These TS 10th Class Physical Science Chapter Wise Important Questions Chapter 3 Acids, Bases, and Salts will help the students to improve their time and approach.
TS 10th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 3 Acids, Bases, and Salts
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
What are olfactory indicators?
Answer:
Olfactory indicators are substances which have different odour In aced and base solutions.
Eg : Vanilla essence has characteristic pleasant smell in acid solution and no smell in alkali solution.
Question 2.
What is Plaster of Paris? Give its chemical formula. (AS1)
Answer:
Plaster of Paris the substance which doctors use as plaster for supporting fractured bones in the right position. Its chemical formula Is CaSO4. 1/2 H2O.
Question 3.
What are alkalis?
Answer:
Bases which are soluble In water are called alkalis.
Question 4.
What is pH scale?
Answer:
A scale for measuring hydrogen Ion concentration In a solution Is called pH scale. pH Is a negative longarithm of hydrogen ions [H+].
![]()
Question 5.
Write a short note about the pH of the soil? (AS1)
Answer:
Plants require a specific pH range for their healthy growth. To find out the pH required for the healthy growth of a plant you can collect the soil samples from various places.
Question 6.
Give pH of neutral, acid, base? (ASI)
Answer:
Neutral = 7
Acid <7 Base > 7
Question 7.
Is the substance present in antacid tablet acidic or basic?
Answer:
The substance present in antacid tablet is basic.
Question 8.
What type of reaction takes place in stomach when an antacid tablet is consumed?
Answer:
Neutralisation reaction takes place In stomach when an antacid tablet is consumed.
Question 9.
What is the name of aqueous sodium chloride?
Answer:
Brine solution.
Question 10.
Write the common name of sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Answer:
Baking soda [NaHCO3]
Question 11.
Which salt Is used in the manufacture of borax?
Answer:
Washing soda (Na2CO3)
Question 12.
Give example for salt possesses water of crystallization.
Answer:
Gypsum (CuSO4.2H2O)
Question 13.
What Is the chemical formula for Plaster of Paris?
Answer:
CaSO4. H2O
![]()
Question 14.
Which gas evolves when acids are react with metals?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas.
Question 15.
The reaction in which acid reacts with base forming salt and water is called as.
Answer:
Neutralization.
Question 16.
Bases which are soluble in water are called as.
Answer:
Alkali
Question 17.
Who introduced pH?
Answer:
Sorensen,
Question 18.
Classify the following examples as acid, base (or) salt. (ASI)
Mg[OH]2, H3PO4, KNO2, Ba[OH]2, KCl, HBr, NaCl, HFO4, HCl, Al[OH]3.
Answer:
Acids: H3PO4, HBr, HFO4, HCl
Bases : Mg[OH]2, Ba(OH)2, Al(OH)3
Salts: KNO2, NaCl, KCl
Question 19.
What Is the change you observe in litmus paper with acid?
Answer:
In acidic medium, blue litmus turns red and red litmus remains unchanged.
Question 20.
What is a litmus solution?
Answer:
Litmus solution is a dye extracted from lichen, a plant belonging to tIie division of Thallophyta and is used as indicator.
Question 21.
What is the change you observe in litmus paper with base?
Answer:
In the presence of base, red litmus turns blue and blue litmus remains unchanged.
Question 22.
What is the action of acids and bases with metals? Give examples.
Answer:
When acids and bases reacts with metals, H, gas is evolved.
Eg:
- 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl + H2O
- 2NaOH + Zn → Na2ZnO2+H2
Question 23.
What is the action of acids with carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates?
Answer:
The reaction of metal carbonates and hydrogen carbonates with acids give a corresponding salt, CO2 and water.
Eg:
1) Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
2) NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
Question 24.
What Is a neutralIzation reaction?
Answer:
The reaction of an acid with a base to give a salt and water is known as a neutralization reaction.
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
![]()
Question 25.
What Is the reaction of metal oxides with acids?
Answer:
Metal oxides react with acid to give salt and water.
Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water
Question 26.
Metal oxide reacts with acid and gives salt and water. What is the nature of metal oxides’
Answer:
Metal oxides are basic in nature.
