Students can practice TS Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Similar Triangles Ex 8.2 to get the best methods of solving problems.
TS 10th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Similar Triangles Exercise 8.2
Question 1.
In the given figure, ∠ADE = ∠B
i) Show that ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE
ii) If AD = 3.8 cm, AE = 3.6 cm, BE = 2.1 cm, BC = 4.2 cm. Find DE. (AS1, AS2)
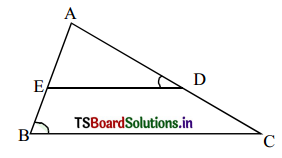
Solution:
In ∆les ADE and ABC, we have
i) ∠ADE = ∠ABC (Given)
∠A = ∠A (Common)
∴ ∠AED = ∠ACB
Hence, ∆ADE ~ ∆ABC Therefore, their corresponding sides are proportional.
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AD}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{AD}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{AE}}\)
ii) Given that AD = 3.8 cm; AE = 3.6 cm; BE = 2.1 cm; BC = 4.2 cm; DE = ?

∴ DE = 2.8 cm
Question 2.
The perimeters of two similar triangles are 30 cm and 20 cm respectively. If one side of the first triangle is 12 cm., determine the corresponding side of the second triangle. (AS1)
Solution:
Let ∆ABC and ∆DEF be two similar triangle of perimeters 30 cm and 20 cm.
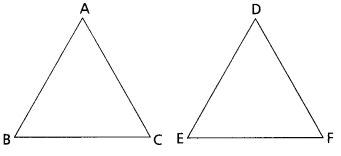
The ratio of the perimeters = 30 : 20 = 3 : 2
Let AB = 12 cm
We have \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{EF}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{DF}}\)
We know that the ratio of corresponding sides of similar triangles is equal to the ratio of their perimeters.
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{12}{\mathrm{DE}}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
⇒ 3 × DE = 12 × 2
⇒ DE = \(\frac{12 \times 2}{3}\) = \(\frac{24}{3}\) = 8 cm
Hence, the corresponding side of the triangle = 8 cm.
![]()
Question 3.
A girl of height 90 cm is walking away from the base of a lamp post at a speed of 1.2m/sec. If the lamp post is 3.6m above the ground, find the length of her shadow after 4 seconds. (AS4)
Solution:
In the adjacent figure, AB represents the height of the lamp post, DE, the height of the girl. EC represents the length of girls shadow let EC = x.
The distance between the foot of the lamp post and the girl = 1.2 × 4 = 4.8 meters = 480 cm
DE = 90 cm = 0.9 meters
AB = 3.6 meters
∆ABC ~ ∆DEC
∴ The corresponding sides are proportional.
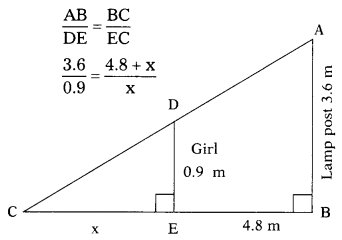
⇒ 3.6 × x = (4.8 × 0.9) + (0.9 × x)
⇒ 3.6x = 4.32 + 0.9x
⇒ 3.6x – 0.9x = 4.32
⇒ 2.7x = 4.32
⇒ x = \(\frac{4.32}{2.7}\) = \(\frac{432}{100}\) × \(\frac{10}{27}\) = \(\frac{16}{10}\) = 1.6
∴ The length of the girl’s shadow = 1.6 meters.
Question 4.
Given that ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR, CM and RN are respectively the medians of similar triangles ∆ABC and ∆PQR. Prove that (AS2)
i) ∆AMC ~ ∆PNR (AS2)
ii) \(\frac{\mathrm{CM}}{\mathrm{RN}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{PQ}}\)
iii) ∆CMB ~ ∆RNQ
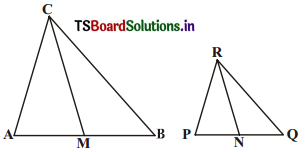
Solution:
i) ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR (Given)
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{PQ}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{QR}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{CA}}{\mathrm{RP}}\) ………………. (1)
(Corresponding sides are proportional)
And ∠A = ∠P; ∠B = ∠Q; ∠C = ∠R ……………… (2)
(Corresponding angles are equal)
AB = 2AM and PQ = 2PN (∵ CM and RN are medians)
From (1) we have
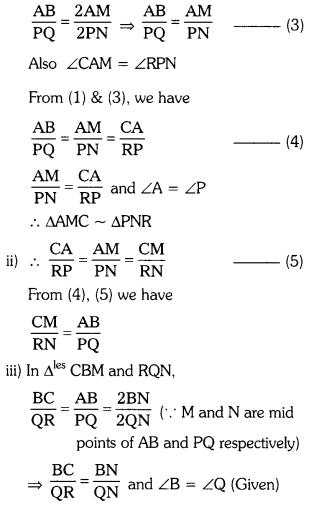
∴ ∆CMB ~ ∆RNQ
![]()
Question 5.
