Telangana SCERT TS 10th Class Physical Science Study Material Pdf 3rd Lesson Acids, Bases and Salts Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 10th Class Physical Science 3rd Lesson Questions and Answers Acids, Bases and Salts
Improve Your Learning
I. Reflections on concepts
Question 6.
An acid or a base is mixed with water. Is this process exothermic or endothermic one?
Answer:
When acid or base is mixed with water heat is liberated. So, this process is exothermic.
Question 2.
Distilled water does not conduct electricity. Why?
Answer:
- Water consists of H3O+ and OH– ions.
- In distilled water, the concentration of both H3O+ and OH– is same. Hence they do not form as ions, so distilled water can be treated as a neutral solution.
- As there is no flow of ions, distilled water does not conduct electricity.
- On the other hand, while falling to earth through the atmosphere rainwater dissolves some acidic gases like CO2, SO2, and N2O and forms acids such as H2CO3, H2SO3, HNO3.
- These acids produce Ions. Due to presence of Ions, rainwater conducts electricity.
Question 3.
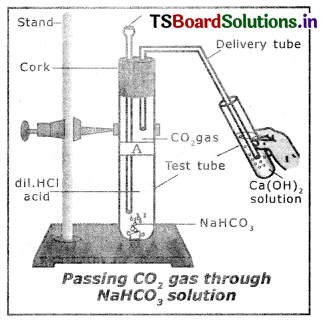
Draw a neat diagram for showing acid solution In water conducting electricity.
Answer:
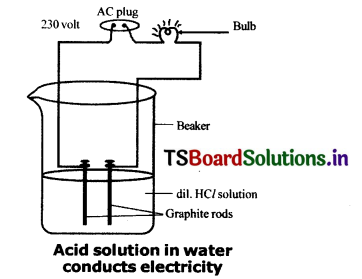
Question 4.
Why the flow of acid rain Into a river make the survival of aquatic lite in a river difficult?
Answer:
- When pH value of rainwater is less than 5.6, it is called acid rain.
- When acid rain flows into the rivers, it lowers the pH of the river water.
- Living organisms can survive only in a narrow range of pli change.
- So flow of acid rainwater into rivers Is dangerous to the survival of aquatic “ life. These acids have free ions that conduct electric current.
![]()
Question 5.
What Is baking powder? How does It make the cake soft and spongy?
Answer:
Baking powder s a mixture of baking soda and mild edible acid such as tartaric acid.
- The chemical name of baking powder is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3).
- It is added to the dough while making cake because on heating It Is converted to sodium carbonate with release of carbon dioxide.
NaHCO3 + H+ → CO2 + H2O + Sodium salt of acid - While baking the cake the CO2 released by baking powder causes the cake or bread to rise making them soft and spongy.
Question 6.
What is a neutralization reaction? Give two examples.
Answer:
Neutralization reaction: The reaction between an acid and a base to give a salt and water is known as a neutralization reaction.
Examples:
(i) When diluted NaOH solution reacts with HCl solution, NaCl (Sodium chloride) salt and water are formed.
NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) +H2O
(ii) When diluted KOH solution reacts with Nitric acid solution, KNO3 (Potassium nitrate) salt and water are formed.
KOH (aq) + HNO3 (aq) → KNO3 (aq) + H2O
Question 7.
Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not turn blue litmus to red whereas aqueous hydrogen chloric acid does. Why?
Answer:
- Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not dissociate in the absence of water. Hence it does not turn blue litmus to red. So dry hydrogen chloride gas is not acidic.
- The HCl (hydrochloric acid) dissociates in the presence of water. Hence it turns blue litmus to red. So. HC (Hydrochloric acid) is acidic.
The dissociation wIll be as follows:
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl–
Question 8.
Give two important uses for each of washing soda and baking soda.
Answer:
Uses of Washing soda (Na2CO3):
- Washing soda (sodium carbonate) is used in glass, soap and paper industries.
- It is used In the manufacture of sodium compounds such as borax.
- Sodium carbonate can be used as a cleaning agent for domestic purposes.
- It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
Uses of Baking soda (NaHCO3):
- Baking soda (Sodium hydrogen carbonate) is used for faster cooking.
- Baking powder (a mixture of baking soda and a mild acid) is used in preparation of cakes.
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate Is also an ingredient in antacids.
- It is also used in soda-acid, fire extinguishers.
- It acts as a mild antiseptic.
Application Of Concepts
Question 1.
Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9 respectively. Classify the solutions given below.
(a) neutral
(b) strongly alkaline
(c) strongly acidic
(d) weakly acidic
(e) weakly alkaline
| Type | Required pH | Given pH | Solution |
| a) Neutral | 7 | 7 | D |
| b) Strongly alkalIne | 10-14 | 11 | C |
| c) Strongly Acidic | 0-3 | 1 | B |
| d) Weakly AcIdic | 4-7 | 4 | A |
| e) Weakly Alkaline | 7-9 | 9 | E |
Order of pH is In increasing order of hydrogen Ion co4centratIon, higher the hydrogen ion concentration lower is the pH value.
11<9< 7<4< 1
C<E<D<A<B
![]()
Question 2.
Why does tooth decay start when the pH of mouth is lower than 5.5?
(or)
What value of pH in the mouth leads to tooth decay? Why?
Answer:
- Tooth decay starts when the pH of the mouth is lower than 5.5.
- Tooth enamel, made up of calcium phosphate is the hardest substance in the body.
- It does not dissolve ¡n water but is corroded when the pH in the mouth is below 5.5 due to acids.
