Students must practice these Maths 1B Important Questions TS Inter First Year Maths 1B Straight Lines Important Questions Very Short Answer Type to help strengthen their preparations for exams.
TS Inter First Year Maths 1B Straight Lines Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Find the condition for the points (a, 0), (h, k), and (0, b), where ab ≠ 0, to be collinear. [Mar. ’10]
Solution:
Let A(a, 0), B(h, k), C (0, b) be the given points.
Slope of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}=\frac{\mathrm{y}_2-\mathrm{y}_1}{\mathrm{x}_2-\mathrm{x}_1}=\frac{\mathrm{k}-0}{\mathrm{~h}-\mathrm{a}}=\frac{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{h}-\mathrm{a}}\)
Slope of \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}=\frac{\mathrm{y}_2-\mathrm{y}_1}{\mathrm{x}_2-\mathrm{x}_1}=\frac{\mathrm{b}-\mathrm{k}}{0-\mathrm{h}}=\frac{\mathrm{b}-\mathrm{k}}{-\mathrm{h}}\)
Since points A, B, C are collinear, then
Slope of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) = Slope of \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\)
\(\frac{k}{h-a}=\frac{b-k}{-h}\)
⇒ -hk = (h – a) (b – k)
⇒ -hk = bh – hk – ab + ak
⇒ bh + ak = ab
⇒ \(\frac{b h}{a b}+\frac{a k}{a b}=1\)
\(\frac{h}{a}+\frac{k}{b}=1\), which is the required condition.
![]()
Question 2.
Find the value of x, if the slope of the line passing through (2, 5) and (x, 3) is 2. [Mar. ’18 (AP & TS); May ’12; B.P.]
Solution:
Let A = (2, 5), B = (x, 3) are the given points.
Given, Slope of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) = 2
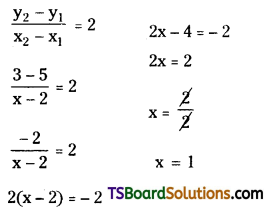
Question 3.
Find the value of y, if the line joining the points (3, y) and (2, 7) is parallel to the line joining the points (-1, 4) and (0, 6). [Mar. ’17 (TS), ’14, ’08]
Solution:
Let A = (3, y), B = (2, 7), C = (-1, 4), and D = (0, 6) are the given points.
Given,
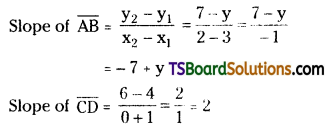
Since, the lines \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\) are parallel then the
Slope of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) = Slope of \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\)
⇒ y – 7 = 2
⇒ y = 9
Question 4.
Find the equation of the straight line which make 150° with the X-axis in the positive direction and which pass through the point (-2, -1). [May ’04]
Solution:
Given that inclination of a straight line is θ = 150°
The slope of a line is, m = tan θ
= tan (150°)
= tan (90° + 60°)
= -cot 60°
= \(\frac{-1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
Let the given point A(x1, y1) is (-2, -1).
∴ The equation of the straight line passing through A(-2, -1) and having slope \(\frac{-1}{\sqrt{3}}\) is y – y1 = m(x – x1)
⇒ y + 1 = latex]\frac{-1}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] (x + 2)
⇒ √3(y + 1) = -1(x + 2)
⇒ √3y + √3 = -x – 2
⇒ x + √3y + √3 = -2
⇒ x + √3y + √3 + 2 = 0
![]()
Question 5.
