Students can practice TS SCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Perimeter and Area Ex 10.2 to get the best methods of solving problems.
TS 6th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Perimeter and Area Exercise 10.2
Question 1.
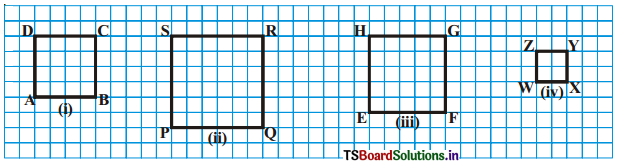
Find the areas of the following figures by counting squares.
(i) 50 cm and 20 cm
(ii) 65 in and 45 in
(iii) 25 cm and 16 cm
(iv) 7 kin and 19 km
Answer:
(i) Length of the rectangle = 50 cm
Breadth of the rectangle = 20 cm
∴ Area of the rectangle
= length × breadth
= 50 cm × 20 cm
= 1000 sq. cm (cm2)
(ii) Length of the rectangle = 65 m
Breadth of the rectangle = 45 m
∴ Area of the rectangle
= length × breadth
= 65 cm × 45 cm
= 2925 sq. m (m2)
(iii) Length of the rectangle = 25 cm
Breadth of the rectangle = 16 cm
∴ Area of the rectangle
= length × breadth
= 25 cm × 16 cm
= 400 sq. cm (cm2)
(iv) Length of the rectangle = 7 km
Breadth of the rectangle =19 km
∴ Area of the rectangle
= length × breadth
= 7 cm × 19 cm
= 133 sq. km (km2)

Question 2.
Find the area of squares with the given sides:
(i) 26 m
(ii) 17 km
(iii) 52 cm
(iv) 8 cm
Answer:
(i) Side of the square = 26 m
Area of the square = side × side
= 26m × 26m
= 676 m2
(ii) Side of the square =17 km
Area of the square = side × side
= 17 cm × 17cm
= 289 km2
(iii) Side of the square = 52 cm
Area of the square = side × side
= 52 cm × 52cm
= 2704 cm2
iv) Side of the square = 8 cm
Area of the square = side × side
= 8 cm × 8 cm
= 64 cm2
Question 3.
The area of rectangular frame is 1,125 sq. cm. If its width is 25 cm, what is its length ?
Answer:
Area of rectangular frame =1125 sq.cm
Width of the frame = 25 cm
Area of rectangular frame
= length × width

Question 4.
The length of a rectangular field is 60 m and the breadth is half of its length. Find the area of the field.
Answer:
The length of a rectangular field = 60 m By problem,
Area of the rectangular field = \(\frac{60 \times 1}{2}\) = 30 m
= length × breadth
= 60 m × 30 m
= 1800 m2
Question 5.
A square sheet of paper has a perimeter of 40 cm. What is the length of its side ? Also find the area of the square sheet ?
Answer:
Let the side of the square sheet of paper = x cm.
Perimeter of the sheet of paper = 4 × side
= 4 × x
= 4x cm
By problem,
4x = 40
∴ x = \(\frac{40}{4}\) = 10 cm
Side of the square sheet of paper = 10 cm
Area of the sheet of paper = side × side
= 10 cm × 10 cm
= 100 cm2
Area of sheet of paper = 100 cm2
Question 6.
The area of rectangular plot is 2400 square meters and it’s length is 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) times to it’s breadth.What is the perimeter?
Answer:
Area of rectangular plot = 2400 m2
Length is 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) to its breadth i.e, their ratio of its sides = 3:2
Let the length of the plot be 3x m.
Breadth of the plot = 2x m
Area of the plot = length × breadth
= 3x m × 2x m
= 6x2
By problem, 6x2 = 2400
x2 = \(\frac{2400}{6}\) = 400
x2 = 400 = 20 × 20
∴ x = 20
Length of the plot = 3x = 3 × 20 = 60 m
Breadth of the plot = 2x = 2 × 20 = 40 m
Perimeter of the plot
= 2(length + breadth)
= 2(60 + 40) m
= 2 × 100
= 200 m