Question 27.
What do acids have In common
Answer:
Hydrogen is common element in all acids.
Question 28.
What is responsible for acidic property of acids?
Answer:
Acids produce H ions in aquatic solution, which are responsible for their acidic properties.
Question 29.
What do bases have in common?
Answer:
OH’ ion (Hydroxide) s common in all bases.
Question 30.
What does the given symbol represent?
Answer:
The given symbol represents that the container is filled with concentrated acids or bases.

Question 31.
When acid Is added to water, what type of reactIon Is It?
Answer:
When acid Is added to water, it is an exothermic reaction.
Question 32.
How do you decide the strength of acid or base?
Answer:
The strength of acid or base can be deoded on the basis of no. of H3O+ ions or OH– ions produced in a solution.
Question 33.
How does the universal indicator help us to know the strength of acid or base?
Answer:
1. Universal indicator is a mixture of several indicators,
2. The universal Indicator shows different colours at different concentrations of hydrogen ions In a solution.
![]()
Question 34.
What Is a pH scale?
Answer:
A scale for measuring hydrogen Ion concentration in a solution is called pH scale.
Question 35.
What Is pH value of a solution?
Answer:
pH value of a solution is simply a number, which Indicates the acidic or basic nature of a solution. ¡t is the negative logarithm of R’ ion concentration in a solution.
Question 36.
What is the range of a pH scale?
Answer:
The range of pH scale is from O to 14.
Question 37.
How do you use pH scale to know whether a solution Is acid or base?
Answer:
If the pH value of a solution is 7, it is a neutral solution. If pH is less than 7, it is an acid and if pH is greater than 7, it Is a base.
Question 38.
What is the chemical name and formula of table salt?
Answer:
The chemical name of table salt is sodium chloride. Its formula is NaCl.
Question 39.
What is the nature of the salt CaSO4 formed by the reaction between calcium hydroxide and sulphuric acid?
Answer:
Calcium hydroxide and sulphuric acid are strong acid and bases. Hence the salt (CaSO4) formed is neutral.
Question 40.
What are the uses of Hydrochloric acid (HCl)?
Answer:
HCl is used as cleaning agent for silts, floor and toilets. It is also used in preparation of medicines, cosmetics etc.
Question 41.
What Is bleaching powder? Write Its formula.
Answer:
Bleaching powder Is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime.
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Formula of bleaching powder is CaOCl2.
Question 42.
Write the chemical equation for preparation of Baking soda.
Answer:
The chemical name of baking soda is Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate (NaHCO3).
The chemical equation for preparation of baking soda is
NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
Question 43.
What Is Baking powder?
Answer:
Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid.
Question 44.
What is water of crystallization?
Answer:
Water of crystallization is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of salt.
![]()
Question 45.
How is plaster of Paris obtained from gypsum?
Answer:
On careful heating of gypsum at 373 K. it loses water molecules partially to become calcium sulphate hemihydrate. This is called plaster of Paris (CaSO4. 1/2 H20).
Question 46.
What Is the reaction of plaster of Paris with water?
Answer:
Plaster of Paris is a white powder and on mixing with water, It sets Into hard solid mass due to the formation of gypsum.
CaSO4 1/2 HO+ 1’/2H2O → CaSO4.2H2O.
Question 47.
What are the salts obtained from common salt?
Answer:
The various salts obtained from common salt are sodium hydroxide, and baking soda. washing soda, bleaching powder sodium silicate and, many more.
Question 48.
What is a rock salt
Answer:
- Deposits of solid salts are found In several parts of the earth. These deposits of large crystals are often brown due to impurities. This Is called rock salt.
- Beds of rock salt are formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. Rock salt is mined like coal.
Question 49.
What does 10H20 signify in the formula Na2CO310H2O?
Answer:
1) 10H2O in Na2CO3 10H2O represents that there are 10 water molecules In one formula unit of sodium carbonate.
2) But sodium carbonate is not wet.
Question 50.
How do acids neutralize bases? (OR) How do acids and bases react with each other?
