These TS 10th Class Physics Chapter Wise Important Questions Chapter 1 Reflection of Light at Curved Surfaces will help the students to improve their time and approach.
TS 10th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Reflection of Light at Curved Surfaces
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Can you find out the rough focal length of a convex mirror?
Answer:
No, because it always forms a virtual image for any position of the object.
Question 2.
What type of mirror ¡s used to obtain real image?
Answer:
Concave mirror is used to obtain real image.
Question 3.
Which mirror has large field of view?
Answer:
Convex mirror.
Question 4.
For what position of an object, a real and diminished image is formed by a concave mirror.
Answer:
The position of an object is beyond centre of curvature.
Question 5.
What is reflection?
Answer:
The light rays falling on a surface are returned Into the original medium, this phenomenon is called reflection.
Question 6.
What Is meant by lateral Inversion?
Answer:
The right appears as left in the image is called lateral inversion.
Question 7.
Which spherical mirror will be bent outward?
Answer:
Convex mirror will be bent outward.
Question 8.
Which mirror is called converging mirror?
Answer:
Concave mirror is called converging mirror.
Question 9.
Which spherical mirror will be bent inward?
Answer:
Concave mirror will be bent inward.
Question 10.
Which mirror is called diverging mirror?
Answer:
Convex mirror is called diverging mirror.
Question 11.
What is the relation between focal length and radius of curvature?
Answer:
Radius of curvature = 2 x focal length
∴ R=2f(or)f = \(\frac{R}{2}\)
Question 12.
Which mirror always give virtual image?
Answer:
Convex mirror always give virtual image.
Question 13.
What is the mirror formula for spherical mirrors?
Answer:
The mirror formula is
f = focal length of mirror, u = object distance, v = image distance
Question 14.
What is vertex?
Answer:
The point at which the central axis touches the mirror is called vertex.
Question 15.
What is focus?
Answer:
The light rays coming from distint object appear to meet at point in case of concave mirror and tends to meet at point when drawn backwanl in case of convex mirror. That point is called focus.
Question 16.
What is centre of curvature?
Answer:
The centre of sphere to which the mirror belongs is called centre of curvature.
Question 17.
What is focal length?
Answer:
The distance between vertex and centre of curvature.
Question 18.
Define magnification.
Answer:
The ratio of size of image to size of object is called magnification.

Question 19.
How do you get a virtual Image with a concave mirror?
Answer:
When we place the object between vertex and focus then we will get a virtual Imagre.
Question 20.
Why concave and convex mirrors are called spheilcal mirrors?
Answer:
The reflecting surface of convex and concave mirror is considered to form a part of the surface of a sphere so they are called spherical mirrors.
Question 21.
Which mirrors are used in saloons?
Answer:
Plane mirrors are used In saloons.
Question 22.
Which mirrors will act as rare view mirror?
Answer:
Convex mirrors will act as rare view mirror.
Question 23.
Which Image does not form on a screen?
Answer:
Virtual image.
Question 24.
Which mirrors has magnification always same?
Answer:
Plane mirrors has magnification always same.
Question 25.
What Is the magnification of plane mirror?
Answer:
The size of object = size of Image
∴ magnificatIon = 1
Question 26.
Where do you place the vessel In solar cooker?
Answer:
We place the vessel In solar cooker at the focal point.
Question 27.
Write any two uses of concave mirror in our daily life.
Answer:
Uses of concave mirror:
- Concave mirrors are used by dentists to see enlarged image of tooth.
- Concave mirrors are used In car headlights.
Question 28.
Which objects at your home act as spherical mirrors?
Answer:
Objects at home act as spherical mirrors.
- Spoons
- Spectacles
- Sink
- Cooking vessel
Question 29.
Suggest a new use with a spherical mirror?
Answer:
Spherical mirrors are newly adapted in AThis.
Question 30.
What are needed to form a shadow?
Answer:
A source of light, an opaque object and a screen are needed to form a shadow.
Question 31.
Which rays are called paraxial rays?
Answer:
The rays which are very nearer to the principal axis are called paraxial rays.
Question 32.
Which property of concave mirror Is used by dentists?
Answer:
When a bulb is placed at the focus of a concave mirror light from the bulb gets reflected to produce a strong, parallel beam. By using this property, dentists are able to see the Inner parts of the tooth clearly.
