Students must practice these TS Intermediate Maths 1B Solutions Chapter 4 Pair of Straight Lines Ex 4(c) to find a better approach to solving the problems.
TS Inter 1st Year Maths 1B Pair of Straight Lines Solutions Exercise 4(c)
I.
Question 1.
Find the equation of the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of x2 + y2 = 1 and x + y = 1. (V.S.A.Q.)
Answer:
Given equations are
x2 + y2 = 1 ………………. (1)
and x + y = 1 ………………. (2)
Homogenising (1) with (2) we get
(x2 + y2) = 12
= (x + y)2
⇒ x2 + y2 = x2 + y2 + 2xy ⇒ xy = 0
![]()
Question 2.
Find the angle between the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of y2 = x and x + y = 1. (V.S.A.Q.)
Answer:
Given equations are
y2 = x …………….. (1)
and x + y = 1 ……………… (2)
Homogenising (1) with (2) we get
y2 = x (1)
= x (x + y) ⇒ x2 + xy – y2 = 0
Coefficient of x2 + coefficient of y2 = 1 – 1 = 0
∴ Angle between lines is 90°, lines being perpendicular.
II.
Question 1.
Show that the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of the curve x2 – xy + y2 + 3x + 3y – 2 = 0 and the straight line x – y – √2 = 0 are mutually perpendicular. (S.A.Q.) (May, March ’12)
Answer:
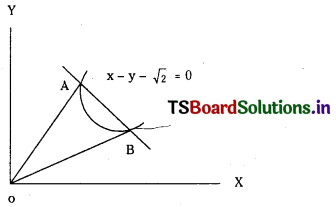
The given equation of the curve is
x2 – xy + y2 + 3x + 3y – 2 = 0 ………………… (1)
Equation of AB is x – y – √2 = 0
⇒ x – y = √2
⇒ \(\frac{x-y}{\sqrt{2}}\) = 1 …………………. (2)
Homogenising (1) using (2) we get
x2 – xy + y2 + (3x + 3y) (1) – 2 (1)2 = 0
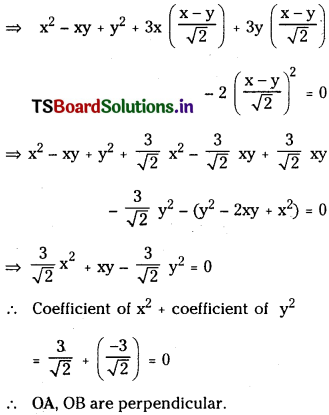
![]()
Question 2.
Find the values of k, if the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of the curve 2×2 – 2xy + 3y2 + 2x – y – 1 = 0 and the line x + 2y = k are mutually perpendicular. (E.Q.) (Board New Model Paper)
Answer:
Given equation of the curve is
2x2 – 2xy + 3y2 + 2x – y – 1 = 0 ……………… (1)
and equation of the line is x + 2y = k
We have \(\frac{x+2 y}{k}\) = 1 ……………….. (2)
Homogenising equation (1) with equation (2) we get
2x2 – 2xy + 3y2 + 2x (1) – y (1) – (1)2 = 0
⇒ 2×2 – 2xy + 3y2 + 2x\(\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}+2 \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{k}}\right)\) – y\(\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}+2 \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{k}}\right)\) – \(\left(\frac{x+2 y}{k}\right)^2\) = 0
⇒ 2k2x2 – 2k2xy + 3k2y2 + 2kx (x + 2y) – ky (x + 2y) – (x + 2y)2 = 0
⇒ 2k2x2 – 2k2xy + 3k2y2 + 4kxy + 2kx2 – kxy – 2ky2 – (x2 + 4xy + 4y2) = 0
⇒ (2k2 + 2k – 1) x2 + (- 2k2 + 3k – 4) xy + (3k2 – 2k – 4) y2 = 0
Since the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection are mutually perpendicular, coefficient of x2 + coefficient of y2 = 0
⇒ (2k2 + 2k – 1) + (3k2 – 2k – 4) = 0
⇒ 5k2 – 5 = 0 ⇒ k2 = 1 ⇒ k = ± 1
Question 3.
Find the angle between the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of the curve x2 + 2xy + y2 + 2x + 2y – 5 = 0 and the line 3x – y + 1 = 0 (E.Q.) (May 2014, 11, Mar.13, 07, June 04)
Answer:
Given equation of the curve is
x2 + 2xy + y2 + 2x + 2y – 5 = 0 …………….. (1)
Equation of the line is 3x – y + 1 = 0
⇒ y – 3x = 1 ……………….. (2)
Homogenising (1) with equation (2) we get the equation of lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of curve and the line.