Find the equations of the straight lines passing through the origin and making equal angles with the coordinate axes. [May ’05]
Solution:
Let l1, l2 are the equations of the straight lines passing through the origin and making equal angles with the co-ordinate axes
Case I: Inclination of a straight line l1 is θ = 45°
Slope of a line l1 is, m = tan θ = tan 45° = 1
Let the given point O = (0, 0)
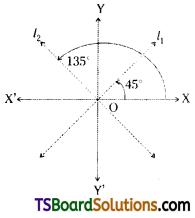
∴ The equation of a straight line l1 passing through O(0, 0) and having slope ‘1’ is y – y1 = m(x – x1)
y – 0 = 1(x – 0)
⇒ y = x
⇒ x – y = 0
Case II: Inclination of a straight line l2 is θ = 135°
The slope of a line l2 is, m = tan θ
= tan 135°
= tan (90° + 45°)
= -tan 45°
= -1
Let the given point O = (0, 0)
∴ The equation of a straight line l2 passing through O(0, 0) and having slope ‘-1’ is y – y1 = m(x – x1)
⇒ y – 0 = -1(x – 0)
⇒ y = -x
⇒ x + y = 0
∴ Required equations of the straight lines are x – y = 0; x + y = 0
Question 6.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through (-4, 5) and cutting off equal and non-zero intercepts on the coordinate axes. [Mar. ’15 (TS) ’13 (Old), ’07, ’00; May ’10, ’08]
Solution:
The equation of a straight line in the intercept form is \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\) …….(1)
Given that, the straight line making equal intercepts on the co-ordinate axis, then a = b
From (1),
\(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{a}=1\)
x + y = a ……….(2)
Since equation (2) passes through the point (-4, 5) then,
-4 + 5 = a
∴ a = 1
Substitute the value of ’a’ in equation (2)
∴ x + y = 1
Question 7.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through (-2, 4) and making non-zero intercepts whose sum is zero. [Mar. ’15 (AP), ’13; May ’15 (TS), ’02]
Solution:
The equation of a straight line in the intercept form is \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\) ……..(1)
Given that, the straight line-making intercepts whose sum is ‘0’
i.e., a + b = 0
b = -a
From (1)
\(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{-a}=1\)
x – y = -a …….(2)
Since equation (2) passes through the point (-2, 4) then,
-2 – 4 = a
∴ a = -6
Substitute the value of ‘a’ in equation (2)
x – y = -6
x – y + 6 = 0
![]()
Question 8.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (3, -4) and making X and Y-intercepts which are in the ratio 2 : 3. [Mar. ’08]
Solution:
The equation of a straight line in the intercept form is \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\) ……..(1)
Given that, the ratio of intercepts = 2 : 3
X-intercept = 2a
Y-intercept = 3a
From (1),
\(\frac{x}{2 a}+\frac{y}{3 a}=1\)
\(\frac{3 x+2 y}{6 a}=1\)
3x + 2y = 6a ……..(2)
Since equation (2) passes through point (3, -4) then,
3(3) + 2(-4)= 6a
⇒ 9 – 8 = 6a
⇒ 6a = 1
⇒ a = \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Substitute the value of ‘a’ in equation (2)
3x + 2y = 6(\(\frac{1}{6}\))
∴ 3x + 2y = 1
Question 9.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the points \(\left(a t_1^2, 2 at_1\right)\) and \(\left(a t_2^2, 2 at_2\right)\). [Mar. ’14. ’04; May ’15 (AP), ’00]
Solution:
Let A\(\left(a t_1^2, 2 at_1\right)\) and B\(\left(a t_2^2, 2 at_2\right)\) are the given points
The equation of the straight line passing through the points A\(\left(a t_1^2, 2 at_1\right)\) and B\(\left(a t_2^2, 2 at_2\right)\) is
(y – y1) (x2 – x1) = (x – x1) (y2 – y1)

Question 10.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through A(-1, 3) and (i) parallel (ii) perpendicular to the straight line passing through B(2, -5) and C(4, 6). [May ’12; Mar. ’11]
Solution:
A(-1, 3), B(2, -5), C(4, 6) are the given points.
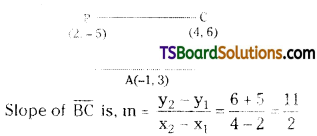
(i) Slope of the parallel line = m = \(\frac{11}{2}\)
∴ The equation of the straight line passing through A(-1, 3) and having slope \(\frac{11}{2}\) is y – y1 = m(x – x1)
y – 3 = \(\frac{11}{2}\)(x + 1)
⇒ 2y – 6 = 11x + 11
⇒ 11x – 2y + 17 = 0
(ii) Slope of the perpendicular line = \(\frac{-1}{m}=\frac{-1}{11 / 2}=\frac{-2}{11}\)
∴ The equation of the straight line passing through A(-1, 3) and having slope \(\frac{-2}{11}\) is y – y1 = \(\frac{-1}{m}\) (x – x1)
y – 3 = \(\frac{-2}{11}\) (x + 1)
⇒ 11y – 33 = -2x – 2
⇒ 2x + 11y – 31 = 0
![]()
Question 11.