Question 33.
What is meant by converging of light rays?
Answer:
If light rays after reflection meet at a point then we say the light rays are converging.
Question 34.
When do you say light rays are diverging?
Answer:
If lights rays appear as if they are coming from a point after reflection then we say light rays are diverging.
Question 35.
If focal length is 20 cm then what Is radius of curvature of mirror?
Answer:
f = 20 cm
r = 2f = 2 x 20 40 cm. So radius of curvature = 40 cm
Question 36.
When does a ray reflect along the same path from a concave mirror?
Answer:
When it passes through centre of curvature.
Question 37.
When a light ray travelling parallel to principal axis falls on concave mirror, then what is the path of reflected ray?
Answer:
The reflected ray passes through focal point.
Question 38.
Where do you place the vessel in solar cooker?
Answer:
We place the vessel in solar cooker at the focal point.
Question 39.
If the magnification Is atways less than 1 then what Is the mirror?
Answer:
The mirror is convex.
Question 40.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror Is 20 cm. What is the focal length?
Answer:
Radius of curvature (R) = 20 cm
Focal length (f) = \(\frac{R}{2}=\frac{20}{2} \) = 10cm.
Question 41.
Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Answer:
Concave mirror can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Question 42.
The focal length of convex mirror is 16 cm. What is lts radius of curvature?
Answer:
f = 16 cm.
R = 2f = 2 x 16= 32 cm.
Question 43.
A concave mirror produces three times magnified real image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where Is the image located?
Answer:
30 cm.
Question 44.
Write any two uses of concave mirror in our daily life.
Answer:
Uses of concave mirror:
- Concave mirrors are used by dentists to see enlarged image of tooth.
- Concave mirrors are used in car headlights.
Question 45.
Write any two uses of convex mirror in our daily life.
Answer:
Uses of convex mirror:
- Convex mirrors are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles because convex mirrors increase field of view.
- Convex mirrors are used in street light reflectors as they spread light over greater area.
Question 46.
Which objects at your home act as spherical mirrors?
Answer:
Objects at home act as spherical mirrors are.
- Spoons
- Spectacles
- Door-knobs
- Cooking vessel
Question 47.
What is your opinion on elevating buildings with mirrors.
Answer:
The mirrors used in elevating buildings are reinforced, tough and laminated glasses. These mirrors provide safety and make the buildings attractive but the reflection caused by mirrors is dangerous to people travelling on roads and also to the birds.
Question 48.
Suggest a new use with a spherical mirror.
Answer:
Spherical mirrors are newly adopted in ATMs.
Question 49.
Can a convex mirror burn a paper? If not? Why?
Answer:
The rays’coming parallel to principal axis after reflection diverge from the mirror. So we cannot burn a paper by using a convex mirror as they do not converge light at a point.
Question 50.
Which mirror has wider field of view?
Answer:
A convex mirror has wider field of view, that’s why they are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles.
Question 51.
Why does our image appear thin or bulged In spherical mirrors?
Answer:
Due to covering or diverging of light rays from the mirror.
Question 52.
Can we focus a sunlight at a point using a mirror instead of magnifying glass?
Answer:
Yes, by using concave mirror we can focus sunlight at a point.
Question 53.
Why is angle of Incidence equal to angle of reflection when a light ray is reflected from a surface.
Answer:
Because light selects the path that takes least time to cover a distance.
Question 54.
Are angle of reflection and angle of incidence also equal for curved surface?
Answer:
Yes, it Is equal for curved surfaces like spherical mirrors..
Question 55.
What is a spherical mirror? Give different types of spherical mirrors.
Answer:
If the reflecting surface of mirror Is considered to form a part of the surface of sphere then it is called spherical mirror. Spherical mirrors are of two types:
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
Question 56.
Why does an image suffer lateral Inversion?
Answer:
The light rays which come from an object get reflected from the plane mirror and reach our eye, our brain feels that the ray (reflected ray) is coming from inside the mirror. That is why the right of object looks like left in the image.
Question 57.
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object using a ‘concave mirror of focal length of 15 cm. What should be range of distance of the object from the mirror ? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object?
Answer:
- The range of distance of object is between 0 and 15 cm.
- The image is virtual and erect.
- The Image Is larger than the object.
Question 58.
