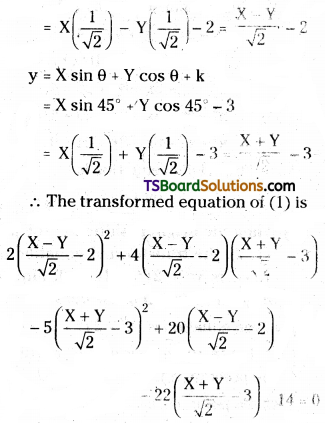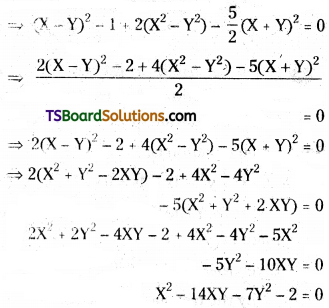Students must practice these Maths 1B Important Questions TS Inter First Year Maths 1B Transformation of Axes Important Questions to help strengthen their preparations for exams.
TS Inter First Year Maths 1B Transformation of Axes Important Questions
Question 1.
When the origin is shifted to (3, 4) by the translation of axes, find the transformed equation of 2x2 + 4xy + 5y2 = 0. [Mar. ’00]
Solution:
Given equation is 2x2 + 4xy + 5y2 = 0 ……..(1)
Let (X, Y) be the new coordinates of the point (x, y).
Given a point, (h, k) = (3, 4)
By the translation of axes,
x = X + h, y = Y + k
x = X + 3, y = Y + 4
The transformed equation of (1) is,
2(X + 3)2 + 4(X + 3)(Y + 4) + 5(Y + 4)2 = 0
⇒ 2(X2 + 6X + 9) + 4(XY + 4X + 3Y + 12) + 5(Y2 + 8Y + 16) = 0
⇒ 2X2 + 12X + 18 + 4XY + 16X + 12Y + 48 + 5Y2 + 40Y + 80 = 0
⇒ 2X2 + 5Y2 + 28X + 52Y – 4XY + 146 = 0
⇒ 2X2 + 4XY + 5Y2 + 28X + 52Y + 146 = 0
Question 2.
When the origin is shifted to the point (2, 3), the transformed equation of a curve is x2 + 3xy – 2y2 + 17x – 7y – 11 = 0. Find the original equation of the curve. [Mar. ’16 (TS), ’13, ’11, ’10, ’09; May ’15 (AP), ’09]
Solution:
The given equation is,
X2 + 3XY – 2Y2 + 17X – 7Y – 11 = 0 ………(1)
Let (x, y) be the original coordinates of the point (X, Y).
Given a point, (h, k) = (2, 3).
By the translation of axes,
x = X + h, y = Y + k
⇒ x = X + 2, y = Y + 3
⇒ X = x – 2, Y = y – 3
The original equation of (1) is
(x – 2)2 + 3(x – 2)(y – 3) – 2(y – 3)2 + 17(x – 2) – 7(y – 3) – 11 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4 – 4x + 3(xy – 3x – 2y + 6) – 2(y2 + 9 – 6y) + 17x – 34 – 7y + 21 – 11 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4 – 4x + 3xy – 9x – 6y + 18 – 2y2 – 18 + 12y + 17x – 34 – 7y + 21 – 11 = 0
⇒ x2 + 3xy – 2y2 + 4x – y – 20 = 0
∴ The original equation is x2 + 3xy – 2y2 + 4x – y – 20 = 0
![]()
Question 3.
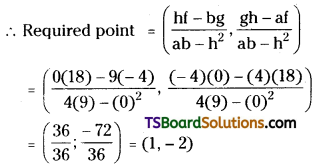
Find the point to which the origin is to be shifted so as to remove the first-degree terms from the equation 4x2 + 9y2 – 8x + 36y + 4 = 0. [May ’03]
Solution:
Given equation is 4x2 + 9y2 – 8x + 36y + 4 = 0
Comparing the given equation with ax2 + 2hxy + by2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0
We get a = 4, h = 0, b = 9, g = -4, f = 18, c = 4.
Question 4.
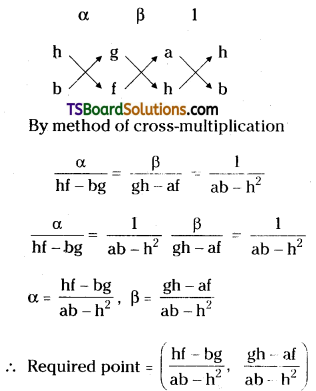
Find the point to which the origin is to be shifted by the translation of axes 50 as to remove the first-degree terms from the equation ax2 + 2hxy + by2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 where h2 ≠ ab. [May ’97]
Solution:
Given equation is ax2 + 2hxy + by2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 …….(1)
Let (α, β) be the required point.