Diagonals AC and BD of a trapezium ABCD with AB || DC intersect each other at the point ‘O’. Using the criterion of similarity for two triangles, show that \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OC}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{OB}}{\mathrm{OD}}\). (AS2)
Solution:
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC.
The diagonals AC and BD intersect at ‘O’.
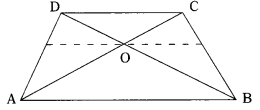
AB || CD and AC is a transversal
∴ ∠DCA = ∠CAB (Alternate angles)
⇒ ∠DCO = ∠OAB
Lines AC and BD intersect at ‘O’.
∴ ∠AOB = ∠COD (Vertically opposite angles)
Now is triangles COD and AOD, we have
∠DCO = ∠OAB
∠AOB = ∠COD
∴ ∠CDO = ∠ABO
Hence, ∆AOB ~ ∆COD
Therefore, their corresponding sides are proportional.
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OC}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{OB}}{\mathrm{OD}}\)
Question 6.
AB, CD, PQ are perpendicular to BD. AB = x, CD = y and PQ = ∠. Prove that \(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{z}\) (A.P. Mar. ’15)
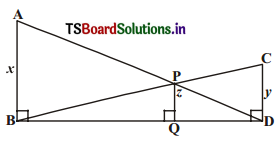
Solution:
In ∆ABD, PQ || AB.
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{PQ}}{\mathrm{AB}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{DQ}}{\mathrm{DB}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{z}}{\mathrm{x}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{DQ}}{\mathrm{DB}}\) …………. (1)
In ∆BDC, PQ || CD.
![]()
Question 7.
A flag pole 4m tall casts a 6m., shadow. At the same time, a nearby building casts a shadow of 24m. How tall is the building ? (AS4)
Solution:
∆ABC ~ ∆DEF
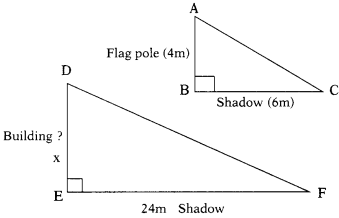
∴ Their corresponding sides are proportional.
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{EF}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{x}}\) = \(\frac{6}{24}\)
⇒ x × 6 = 4 × 24
⇒ x = \(\frac{4 \times 24}{6}\) = 16
∴ The height of the building = 16 meters
Question 8.
CD and GH are respectively the bisectors of ∠ACB and ∠EGF such that D and H lie on sides AB and FE of ∆ABC and ∆FEG respectively. If ∆ABC ~ ∆FEG then show that G
i) \(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{GH}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{FG}}\)
ii) ∆DCB ~ ∆HGE
iii) ∆DCA ~ ∆HGF (AS2)
Solution:
Given that ∆ABC ~ ∆FEG
∴ Corresponding angles are equal.
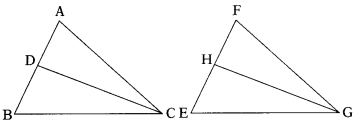
∠CAB = ∠GFE ⇒ ∠CAD = ∠GFH
∠ACB = ∠FGE ⇒ \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠ACB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠FGE
∠ACD = ∠FGH
(∵ CD and GH are bisectors of ∠C and ∠G respectively)
Now in ∆ACD and ∆FGH,
∠CAD = ∠GFH
∠ACD = ∠FGH
∴ ∆ACD ~ ∆FGH (A. A similarity criterion)
\(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{GH}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{FG}}\) (Corresponding sides are in proportion)
Since, ∆ABC ~ ∆FEG, ∠ACB = ∠FGE
⇒ \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠ACB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ∠FGE
⇒ ∠DCB = ∠HGE
(∵ CD and GH are the bisectors of ∠C and ∠G respectively)
Moreover, ∠CBA = ∠GEH
⇒ ∠CBD = ∠GEH
Now in ∆les DCB and HGE, we have
∠DCB = ∠HGE
∠CBD = ∠GEH
∴ ∆ DCB ~ ∆ HGE (A. A similarity criterion)
![]()
Question 9.