To reduce glaze of surroundings the windows of sorne department stores, rather than being vertical, slant Inward at the bottom. How does this reduce glaze?
Answer:
Thts slant reflects the sunlight further down towards the ground, than it would have happened If they are vertical.
Question 59.
Predict and write the reason, why the value of the distance of the object (u) is always negative in the mirror equation.
Answer:
Because, the object Is always placed infront of the mirror and the object distance is measured opposite to the incident rays, the sign of object distance is taken as negative.
Question 60.
Which property of concave mirror Is used in making the solar cooker?
Answer:
When the light rays which travels parallel to the principal axis of concave mirror, they will meet at Focus after reflection.
Question 61.
Draw the ray diagram to show the formation of image for the object of height 1 cm. placed at 5cm. distance, in front of a convex mirror having the radius of curvature R = 5cm.
Answer:
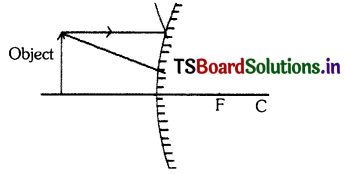
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
A fish looks up from the water making a perpendicular angle 45°C. Can the fish see the sky on the surface of water? Explain.
Answer:
If the incidence angle is less than the critical angle takes place.
Given incidence angle = θ1 = 45°
nwaterXsinθc = nairXsin90°
Refractive index of water = \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Refractive index of air = 1
\(\frac{4}{3} \times \sin \theta_c=1 \times 1 \)
\(\sin \theta_c=1 \times \frac{3}{4}=\frac{3}{4} \Rightarrow \theta_c=\sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)=47.85^{\circ}\)
∴ θc θ1 So fish can see the sky.
Question 2.
The focal length of. huge concave mirror is 120 cm. A man Is standing in front of it at a distance of 40cm. What are the characteristics of his image in that mirror?
Answer:
Object distance = u = – 40 cm
Focal length f = -120 cm (∵ concave mirror)
Image distance v =?
Mirror formula \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{120}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{40} \)
\(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{40}-\frac{1}{120}=\frac{3-1}{120}=\frac{2}{120}=\frac{1}{60}\)
∴ v = 60 cm
Image distance = 60 cm.
Magnification = m = \(\frac{\text { Image distance }}{\text { Object distance }}=\frac{-60}{-20} \) = 3 cm
Here ‘+‘ represents Image is virtual, erect and magnified.
Question 3.
There Is an object in front of convex mirror at a distance of 5 cm. If Its focal length Is 10 cm then
a) What Is the image distance?
b) What is Its magnification
Answer:
a) In the case of convex mirror.
Object distance = u = – 5 cm
Focal length = f = + 10 cm
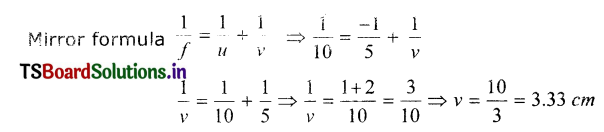
b) Magmfication (m) = \(-\frac{v}{u}=\frac{-3.33}{-5}\) = 0.66
Question 4.
Write any two uses of each of concave and convex mirrors In our daily life.
Answer:
Uses of Convex mirrors:
- Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors In cars, scooters, motorcycles, buses and trucks etc.
- Convex mirrors are used In telescopes.
Concave mirrors:
- Concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors and used by dentists, eye specialists etc.
- Coeica”e mirrors at e use1 as reflectors in the headlights of vehicles such as motorcycles, cars etc.
- Large concave mirrors can be used to concentrate sunlight to produce neat ifl a solar heating device.
- Concave mirrors are also used in telescopes.
Question 5.
Which objects at your home act as spherical mirrors?
Answer:
- TIe outer surfaces of stainless steel utensils,. spoons, plates, etc., act as convex mirrors.
- The inner surfaces of the above said articles act as concave mirrors.,
- Any bought surface with high polish acts as a convex mirror.
Question 6.
Suggest a new use with a spherical mirror.
Answer:
- Concave mirrors are used in long focal-length camera lenses.
- In ‘Super sniper to focus arid gritty sound from a great distance onto a microphone pick up.
- At one end of some gas LASERS to focus the emerging beam of light.
- In the telescopes to focus the very weak radio waves onto the suspended antenna.
Question 7.
Write about different points related to mirrors.
