Solving these TS 6th Class Maths Bits with Answers 13th Lesson Practical Geometry Bits for 10th Class will help students to build their problem-solving skills.
TS 6th Class Maths Bits Chapter 13 Practical Geometry
Choose the correct answer and write it in the brackets.
Question 1.
\(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) = 4.6 cm. \(\overline{\mathrm{MN}}\) is constructed such that the length of \(\overline{\mathrm{MN}}\) is twice that of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\). Then the length of \(\overline{\mathrm{MN}}\) is
A) 13.8 cm
B) 9.2 cm
C) 2.3 cm
D) 6.4 cm
Answer:
B) 9.2 cm
Question 2.
Line segment AB is denoted by
A) \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
B) \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)
C) \(\stackrel{\leftrightarrow}{\mathrm{AB}}\)
D) AB
Answer:
A) \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
Question 3.
A line segment has _______ end points.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
Answer:
C) 2
![]()
Question 4.
\(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) = 9 cm ’P’ is the mid point of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) then \(\overline{\mathrm{AP}}\) = _______ cm.
A) 13.5
B) 4.5
C) 4
D) 5
Answer:
B) 4.5
Question 5.
If the diameter of a circle 10 cm then its radius is _______ cms.
A) 4.5
B) 5.5
C) 20
D) 5
Answer:
D) 5
Question 6.
A circle divides the plane into _______ parts.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Answer:
C) 3
![]()
Question 7.
From the given figure which points lie inside the circle ______.

A) O, A
B) C
C) B
D) B, P
Answer:
A) O, A
Question 8.
From the above the points which lie on the circle
A) O, A
B) C
C) B
D) P
Answer:
B) C
Question 9.
From the given figure \(\overline{\mathbf{x y}}-\overline{\mathbf{z w}}\) = ______?
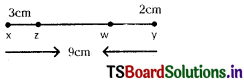
A) 3 cm
B) 4 cm
C) 4 cm
D) 5 cm
Answer:
D) 5 cm
![]()
Question 10.
From the above sum \(2 \overline{x y}+\overline{w y}-3 \overline{x z}\) = ?
A) 9 cm
B) 11 cm
C) 12cm
D) 10 cm
Answer:
B) 11 cm
Question 11.
What is the angular bisector of 90° ?
A) 45°
B) 60°
C) 50°
D) 55°
Answer:
A) 45°
Question 12.
Protractor is used to measure _______.
A) lengths of line segments
B) angles
C) to make equal line segments
D) to mark points on a line
Answer:
B) angles
![]()
Question 13.
Any two circles can be constructed as follows ?
A) concentric circles 
B) Intersecting circles ![]()
C) Circles touch each other externally at a point ![]()
D) All the above
Answer:
D) All the above
Question 14.
Statement (X) : If two circles are congruent their radii are equal
Statement (Y): Length of a line segment is measured by a ruler
Statement (Z): If two line segments are equal then their lengths are need not to be equal
A) X, Y, Z are true
B) X is true Y is false, Z is true
C) X is false, Y is true, Z is false
D) X, Y are true, Z is false
Answer:
D) X, Y are true, Z is false
Question 15.

Statement (P) : Points O, S, R are lie inside the circle
Statement (Q): points M, N, L are on the circle
Statement (R) : Q, P points lie outside the circle
A) P, Q, R are true
B) P is true, Q is false, R is true
C) P, Q are true, R is false
D) P is true, Q, R are false
Answer:
A) P, Q, R are true
![]()
Question 16.
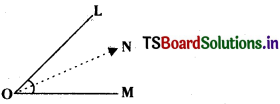
From the adjacent figure \(\overline{\mathbf{O N}}\) is the angular bisector of ∠LOM
Statement (L) : ∠LON = ∠MON
Statement (M) : 1/2 ∠MON = ∠LOM
Statement (N): ∠LON + ∠MON = ∠LOM
A) L, M and N are true
B) L is true M is false, N is true
C) L and M are, N is false
D) L and are false, N is true
Answer:
B) L is true M is false, N is true
Question 17.
