68 + 32] = 49 × 100 = 4900
(Try These)
Question 1.
Which numbers can be shown as a line only ?
Answer:
Every number can be shown as a line.
But out of these numbers some numbers can be shown as triangles, some as squares and some as rectangles.
∴ The numbers that can be shown only as lines are 2, 5, 7, 11, 13, ……………..
Question 2.
Which numbers can be shown as rectangles ?
Answer:
The numbers that can be expressed as the product of two numbers can be shown as rectangles.
6 = 2 × 3
8 = 2 × 4
10 = 2 × 5
12 = 2 × 6 (or) 3 × 4
…………….
Question 3.
Which numbers can be shown as squares ?
Answer:
The perfect square numbers such as 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, ………. can be shown as squares.
Question 4.
Which numbers can be shown as triangles ? eg. 3, 6, ……..
Answer:
The numbers that can be shown as triangles are 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, etc.