Answer:
The different points related to mirrors are
- Vertex (P): The point where the central axis touches the mirror is called vertex.
- Focus or focal point (F): The rays coming from a distant object meet at a point on principal axis after reflection. That point is known as focus or focal point.
- Centre of curvature (C): It is the centre of the sphere to which The mirror belongs.
Question 8.
Write about various distances related to mirrors.
Answer:
The various distances related to mirrors are
- Focal length (f): The distance between vertex and focus is called focal length.
- RadIus of curvature (R): The distance between vertex and centre of curvature is called radius of curvature.
- Object distance: It is the distance between the object and pole of mirror and is denoted by ‘u.
- Image distance: It is the distance between the Image and pole of the mirror and is denoted by ‘y’.
Question 9.
What happens If an object is placed at centre of curvature of a mirror?
Answer:
From the ray diagram, we conclude that the image of the object will be formed at the same distance as the object and it will be inverted and of the same size. The image Is real because it forms on a screen.
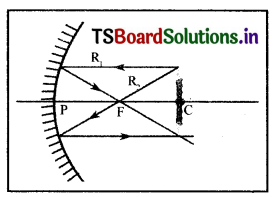
Question 10.
Would you be able to burn a paper using concave mirror?
Answer:
1. Concave mirror focuses the parallel sun rays at focal point of the mirror.
2. So with a small concave mirror we can heat up and bum a paper.
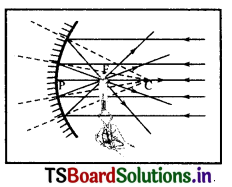
Question 11.
Cana plane mirror ever form a real image?
Answer:
- Real images can only be formed when the reflected rays converge.
- For plane mirrors it is not possible.
- However if the reflected rays are converged it can form a real image.
- Consider a source of light at infinity (say sun) and plane mirror is very small in size, its reflected image will show a circular bright spot (Image of sun) on the screen.
Question 12.
Identify types of mirrors without actually touching it. (move the mirror to and from)
Answer:
- Plane mirror: It forms the mage es of same size.
- Concave mIrror: Image es curved, bringing the mirror closer, magnifying the image. Moving it away, the Image Is Inverted and reduced.
- Convex mirror: Mirror image is always diminished but erect. The viewpoint is wider.
Question 13.
Why there is right-left inversion (lateral Inversion) when we look into mirror?
Answer:
- The light rays which come from object get reflected from the plane mirror and reach our eye.
- Our brain feels that the ray Is coming from the inside of mirror.
- So there Is right-left inversion.
Question 14.
List out the four properties of the Image formed by a convex mirror.
Answer:
Properties of the image formed by a convex mirror:
- The image is always virtual and erect.
- The image is highly diminished or point sized.
- It is always formed between F and R
- The object and image are on opposite sides of mirror.
Question 15.
The magnification of the image by the concave mirror is -1. Mention the four characteristics of Image from the above Information.
Answer:
Magnification = -1.
This means the image size is equal to the object size. In this case the object will be at centre of curvature ‘C’ and the image also will be formed at ‘C’.
Characteristics of image :
→ Image is real
→ Image is inverted
→ Size of image Is equal to the size of the object
→ Image will be formed at ‘C’
Question 16.
Why periscopes are in ‘Z’ shape? Why not In other shapes? Make a guess. Try to check whether your guess Is correct or not.
Answer:
Generally, periscopes are used to see the objects which are at a greater height by hiding In ground. The beam of light which is incident on the first mirror must be Incident on second mirror after reflection from the first mirror. The mirrors are arranged at an angle of 45°. It is possible only when It Is in the shape of ‘Z’ and In other shapes it Is impossible to see the object by hiding. So periscopes are in ‘Z’ shape. Eg : Let us assume that periscope is in T shape. It is impossible to see the object by hiding.
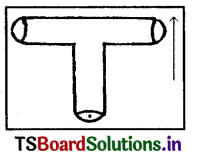
Question 17.
State the laws of reflection of light.
Answer:
1. When light gets reflected from a plane surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of Incidence.i.e.,
∠i = ∠r
2. The Incident ray, the normal at the point of Incidence and the reflected ray lie in the same plane. i.e. AO, ON, OB are in same plane.
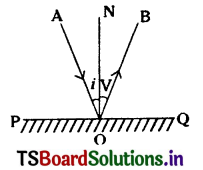
Question 18.