Answer:
According to Arrhenius, theory acids produce H+ ions and bases produce OH– ions in aqueous media.
The combination of H+ and OH– ions is called ‘neutralization’. Thus acids neutralize bases.
(OR)
The reaction of acids neutralizing bases by producing salt (respective) and water. Thus acids neutralize bases.
Question 51.
How strong are acids and base solutions?
Answer:
The acids of pH value as much less as possible have more concentration [pH<7] Basic nature increases as pH value increases.
(Or)
Acidic nature increases with decrease in Its pH value whereas basic nature increases as pH value increases.
Question 52.
Write the chemical formulae of the following
(i) Bleaching powder
(ii) Sodium Chloride
(iii) Slaked lime
(iv) Baking Soda
(v) Washing Soda
(vi) Gypsum
(vii) Plaster of Paris
(viii) Acetic acid
(ix) Sodium Hydroxide
(x) Common salt
Answer:
(i) Bleaching powder = CaOCl2
(ii) Sodium Chloride = NaCl
(iii) Slaked lime = Ca(OH)2
(iv) Baking Soda = NaHCO3
(v) Washing Soda = Na2CO3.10H2O
(vi) Gypsum = CaSO4.2H2O
(vii) Plaster of Paris — CaSO4.t/2H20
(viii) Acetic acid = CH3COOH
(ix) Sodium Hydroxide = NaOH
(x) Common salt = NaCI
Question 53.
Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Answer:
Aods dont show acidic behaviour in the absence of water as H ions are absent In them.
![]()
Question 54.
If someone in the family is suffering from a problem of acidity, which of the following would you suggest as a remedy: lemon juice, vinegar or baking soda solution? Which property do you think of while suggesting the remedy?
Answer:
- I suggest a baking soda solution. As acidity can be neutralized by baking soda solution. We can use it.
- Acidity is caused due to excess secretion of hydrochloric acid In the stomach. Baking soda is a mild base and it can neutralize the acid in the stomach.
Question 55.
Tap water conducts electricity whereas distilled water does not. Why?
Answer:
Tap water contains some impurities in the form of salts. Due to the presence of salts it conducts electricity. Distilled water is free from all kinds of salts and hence does not conduct electricity.
Question 56.
What do you mean by dilution of an acid or base? Why is it done?
Answer:
Dilution of an acid or base means mixing an acid or base with water, This is done to decrease the concentration of ions per unit volume. In this way the acid or the base is said to be diluted.
Question 57.
Which bases are called alkalies? Give an example of alkali.
Answer:
Water-soluble bases are called alkalies. Examples of Alkalies are NaOH, KOH etc.
Question 58.
Two solutions A and B have pH values of 5 and 8 respectively. Which solution will be basic in nature?
Answer:
Solution B(pH=8) will be basic because Its pH is more than 7.
Question 59.
Why acetic acid is called as weak acid though there are four H atoms in the molecule?
A. Only one of the four H atoms of the monobasic is released as H+ Ion in solution. So acetic acid is called as weak acid.
Question 60.
How does a strong acid differ from a concentrated acid?
Answer:
The strength of an acid depends upon its dissociation power where as concentration depends on water content in the acid.
Question 61.
A student took test tubes containing 2 ml of dilute HCI and added Zn granules to test tube
(A) and solid sodium carbonate to test tube
(B) as shown below.
What would be the correct observation given by the student?
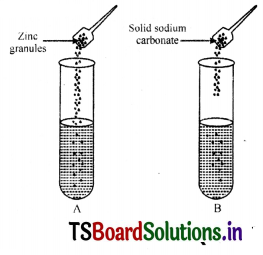
Answer:
There will be rapid reactions In both the test tubes.
Question 62.
Who am I?
(1) I can roughly measure pH value from O-14.
Answer:
pH scale.
(2) I am called antichlor and am used to remove excess chlorine from clothes when treated with bleaching powder.
Answer:
Slaked lime.
(3) I am a product of gypsum and am used for making chalks and fireproof materials.
Answer:
Plaster of Paris.