- Bacteria present In the mouth produce free acids whose pH is lower than 5.5, due to degradation of sugar and food particles present in the mouth. Due to this the pH of the mouth falls.
Question 3.
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Answer:
(a) There is a shift In p’ of fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline when a little of baking soda is added to It is because the W ion concentration has been decreased and so the nature of solution has become slightly alkaline.
(b) Lactic acid which was formed initially, reduce the basic nature of the baking soda. Then more lactic acid is needed to convert milk Into curd. That is why it takes time to produce more lactic acid and hence the milk take a long time to set as curd.
Question 4.
Plaster of Parts should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why.
Answer:
- Plaster of Paris means calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4. ½H2O).
- Plaster of París on mixing with water, sets into hard solid mass due to the formation of gypsum (CaSO4. 2H2O)
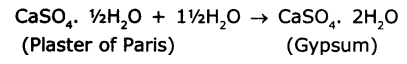
Because of the above reason Plaster of Pans should be stored in a moisture-proof container so that it won’t turn into gypsum.
Question 5.
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid is added to test tube A, while acetic acid Is added to test tube B. The valances and concentration of both the acids Is same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Answer:
- The fizzing occur more vigorously In test tube A.
- Hydrochloric acid contains more H3O+ ions and it is a strong acid. Hence the reaction will be faster in test tube A.
- Acetic acid contains fewer H3O+ ions and it is a weak acid. Hence the reaction will be slower.
Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
Fresh milk has a pH of 6.6 Explain why the pH changes as it turns into curd?
Answer:
- pH value of milk decreases as milk turns to curd.
- Lactobacillus bacteria turn milk to curd by releasing lactic acid.
- That means curd contains lactic acid. So its pH decreases than 6, so. curd Is acidic in nature.
![]()
Question 2.
How do you prepare an indicator, using beetroot? Explain.
Answer:
Aim: To prepare own indicator.
Materials required:
- Beetroot corms -2 or 3,
- Knife,
- Bowls,
- Water,
- Spoon,
- Mixy,
- Orange juice
Procedure:
- Take the beetroots and peel them with the help of a knife. (At first, wash them).
- Chop them into pieces.
- Put those pieces into a mixie jar and make a paste.
- Add some water to the paste. Now filter this and collect only juice from this.
Observation & Result:
- Now add 5 to 6 drops of this juice (beetroot juice (indicator)) to orange juice (5 to 6 drops) and mix it.
- We can see the colour change. This indicates the presence of acidic nature in orange Juice.
IV. Multiple choices questions
Question 1.
The colour of methyl orange indicator in acidic medium is ………………….. ( )
(A) yellow
(B) green
(C) orange
(D) red
Answer:
(D) red
Question 2.
The colour of phenolphthalein Indicator in basic solution is ………………….. ( )
(A) yellow
(B) green
(C) pink
(D) orange
Answer:
(C) pink
Question 3.
Colour of methyl orange In alkali conditions ……………………………. ( )
(A) orange
(B) yellow
(C) red
(D) blue
Answer:
(B) yellow
Question 4.
A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be …………………………….. ( )
(A) 1
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 10
Answer:
(D) 10
Question 5.
One of the following solutions reacts with crushed egg shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky, the solution is of …………………………….. ( )
(A) NaCl
(B) HCl
(C) LiCl
(D) KCl
Answer:
(B) HCl
![]()
Question 6.
If a base dissolves in water, by what name is it better known’ ……………………….. ( )
(A) neutral
(B) base
(C) acid
(D) alkali
Answer:
(D) alkali
Question 7.
Which of the following substances when mixed together will produce table salt? ( )
(A) Sodium thiosulphate and sulphur dioxide
(B) Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide
(C) Chlorine and oxygen
(D) Nitric acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate
Answer:
(B) Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide
Question 8.
What colour would hydrochloric acid (pH=1) turn universal indicator? ()
(A) orange
(B) purple
(C) yellow
(D) red
Answer:
(D) red
Question 9.
Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating Indigestion? ()
(A) antibiotic
(B) analgesic
(C) antacid
(D) antiseptic
Answer:
(C) antacid
Question 10.
What gas is produced when magnesium is made to react with hydrochloric acid? ()
(A) hydrogen
(b) oxygen
(C) carbon dioxide
(D) no gas is produced
Answer:
(A) hydrogen
Suggested Experiments
Question 1.
Compounds such as alcohol and glucose contain hydrogen but are not categorized as acids. Describe an activity to prove It.
Answer:
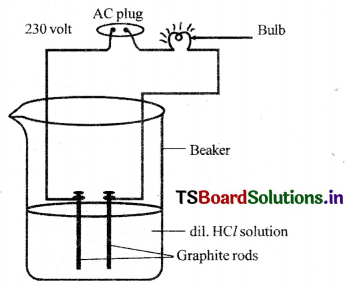
- Prepare solutions of glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid etc.
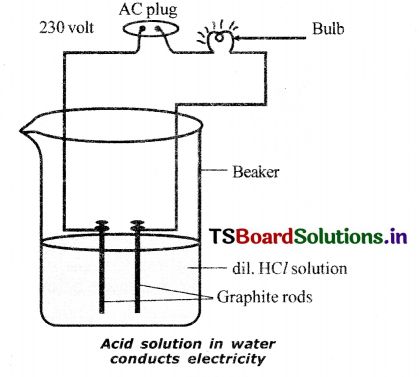
- Connect two different coloured electrical wires to graphite rods separately in a 100 ml beaker as shown In the figure.