AX and DY are altitudes of two similar triangles ∆ABC and ∆DEF. Prove that AX : DY = AB : DE. (AS2)
Solution:
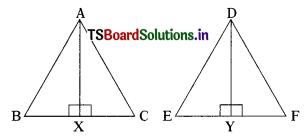
∆ABC ~ ∆DEF
∠B = ∠E; ∠C = ∠F and ∠A = ∠D
In ∆les ABX and DEY,
∠B = ∠E
∠AXB = ∠DYE = 90°
∠AXJ-BC = ∠DY ⊥ EF
∴ ∆ABX ~ ∆DEY
Hence, their corresponding sides are proportional.
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{AX}}{\mathrm{DY}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{BX}}{\mathrm{EY}}\)
⇒ AB : DE = AX : DY
⇒ AX : DY = AB : DE
Question 10.
Construct a triangle shadow similar to the given ∆ABC, with its sides equal to \(\frac{5}{3}\) of the corresponding sides of the triangle ABC. (AS5)
Solution:
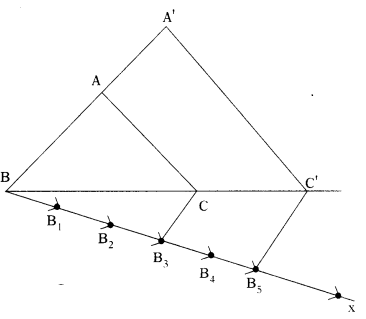
Construction :
- Draw ∆ ABC
- Make an acute angle CBX with BC.
- Locate the points B1, B2, B3, B4 and B5 on BX such that BB1 = B1B2 = B2B3 = B3B4 = B4B5.
- Join B3C. Draw B5 C’ parallel to B3C to meet BC produced at C’.
- Draw CA’ parallel to CA to meet BA produced at A’.
- Now BCA’ is required triangle.
![]()
Question 11.
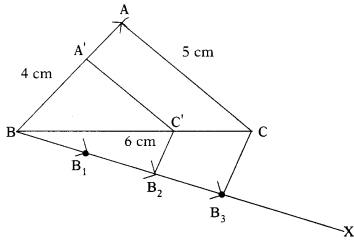
Construct a triangle of sides 4 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm. Then, construct a triangle similar to it. Whose sides are \(\frac{2}{3}\) of the corresponding sides of the first triangle. (AS5)
Solution:
Construction :
![]()
- Draw the triangle ABC in which BC = 6 cm, CA = 5 cm, AB = 4 cm.
- Draw a ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{BX}}\), making an acute angle with BC on the side opposite to vertex A.
- Locate 3 points B1, B2 and B3 on BX such that BB1 = B1 B2 = B2 B3.
- Join B3C and draw a line from B2 to C’ which is parallel to B2C and intersecting BC atC’.
- Draw a line through C’ parallel to CA to intersect AB at A’.
- Now ∆A’ BC is the required triangle.
Question 12.
Construct an Isosceles triangle whose base is 8 cm and altitude is 4 cm. Then, draw another triangle whose sides are 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\) times the corresponding sides of the isosceles triangle. (AS5)
Solution:
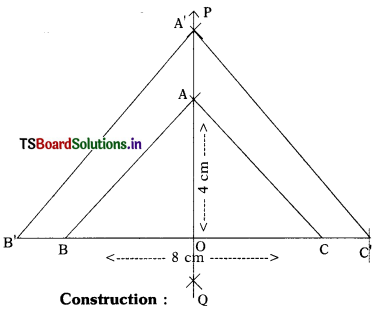
Construction :
- Draw a line segment BC = 8 cm.
- Draw the perpendicular bisector PQ of BC intersecting BC at ‘O’.
- Mark a point A’ on PQ such that OA = 4 cm.
- Join AB and AC to get the isosceles triangle ABC.
- Extend BC on either side so that BC = 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\) times, BC = \(\frac{3}{2}\) × 8 = 12 cm
- Similarly extend OA so that OA’ = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) times, A = \(\frac{4 \times 3}{2}\) = 6 cm.
- Join A’B’ and AC’.
- Now, A’B’C’ is the required triangle.