How do you appreciate the role of spherical mirrors In our daily life?
(OR)
Write the usage of spherical mirror In daily life situations.
(OR)
How do you appreciate the importance of spherical mirrors In our daily usage?
Answer:
- Spherical mirrors are useful in our daily life in many ways.
- Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors In cars, scooters, buses, etc. This helps us to see the traffic behind the vehicle, which avoids accidents while taking turns.
- Concave mirrors are used by dentists, ophthalmologists, to see the smaller parts of teeth, eyes and ears.
- Concave mirrors are also used in solar heating devices.
- Concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors to see a large image of the chin (or) face.
Question 19.
How do you appreciate the use of reflection of light by a concave mirror In making of TV antenna dishes?
Answer:
- I appreciate the working process of TV antenna dishes.
- They contain the concave surfaces to receive the signals from the distinct communication satellites.
- The concave (parabolic) shape of a dish antenna helps to reflect signals to the focal point of the dish.
- A device known as feed horn is mounted at the focal point which gathers the signais and sends them to a processing unit.
Question 20.
Have you ever observed the image of the sky In rainwater pools on earth? Explain the reflection of light In this context.
Answer:
- The image of the sky Is formed in the rainwater pool on earth.
- Ught rays coming from blue sky travel through nearly the same air layers and all are bent over to the same amount.
- Therefore, rays coming from the top of object will arrive lower than those from the bottom.
- The image usually is upside down, enhancing the illusion that the Image of the sky is seen in the water which is acting as a mirror.
Question 21.
Discuss the merits and demerits of using mirrors in building elevation.
Answer:
Merits:
- When sunlight falls on the building, the light rays reflect back and building does not heat up.
- Mirrors do not get rust and can be cut into different shapes and sizes.
Demerits:
- Elevation of buildings with mirrors is not suggestable.
- These mirrors reflect sun rays at day time and reflectS lighting from nearby electrical bulbs at night time, which causes confusion and disturbance for the vehicles and people who are running on the nearby roads lead to accidents.
- Birds like sparrows, crows will get confusion while flying on roads.
- They are also not safe enough to the buildings, as they cause easy access to thieves.
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Focal length of a concave mirror Is f. The distance from Its focal point to the object is P. Find the ratio of heights of image.
Answer:
Concave mirror Is a part of spherical mirror.
Magnification of a spherical mirror = m = \(\frac{f}{f-u}\)
Focal length of a mirror = f
The distance from focal point to the object is = p.
i) When the object is placed within the focus, then
u = – (f- P), f = f
Magnificatlon of the mirror = m = \(\frac{\text { Size of image }}{\text { Size of object }}=\frac{-f}{-f+(f-p)}=\frac{f}{p}\) ……………………….. (1)
ii) If the object placed beyond F at a distance P. So = u = – (f + P) = f = – f
Magnification of the mirror = \(\frac{f}{f-u}=\frac{-f}{p} \) ……………………. (2)
\(\frac{(1)}{(2)}=\frac{h_1}{h_2}=\frac{O J \times \frac{f}{p}}{-O J \times \frac{f}{p}}\) = -1
Question 2.
In the following cases calculate the magnification values for a concave mirror. Give reason.
a) When the object is at the focal point of the mirror
b) When the object Is between focal point and the pole.
Answer:
In the case of concave mirror
a) When the object Is at the focal point of the mirror then its magnification value is -1.
Reason: In this case size of the image is large, compare with the object. It is called virtual image.
Image is formed behind the mirror so magnification has negative sign.
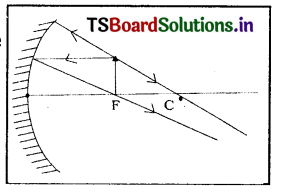
Nature of the image: It ¡s real, inverted, enlarged and forms at infinity.
b) When the object Is between focal point (F) and the pole (P) of the mirror, then its magnification value is + 1.
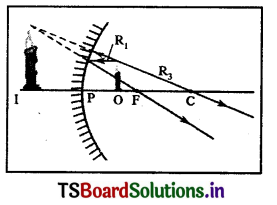
Reason: In this case image is formed on the same side of the object and it is also virtual Image so, the sign of the magnification Is positive. Nature of the Image: It is virtual, erect, enlarged and on the same side of the object.