- Connect free ends of the wire to 230 V AC plug and complete the circuit, by connecting a bulb to one of the wires.
- Now pour some dilute H in the beaker and switch on the current.
- We observe that the bulb glows.
- Repeat the activity with dilute sulphuric acid, glucose and alcohol.
- We observe that the bulb glows only in sulphuric acid solution, but not in glucose and alcohol solutions.
- Glowing of bulb indicates that there Is a flow of electric current through the solution.
- Acid solutions have ions and the moment of these ions in solution helps for flow of electric current through the solution.
- 10) The positive Ion present In HCl solution is H+. This suggests that acids produce hydrogen ions (H+) in solution, which are responsible for their acidic properties.
- In glucose and alcohol solution, the bulb does not glow indicating the absence of H+ Ions, though they contain hydrogen.
- Hence glucose and alcohol are not categorized as acids.
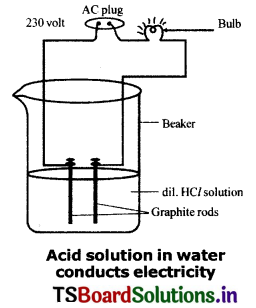
Question 2.
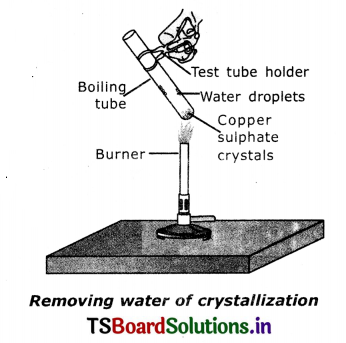
What is meant by “water of crystallization” of a substance? Describe an activity to show the water of crystallization.
Answer:
Water of Crystallization: Water of crystallizatIon Is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt in its crystalline form.
Eg: CuSO4. 5H2O.
It means that five water molecules are present in one formula unit of copper sulphate.
![]()
Activity to show the water of crystallization:
- Take a few crystals of copper sulphate In a dry test tube and heat the test tube.
- We observed water droplets on the walls of the test tube and sat turns white.
- Add 2 – 3 drops of water on the sample of copper sulphate obtained after heating
- We observe the blue colour of copper sulphate crystals is restored.
Suggested Projects
Question 1.
How do you select a good place to plant a tree in your school/at home? lest the soil and investigate and write a report on it.
Answer:
You have to select a good place to plant a tree in your school at home which satisfies following requirements.
(1) Water: Close, easy access to a water source essential. The water must be from a potable source. The water source must also be nearly because it will be used almost daily.
2) sunlight: A minimum of six flours of direct sunlight per day is necessary to grow most vegetables and flowers, Watch out for shading from nearby trees, buildings, hills and so on.
(3) Access: The site should be dose to classrooms/house and easily accessible. if the garden too For away, it will be difficult to get and keep the plants checking daily.
(4) Secured: the site should be secured from animals and birds. So s should have fencing to protect the plants from, animals and birds.
(5) Healthy sell: The soil where you want to plant it shouid be healthy and safe. the sod should not have more acidic nature or more basic nature which prevents the healthy growth of s plant. To confirm that the soil is safe, conduct a soil test
Procedure:
Put about 2 gm. of soil in a test tube and add 5 mi water to It. shake the contents of the test tube. Filter the contents and coiled the filtrate in test tube. Check the pH of this filtrate with the help of universal indicator paper.
Observations :
- If the soil is too acidic (having low pH ) then it is treated with materials like quick lime (Calcium Oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate).
- If the soil Is too basic leaving a high pH its alkalinity can be reduced by adding decaying organic matter (manure or compost) which contains acidic materials.
Conclusions: Plants require a specific pH range for their healthy growth. Chemicals can be added to soil to adjust its pH and make it suitable for growing plants.
Question 2.
Do all vegetables are acids? To find this Investigate with pH paper and tabulate the values and write a report on It?
Answer:
Yes, most of the vegetables are slightly acidic cut a small piece of the following vegetables and test it with universal pH paper and note the values In the table given below :
| Vegetable | Colour with Universal pH paper | Ph Value |
| 1. Bean | Greenish Yellow | 5.60 – 6.50 |
| 2. Beetroot | Orange Yellow | 5.30 – 6.60 |
| 3. Broccoli | Orange Yellow | 5.33 |
| 4. Cabbage | Greenish Yellow | 5.20 – 6.80 |
| 5. Capsicum | Greenish Yellow | 6.0 – 6.5 |
| 6. Cauliflower | Greenish Yellow | 5.60 |
| 7. Cucumber | Orange Yellow | 5.12 – 5.78 |
| 8. Garlic | Greenish Yellow | 5.80 |
| 9. Onions (red) | Orange Yellow | 5.30 – 5.80 |
| 10. Pea | Greenish Yellow | 5.70 – 600 |
| 11. Potato | Orange Yellow | 5.40 – 5.90 |
| 12. Pumpkin | Orange Yellow | 4.90 – 5.50 |
| 13. Radish (white) | Greenish Yellow | 5.52 – 5.69 |
| 14. Spinach | Greenish Yellow | 5.50 – 6.80 |
| 15. Sweet corn | Greenish Yellow | 6.0 |
| 16. Sweet potato | Orange Yellow | 5.30 – 5.60 |
| 17. Tomato | Orange | 4.30 – 4.90 |
| 18. Ginger | Greenish Yellow | 5.60 – 5.90 |
| 19. Mushrooms | Greenish Yellow | 6.00 – 6.70 |
Question 3.