Construction of 40° with theprotractor
Step (1) : Mark a point P at 40°
Step (2) : Place the centre point of the protractor at Q and the line aligned with \(\overline{\mathrm{QR}}\).
Step (3): Joint QP. ∠RPQ is the required angle
Step (4) : Draw a ray of an length \(\overline{\mathrm{QR}}\).
A) (4) – (2) – (1) – (3)
B) (4) – (3) – (2) – (1)
C) (4) – (1) – (2) – (3)
D) (4) – (2) – (3) – (1)
Answer:
A) (4) – (2) – (1) – (3)
Question 18.
Construction to bisect a given angle ∠MON
Step (1) : With P as centre draw any radius more than half of PQ in the interior of ∠MON
Step (2) : With Q as centre without altering radius draw another arc in the interior of ∠MON
Step (3) : With ’O’ as centre and any convenient radius, draw an arc \(\overparen{P Q}\) cutting OM and ON at P and Q resp.
Step (4): Draw ray \(\overline{\mathrm{OZ}}\). Then \(\overline{\mathrm{OZ}}\) is the designed bisector of ∠MON
∴ ∠MOZ = ∠ZON
A) (1) – (2) – (3) – (4)
B) (1) – (3) – (2) – (4)
C) (3) – (1) – (2) – (4)
D) (3) – (2) – (1) – (4)
Answer:
C) (3) – (1) – (2) – (4)
![]()
Question 19.
Which of the following instrument is not used to construct the shapes ?
A) the compass
B) the divider
C) the protractor
D) barometer
Answer:
D) barometer
Question 20.
Using ruler and compass which of the following construction can be made ?
A) A circle, with given radius
B) A line segment, with given length
C) Perpendicular bisector of a line segment
D) All the above
Answer:
D) All the above
Question 21.
The line segment MN is denoted by
A) \(\stackrel{\leftrightarrow}{\mathrm{MN}}\)
B) \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{MN}}\)
C) \(\overleftarrow{\mathrm{MN}}\)
D) \(\overline{\mathrm{MN}}\)
Answer:
D) \(\overline{\mathrm{MN}}\)
![]()
Question 22.
The instrument used to measure an angle is a
A) Protractor
B) Compasses
C) Ruler
D) Divider
Answer:
A) Protractor
Question 23.
The instrument used to measure a line segment is
A) Compasses
B) Divider
C) Ruler
D) Protractor
Answer:
C) Ruler
Question 24.
The instrument used to mark points on a line is a
A) Protractor
B) Divider
C) Compasses
D) Ruler
Answer:
B) Divider
![]()
Question 25.
Which of the following is a divider ?
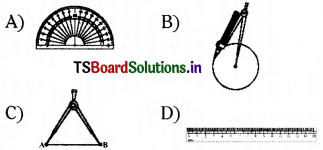
Answer:
C) 
Question 26.
Which of the following is a protractor?
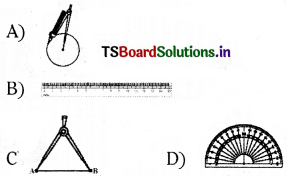
Answer:
D) 
Question 27.
Which of the following is a compass?
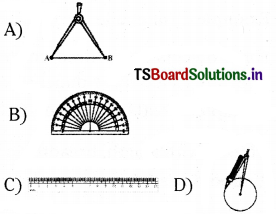
Answer:
D) 
![]()
Question 28.
Which of the following circles intersect at two points ?
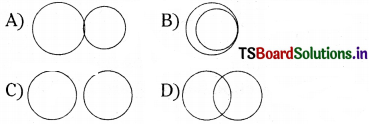
Answer:
D) 
Question 29.
The instruments needed to draw the perpendicular bisector of a line segment are
A) Ruler and compasses
B) Protractor and ruler
C) Compasses and protractor
D) Divider and ruler
Answer:
A) Ruler and compasses