∴ x2 + 2xy + y2 + 2x (1) + 2y (1) – 5 (1)2 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2xy + y2 + 2x (y – 3x) + 2y (y – 3x) – 5 (y – 3x)2 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2xy + y2 + 2xy – 6x2 + 2y2 – 6xy – 5(y2 – 6xy + 9x2) = 0
⇒ – 5x2 – 2xy + 3y2 – 5y2 – 45x2 + 30xy = 0
⇒ – 50x2 + 28xy – 2y2 = 0
⇒ 25x2 – 14xy + y2 = 0
Let θ be the angle between lines then by the formula
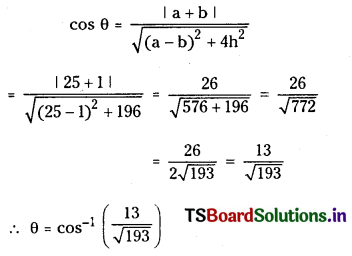
![]()
III.
Question 1.
Find the condition for the chord lx + my = 1 of the circle x2 + y2 = a2 (whose centre is the origin) to subtend a right angle at the origin. (Mar. 14) (SA.Q.)
Answer:
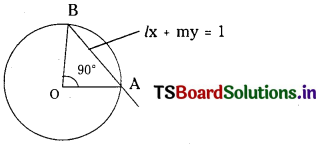
Equation of the circle is x2 + y2 = a2 ………………. (1)
Equation of the line AB is lx + my = 1 ……………….. (2)
Homogenising (1) with equation (2) we get
x2 + y2 = a2 (1)2
⇒ x2 + y2 = a2(lx + my)2
⇒ x2 + y2 = a2 (l2 x2 + 2lmxy + m2y2)
⇒ (a2l2 – 1)x2 + 2a2 lmxy + (a2m2 – 1) y2 = 0
Since OA, OB are perpendicular, we have coefficient of x2 + coefficient of y2 = 0
⇒ (a2 l2 – 1) + (a2m2 – 1) = 0
⇒ a2 (l2 + m2) – 2 = 0
⇒ a2 (l2 + m2) = 2
Question 2.
Find the condition for the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of the circle x2 + y2 = a2 and the line lx + my = 1 to coincide. (S.A.Q.)
Answer:
The given equation of the curve is
x2 + y2 = a2 ……………. (1)
and the equation of line is
lx + my = 1 ………………… (2)
Homogenising (1) with equation (2) we get
x2 + y2 = a2(1)2 = a2 (lx + my)2
⇒ x2 + y2 = a2 (l2x2 + 2lmxy + m2y2)
⇒ x2 (1 – a2l2) + y2 (1 – a2m2) – 2 lma2xy = 0
This equation represents combined equation of lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of (1) and (2)
If the lines are coincident then h2 = ab
l2m2a4 = (1 – a2m2) (1 – a2m2)
= 1 – a2 (l2 + m2) + a4l2m2
⇒ a2 (l2 + m2) = 1
![]()
Question 3.
Write down the equation of the pair of straight lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of the line 6x – y + 8 = 0 with the pair of straight lines 3x2 + 4xy – 4y2 – 11x + 2y + 6 = 0. Show that the lines so obtained make equal angles with the coordinate axes. (E.Q.)
Answer:
Given equation of pair of lines is
3x2 + 4xy – 4y2 – 11x + 2y + 6 = 0 ……………….. (1)
Given equation of line is 6x – y + 8 = 0 ………………. (2)
Homogenising (1) with equation (2)
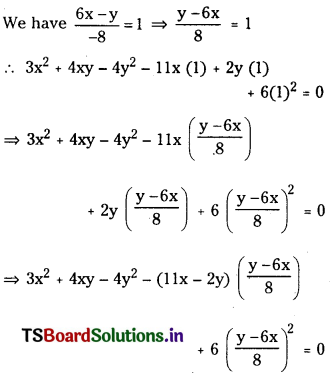
⇒ 64 (3x2 + 4xy – 4y2) – 8 [11xy – 66x2 – 2y2 + 12xy) + 6[y2 + 36x2 – 12xy] = 0
⇒ 936x2 – 256xy + 256xy – 234y2 = 0
⇒ 468x2 – 117y2 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – y2 = 0 …………………. (3)
This equation represents the combined equation of pair of lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of (1) and (2).
The equation of pair of angular bisectors of
(3) is h (x2 – y2) – (a – b) xy = 0
⇒ 0(x2 – y2) – (4 + 1) xy = 0
⇒xy = 0 ⇒ x = 0 or y = 0
Which are the equations of coordinate axes.
∴ The pair of lines are equally inclined to the coordinate axes.