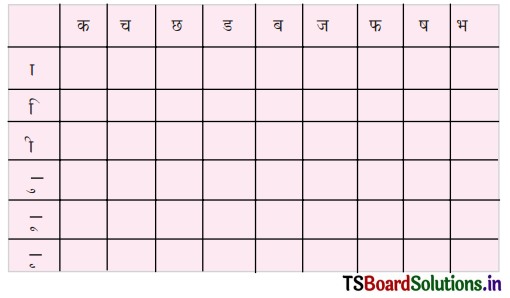
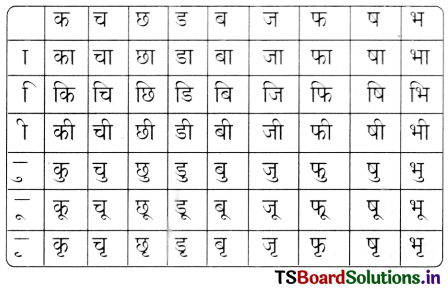
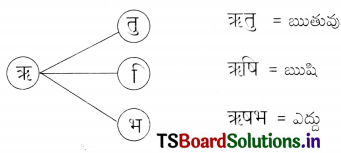
These TS 6th Class Science Important Questions 7th Lesson Separation of Substances serves as a valuable tool for students to prioritize their studying and revision efforts.
TS 6th Class Science Important Questions 7th Lesson Separation of Substances
Question 1.
What type of mixture is our soil?
Answer:
A natural mixture
Question 2.
Can water be used to separate the components of any mixture?
Answer:
No.
![]()
Question 3.
How can you separate rotten fruits from fresh fruits?
Answer:
Hand picking process.
Question 4.
Which property helps in separating the husk from grain?
Answer:
Difference in weights of the husk and grains.
Question 5.
Why sedimentation takes place?
Answer:
Due to gravity.
Question 6.
How does precipitation differ from sedimentation?
Answer:
Precipitation is rapid, whereas sedimentation is a very slow process
![]()
Question 7.
Can you have filter papers with different pore sizes?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 8.
Which of the following does sublime, when heated?
(a) camphor
(b) common salt
(c) Iodine
(d) Ammonium chloride
Answer:
Items a, c and d sublime
Question 9.
Which process can be used to remove impurities from water?
Answer:
Distillation
Question 10.
How is butter taken out from milk or curd?
Answer:
By Churning
Question 11.
Which method is better for separating tea leaves from prepared tea, decantation or filtration?
Answer:
Filtration.
![]()
Question 12.
What is the reverse of evaporation?
Answer:
Condensation.
(Note : The process of conversion of vapour into its liquid form is called condensation.)
Question 13.
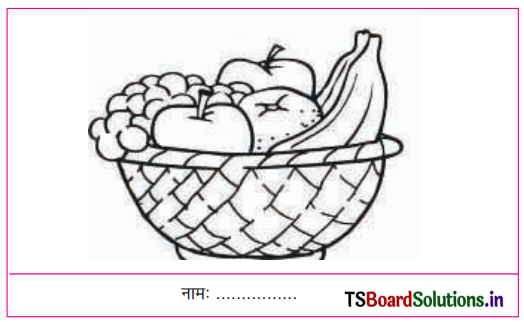
List out the different substances that are used to make the items given in the following table.
(Or)
Define mixtures. Name some of the mixtures, that you have seen, tested in your daily life. List out the different substances that are used to make above said mixtures.
Answer:
Definition: The component having more than one substance is called mixture.
| Item | Substances |
| 1. Tea | Milk, tea leaves, sugar and water. |
| 2. Item | Bengal gram flour; vegetable oil or ghee; cashew nuts, cardamom and sugar (or Jaggery) |
| 3. Lemon Juice | Lemons, sugar and water |
| 4. Concrete | Cement, sand, small stones and water. |
| 5. Soil | Weathered rock, organic material (humus),water and air. |
Question 14.
The materials ghee, wax, sand, sugar, salt, haldi, dal, plastic, wood and iron nails are supplied. Answer the following.
(i) Which materials float on water?
Answer:
Wax, plastic and wood float on water.
(ii) Which materials sink in water?
Answer:
Sand, dal and iron nails sink in water.
(iii) Which materials are soluble in water?
Answer:
Sugar and salt are soluble in water.
![]()
(iv) Which materials are insoluble in water?
Answer:
Ghee and haldi are insoluble in water.
Question 15.A.
You might have come across some situations where you have to separate some components from a mixture. Write down two examples of such situations.
Answer:
Case 1. Stones are separated from pulses.
Case 2. Husk is separated from wheat flour.
Question 15. B.
(i) Did you able to separate each component from the mixture?
Answer:
Yes.
(ii) Are the methods used to separate the components same in all these instances?
Answer:
No.
(iii) What are the properties of the components that are used in separating them?
Answer:
In case 1, hand picking. The colour difference between the pulses and the stones made it possible to separate them by hand picking. In case 2, sieving, difference in size between the flour particles (very fine) and the husk particles (large).
Question 16.
Can you separate salt from sand by hand picking?
Answer:
No.
![]()
Question 17.
What differences in the properties of rice, pulses and stones help us in separating them by the method of hand picking?
Answer:
There are two reasons.
- The size of the stone is different from rice or pulses.
- The colour of stone, rice and pulses are different.
Question 18.
Give some examples of day-to-day life, where the hand-picking method is used.
Answer:
- Separating tomato, green chillis and radish.
- Rotten eggs are removed from fresh eggs.
- Separating pencils and erasers.
Question 19.
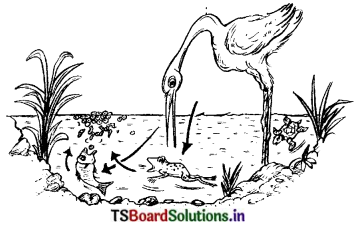
A little of the soil is shaken with water in a glass tumbler. It ¡s kept undisturbed for some time. Then mud particles settle at the bottom of the tumbler. Why is it so?
Answer:
- Mud is not soluble in water.
- Mud is heavier than water.
So mud particles settle at the bottom of the tumbler
Question 20.
(a) Can you separate mud from muddy water using a sieve?
Answer:
No.
(b) How small should be the pores of the sieve to do this?
Answer:
The size of the pores of the sieve should be smaller than the size of the fine mud particles.
(c) Now, you use a cloth as a sieve. Is the water clear after sieving?
Answer:
No, the water is not clear.
![]()
Question 21.
How is salt extracted from sea water?
Answer:
Sea water is captured in wide pans and is exposed to air and sunlight. Then water evaporates and the salt is left behind in the pAnswer: The process is called ‘crystallisation.’
Question 22.
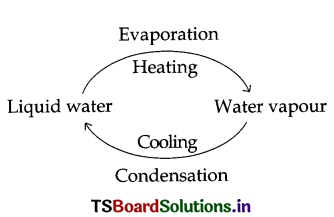
What is ‘distilled water’?
Answer:
When water is boiled, some water vapourises. These vapours are collected in a flask and cooled. Then these vapours turn into water. This water is free from impurities. It is called ‘distilled water’.
Question 23.
What are the uses of ‘distilled water’?
Answer:
- The injection powder is first mixed with distilled water. Then this liquid is injected to patients, by doctors.
- In chemical laboratories, distilled water is used during chemical analysis.
Question 24.
In order to separate the components of a mixture, we make use of their difference in colour, shape, size, weight, solubility.
(a) Can we use these features for separating mixtures of powdered salt and camphor?
Answer:
No. However, property of solubility may be used in common salt dissolves in water, while camphor is insoluble in water. Now the salt is recovered from the salt water, by evaporation process.
(b) What other properties can be use?
Answer:
Sublimation. Camphor sublimes. Salt does not sublime.
Question 25.
What is chromatography?
(Or)
Which method is used to separate colours from a mixture of colours?
Answer:
Chromatography is a technique used for separating mixtures of gases, liquids or dissolved substances.
![]()
Question 26.
Give an example of chromatography.
Answer:
Ink appears to be made of a simple colour but it is actually a mixture of many colours. The qualitative separation of ink into its component colours can be done using chromatography.
Question 27.
Where do we use chromatography method?
Answer:
Chromatography is used to separate the colours and then identify the components of a mixture. Ex: Ink, green pigment of leaf, dyes, etc.
Question 28.
Describe any four methods which separate the material.
Answer:
- Winnowing – Eg: Separation of husk from the paddy grains
- Hand – picking: Eg: Separation of stones from rice and pulses
- Crystallization – Eg : Separation of soluble substances from the solution.
- Decantation – Eg: Floating substance is separated by leaving the sediment in the container.
- Chromatography – Eg: Separation of colours from different mixtures of colours.
Question 29.
How do farmers separate husk from grains?
Answer:
Farmers separate husk from grains by the method called “Winnowing”.
Question 30.
Write the method you follow to separate
(a) Mud from water
(b) Husk and flour
Answer:
(a) Mud from water : Filtration
(b) Husk and flour : Sieving
Question 31.
What is sublimation ? Give an example.
Answer:
The process in which a substance changes directly from solid to gaseous form and vice-versa is called sublimation. Eg: Sublimation of camphor.
![]()
Question 32.
Can you separate salt from salt water, using a filter paper? If not, why?
Answer:
No.
Reason : The particles of salt dissolved in water are so small in size, that they easily pass through the fine pores of the filter paper. So they can’t be separated by filtration.
Question 33.
Rani filtered mud water by using filter paper. You cannot understand how it is possible. Write down some questions which will be asked by you.
Answer:
- How can we separate mud from water?
- is it possible to separa te mud from water?
- What are the tools required to filter mud water?
- Is mud water filtered easily?
- Are there any techniques to filter mud water?
Question 34.
Hemanth purchased green chilli, coriander seeds, tomato, red gram, wheat flour and kept them safely in a bag. While returning he fell and all the items in the bag got mixed. How will he separate?
1. Which material will he separate first?
2. How would he separate tomato and chilli?
3. How would he separate wheat flour?
4. How would he separate coriander seeds?
Answer:
- First tomato and chilli are separated.
- By hand picking.
- Wheat flour is separated by sieving.
- Coriander seeds can be separated from red gram by winnowing.
![]()
Question 35.
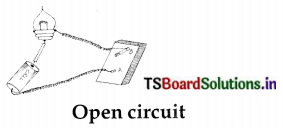
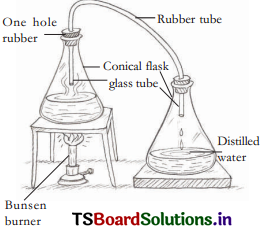
What is distilled water? Write the arrangement of apparatus to make distilled water by distillation with a neat labelled diagram.
(Or)
What process do you follow to obtain distilled water on your own? Explain the procedure. Mention the apparatus.
(Or)
Write the procedure and precautions taken in the extraction of distilled water experiment.
Answer:
The water content that is made free from impurities by the process of vapourisation technique is called distilled water.
Preparation of distilled water:
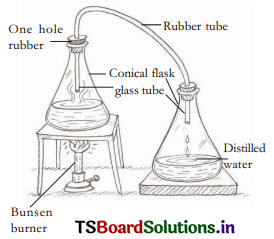
Required apparatus : Two conical flasks, water, plastic tube, bunsen flame, tripod, 2 single holed rubber corks etc.
Precautions:
- Inserting tubes into the rubber holders is done gently.
- Applying heat to the flask should be observed carefully.
Procedure: A conical flask is filled with water and closed with cork having a hole. Take an another conical flask with a cork having a hole and insert another glass tube through it. Connect both tubes with a plastic tube. Water containing flask is heated.
Observation : It is observed that water vapour goes into the empty flask. It turns slowly into water. The water in the second conical flask is called distilled water.
![]()
Question 36.
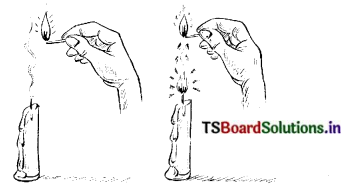
Describe the experiment of sublimation of camphor with a figure.
(Or)
How do you demonstrate the process of sublimation ? What apparatus did you use ?
Answer:
Aim : To observe the sublimation of camphor.
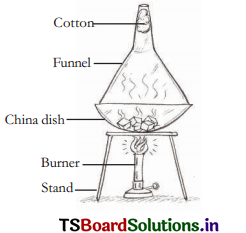
Apparatus : Cotton, glass funnel, china dish,camphor and powdered salt, stand, burner etc.
Procedure : A mixture of camphor and powdered salt is taken in a china dish and covered with a funnel. The dish is placed on a stand. It is heated with a burner.
Observation : When camphor is heated, it transforms into a gaseous form without changing into liquid.
Similarly, on cooling, the gaseous form of a camphor changes directly into a solid without going to the liquid state.
Question 37.
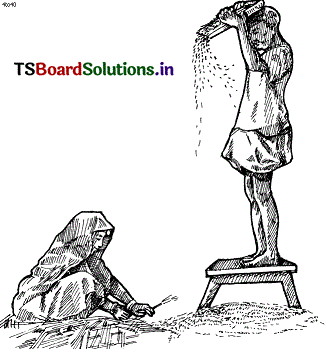
Write the process of separation of husk from grain.
Answer:
Standing on a high platform, the husk and grain mixture is allowed to drop slowly from the flat pan.
As a result the wind carries the husk forward and the grains fall vertically downward. A separate heap of grain is formed.
Question 38.
Which separation method is used to separate the mixture of Suji (Raya) and sugar?
Answer:
The method sieving is used to separate Suji (Rava)and sugar.
The fine and smaller particles of raya pass through sieve holes. The sugar crystals are left on the sieve plate.
Question 39.
Write the experimentation method and precautionary measures to know about chromatography method.
Answer:
Aim : To show the phenomenon of chromatography.
Required materials : Chalk piece, ink, plate, water etc.
Procedure : A stick of white chalk is taken. An ink (blue or black) mark is put around the curved surface of the chalk. A plate is taken and filled with little amount of water. Ensure that the water does not touch the ink mark. The set up is kept undisturbed for sometime.
Observation : It is observed that the chalk piece absorbed water. Water absorption took place upto its tip. Some colours appeared from the ink border. Yellow, red, blue, green etc are seen from the ink mark to tip of the chalk piece.
![]()
Question 40.
A mixture of sand, sawdust and salt Is given in a beaker, half-filled with water. The mixture is stirred well and allowed to settle for 10 minutes. Answer the following.
(a) Which substance floats on the water?
Answer:
Saw dust
(b) How can you collect it?
Answer:
Using a perforated wooden spoon.
(c) Which substance settles at the bottom of the beaker?
Answer:
Sand.
(d) How can you collect it back?
Answer:
Filtration
(e) Which substance is dissolved in the water?
Answer:
Salt
(f) How can you get it back?
Answer:
Crystallisation.
Question 41.
Your teacher conducted the following experiment in the classroom.
(a) What is the name of the experiment?
Answer:
Chromatography
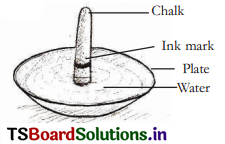
(b) What do you observe in the colour on the chalk piece in this experiment?
Answer: Different colours formed from the ink mark, expanded on the chalk.