Collect Information about the Importance of the pH value In daily life to human beings as well as plants.
Answer:
The pH plays on important role Is many activities of our everyday life.
1. pH is our Digestive system:
Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid (of pH about 1.4) which helps in digesting our food without harming the stomach excess acid is produced in the stomach due to various reasons causes is digestion which produces pain and Irritation. order to cure Indigestion and get rid of pain, we can take bases called ‘antacids’ which neutralise the excess acid produced in the stomach and gives relief to the person.
2. pH change as the cause of tooth decay:
When we eat food containing sugar, then the bacteria present in our mouth break down the sugar to form acids which lowers the pH In the mouth. Tooth decay starts when the pH of acid formed in the mouth falls below 5.5. The best way to present tooth decay is to clear, the mouth thoroughly with toothpaste (pH is about 8.0) being a base it neutralizes the excess acid In the mouth.
3. Plants and Animals are sensitive to pH changes:
(a) Soil pH and Plant Growth: Most of the plants grow best when the pH of the soil is close to 7. If the soil is too acidic or too basic, the plants grow at all. Chemicals can be added to soil to adjust Its pH and make it suitable for growing plants.
(b) pH change and survival of Animlals: The pH plays an important role in the survival of animals, including human beings. Our body works well within a narrow pH range of 7.0 to 7.8. If due to some reason, this pH range gets disturbed in the body of a person, then many ailments can occur. The aquatic animals can survive in the lake or river water within a narrow range of pH change.
4. Self defince by animals and plants through chemical warfare:
Many animals and plants protect themselves from their enemines by injecting painful and Irritating acids and bases into their skin. For example, Bee sting leaves an acid which causes pain and irritation. Rubbing with mild base like baking soda on the stung area gives relief. Stringing hair of leaves of nettle pant, inject methanoic acid causing burning pain. In rubbing the area with the leaf of dock plant which is basic gives relief from pain.
![]()
TS 10th Class Physical Science Acids, Bases and Salts Intext Questions
Page 33
Question 1.
What chemical reaction takes place?
Answer:
The antacid tonic or chewing tablet contains base which neutralises the action of acid in the stomach. So the reaction takes place is called neutralisation reaction.
Page 34
Question 2.
What do you conclude from the observations noted in table – 1?
Answer:
From the table given, I conclude that solutions of HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, CH3COOH change blue litmus into red colour, phenolphthalein solution colourless and methyl orange to red. The solutions of NaOH, KOH, Mg(OH)2 NH4OH and Ca(OH)2 change red litmus to blue colour, phenolphthalein to pink colour and methyl orange to yellow colour.
Page 35
Question 3.
What do you conclude from thIs activity?
Answer:
Chopped onions, clove oil and vanilla essence can also be used as Indicators because we observe a change In the odour of these substances In acid medium and basic medium.
Question 4.
Can you give example for use of olfactory indicators in daily life?
Answer:
We use olfactory Indicators in cooking curries which are stale to eat and have disagreeable smell and change them to give agreeable and pleasant smell. Eg. Onions and cloves.
![]()
Question 5.
Why pickles and sour substances are not stored in brass and copper vessels?
Answer:
Pickles and sour substances contain acids. These acids react with copper and brass vessels to form blue scales and corrode the vessels, These blue scales are harmful to our health. So pickles and sour substances should not be kept In brass and copper vessels.
Page 37
Question 6.
What do you observe by adding dilute HCl to sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate?
Answer:
When dilute HCl is added to sodium carbonate carbon dioxide gas which turns lime water milky is obtained. The reaction is as follows :
NaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
When dilute HCl reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate CO2 and NaCl are formed.
The reaction is as follows :
NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Page 38
Question 7.
Why did the colour of the solution change after adding the HCI solution?
Answer:
The pink colour of the solution of NaOH to which phenolphthalein is added becomes colourless after adding dilute HCl because HCl Is an acid and phenolphthalein becomes colourless in acid medium.
Question 8.
Does the Pink colour reappear?
Answer:
The pink colour reappears on adding NaOH.
Question 9.
Do you guess the reason for reappearance of pink colour?
Answer:
The reaction occurring between acid and base In the above activity can be written as :
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) .
The reason for reappearance of pink colour is the presence of acid in excess.
Page 39
Question 10.
What do you observe in the above reaction?
Answer:
We observe copper oxide present in the beaker dissolves in dilute HCl and the colour of the solution becomes bluish-green due to formation of cupric chloride.
Question 11.
What do you conclude from the activity 5 and 6?
Answer:
By observing both activities 5 and 6, 1 conclude that carbon dioxide which is a non-metallic oxide Is acidic In nature.
![]()
Question 12.
What do acids have in common?
Answer:
We find that hydrogen is common in all acids.
Page 40
Question 13.
What do you notice?
Answer:
When dilute HCl or dilute H2SO4 is poured In the beaker, the electricity is conducted through these solutions.
Question 14.
What do you observe?
Answer:
Acid solutions have ions and the movement of these Ions in solution helps for flow of electric current through solution.
Question 15.
Doesthebulbglowinallcases?
Answer:
No. Bulb glows only when hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid is taken in the beaker.
Question 16.
What do bases have In common?
Answer:
Bases have (OH–) ions in common.
Question 17.
Does the bulb glow?
Answer:
Yes, the bulb glows when current is passed through sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide solutions etc.
Question 18.