A(10, 4), B(-4, 9) and C(-2, -1) are the vertices of a triangle. Find the equation of the altitude through B. [May ’13 (Old)]
Solution:
Slope of \(\overline{\mathrm{AC}}\) is,
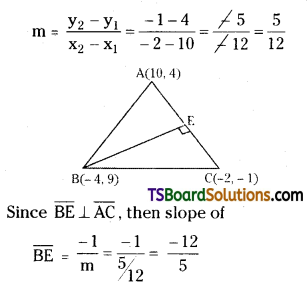
The equation of the altitude through B is, the equation of the straight line passing through B(-4, 9) and having slope \(\frac{-12}{5}\) is
y – y1 = m(x – x1)
y – 9 = \(\frac{-12}{5}\) (x + 4)
5y – 45 = -12x – 48
12x + 5y + 3 = 0
Question 12.
If the portion of a straight line intercepted between the axes of coordinates is bisected at (2p, 2q), write the equation of the straight line. [May ’90]
Solution:
Let a, b be the intercepts of a line.
∴ The line cuts the X-axis at A(a, 0), Y-axis at B(0, b)
Midpoint of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) is,
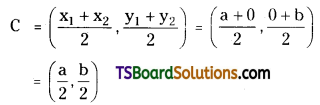
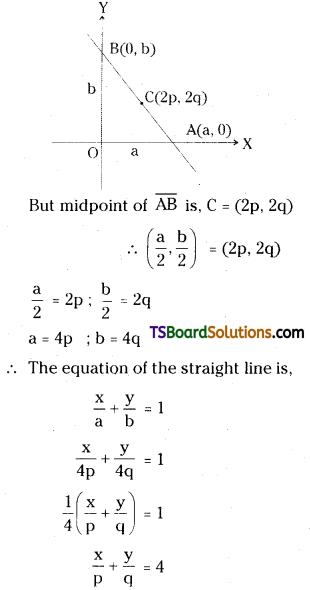
Question 13.
Find the angle made by the straight line y = -√3x + 3 with the positive direction of the X-axis measured in the counterclockwise direction. [May ’94]
Solution:
Given, the equation of the straight line is y = -√3x + 3
Comparing this equation with y = mx + c, We get
m = -√3 (∵ m = tan θ)
⇒ tan θ = -√3
⇒ tan θ = tan \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
⇒ θ = \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
∴ The angle made by the straight line is θ = \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
Question 14.
Transform the equation √3x + y = 4 into (i) slope-intercept form (ii) intercept form (iii) normal form. [May ’16 (TS)]
Solution:
Given, the equation of the straight line is √3x + y = 4
(a) Slope-intercept form:
√3x + y = 4
y = -√3x + 4 which is of the form y = mx + c
where, slope (m) = -√3, y-intercept (c) = 4
(b) Intercept form:
Given, the equation of the straight line is,
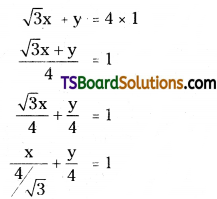
which is in the form \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\)
∴ x-intercept (a) = \(\frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}\), y-intercept (b) = 4
(c) Normal form:
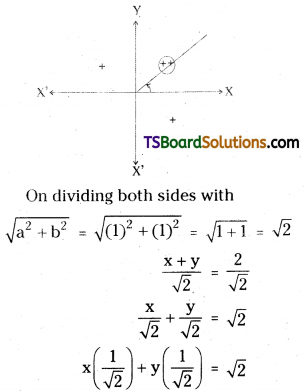
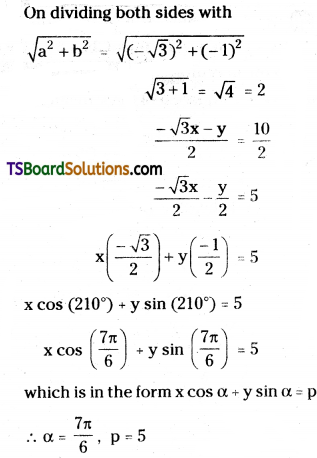
Given the equation of the straight line is √3x + y = 4
On dividing both sides with
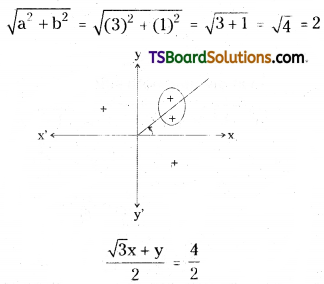
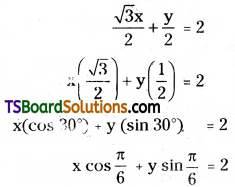
which is in the form x cos α + y sin α = p
∴ α = \(\frac{\pi}{6}\), p = 2
![]()
Question 15.