(4) lama compound of calcium and can be used for disinfecting drinking water as well as for decolourisation.
Answer:
Bleaching powder.
(5) I give different smell in acid and base solution.
Answer:
Olfactory indicator.
(6) I am an oxide capable of showing properties of both acids and bases.
Answer:
Amphoteric oxide
(7) I am a covalent compound and conduct electricity in aqueous medium.
Answer:
Acids.
(8) I am a salt of potassium hydroxide and nitric acid.
Answer:
Potassium Nitrate.
(9) I am derived from tomato and turn blue lItmus Into red.
Answer:
Oxalic acid / Acetic acid.
Question 63.
Mention the precautions to take while conducting an experiment to prove acids produce Ions only in aqueous solutions.
Answer:
- Testing of the evolved gas by using dry litmus paper first. Then with wet litmus paper.
- Using guard tube containing calcium chloride.
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Solution x turned blue litmus red and Solution y turned red litmus blue.
(a) What products could be formed when x and y are mixed?
(b) Which gas is released when we put magnesium pieces in solution X?
(c) Will any chemical reaction take place when zinc pieces are put in solution y?
(d) Which of the above solutions contains more hydrogen ions?
Answer:
Given solution ‘x’ turned blue litmus into red so, X is an acid.
Given solution ‘y’ turned red litmus into blue so, ‘y’ is a base.
a) The reaction of an acid (x) with a base to give a salt and water.
b) When we put magnesium pieces in solution releases hydrogen gas.
c) When zinc pieces are put in solution y a chemical reaction will takes place.
d) Acids contain more H+ ions in the given solutions, ‘x’ has more H’ ions because It Is an acid.
![]()
Question 2.
How do you know the nature of salt formed due to the reaction between acids and bases?
Answer:
The nature of salt depends on the strength of acid and base which form the salt.
Eg strong acid + strong base →b neutral salt
strong acid + weak base → acidic salt
weak acid + strong base → basic salt
weak acid + weak base → depends on relative strength of acid and base.
Question 3.
How washing soda is obtained?
Answer:
- Washing soda can be obtained from sodium chloride.
- Baking soda is obtained from sodium chloride as follows.
NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3 - On heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate.
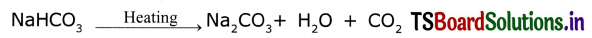
- Recrystallization of sodium carbonate gives washing soda.
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3.10H2O
Question 4.
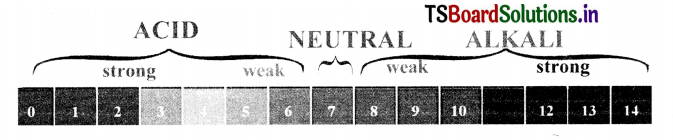
Write a short note on pH scale.
Answer:
- A scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution is called pH scale.
- pH value of a solution is simply a number which indicates the acidic or basic nature of a solution.
- If pH value = 7, it is a neutral solution pH value < , It Is an acidic solution pH value> 7, it Is a basic solution
- The range of pH value is from 0 to 14.
- As pH increases from 7 to 14, it represents a decrease in H3O ion concentration or an increase in OH ion concentration In the solution.
Question 5.
What is the role of pH in our digestive system’
Answer:
- Our stomach produces HCl. It helps in digestion of food without harming the stomach.
- Dunng indigestion, the stomach produces too much acid and this causes pain and Irritation.
- To get rid of this pain, people use bases called antacids.
- These antacids neutralize the exess acid In stomach.
- Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia), a mild base is often used for this purpose.
Question 6.
Explain the self-defence by animals and plants through chemical warfare.
Answer:
- If you have been stung by a honey bee, the sting leaves an acid which causes pain and irritation.
- Use of a mild base like baking soda on the stung area gives relief.
- Stinging hair of leaves of nettle plant, Inject methanoic acid or formic acid causing burning pain.
- A traditional remedy is rubbing the area with the leaf of the dock plant, which often grows beside the nettle in the wild.
Question 7.
Write about universal indicators.
Answer:
- The universal indicator is used to know the strength of acid or base.