What do you conclude from the results of this activity?
Answer:
Aqueous solutions of acids as well as bases conduct electricity, because of the presence of ions.
![]()
Page 41
Question 19.
Do acids produce ions only in aqueous solution? (AS1) (1 Mark)
Answer:
Yes, Acids produce Ions only in aqueous solutions. For example HCl produces W ions in aqueous solutions and shows acidic properties.
But when H gas is dissolved in benzene It does not produce H’ Ions and does not show any acidic properties.
Question 20.
What do you observe? Is there a gas coming out of the delivery tube?
Answer:
I observe a gas coming out of delivery tube. It changes wet blue litmus paper into red colour.
Question 21.
What do you Infer from the above observation?
Answer:
We conclude that dry HCl gas (hydrogen chloride) is not an acid because we notice no change in colour of dry litmus paper but HCl aqueous solution is an acid because wet blue litmus paper turns to red.
Page 42
Question 22.
What do you feel?
Answer:
we feel the test tube has become hot.
Question 23.
Is ¡tan exothermic or endothermic process?
Answer:
It is an exothermic process.
Page 43
Question 24.
What do you observe?
Answer:
We observe that the bulb glows brightly in HCI solution while the glowing intensity of the bulb Is low In acetic acid solution.
Question 25.
Can you guess the reason for the changes you observed?
Answer:
There are more W ions in HO solution and fewer W ions in acetic acid solution.
![]()
Page 44
Question 26.
What is the nature of each substance on the basis of your observations?
Answer:
On the basis of our observations, as PH gradually increases from 1 to 6 the acid becomes weaker and weaker.
As the PH increases from 8 to 14 the basic nature grows stronger and stronger. If the PH is exactly ”7” the solution is neutral.
Page 47
Question 27.
What is the reason for change In colour of solution? (AS 1) (1 Mark)
Answer:
When we add methyl orange indicator to diluted HCI., the colour of methyl orange turns to red. But on adding antacid tablet powder it slightly becomes yellow. The reason is antacid contains a mild base, namely Mg(OH)2 or Al(OH)3.
Question 28.
Can you write the chemical equation for this reaction?
Answer:
3HCI+Al(OH)3 → AlCl3+3H2O
Question 29.
What can you conclude about the Ideal soil PH for the growth of plants In your region?
Answer:
- My region Is nearer to the sea coast of Bay of Bengal. So it is a little basic in nature.
- So fertilizers of acidic nature are to be used in our soil to improve yield of crops in our region.
Question 30.
Under what soil conditions a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quicklime (Callum hydroxide) or calcium carbonate?
Answer:
If the soil Is acidic In nature the farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium hydroxide) or calcium carbonate to neutralize the acidic nature of soil.
Page 48
Question 31.
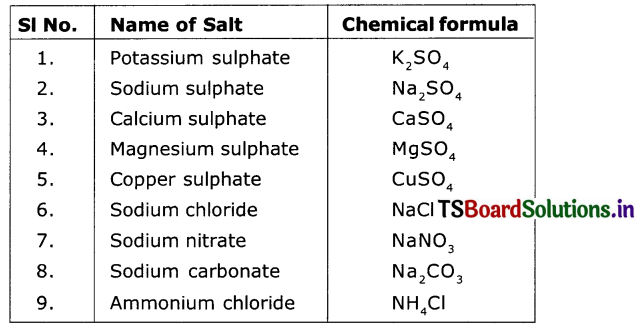
Write the formulae of the following salts.
Answer:
(Salts are mentioned in the following table and answers are given against each)
Question 32.
How many families can you Identity among the salts given above?
Answer:
I can identify: Sodium family, Sulphate family, Chloride family.
Page 49
Question 33.
What do you say about salts of both weak acid and weak base?
Answer:
In such case, the PH depends on the relative strengths of acid and base. Further, the formation of salts does not occur as the heat of neutralization is lost to a large extent to ionize the weak acid and the weak base.
Page 52
Question 34.
What does 10H2O signify?
Answer:
10H2O signifies 10 molecules of water.
Question 35.
Does it make Na2CO3 wet?
Answer:
10 molecules of water do not wet NaCO3. They are chemically added to form solid crystals. These molecules of water are called water of crystallization.
Question 36.
Did you notice water droplets on sides of the test tube? Where did they came from?
Answer:
Yes. They came from crystals of copper sulphate.
![]()
Question 37.
What do you observe? Is the blue colour of copper sulphate restored?
Answer:
Yes, To anhydrous copper sulphate if 2-3 drops of water is added the blue colour of copper sulphate ¡s restored.
Page 53
Question 38.
How can you get half a water molecule?
Answer:
It is written as CaSO4. 1/2H2O (Plaster of Paris) because two formula units of CaSO4 share one molecule of water.
Think And Discuss
Question 1.
Is the substance present in antacid tablet acidic or basic?
Answer:
One of the substance present in antacid tablet Is sodium hydrogen carbonate. It is an alkali.
Question 2.
What type of reaction takes place In stomach when an antacid tablet is consumed?
Answer:
During lndigestion, the stomach produces too much acid and this causes pain and irritation. When we use an antacid, being an alkali it neutralizes the excess acid in the stomach and provides relief. It is a neutralization reaction.
Question 3.
Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Answer:
- When acid reacts with metal, hydrogen gas is evolved.
- When we bring a burning match stick or candle to the mouth of the delivery tube, it turns off with a pop Sound.
Question 4.
A compound of a calcium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle; turns -lime water milky. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction If one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Answer:
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
Question 5.