Transform the equation x + y + 1 = 0 into normal form. [Mar. ’17 (AP), ’08; May ’10; B.P.; Mar. ’18 (TS)]
Solution:
Given, equation of the straight line is x + y + 1 = 0
x + y = -1
– x – y = 1
On dividing both sides with
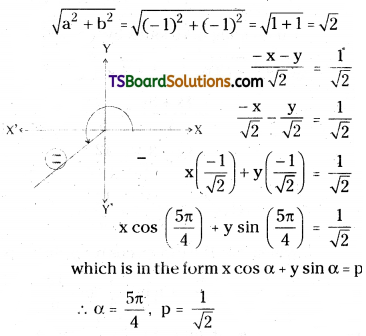
Question 16.
Transform the equation 4x – 3y + 12 = 0 into (i) slope-intercept form (ii) intercept form (iii) normal form.
Solution:
(a) Slope-intercept form:
Given equation of the line is 4x – 3y + 12 = 0
3y = 4x + 12
y = \(\frac{4 x+12}{3}=\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) x+4\)
which is in the form of y = mx + c
∴ Slope = \(\frac{4}{3}\), y-intercept = 4
(b) Intercept form:
Given equation is 4x – 3y + 12 = 0
\(\frac{x}{-3}+\frac{y}{4}=1\)
which is in the form of \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\)
∴ x-intercept = -3, y-intercept = 4
(c) Normal form:
Given the equation of the straight line is 4x – 3y = -12
-4x + 3y = 12
On dividing both sides by \(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
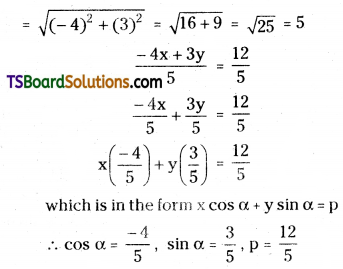
Question 17.
Transform the equation x + y – 2 = 0 into (i) slope-intercept form (ii) intercept form (iii) normal form. [Mar. ’12]
Solution:
(a) Slope-intercept form:
Given equation of the straight line is, x + y – 2 = 0
y = -x + 2
which is in the form of y = mx + c
∴ Slope, m = -1, y-intercept, c = 2
(b) Intercept form:
Given equation of the straight line is, x + y – 2 = 0
x + y = 2
\(\frac{x+y}{2}\) = 1
\(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{y}{2}\) = 1
which is of the form \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\)
∴ x-intercept (a) = 2, y-intercept (b) = 2
(c) Normal form:
Given equation of the straight line is, x + y – 2 = 0
x + y = 2
Question 18.