Let (X, Y) be the new coordinates of the point (x, y).
∴ x = X + α, y = Y + β
Now substitute the values of x, y in equation (1)
∴ The transformed equation is a(X + α)2 + 2h(X + α)(Y + β) + b(Y + β)2 + 2g(X + α) + 2f(Y + β) + c = 0
⇒ a(X2 + α2 + 2Xα) + 2h(XY + βX + αY + αβ) + b(Y2 + β2 + 2βY) + 2gX + 2gα + 2fY + 2fβ + c = 0
⇒ aX2 + aα2 + 2aXα + 2hXY + 2hβX + 2hαY + 2hαβ + bY2 + bβ2 + 2bβY + 2gX + 2gα + 2fy + 2fβ + c = 0
⇒ aX2 + 2hXY + bY2 + 2X(aα + hβ + g) + 2Y(hα + bβ + f) + aα2 + 2hαβ + bβ2 + 2gα + 2fβ + c = 0
Since, x, y terms are eliminated
aα + hβ + g = 0 ……..(2)
hα + bβ + f = 0 ……….(3)
Solving (2) & (3)
Question 5.
Prove that the angle of rotation of the axes to eliminate xy term from the equation ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 is \(\frac{1}{2} \tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{2 h}{a-b}\right)\) where a ≠ b and \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) if a = b. [Mar. ’13 (Old); ’13, ’06, ’02]
Solution:
x = X cos θ – Y sin θ
y = X sin θ + Y cos θ
Given equation is ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 ……..(1)
∴ The transformed equation of (1) is
a(X cos θ – Y sin θ)2 + 2h(X cos θ – Y sin θ) (X sin θ + Y cos θ) + b(X sin θ + Y cos θ)2 = 0
⇒ a[X2 cos2θ + Y2 sin2θ – 2X cos θ . Y sin θ] + 2h(X2 cos θ . sin θ + XY cos2θ – XY sin2θ + Y2 sin θ cos θ + b[X2 sin2θ + Y2 cos2θ + 2XY sin θ cos θ] = 0
⇒ [aX2 cos2θ + aY2 sin2θ – 2aX cos θ . Y sin θ + 2hX2 cos θ . sin θ + 2hXY cos2θ – 2hXY sin2θ + 2hY2 sin θ cos θ + bX2 sin2θ + bY2 cos2θ + 2bXY sin θ cos θ] = 0
⇒ X2[a cos2θ + 2h cos θ . sin θ + b sin2θ) + XY (-2a sin θ cos θ + 2h cos2θ – 2h sin2θ + 2b sin θ cos θ) + Y2 (a sin2θ – 2h sin θ cos θ + b cos2θ] = 0
Since xy term is eliminated, then,
⇒ -2a sin θ . cos θ + 2h cos2θ – 2h sin2θ + 2b sin θ cos θ = 0
⇒ -a sin 2θ + 2h(cos2θ – sin2θ) + b sin 2θ = 0
⇒ -a sin 2θ + 2h cos 2θ + b sin 2θ = 0
⇒ 2h cos 2θ = a sin 2θ – b sin 2θ
⇒ 2h cos 2θ = (a – b) (sin 2θ)
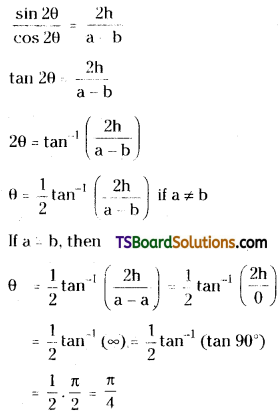
Question 6.
Find the angle through which the axes are to be rotated so as to remove the xy term in the equation x2 + 4xy + y2 – 2x + 2y – 6 – 0. [May ’04, ’96]
Solution:
Given equation is x2 + 4xy + y2 – 2x + 2y – 6 = 0
By comparing the given equation with ax2 + 2hxy + by2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0,
we get a = 1, h = 2, b = 1
The required angle of rotation
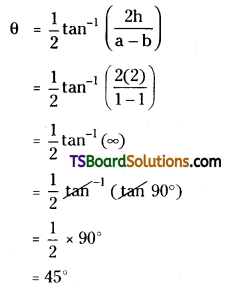
![]()
Question 7.