Question 3.
You are given three mirrors of equal size – concave, convex and plane. How will you identify them without touching their surfaces?
Answer:
We look our face In each mirror, in one after the other. First we keep our face quite close to the mirror and then move It slowly away from the mirror.
- If the image formed Is of same size as our face but laterally Inverted for all positions, then it Is a plane mirror.
- If the Image formed ¡s erect and enlarged Initially but gets inverted as the face is moved away, then it Is a concave mirror.
- If the image formed is erect and smaller In size for aft positions then t is a convex mirror.
Question 4.
Explain the formation of virtual image by a concave mirror.
Answer:
1. Let the object is placed at a distance less than the focal lenqth of the mirror.
2. The first ray (R1) will start from tip of the object and run parallel to axis to get reflected so as to pass through the focal point. ‘
3. The ray (R2) which is passing through focal point is not possible to draw.
4. Let us consider a ray that starts from the tip of the object and goes In such a direction that it would go through the centre of curvature if extended backwards.
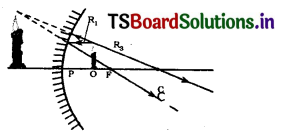
5. This ray Is normal to the surface and so will be reflected along the same line In opposite direction and will go through the centre of curvature.
6. If we extend these two rays (R1 and R3) backward till they meet, an enlarged, erect image is formed which cannot be caught on the screen but visible through mirror. This is the virtual image formed by a concave mirror.
Question 5.
Write the rules to trace an Image forward by a convex mirror.
Answer:
Rule 1. : A ray, running parallel to axis. on meeting the convex mirror,will get the reflected so as to appear as it is coming from the focal point.
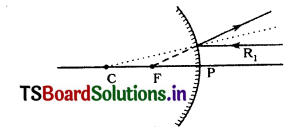
Rule 2: A ray going in the direction of focal point, after reflection, will become parallel to main axis.
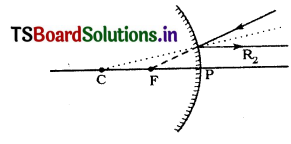
Rule 3: A ray going ¡n the direction of the centre of curvature on reflection, will get back In opposite
direction and looks that it is coming from the centre of curvature.
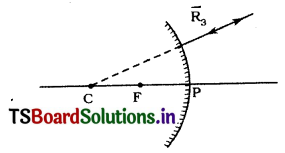
Question 6.
Sukumar saw his face in car rearview mirror. He observed that his Image is smaller than the original.
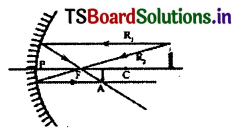
a) What type of mirror it is?
b) What is the nature of image?
c) Draw the ray diagram for it.
Answer:
a) The mirror is convex mirror which is also called as Rear view mirror.
b) The nature of image is erect, virtual, smaller than size of object.
c)
Question 7.
A student conducted an experiment to observe characteristics of images formed by spherical mirrors and recorded his observations as follows. Observe the table and answer the questions.
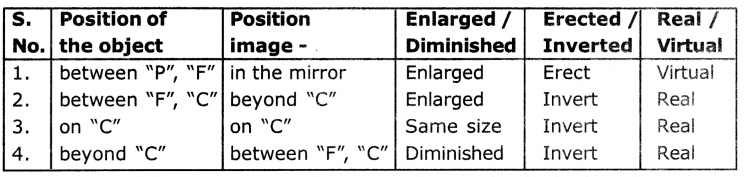
i) Above said Information belongs to which sphencal mirror?
ii) In which situation, magnification Is less than 1.
iii) An object of height 8 cm placed at centre of curvature on principal axis, then where do you get the image and what is its height?
iv) “All real images are inverted”. Justify the statement by using above table.
Answer:
i) It is a Concave mirror.
ii) When object Is kept beyond ‘C’ then magnification is less than 1.
iii) Image formed at ‘C’. The height of the image is 8 cm.
iv) According to the table if the image is erected, it is a real image. In all tne other cases very real image Is Virtual Image.
Question 8.
Make a Solar heater / Cooker and explain the process of making.(AS5)
Answer:
Making of solar heater/cooker:
- Make a wooden/Iron frame in the shape of TV dish antenna.
- Cut the acrylic mirror sheets Into 8 or 12 places in the shape of Isosceles triangle with a height equal to the radius of your dish antenna.