- A universal indicator is a mixture of several indicators.
- The universal Indicator shows different colours at different concentrations of hydrogen ions in a solution.
Question 8.
What do acids have in common?
Answer:
Common characteristics of acids :
- Similar chemical properties.
- Acids generate hydrogen gas on reacting with metals.
- Hydrogen is common to acids.
- Acids are sour to taste and turn blue litmus to red and react with bases to form salt and water.
Question 9.
What do bases have in common?
Answer:
Common characteristics of bases :
- Bitterintaste.
- Soapy to touch.
- Turn red litmus to blue colour.
- On heating decompose into metal oxides and water.
- React with acids to form salt and water.
- Produce OH ions in aqueous solution.
Question 10.
Four setups are given below to identify the gas evolved when dilute hydrochloric acid was added to zinc granules. Which is the most appropriate setup?
Answer:

The gas evolved can be tested as shown in IV set-up because In the delivery tube thistle funnel is -used to drop dilute HCI and to evolve H gas, it should not dip In the acid.
Question 11.
“While constructing a house, a builder selects marble flooring and marble table tops for the kitchen where vinegar and juice of lemon, tamarind etc., are more often used for cooking. Will you agree to this selection and why? Give reasons.
Answer:
No, I didn’t agree with him, because
- The substances like vinegar, tamarind etc., contain acids which accidentally fall on marble will damage it.
- Reason for that marble is calcium carbonate and will react with the acids to undergo chemical changes and thus making marks.
![]()
Question 12.
Why do we use antacids? Write its nature.
Answer:
- Pain and irritation will be caused In stomach during the acidity problem/ indigestion problem. Antacids are used to neutralize the excess acid in the stomach and gives relief from acidity.
- Antacids are basic in nature.
Question 13.
Calcium compound which is a yellowish-white powder is used as a disinfectant and also in textile industry
a) Name the compound.
a) Which gas is released when this compound is left exposed to air?
Answer:
a) The compound s Bleaching powder r calcium oxi chloride. (CaOCl2)
b) When it is exposed to air, it releases Cl gas according to the following reaction with CO2 present in air.
CaOCl2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + Cl2 ↑
Question 14.
Why are some salts called hydrated salts? Give two examples of white-coloured hydrated salts with their chemical formulae.
Answer:
a) Salts which contain water of crystallisation are called as hydrated salts.
b) Two white-coloured hydrated salts are
- Gypsum – CaSO4. 2H2O
- Washing soda – Na2CO3. 10H2O
Question 15.
Discuss briefly the examples showing the importance of pH in daily life.
Answer:
- Living organisms can survive only in a narrow range of pH change. For example it lowers the pH of the river water, the survival of aquatic life in such novels becomes difficult.
- Tooth decay starts when the change In pH value of mouth.
- Our stomach produces HCI which control the digestion of food in our stomach.
- Plants require a specific pH range for their healthy growth.
- Animals and plants use chemical solutions having certain pH value for their self-defence.
Question 16.
Which product will form when CaO is dissolved in water? How do you find the nature of product?
Answer:
- CaO reacts with water and gives calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2].
- The nature of the calcium hydroxide will be tested with red litmus paper or pH paper.
- Calcium hydroxide turns red litmus Into blue. Thus we can say that Ca(OH)2 is basic in nature.
- Ca(OH)2 shows pH value more than 7 on pH paper. Thus we can say that Ca(OH)2 is basic in nature.
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
If the pH values of solutions X, Y and Z are 13, 6 and 2 respectively then
(a) Which solution is a strong acid? Why?
(b) Which solution contains ions along with molecules of solution?
(c) Which solution is a strong base? Why?
(d) Does the pH value of a solution increase or decrease when a base is added to it? Why?
Answer:
The strength of an acid (or) an alkali can be tested by using pH value of a solution. If the value of a pH of a solution is less than, then that solution exhibits acidic nature. If the value of a pH of a solution is more than, then that solution exhibits basic nature.
pH value of a solution “X” is 13
pH value of a solution Y’ is 6
pH value of a solution “Z” Is 2
a) Solution ‘Z’ is strong acid because its pH is 2.
b) Among given solutions, solution ‘Y’ is weakest acid. Weak solution contains ions along with molecules of solution. So ‘y’ exhibits like this character.
c) Solution X is strong base. Because its pH Is 13.
d) If base is added to a solution then its pH will increase.