Transform the equation √3x + y + 10 = 0 into (i) slope-intercept form (ii) intercept form (iii) normal form. [May ’04]
Solution:
(a) Slope-intercept form:
Given the equation of the straight line is, √3x + y + 10 = 0
y = -√3x – 10 = -√3x + (-10)
which is in the form of y = mx + c
∴ Slope, m = -√3, y-intercept, c = -10
(b) Intercept form:
Given the equation of the straight line is √3x + y + 10 = 0
√3x + y = -10 × 1
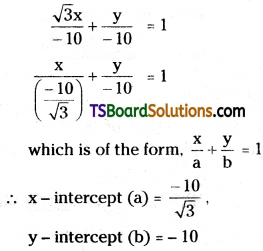
(c) Normal form:
Given equation of the straight line is, √3x + y + 10 = 0
√3x + y = -10
-√3x – y = 10
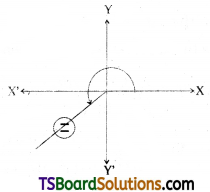
Question 19.
If the area of the triangle is formed by the straight lines, x = 0, y = 0, and 3x + 4y = a [a > 0] is ‘6’. Find the value of ‘a’. [May ’11, Mar. ’09, ’07]
Solution:
Given equations of the straight lines are (a > 0) 3x + 4y = a, x = 0 and y = 0
Comparing with ax + by + c = 0, we get
a = 3, b = 4, c = -a
The area of the triangle formed by this line and the co-ordinate axis is equal to \(\frac{c^2}{2|a b|}\)
Given that area of the triangle = 6
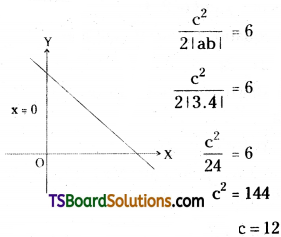
![]()
Question 20.
Find the value of p, if the straight lines x + p = 0, y + 2 = 0 and 3x + 2y + 5 = 0 are concurrent. [Mar. ’17 (TS), ’13; May ’15 (TS)]
Solution:
Given, the equation of the straight lines
x + p = 0 ……..(1)
y + 2 = 0 ………(2)
3x + 2y + 5 = 0 ………(3)
Solving (2) & (3)
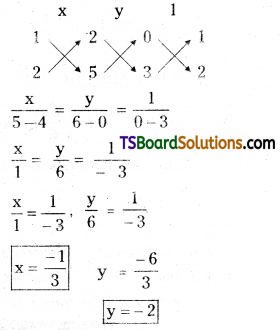
∴ Point of intersection of the lines (2) & (3) is (\(\frac{-1}{3}\), -2)
since given lines are concurrent, then, the point of intersection (\(\frac{-1}{3}\), -2) lies on (1)
x + p = 0
⇒ \(\frac{-1}{3}\) + p = 0
⇒ p = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 21.
Find the ratio in which the straight line 2x + 3y = 5 divides the line joining the points (0, 0) and (-2, 1). [Mar. ’14]
Solution:
Given the equation of the straight line is L = 2x + 3y – 5 = 0
Comparing the equation with ax + by + c = 0, we get
a = 2, b = 3, c = 5
Let the given points are A(x1, y1) = (0, 0) and B(x2, y2) = (-2, 1)
Required ratio = \(\frac{-\left(a x_1+b {y}_1+c\right)}{a x_2+b y_2+c}\)
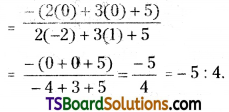
Question 22.
Find the distance between the parallel straight lines 3x + 4y – 3 = 0 and 6x + 8y – 1 = 0. [Mar. ’19 (AP); May ’13]
Solution:
Given, equations of the straight lines are 3x + 4y – 3 = 0, 6x + 8y – 1 = 0
6x + 8y – 6 = 0 …..(1)
6x + 8y – 1 = 0 …..(2)
Comparing (1) with ax + by + c1 = 0, we get
a = 6, b = 8, c1 = -6
Comparing (2) with ax + by + c2 = 0, we get
a = 6, b = 8, c2 = -1
Distance between the parallel lines =
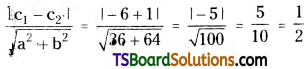
Question 23.