- The bases of 8 or 12 triangles together make the circumference of the dish.
- Stick the triangle mirrors to the dish.
- Face the dish towards the sun. Find the focal point and place a vessel at that point.
- It will become heated. Even you can cook rice in that vessel.
- In this way we will make a solar heater/cooker.

Additional Problems
Question 1.
An object 4 cm In size is placed at 25 cm In front of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Find the nature and size of image.
Solution:
Given that f = -15 cm; u = -25 cm; h0 = 4 cm; v = ?
The mirror formula Is
\( \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{u}+\frac{1}{v} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{-15}=\frac{1}{-25}+\frac{1}{v} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{25}-\frac{1}{15}=\frac{3-5}{75}=\frac{-2}{75}=\)-37.5 cm.
v = -37.5 cm
The screen should be placed 37.5 cm from the pole of mirror and the image is real.
Magnification, m = \(=\frac{h_i}{h_o}=\frac{-v}{u} \Rightarrow \frac{h_i}{4}=-\frac{37.5}{25} \Rightarrow h_i=-\frac{37.5}{25} \times 4 \) = -6cm
So the image is enlarged and inverted.
Question 2.
An object of size 7 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtaIn a sharp Image ? FInd size and nature of the Image.
Solution:
Given that h0 = 7cm; u =- 27cm; f= -18cm; v = ?
The mirror formula is \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{-18}=\frac{1}{-27}+\frac{1}{v}\)
\(\frac{1}{v}=-\frac{1}{18}+\frac{1}{27} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{-3+2}{54}=\frac{-1}{54} \)
So, v = – 54 cm,
So the screen should be placed 54 cm from the mirror and the image is real and inverted.
MagnifIcation, m=\(\frac{h_i}{h_o}=\frac{-v}{u} \Rightarrow \frac{h_i}{7}=-\frac{(-54)}{27} \Rightarrow h_i=-\frac{(-54)}{27} \times 7\) = -14 cm(Hence the image is inverted). As the size of the object Is 7cm the image is enlarged two times.
Question 3.
An object 3 cm high Is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror, the radius curvature is 20 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image. (V = -30 cm, m = -2, h2 = -6 cm)
Answer:
h0 = 3 cm
u = -15 cm
r = -20 cm
f= \(\frac{r}{2}\) =-10cm
Mirror formula is = \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{u}+\frac{1}{v} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{-10}=\frac{1}{-15}+\frac{1}{v}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{15}-\frac{1}{10}=\frac{2-3}{30}=\frac{-1}{30} \) = -30 cm
So the Image Is real and Inverted and beyond C.
Magnification = \(\frac{-v}{u}=\frac{-(-30)}{-15}\) = -2
Therefore the image is enlarged \(\frac{h_i}{h_o} \) = -2 ⇒ \(\frac{h_i}{3}\) = -2
⇒ hi = -6 cm
∴ Size of the image = 6 cm.
Question 4.
An object is placed at a distance of lo cm. from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of image.
Answer:
According to the sign convention.
Focal length, f = 15 cm.
Object distance, u = – 10cm (negative sign)
Image distance, v = ?
Formula: \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{u}+\frac{1}{v}\)
\(\frac{1}{15}=-\frac{1}{10}+\frac{1}{v}\)
⇒ The image Is formed at a distance of 6 cm. at the back of the mirror.
Magnification, m = \(\frac{h_i}{h_0}=-\frac{v}{u}=\frac{-6}{-10}=\frac{3}{5} \) = 0.6
The image is virtual, erect and diminished 0.6 times of the size of object.
Do You Know ?
How does light travel?
Light Is a form of electromagnetic radiation. It travels as waves that do not require any medium for their propagation.
Light is the visible part of these waves having a wavelength of 0.4 to 0.7 tm. The colour of light emitted by a particular substance is characteristic of the atoms present in the substance. Although light travels In straight lines, It can be bent around curves and edges by making use of optical fibres. Optical fibers are bundles of very thin strands of exceptionally clear glass.
Lasers and their use:
Full form of LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. LASER are used in shops, banks to scan bank notes to see whether they are Fake. This is done by passing the note under an ultraviolet light scanner, Gold Is one of the most valuable of elements has been prized since antiquity for Its beauty and resistance to corrosion.