Question 2.
Describe how sodium hydroxide Is obtained from common salt?
Answer:
1. When electricity Is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (called brine), It decomposes to form sodium hydroxide
2. The process is called choir-alkali process – because of the products formed chior for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide.
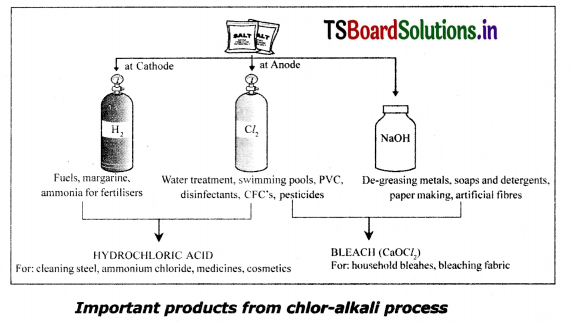
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)+Cl2(g)+H2(g)
3. Chlorine gas is liberated at the anode and hydrogen gas at the cathode.
4. Sodium hydroxide solution is formed near the cathode.
5. The three products produced in this process are all useful.
Question 3.
Describe process of preparation of bleaching powder? Write its uses.
Answer:
Preparation of Bleaching Powder:
- Chlorine gas is produced during electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride.
- This chlorine gas is used for the manufacture of bleaching powder.
- Bleaching powder is produced by the action of chlorine on slaked lime.

Uses of Bleaching powder:
- It is used for bleaching cotton and linen in the textile industry, for bleaching wood pulp in paper Industry and for bleaching washed clothes in laundry.
- Used as an oxidizing agent in many chemical industries.
- Used for disinfecting drinking water to make it free of germs.
- Used as a reagent in the preparation of chloroform.
![]()
Question 4.
Write the chemical equation of preparation of baking soda. What are the uses of baking soda?
Answer:
Preparation of Baking Soda:
- The chemical name of baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate and the formula is NaHCO3.
- It is prepared as follows.
NaCl+ H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
Uses of Baking soda:
- Baking soda is added for faster cooking.
- It is used as an ingredient ¡n antacids.
- It Is also, used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
- It acts as a mild antiseptic.
- Baking powder can be prepared as a mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid.
- Baking powder is used in preparation of bread or cake to make them soft and spongy.
Question 5.
How do you prepare washing soda? What are its uses?
Answer:
Preparation of Washing soda:
1. Washing soda can be obtained from sodium chloride.
2. Baking soda is obtained from sodium chloride as follows.
NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl+ NaHCO3
3. On heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate
![]()
4. Recrystallization of sodium carbonate gives washing soda.
Na2CO3 → 10H2O+ Na2CO3.10H2O.
Uses of Washing soda:
- Washing soda (sodium carbonate) is used in glass, soap and paper industries.
- It is used in the manufacture of sodium compounds such as borax.
- Sodium carbonate can be used as a cleaning agent for domestic purposes.
- it Is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
Question 6.
Draw a neat diagram showing variation of pH with the change in concentration of H+(aq) ions and OH–(aq) ions.
Answer:
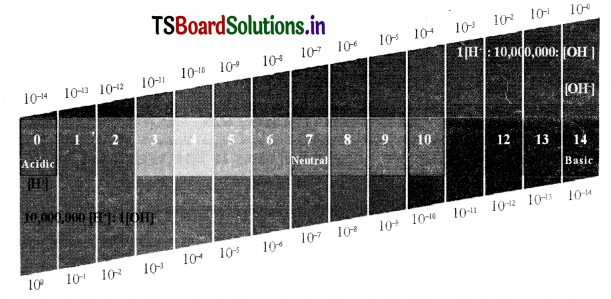
Variation of pH with the change in concentration of H+ ions and OH–(aq) ions.