Why do HCl, HNO3 etc, show acidic characters In aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Answer:
HCl, HNO3 etc., show acidic characters in aqueous solutions because they release H+ ions in water solutions.
But alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character because they do not release H+ ions in aqueous solutions.
Question 6.
While diluting an acid, why is It recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to acid?
Answer:
- The process of diluting an acid or a base in water is exothermic process.
- If water is added to concentrated acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause burns on the skin.
- So acid must always be added to water slowly with constant stirring.
Question 7.
What will happen if the pH value In our body Increases?
Answer:
Bacteria present in the mouth produce acids by degradation of sugar and food particles in the mouth. The acidic nature of chemicals in our body increases and causes irritation in the digestive system and finally leads to ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
Question 8.
Why do living organisms have narrow pH range?
Answer:
Our body carries metabolic activities with the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8. Living organisms can survive only in a narrow range of pH range. If the PH range exceeds this limit, acids form in the body and cause irritation in the stomach and throat and develop acidity which corrodes the membrane in the digestive
system and finally it leads to ulcers and cancer.
TS 10th Class Physical Science Acids, Bases and Salts Activities
Activity 1
Question 1.
Testing the acids and bases with indicators viz.. Red litmus, blue litmus, phenolphthalein solution and methyl orange solution.
Answer:
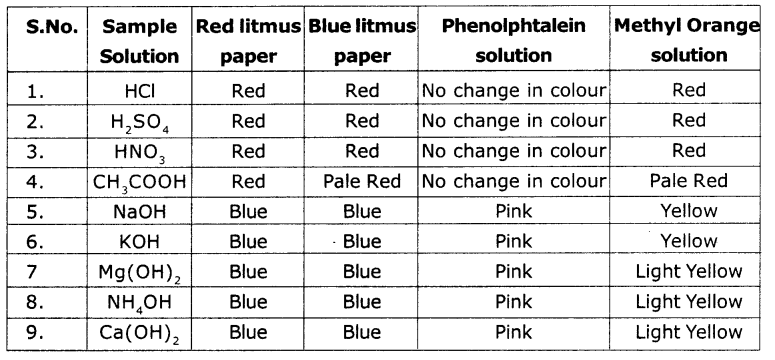
From the above table, we conclude that the acids and bases change the colour of indicators.
Activity 2
Question 2.
What are Olfactory indicators? Write an activity to prove them.
Answer:
Olfactory Indicators: There are some substances whose odour changes in acidic or basic media. These are called olfactory indicators.
Aim: To check the olfactory indicator.
Required materials :
- Onions
- Knife
- Plastic bag
- Clean clothes.
Procedure:
- Take some onions and finely chop them.
- Put the chopped onions in a plastic bag with some clean cloth.
- Tie up the bag tightly and keep It overnight in the fridge.
Observation: Check the odour of the cloth strips.
Result: It is used as the acid indicator.
Lab Activity 1
Question 3.
Show that acids produce hydrogen gas when react with mals.
Answer:
Aim: To show that acid produces hydrogen gas when react with metals.
Materials required: Test tube, delivery tube, grass trough, candle, soap water, dii HCl, zinc granules and cork
Procedure:
1. Set the apparatus as shown In figure.
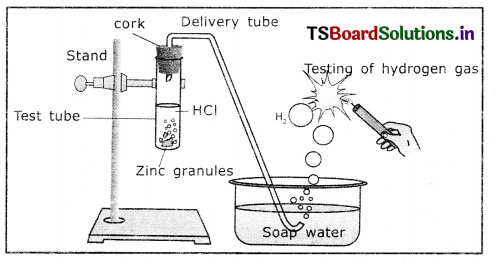
Reaction of zinc granules with dil.HCl and testing of hydrogen gas by a burning matchstick
2. Take about 10 ml of dilute MCI In a test tube and add a few zinc granules to It.
3. We observe a gas evolving from the test tube
4. Pass the gas released by through the soap water.
5. We observe some bubbles formed in the soap solution.
6. Bring a burning matchstick near the gas-filled bubble.
7. The burning matchstick is put out with a pop sound.
8. The pop sound indicates that the gas evolved is H2.
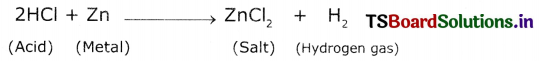
9. Repeat this experiment with H2SO4, HNO3 etc.
From the above experiment, we conclude that hydrogen gas is produced when an acid reacts with metals.
![]()
Activity 3
Question 4.
Show that the reaction of metal with a base produces hydrogen gas.
Answer:
- Place a few granules of zinc in a test tube and add 10 ml of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution and warm the contents of the test tube.
- Pass the gas being evolved through the soap water.
- Some bubbles are observed In the test tube.
- Bring a burning candle near the gas filled bubble.
- The candle is put out with a pop sound.
- The pop sound indicates that the gas produced is hydrogen.
- In this activity we also notice that evolved gas is hydrogen and salt formed is sodium zincate.
2NaOH +Zn → Na2ZnO2 + H2
But these reactions are not possible with all metals.
Activity 4
Question 5.
Show that the reaction of acids with carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates produce carbon dioxide gas.
Answer:
- Take two test tubes, label them as A dnd B.
- Take about 0.5 gm of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3, in test tube A and about 0.5 gm of sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) in test tube B.
- Add about 2 ml. of dilute HCl to both the test tubes.
- Pass the gas produced In each case through lime water and record your observation.