When the axes are rotated through an angle of 60°, the new coordinates of the point are (3, 4). Find their original coordinates. [May ’03]
Solution:
Let (x, y) be the original coordinates of (X, Y).
Given that, the angle of rotation θ = 60°
(X, Y) = (3, 4) then
x = X cos θ – Y sin θ
= 3(cos 60°) – 4(sin 60°)
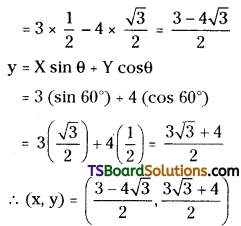
Question 8.
When the axes are rotated through an angle of 45°, the transformed equation of a curve is 17x2 – 16xy + 17y2 = 225. Find the original equation of the curve. [May ’15 (TS), ’12, ’10, ’01; Mar. ’15 (TS), ’08]
Solution:
Given equation is 17x2 – 16xy + 17y2 = 225 ………(1)
Angle of rotation θ = 45°
Let (x, y) be the original coordinates of (X, Y) then
X = x cos θ + y sin θ
= x cos 45° + y sin 45°
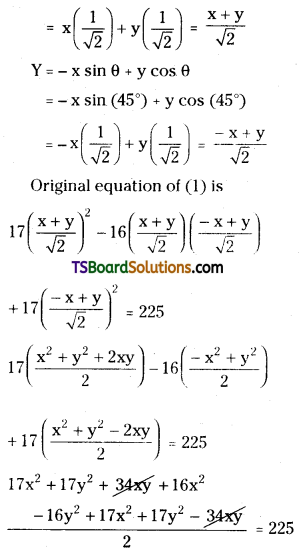
50x2 + 18y2 = 450
25x2 + 9y2 = 225
Question 9.
When the axes are rotated through an angle α, find the transformed equation of x cos α + y sin α = P. [Mar. ’19 (TS); Mar. ’14, ’00; May ’07]
Solution:
Given equation is x cos α + y sin α = P ………..(1)
Let (X, Y) be the new coordinates of (x, y)
Given that, the angle of rotation θ = α, then
x = X cos θ + Y sin θ = X cos α + Y sin α
y = X sin θ + Y cos θ = X sin α + Y cos α
The transformed equation of (1) is
(X cos α – Y sin α) cos α + (X sin α + Y cos α) sin α = P
⇒ X cos2α – Y sin α cos α + X sin2α + Y cos α sin α = P
⇒ X cos2α + X sin2α = P
⇒ X(cos2α + sin2α) = P
⇒ X(1) = P
⇒ X = P
Question 10.
When the axes are rotated through an angle \(\frac{\pi}{6}\), find the transformed equation of x2 + 2√xy – y2 = 2a2. [Mar. ’15 (AP); May ’13, ’06, ’03; Mar. ’12, ’07, ’03; B.P.; Mar. ’18 (TS)]
Solution:
Given equation is x2 + 2√3 xy – y2 = 2a2 ………(1)
Let (X, Y) be the new coordinate of (x, y).
Given that, angle of rotation θ = \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) = 30°, then
x = X cos θ – Y sin θ
= X cos 30° – Y sin 30°
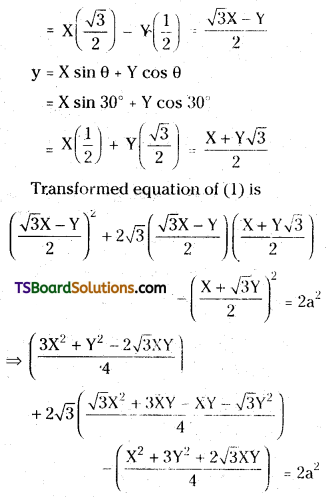

![]()
Question 11.
When the axes are rotated through an angle \(\frac{\pi}{4}\), find the transformed equation 3x2 + 10xy + 3y2 = 9. [Mar. (AP & TS) ’17; May ’14, ’11, ’05; Mar. ’08]
Solution:
Given equation is, 3x2 + 10xy + 3y2 = 9 ……(1)
Let (X, Y) be the new coordinates of (x, y).
Given that, angle of rotation θ = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) = 45°
x = X cos θ – Y sin θ
= X cos 45° – Y sin 45°
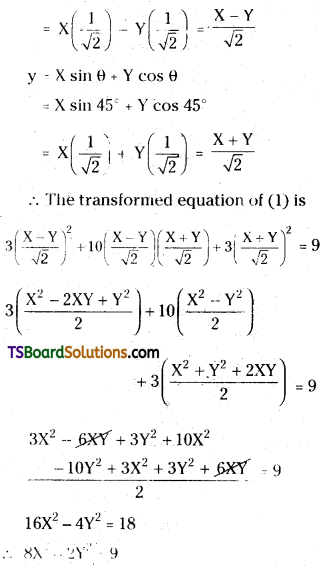
Some More Maths 1B Transformation of Axes Important Questions
Question 12.