Question 7.
Write the pH values of some things.
Answer:
| pH value | Things |
| 0 | Battery Acid |
| 1 | Con.H2SO4 |
| 2 | Lemon juice |
| 3 | Orange Juice |
| 4 | Tomato juice |
| 5 | Black coffee, Bananas |
| 6 | Milk, urine |
| 7 | Pure water |
| 8 | Sea water, eggs |
| 9 | Baking soda |
| 10 | Milk of magnesia |
| 11 | Ammonia solution, |
| 12 | Soapy water |
| 13 | Bleach oven cleaner |
| 14 | Liquid drain cleaner |
Question 8.
Distinguish between acids and bases.
Answer:
| Acids | Bases |
| 1) An acid is a substance which gives H+ ions In water solution. | 1) A base is a solution which contains OH– group in water solution and gives hydroxyl Ions OH–. |
| 2) Acids are sour in taste. | 2) Bases are bitter In taste. |
| 3) Acid turns blue litmus to red. | 3) Bases turn red litmus to blue. |
| 4) The orange colour of methyl orange indicator changes to red In acid medium. | 4) The orange colour of methyl orange indicator changes to yellow in bases medium. |
| 5) Acids are formed when non-metal oxides are dissolved in water. | 5) Bases are formed when metal oxides are dissolved in water. |
| 6) pH value of acid is less than 7. | 6) pH value of base is greater than 7. |
Question 9.
Observe the following table and answer the questions given below. The table contains the aqueous solutions of different substances with the same concentrations and their respective pH value.
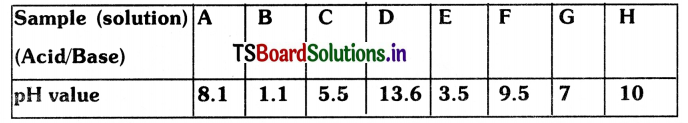
(i) Which one of the above acid solutions is the weakest acid? Give a reason.
(ii) Which one of the above solutions is the strongest base? Give reason.
(iii) Which of the above two produce maximum heat when they react? What does that heat energy called?
(iv) Which one of the above solutions has the pH equal to that of the distilled water? What is the name given to solutions of that pH value?
Answer:
(i) ‘C’ Is the weakest acid because it has less H ior concentration.
(ii) ‘H’ is the strongest base because It contains more OH ion concentration.
(iii) ‘B’ and ‘H’ produce maximum heat energy. This heat energy ¡s called ‘Heat of Neutralization’.
(iv) ‘G’. It ¡s named as Neutral solution.
Question 10.
List out the materials required to test whether the solutions of given acids and bases contain ions or not. Explain the procedure of the experiment.
Answer:
Materials Required:
Beaker, Graphite rods, dil.HCl solution, bulb, glucose, alcohol solutions and connecting wires.
Aim:
To test whether the solutions of given acids and bases contain ions or not.
Procedure:
1. Prepare solutions of glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid.
2. Dril two holes on a rubber cork and introduce two iron nails Into the holes.
3. Connect two different coloured electrical wires and keep it in a loo ml. beaker.
4. Connect free ends of the wire to 6V battery and complete the circuit.
5. Pour some diluted HCl in the beaker and switch on the current.
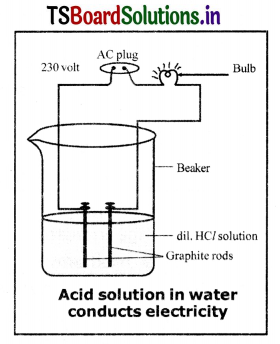
6. We find that the bulb glows.
7. Repeat the activity with diluted H2SO4, glucose and alcohol solutions separately.
8. The bulb glows when acid is taken in the beaker. But the bulb does not glow when glucose and alcohol are taken in the beaker.
9. Glowing of bulb indicates that there Is flow of electric current through the solution.
10. Acid solutions have ions and the movement of these ions helps flow of current but glucose and alcohol solutions do not have free ions and so current does not pass through them.
![]()
Question 11.
Write any four chemical properties of acids.