- We observe that the lime water turns to milky white colour.
- The reactions are
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCI + H2O + CO2
NaHCO3+ HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
Reactions when the gas Is passed through lime water.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 ↓+ H2O
On passing excess of carbondioxide, the following reaction takes place.
CaCO3 + H2O+ CO2 → Ca(HCO3)2
Thus from the above activity we can conclude that the reaction of metal carbonates and hydrogen carbonates with acids give a corresponding salt, carbondioxide and water.
Activity 5
Question 6.
What Is neutralization? Explain an activity to demonstrate neutralization.
Answer:
Neutralization: The reaction of an acid with a base to give a salt and water is known as a neutralization reaction.
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
Activity:
- Take about 2 ml of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube and add one drop of phenolphthalein indicator. The solution turns to pink.
- Add dilute HCI solution to the above solution drop by drop. The pink colour disappears.
- Now add one or two drops of NaOH to the above mixture.
- Now the pink colour reappears.
- In the above reaction first the pink colour disappears on adding HCl because NaOH Is completely reacted with HCl The effect of base Is nullified by an acid.
- Pink colour reappears on adding a drop of NaOH because the solution becomes basic once again. The reaction occu ring between acid and base in this activity
can be written as :
NaOH + HCI → NaCl + H2O
This is neutralization reaction.
Activity 6
Question 7.
Show that the metal oxides are basIc In nature through an actIvity.
(OR)
Describe an activity to observe the reaction of acids with metal oxides. What do you observe?
Answer:
- Take a small amount of copper oxide In a beaker and slowly add dilute HCl acid while stirring.
- We will notice that the copper oxide present in the beaker dissolves In dilute HCl and the colour of the solution becomes bluish-green.
- The reason for this change is the formation of copper chloride in the reaction.
- The general reaction is : Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water.
- In this reaction, metal oxide reacts with acid to give salt and water. This reaction is similar to the neutralization reaction.
- In this reaction metal oxide gives salt and water when it reacts with acid. Thus we can conclude that metal oxides are basic in nature.
![]()
Activity 7
Question 8.
Write an activity to show that whether all compounds containing hydrogen are acids or not.
(or)
Write an activity which proves acids are good conductors of electricity.
Answer:
Procedure:
- Prepare glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid solutions.
- Fix two iron graphite rods on a rubber cork and place the cork in a lOOmI beaker.
- Connect two different coloured electrical wires to graphite rods separately as shown In figure.
- Connect free ends of the wire to 230 volts AC plug.
- Complete the circuit as shown in the figure by connecting a bulb to one of the wires.
- Now pour some dilute HCl in the beaker and switch on the current.
Observation: The bulb starts glowing.
Repetition: Repeat activity with dilute sulphuric acid, glucose and alcohol solutions separately.
Observation :
- We will notice that the bulb glows only In acid solutions.
- But the bulb does not glow in glucose and alcohol solutions.
Result:
- GlowIng of bulb indicates that there Is flow of electric current through the solution.
- Acid solutions have ions and the movement of these ions in solution helps for flow of electric current through the solution.
Conclusion:
- The positive ion (cation) present in HCl solution is W.
- This suggests that acids produce hydrogen ions W in solution, which are responsible for their acidic properties.
- In glucose and alcohol solution the bulb did not glow Indicating the absence of W ions in these solutions. .
- The acidity of acids is attributed to the W ions produced by them in solutions.
Activity 8
Question 9.
Do acids produce ions only in aqueous solution? Explain an activity to observe this.
Answer:
1. Take about 1.0 gm of solid NaCl in a clean and dry test tube.
2. Add some concentrated sulphuric acid to the test tube.
3. We observe a gas is liberated.
4. The reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 → 2HCl + Na2SO4
5. Test the gas evolved successively with dry and wet blue litmus paper.
6. We observe that there is no change in the colour of dry litmus paper, because dry HCl is not an acid. But aqueous solution of HCl Is an acid because wet blue litmus paper turned into red.
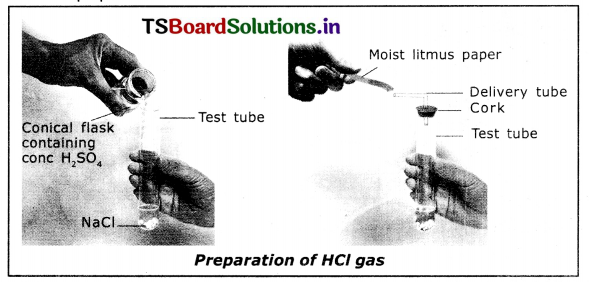
The HCl gas evolved from delivery tube dissociates in presence of water to produce hydrogen ions. In the absence of water, dissociation of HCl molecules does not occur.
7. The dissociation of HCI In water is shown below.
HCl + H2O → H3O++ Cl–
Hence acids give H3O+ ions in water.
Question 10.
What happens when a base is dissolved in water?
Answer:
1. Take some bases like NaOH, KOH, Mg(OH)2 in different test tubes and add water to them.
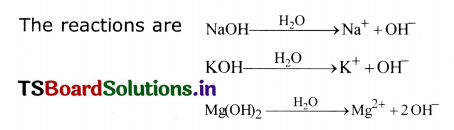
2. Bases in water produce hydroxide (OH–)ions.
Activity 9
Question 11.
Write an activity to show that dissolving of an acid in water is an exothermic process (or) endothermic process.
Answer:
Experiment:
- Take 10 ml water in a beaker.