Question 7.
The length and breadth of a room are 6 m and 4 m respectively. How many square meters of carpet is required to completely cover the floor of the room ? If the carpet costs ₹ 240 a square meter, what will be the total cost of the carpet for completely covering the floor ?
Answer:
Length of the room = 6 m
Breadth of the room = 4 m
Area of the floor of the room
= length × breadth
= 6m × 4m
= 24m2
The carpet required to completely cover the floor of the room = 24 m2
The cost of 1 sq. m of the carpet
= Rs. 240
∴ The cost of 24 sq. m of the carpet
= Rs. 240 × 24 = Rs. 5760
Question 8.
Two fields have the same perimeter. One is a square of side 72 m and another is a rectangle of length 80 m. Which field has the greater area and by how much ?
Answer:
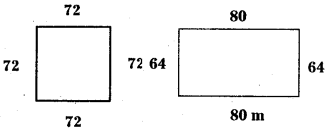
Area of square = l × b
= 72 m × 72 m = 5184 sq.m
Length of a rectangle l = 80 m
Perimeter of a rectangle 2(l + b) = 288 m
= 2 × 80 m + 2b
= 288 m
= 160 m + 2b
= 288 m
⇒ 2b = 288 – 160 = 128 m
b = \(\frac{128}{2}\) = 64 m
Area of rectangle = 80 m × 64 m
= 5120 sq.m
∴ The area of square field is greater than that of rectangular field.
5184 – 5120
= 64 sq.m
Question 9.
The area of a square is 49 sq. dm. A rectangle has the same perimeter as the square. If the; length of the rectangle is 9.3 cm., What is its breadth ? Also find which has greater area ?
Answer:
Area of the square = 49 sq. cm
side × side = 7 cm × 7 cm
Side of the square = 7 cm
The perimeter of the square = 4 × side = 4 × 7 cm
= 28 cm
By problem,
The perimeter of the rectangle = 28 cm
2(l + b) = 28 cm 28
(l + b) = \(\frac{28}{2}\) = 14 cm
9.3 + b = 14
∴ b= 14 – 9.3 = 4.7 cm
Area of the rectangle = length × breadth
= 9.3 cm × 4.7 cm = 43.71 cm2
∴ The square has greater area when compared to the rectangle.
Question 10.
Rahul owns a rectangular field of length 400 m and breadth 200 m. His friend Ramu owns a square field of length 300 m. Find the cost of fencing the two fields at ₹ 150 per meter. If one tree can be planted in an area of 10 sq. m. who can plant more trees in his field ? How many more trees can he plant ?
Answer:
Length of the rectangular field of Rahul
= 400 m
Breadth of the rectangular field of Rahul
= 200 m
Perimeter of rectangular field of Rahul
= 2 [length + breadth]
= 2 [400 + 200]m = 2 × 600 m = 1200 m
Side of the square field of Ramu
= 300 m
Perimeter of square field of Ramu = 4 × side
= 4 × 300 m = 1200 m
Total length of the wire to be fenced = 1200 + 1200 = 2400 m
Cost of fencing 1 meter = Rs. 150
Cost of fencing 2400 meters
= Rs. 2400 × 150
= Rs. 3,60,000
Cost of fencing Ramu’s field
= Rs. 1200 × 150
= Rs. 1,80,000
Area of Rahul’s field = length × breadth
= 400 m × 200 m
= 80,000 m2
A tree occupies an area of 10 m2
Number of trees that can planted in 80,000
Rahul’s field = \(\frac{80,000}{10}\) = 8000
Area of Ramu’s field = side × side
= 300 × 300
= 90,000 m2
A tree occupies an area of 10 m2
Number of trees that can be planted in
Ramu’s field = \(\frac{90,000}{10}\) = 9000
Ramu can plant 1000 trees
(= 9000 – 8000) more.
Question 11.
The length of a rectangular floor is 20 m., more than its breadth. If the perimeter of the floor is 280 m, what is its length ?
Answer:
Let the breadth of the rectangular field = x m
∴ The length of the rectangular field = (x + 20) m
Perimeter of the rectangular field
= 2(length + breadth)
= 2(x + 20 + x) m
= 2(2x + 20)m
= 4x + 40 m
By problem,
4x + 40 = 280 m
4x = 280 – 40
= 240 m
x = \(\frac{240}{2}\) = 60 m
The breadth of the rectangular field
= 60 m
The length of the rectangular field
= x + 20 m
= 60 + 20 m
= 80 m
Its length is 80 m.

Question 12.
A rectangular plot of land is 240 m. by 200 m. The cost of fencing per meter is ₹ 30. What is the cost of fencing the entire field ?
Answer:
The dimensions of the rectangular plot of land are 240 m and 200 m.
Perimeter of the plot of land
= 2 [240 + 200]
= 2[440]m
= 2 × 440 m
= 880 m
Cost of fencing 1 meter is Rs. 30.
Cost of fencing 880 metres is x
Rs. 880 × 30 = Rs. 26400
Question 13.
The side of a square field is 120 meters. The cost of preparing a grass lawn is ₹ 35 per square meter. How much will it cost, if the entire field is converted into a lawn ?
Answer:
The side of the square field = 120 m
Area of the square field = side × side
= 120 m × 120 m
= 14,400 m2
Cost of preparing a sq. m of grass lawn is Rs. 35.
Cost of converting the entire field (14400 m2) into a lawn
= Rs. 14,400 × 35
= Rs. 5,04,000
Question 14.
What will happen to the area of rectangle, if
(i) its length and breadfii are doubled?
(ii) its length is doubled and breadth is tripled ?
Answer:
(i) Let the length of a rectangle be x m and the breadth be y m.
∴ Area of the rectangle = x × y = xy m2
The length and breadth of it are doubled.
Then the length will be 2x (= x + x) and breadth 2y (= y + y).
The area of the rectangle will be
2x × 2y = 4xy m2 = 4 (xy m2)
∴ The area of the rectangle increases by 4 times.
(ii) The length after it is doubled will be
x + x = 2x
The breadth after it is tripled will be y + y + y = 3y
The area of the rectangle will be 2x × 3y
= 6 xy m2
= 6 × (xy m2)
∴ The area of the rectangle increases by 6 times.

Question 15.
What will happen to the area of square if its side is:
(i) doubled
(ii) halved
Answer:
(i) Let the side of a square be x metres.
Area of the square = side × side
= x × x
= x2 sq. metres
If the side is doubled, it becomes x + x
= 2x metres
Area of the square = side x side
= 2x m × 2x m
= 4x2 sq. metres
= 4 x (x2 sq. metres)
The area increases by 4 times,
(ii) If the side of the square is halved, it
Area of the square = side × side
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x m x \(\frac{1}{2}\) x m
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) x2 sq. metres
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) × (x2 sq. metres)
∴ The area of the square becomes \(\frac{1}{4}\) of the original area.
![]()

![]()