Answer:
Chemical properties of acids:
- Active metal react with acids and liberate hydrogen gas.
Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 ↑ - Acids react with bases to form salt and water.
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) - Acids react with metallic oxides to form salt and water.
MgO(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) - Acids react with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates and release” carbon dioxide gas.
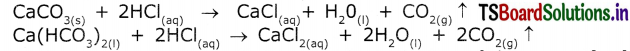
Question 12.
Six solutions A, B, C, D, E, F as 5, 2, 1, 3, 7 and 9 respectIvely which solution is
a) Neutral
b) Strongly alkaline
c) Strongly acid
d) Weakly acidic
Arrange the pH in increasing order of Hydrogen ion concentration.(ASI)
Answer:
a) solution E is neutral
b) solution F is Alkaline
C) solution C is strongly acidic
d) solution A is weakly acidic
e) Solution B is strongly acidic
f) solution D is strongly acidic.
g) Ascending order of increase of Hydrogen ion concentration is F, E, A, D, B, C
Question 13.
By observing the given pH scale, answer the following.
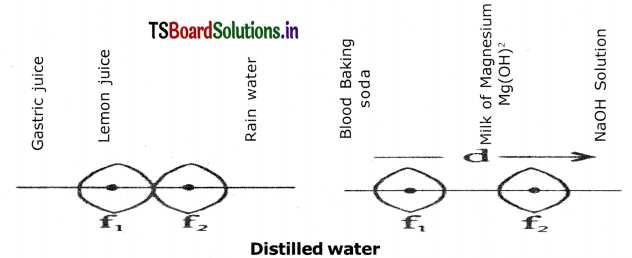
(i) Which of the body fluid Is basic in nature?
(ii) Is lemon juice a strong acid or weak acid?
(iii) Which of the above liquid have strong basic character?
(iv) What is the pH of distilled water?
Answer:
From the above pH scale:
(i) The body fluid that is basic in nature is blood (pH>7).
(ii) The pH of lemon juice is less than three. So t is a strong acid.
(iii) NaOH is the strong base because it has highest pH value.
(iv) The pH of distilled water is 7.
Do You Know
1. Litmus solution is a dye extracted from lichen, a plant belonging to the division of Thallophyta and is used as indicator. In neutral solution litmus colour is purple. Coloured petals of some flowers such as Hydrangea, Petunia and Geranium are also used as indicators.
2. To avoid the negative powers of H+ concentration in dilute acid and base solutions Sorensen introduced the concept of pH. Due to this pH concept may be restricted for solutions of [H+] less than 1 molar.
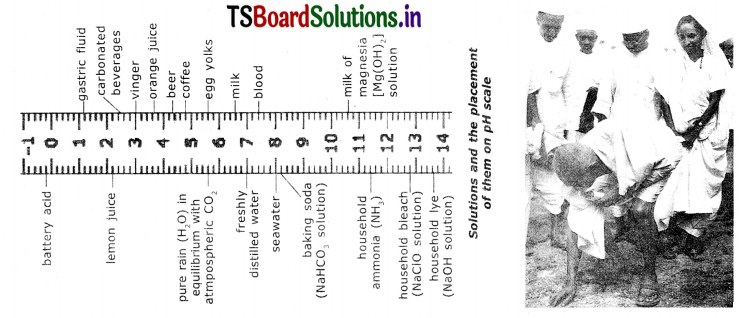
The pH scale is from 0-14. The ph Is an indication of concentration of H. For example, at a ph of zero the hydronium ion concertration is one molar.
Typically the concentrations of H in water in most solutions fall between a range of 1 M (pHO) and 10-14 M (pH=14). Figure 8 depicts the pH scale with common solutions.
3. Sait – a symbol of freedom struggle: You know common salt is a substance which enhances the taste of food; it also has played a remarkable role in motivating the people towards freedom struggle. The tax levied by the British government on common food substance (salt), for both the poor and the rich, made them to become united in the freedom struggle. You must have heard about Mahatma Gandhi’s Dandi March and about ‘salt satyagraha’ in the struggle for freedom of India.