- Add a few drops of concentrated H2SO4 to it and swirl the beaker slowly.
- Touch the base of the beaker.
- The base of beaker is hot.
Result:
This is an exothermic process called as dilution.
Activity 10
Question 12.
Explain a test to know whether the acid (or base) is strong or weak.
Answer:
1. Take two beakers A and B.
2. Fill the beaker A with dil. CH3COOH and beaker B with dii. HCI.
3. Arrange the apparatus as shown in the figure and pass electricity through the solutions in separate beakers.
4. We notice that the bulb glows brightly in HCl solution while the intensity of the bulb is low in acetic acid solution.
5. This indicates that there are more ions in HCl solutions and fewer ions are than is In acetic acid solution.
6. But in H solution means more H3O+ ions. Therefore it is a strong acid. But acetic add has fewer H3O+ ions and hence it is weak acid.
7. Carry out the same experiment by taking bases like dii. NaOH and dil. NH4OH instead of acids.
8. We observe that NaOH is a strong base and NH4OH is a weak base.
![]()
Activity 11
Question 13.
Test the pH value of solution given in table. Record your observations. What s the nature of each substance on the basis of your observations?
Answer:
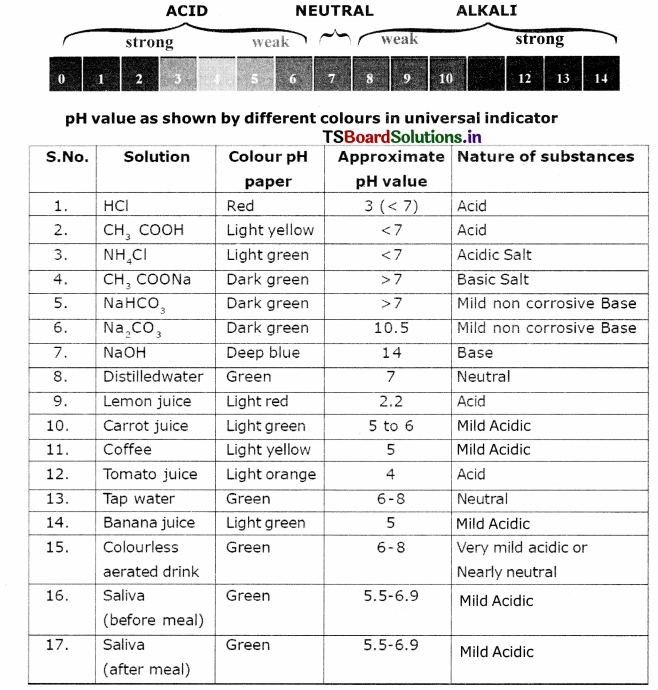
Activity 12
Question 14.
Check the action of antacid tablet with acid.
Answer:
- Take dii. HCl in a beaker and add two to three drops of methyl orange indicator. The solution turns to red.
- Mix antacid tablet powder to the above solution in the beaker. Now the solution becomes normai i.e., the red colour disappears.
- We can conclude that the antacid tablet neutralizes the acid.
Activity 13
Question 15.
How can we test the pH value of the soil?
Answer:
- Collect the soil samples from various places Into different bags.
- Put about 2g of soil In a test tube and add 5 ml water to it. Shake the contents of the test tube. Fitter the contents and collect the filtrate In a test tube.
- Check the pH of this filtrate with the help of universal indicator paper.
- The colour of universal indicator paper shows the pH of the soil as per the colour code.
Activity 14
Question 16.
Write the formulae of the following salts and classify them as families based on radicals.
Potassium sulphate, sodium sulphate, calcium sulphate, magnesium sulphate, copper sulphate, sodium, chloride, sodium nitrate, sodium carbonate and ammonium chloride.
Answer:
Potassium sulphate → K2SO4 Sodium sulphate → Na2SO4
Calcium sulphate → CaSO4 Magnesium sulphate → MgSO4
Copper sulphate → CuSO4 Sodium chloride → NaCl
Sodium nitrate → NaNO3 Sodium Carbonate → Na2CO3
Ammonium chloride → NH4Cl
Sodium family:Na2SO4, NaCl, NaNO1, Na,Co etc.
Family of chloride salts : NaCl, NH4Cl. etc.
Family of sulphate salts: K2SO4, Na2SO4, CaSO4, MgSO4, CuSO4 etc.
Family of carbonate salts: Na2CO3, MgCO3, CaCO3 etc.
Activity 15
Question 17.
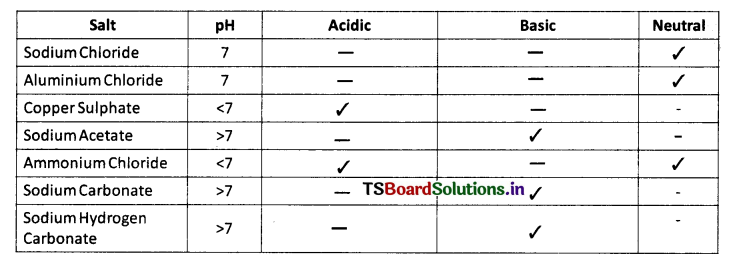
Collect the salt samples like sodium chloride, aluminium chloride, copper sulphate, sodium acetate, ammonium chloride, sodium hydrogen carbonate and sodium carbonate. Dissolve them in distilled water. Check the action of these solutions with litmus papers. Find the pH using pH paper. Classify them into acidic, basic or neutral salts. Identify the acid & base used to form the above salts. Record your observations in table.
Answer: