These TS 10th Class Physical Science Bits with Answers Chapter 9 Electric Current will help students to enhance their time management skills.
TS 10th Class Physical Science Bits Chapter 9 Electric Current
Question 1.
If work done is W and the charge that flows through conductor is Q, then, P.D., V= ( )
(A) Q/w
(B) WxQ
(C) W/Q
(D) W2/Q
Answer:
(C) W/Q
Question 2.
The work done in moving a charge of 2 columns across two points having a potential difference 12v : ( )
(A) 6 J
(B) 48 J
(C) 3 J
(D) 24 J
Answer:
(D) 24 J
Question 3.
1volt/1ampere ( )
(A) 1 watt
(B) 1 ohm
(C) Farad
(D) 1 kIlo watt
Answer:
(B) 1 ohm
Question 4.
The resistance per unit length of a unit cross-section of a material is called its : ( )
(A) power
(B) thermal equivalent
(C) resistivity
(D) capacity
Answer:
(C) resistivity
Question 5.
The product of power and time is ( )
(A) electrical energy
(B) induction
(C) electrical resistance
(D) flux
Answer:
(A) electrical energy
![]()
Question 6.
Unit of electrical energy is ……………………….. . ( )
(A) KWH
(B) watts/hour
(C) ohms/hour
(D) Ω-s
Answer:
(A) KWH
Question 7.
Opposition to the motion of electrons is ………………………. . ( )
(A) charge
(B) resistance
(C) induction
(D) capacitance
Answer:
(B) resistance
Question 8.
At any junction point in a circuit where the current can divide, the sum of the currents into the junction must be equal to the sum of the currents leaving the Junction ……………… This is …………………… . ( )
(A) junction law
(B) loop law
(C) induction law
(D) associative law
Answer:
(A) junction law
Question 9.
Ohm’s law is not applicable to ( )
(A) metal conductors
(B) gaseous conductors
(C) semiconductors
(D) both B&C
Answer:
(D) both B&C
Question 10.
An electronic measuring Instrument that combines several measuring functions in one unit is called : ( )
(A) ammeter
(B) volt meter
(C) sonometer
(D) multimeter
Answer:
(D) multimeter
Question 11.
1000 J/s ……………………….. ( )
(A) 1 kWh
(B) 1kw
(C) 1 kJ
(D) 1 kg
Answer:
(B) 1kw
Question 12.
Power is given by the formula : ( )
(A) V/R
(B) V/R2
(C) V2/R
(D) V+R/R
Answer:
(C) V2/R
![]()
Question 13.
The potential difference between the two line wires that bring electric power supply into the houses is ……………………….. . ( )
(A) 1200 v
(B) 500 v
(C) 420 v
(D) 240 v
Answer:
(D) 240 v
Question 14.
The physical quantity that determines the direction of flow of current through a conductor is called ( )
(A) capacity
(B) resistance
(C) electrical potential
(D) none of these
Answer:
(C) electrical potential
Question 15.
The rate of flow of electrical charge is called ( )
(A) emf
(B) e.c.e.
(C) current
(D) resistance
Answer:
(C) current
Question 16.
An electric cell produces ……………………. . ( )
(A) alternating current
(B) direct current
(C) both 1 & 2
(D) none of 1 & 2
Answer:
(B) direct current
Question 17.
The unit of specific resistance is …………………………. . ( )
(A) ohm/m
(B) nho/m
(C) amp/m
(D) ohm-meter
Answer:
(D) ohm-meter
Question 18.
The current through 1 ohm. resistance in the adjacent circuit: ( )
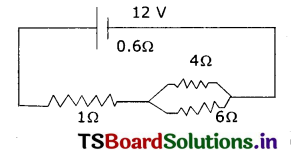
(A) 1 A
(B) 12 A
(C) 6 A
(D) 3 A
Answer:
(D) 3 A
Question 19.
The expression that represents Ohm’s law Is ( )
(A) i= \(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{\mathrm{v}}\)
(B) i = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{R}}\)
(C) i = V x R
(D) i = V2/R
Answer:
(B) i = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{R}}\)
Question 20.
The current flowing through a circuit is 2 Amps.” – This statement means :
(A) 2 coulombs/sec
(B) 2 Newtons/sec ( )
(C) 2 joules/sec
(D) 2 volts/sec
Answer:
(A) 2 coulombs/sec
Question 21.
If two resistors each of resistance ‘R’ are connected in parallel, then the effective resistance is ( )
(A) RΩ
(B) 2R Ω
(C) \(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{2} \) Ω
(D)
Answer:
(C) \(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{2} \) Ω
![]()
Question 22.
The electric current is a ………………………. . ( )
(A) vector
(B) sealer
(C) both A&B
(D) neither A nor B
Answer:
(B) sealer
Question 23.
A manganine wire of cross section area 1mm2 has a resistance of 15w. The resistance of a magazine wire of area of cross-section 3 mm2 having same
length is …………………. . ( )
(A) 15 Ω
(B) 10 Ω
(C) 20 Ω
(D) 5 Ω
Answer:
(D) 5 Ω
Question 24.
The “makes and breaks’ of an electrical circuit can be caused by …………………… . ( )
(A) plug key
(B) rheostat
(C) fuse
(D) ammeter
Answer:
(A) plug key
Question 25.
The resistance of a material depends on ……………………… . ( )
(A) length of conductor
(B) the substance with which it Is made
(C) area of cross-section
(D) all of these
Answer:
(D) all of these
Question 26.
The unit of electrical conductivity is ( )
(A) ohm
(B) watt
(C) Mho/m
(D) J/sec
Answer:
(C) Mho/m
Question 27.
When short circuit occurs, the flow of current ………………………… . ( )
(A) decreases
(B) increases
(C) doesn’t change
(D) becomes zero
Answer:
(B) increases
Question 28.
If 0.5 Amps of current flows through a conductor of resistance 10W, the potential difference between its ends is ………………………. . ( )
(A) 5V
(B) 9.5V
(C) 0.05V
(D) 20V
Answer:
(A) 5V
Question 29.
The reciprocal of conductivity is called ……………………… . ( )
(A) density of flow
(B) resistance
(C) resistivity
(D) flux density
Answer:
(C) resistivity
![]()
Question 30.
The resistivity of copper is ……………………. . (in W-m) ( )
(A) 1.68 x 10-8
(B) 220 x 10-7
(C) 5.60 x 10-8
(D) 1.59 x 10-8
Answer:
(A) 1.68 x 10-8
Question 31.
The resistivity of rubber is ………………………. . (in W-m) ( )
(A) 2.82 x 10 -8
(B) 2.44 x 10-7
(C) 1.00 x 10-8
(D) 1.30 x 10 -8
Answer:
(C) 1.00 x 10-8
Question 32.
The heating element in an electric iron is made of …………………….. . ( )
(A) copper
(B) nichrome
(C) tungsten
(D) silicon
Answer:
(B) nichrome
Question 33.
These are used in all sorts of electronic devices – ( )
(A) rheostats
(B) transformers
(C) Ics
(D) valves
Answer:
(C) Ics
Question 34.
Three resIstances 4 ohms, 8 ohms, and R ohms are connected in series. If the effective resistance of the combination is 20 ohms, the value of R is ( )
(A) 4 ohms
(B) 8 ohms
(C) 2 ohms
(D) 10 ohms
Answer:
(B) 8 ohms
Question 35.
The effective resistance of the combination between points A and B as shown in the following figure is: ( )

(A) \(\frac{20}{3} \) Ω
(B) 20 Ω
(C) 30 Ω
(D) \(\frac{3}{20} \) Ω
Answer:
(A) \(\frac{20}{3} \) Ω
Question 36.
An example of a Ohmic conductor is : ( )
(A) Transistor
(B) Vacuum tube
(C) Thermistor
(D) Copper wire
Answer:
(D) Copper wire
Question 37.
Ten identical resistances each having a resistance of 1W are joined in parallel. The combination has resultant resistance of ……………………… . ( )
(A) 10 Ω
(B) 1 Ω
(C) 0.01 Ω
(D) 0.1 Ω
Answer:
(D) 0.1 Ω
Question 38.
The reciprocal of resistance is called : ( )
(A) inductance
(B) conductance
(C) specific resistance
(D) conductivity
Answer:
(B) conductance
Question 39.
Example of an insulator is ( )
(A) graphite
(B) Silver
(C) aluminum
(D) Diamond
Answer:
(D) Diamond
Question 40.
If five 100w bulbs are used for 4 hours a day, the current bill in the month of June at the rate of ‘4 for unit is ………………………. . ( )
(A) ₹ 60
(B) ₹ 180
(C) ₹ 120
(D) ₹ 140
Answer:
(C) ₹ 120
![]()
Question 41.
If a number of bulbs are connected in series, their brightness ………………….. . ( )
(A) increases
(B) decreases
(C) doesn’t change
(D) A or B
Answer:
(B) decreases
Question 42.
If the length of a conductor is ‘r and its cross-section area is ‘A’, then its conductance is ( )
(A) R α \(\frac{l}{\mathrm{~A}}\)
(B) \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}} \alpha \frac{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{l}}\)
(C) R= l x A
(D) none of those
Answer:
(B) \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}} \alpha \frac{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{l}}\)
Question 43.
II four wires each of resistance are connected end to end to form a square, the resistance between its opposite vertices is ( )
(A) R
(B) 2R
(C) \(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{2}\)
(D) \(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{4}\)
Answer:
(A) R
Question 44.
One kilowatt hour (kwh) = ( )
(A) 36 x 106J
(B) 36 x 1010J
(C) 3.6 x 106J
(D) 8.314 x 108J
Answer:
(C) 3.6 x 106J
Question 45.
A bulb of internal resistance 240 W is connected across a potential difference of 240v. The current through the bulb is ( )
(A) 480 A
(B) 57600 A
(C) 1 A
(D) 0.1 A
Answer:
(C) 1 A
Question 46.
To prevent damage due to overloading the device connected in a circuit is ………………. . ( )
(A) transformer
(B) inverter
(C) Junction box
(D) fuse
Answer:
(D) fuse
Question 47.
The unit of measurement usually used to measure work done is ( )
(A) Calorie
(B) Joule
(C) Ampere
(D) Newton
Answer:
(B) Joule
Question 48.
The instrument used to measure potential difference is ………………………. . ( )
(A) voltameter
(B) ammeter
(C) galvanometer
(D) volt meter
Answer:
(D) volt meter
Question 49.
1 Volt / 1 Ampere = ( )
(A) 1 Joule
(B) 1 watt-hour
(C) 1 ohm
(D) 1 Neuton
Answer:
(C) 1 ohm
Question 50.
An example of Ohmic conductor. ( )
(A) silicon
(B) copper
(C) nichrome
(D) air
Answer:
(B) copper
Question 51.
Fuse wire is an alloy of ( )
(A) tin & lead
(B) Iron, copper, zinc
(C) nickel & chromium
(D) iron, nickel, and chromium
Answer:
(A) tin & lead
![]()
Question 52.
The electrical property that opposes the flow of free electrons in a conductor is ……………… . ( )
(A) potential difference
(B) magnetic flux
(C) resistance
(D) electromotive force
Answer:
(C) resistance
Question 53.
In the formula Rα \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~A}}\) the letter A’ stands for ( )
(A) length of conductor
(B) specific resistance
(C) nature of material
(D) cross-sectional area
Answer:
(D) cross-sectional area
Question 54.
The current in the wire depends ( )
(A) only on the potential difference applied
(B) only on the resistance of the wire
(C) on both of them
(D) none of them
Answer:
(C) on both of them
Question 55.
Consider the following statements. ( )
(A) In series connection, the same current flows through each element.
(B) In parallel connection, the same potential difference gets applied across each element.
(A) both A arid B are correct
(B) A is correct but B is wrong
(C) A is wrong but B is correct
(D) both A and B are wrong
Answer:
(A) both A arid B are correct
Question 56.
The surface of the earth Is taken to be at potential ( )
(A) negative
(B) positive
(C) zero
(D) infinite
Answer:
(C) zero
Question 57.
The resistance of an Ideal voltmeter s ( )
(A) zero
(B) very low
(C) very large
(D) infinite
Answer:
(C) very large
Question 58.
Ampere – second is the unit of ( )
(A) power
(B) charge
(C) e.m.f.
(D) energy
Answer:
(B) charge
Question 59.
Work done by the electric force on unit’s positive charge to move It through a distance is called ( )
(A) resistance
(B) voltage
(C) current
(D) conductivity
Answer:
(B) voltage
Question 60.
The SI unit of voltage is …………………….. . ( )
(A) volt
(B) ampere
(C) ohm
(D) ohm-meter
Answer:
(A) volt
Question 61.
………………………… obey Ohms law. ( )
(A) metals
(B) non-metals
(C) alloys
(D) none
Answer:
(A) metals
Question 62.
The metals which obey Ohms law are called ………………………. conductors. ( )
(A) Ohmic
(B) Non-ohmic
(C) Drudes
(D) Lorentz’s
Answer:
(A) Ohmic
Question 63.
The Nament an electric bulb is made of ………………………. . ( )
(A) Tungsten
(B) Silver
(C) Gold
(D) Copper
Answer:
(A) Tungsten
![]()
Question 64.
……………………….. are used to make diodes. ( )
(A) Metals
(B) Nonmetals
(C) semiconductors
(D) None
Answer:
(C) semiconductors
Question 65.
Electric power = ………………………… . ( )
(A)V=IR
(B) p=VI
(C) ε = pt
(D) none of these
Answer:
(B) p=VI
Question 66.
Electric energy = ( )
(A)V=IR
(B) p = VI
(C) ε = Pt
(D) none of these
Answer:
(C) ε = Pt
Question 67.
An unknown &cuit draws a current of 2A from a 12V battery Its equivalent resistance is ……………………….. . ( )
(A) 2 Ω
(B) 6 Ω
(C) 24 Ω
(D) 10 Ω
Answer:
(B) 6 Ω
Question 68.
Three resistors of values 2W. 4W. 6W are connected in series. The equivalent resistance of a combination of resistors is ………………………… . ( )
(A) 12 Ω
(B) 6 Ω
(C) 2 Ω
(D)
Answer:
(A) 12 Ω
Question 69.
The power delivered by a battery at emf, lOVe 10W. Then the current delivered by the battery is ( )
(A) 100 amps
(B) 1 amp
(C) 20 amps
(D) 10 amps
Answer:
(B) 1 amp
Question 70.
If two or more resistors are connected in scenes, then …………………. flows thrOugh them is same. ( )
(A) current
(B) potential difference
(C) resistance
(D) heat
Answer:
(A) current
Question 71.
……………………………… is used to measure voltage. :
(A) Ammeter
(B) Voltmeter
(C) Galvanometer
(D) Speedometer
Answer:
(B) Voltmeter
Question 72.
1Kw = …………………………. watt. ( )
(A) 106
(B) 102
(C) 103
(D) 104
Answer:
(C) 103
Question 73.
Electricity enters our homes through two wires called ……………………… . ( )
(A) copper wires
(B) parallel wires
(C) line wires
(D) Insulated wires
Answer:
(C) line wires
Question 74.
Symbol for battery ( )

Answer:
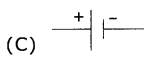
Question 75.
Symbol for rheostat ( )
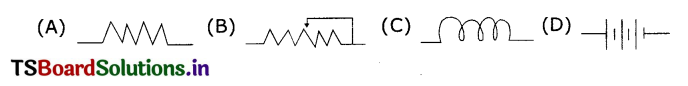
Answer:
![]()
Question 76.
Consider the following statements ( )
(I) In senes connection, the same current flows through each element
(ii) In parallel connection, the same potential difference gets applied across each element.
(A) both A and B are correct
(B) A is correct but B Is Wrong
(C) A Is wrong but B is correct
(D) both A and B are wrong
Answer:
(A) both A and B are correct
![]()
Question 77.
The S.I. Unit of electrical potential difference is ………………………… . ( )
(A) ohm
(B) ampere
(C) volt
(D) farad
Answer:
(C) volt
Question 78.
Flow of positive charges is called ( )
(A) electric current
(B) magnetic force
(C) electrical resistance
(D) power
Answer:
(C) electrical resistance
Question 79.
Potential difference is measured with …………………. . ( )
(A) Ammeter
(B) Galvanometer
(C) Battery
(D) Voltmeter
Answer:
(D) Voltmeter
Question 80.
The instrument used to check the EMF of a battery is …………………. .( )
(A) Voltmeter
(B) Ammeter
(C) Galvanometer
(D) Electric Tester
Answer:
(A) Voltmeter