Find the equation of ‘k’, if the angle between the straight lines 4x – y + 7 = 0 and kx – 5y – 9 = 0 is 45°. [Mar. ’12, ’08, ’82; May ’11, ’02]
Solution:
Given, the equations of the straight lines are
4x – y + 7 = 0 ……..(1)
kx – 5y – 9 = 0 ……..(2)
Comparing (1) with a1x + b1y + c1 = 0, we get
a1 = 4, b1 = -1, c1 = 7
Comparing (2) with a2x + b2y + c2 = 0, we get
a2 = k, b2 = -5, c2 = -9
Given that, θ = 45°
If ‘θ’ is the angle between the given lines then,
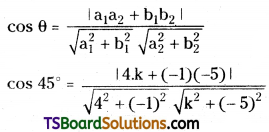
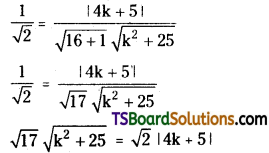
Squaring on both sides
⇒ 17(k2 + 25) = 2(4k + 5)2
⇒ 17k2 + 425 = 2(16k2 + 25 + 40k)
⇒ 17k2 + 425 = 32k2 + 50 + 80k
⇒ 15k2 + 80k – 375 = 0
⇒ 3k2 + 16k – 375 = 0
⇒ 3k2 + 25k – 9k – 75 = 0
⇒ k(3k + 25) – 3(3k + 25) = 0
⇒ (3k + 25) (k – 3) = 0
⇒ 3k + 25 = 0; k – 3 = 0
⇒ 3k = -25; k = 3
⇒ k = 3 or \(\frac{-25}{3}\)
![]()
Question 24.
Find the equation of the straight line parallel to the line 2x + 3y + 7 = 0 and pass through the point (5, 4). [Mar. ’13, ’03]
Solution:
Given, the equation of the straight line is 2x + 3y + 7 = 0
Given points (5, 4)
The equation of the straight line parallel to 2x + 3y + 7 = 0 is 2x + 3y + k = 0
Since equation (1) passes through the point (5, 4) then,
2(5) + 3(4) + k = 0
⇒ 10 + 12 + k = 0
⇒ 22 + k = 0
⇒ k = -22
∴ The required equation of the straight line is 2x + 3y – 22 = 0
Question 25.
Find the value of k, if the straight lines y – 3kx + 4 = 0 and (2k – 1)x – (8k – 1)y – 6 = 0 are perpendicular. [Mar. ’10]
Solution:
Given, the equations of the straight lines are
y – 3kx + 4 = 0 ………(1)
(2k – 1)x – (8k – 1)y – 6 = 0 ……….(2)
Slope of the line (1) is m1 = \(\frac{-(-3 k)}{1}\) = 3k
Slope of the line (2) is m2 = \(\frac{-(2 k-1)}{-(8 k-1)}=\frac{(2 k-1)}{(8 k-1)}\)
Since the given lines are perpendicular then m1 × m2 = -1
\(3 \mathrm{k}\left(\frac{2 \mathrm{k}-1}{8 \mathrm{k}-1}\right)\) = -1
⇒ 3k(2k – 1) = -1(8k – 1)
⇒ 6k2 – 3k = -8k + 1
⇒ 6k2 + 5k – 1 = 0
⇒ 6k2 + 6k – k – 1 = 0
⇒ 6k(k + 1) – 1(k + 1) = 0
⇒ (k + 1)(6k – 1) = 0
⇒ k + 1 = 0 (or) 6k – 1 = 0
⇒ k = -1 (or) k = \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Question 26.
Find the perpendicular distance from the point (3, 4) to the straight line 3x – 4y + 10 = 0. [Mar. ’16 (AP); May. ’15 (AP)]
Solution:
Given the equation of the straight line is 3x – 4y + 10 = 0
Comparing with ax + by + c = 0, we get
a = 3; b = -4, c = 40
Let the given point p(x1, y1) = (3, 4)
The perpendicular distance from the point (3, 4) to the line 3x – 4y + 10 = 0 is

![]()
Question 27.
Find the slopes of the lines x + y = 0 and x – y = 0. [Mar. ’17 (AP)]
Solution:
Slope of x + y = 0 is \(\frac{-a}{b}=\frac{-1}{1}\) = -1
Slope of x – y = 0 is \(\frac{-a}{b}=\frac{-1}{-1}\) = 1