When the origin is shifted to (-1, 2) by the translation of axes find the transformed equation of x2 + y2 + 2x – 4y + 1 = 0.
Solution:
Given equation is x2 + y2 + 2x – 4y + 1 = 0 ……(1)
Let (X, Y) be the new coordinates of the point (x, y).
Given that, (h, k) = (-1, 2)
By the translation of axes,
x = X + h, y = Y + k
⇒ x = X- 1, y = Y + 2
The transformed equation of (1) is
(X – 1)2 + (Y + 2)2 + 2(X – 2) – 4(Y + 2) + 1 = 0
⇒ X2 – 2X + 1 + Y2 + 4 + 4Y + 2X – 2 – 4Y – 8 + 1 = 0
⇒ X2 + Y2 – 4 = 0
∴ The transformed equation is X2 + Y2 – 4 = 0
Question 13.
When the origin is shifted to (-1, 2) by the translation of axes, find the transformed equation of 2x2 + y2 – 4x + 4y = 0.
Solution:
Given equation is 2x2 + y2 – 4x + 4y = 0 …..(1)
Let (X, Y) be the new coordinates of the point (x, y).
Given that, (h, k) = (-1, 2)
By the translation of axes,
x = X + h, y = Y + k
⇒ x = X – 1, y = Y + 2
The transformed equation of (1) is,
2(X – 1)2 + (Y + 2)2 – 4(X – 1) + 4(Y + 2) = 0
⇒ 2(X2 – 2X + 1) + (Y2 + 4 + 4Y) – 4X + 4 + 4Y + 8 = 0
⇒ 2X2 – 4X + 2 + Y2 + 4 + 4Y – 4X + 4 + 4Y + 8 = 0
⇒ 2X2 + Y2 – 8X + 8Y + 18 = 0
∴ The transformed equation is 2X2 + Y2 – 8X + 8Y + 18 = 0
![]()
Question 14.
When the origin is shifted to the point (3, -4), the transformed equation of a curve is x2 + y2 = 4. Find the original equation of the curve.
Solution:
Given equation is X2 + Y2 = 4 ………(1)
Let (x, y) be the original coordinates of the point (X, Y).
Given point, (h, k) = (3, -4)
By the translation of axes,
x = X + h, y = Y + k
⇒ x = X + 3, y = Y – 4
⇒ X = x – 3, Y = y + 4
The original equation of (1) is (x – 3)2 + (y + 4)2 = 4
⇒ x2 + 9 – 6x + y2 + 16 + 8y = 4
⇒ x2 + y2 – 6x + 8y + 25 = 4
⇒ x2 + y2 – 6x + 8y + 25 – 4 = 0
⇒ x2 + y2 – 6x + 8y + 21 = 0
∴ The original equation is x2 + y2 – 6x + 8y + 21 = 0.
Question 15.
When the origin is shifted to the point (-1, 2), the transformed equation of a curve is x2 + 2y2 + 16 = 0. Find the original equation of the curve.
Solution:
Given equation is X2 + 2Y2 + 16 = 0 …….(1)
Let (x, y) be the original coordinates of the point (X, Y).
Given a point, (h, k) = (-1, 2)
By the translation of axes,
x = X + h, y = Y + k
⇒ x = X – 1, y = Y + 2
⇒ X = x + 1, Y = y – 2
The original equation of (1) is (x + 1)2 + 2(y – 2)2 + 16 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2x + 1 + 2(y2 + 4 – 4y) + 16 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2x + 1 + 2y2 + 8 – 8y + 16 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2y2 + 2x – 8y + 25 = 0
∴ The original equation is x2 + 2y2 – 2x – 8y + 25 = 0.
![]()
Question 16.
When the origin is shifted to (-2, -3) and the axes are rotated through an angle of 45°, find the transformed equation of 2x2 + 4xy – 5y2 + 20x – 22y – 14 = 0.
Solution:
Given equation is 2x2 + 4xy – 5y2 + 20x – 22y – 14 = 0 ………(1)
Let (X, Y) be the new coordinates of (x, y).
Given that, (h, k) = (-2, -3)
angle of rotation θ = 45°
x = X cos θ – Y sin θ + h
= X cos 45 – Y sin 45 + (-2)