Students can practice 10th Class Maths Textbook SSC Solutions Telangana Chapter 12 Applications of Trigonometry Optional Exercise to get the best methods of solving problems.
TS 10th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 12 Applications of Trigonometry Optional Exercise
Question 1.
A 1.2 m tall girl spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a height of 88.2 m from the ground. The angle of elevation of the ballon from the eyes of the girl at any instant is 60°. After sometime, the angle of elevation reduces to 30°. Find the distance travelled by the balloon during the interval.
Solution:
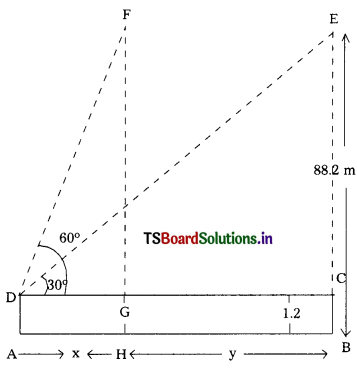
From the figure,
Let AD be the height of a tall girl standing on the horizontal line AB is 1.2 m.
Let FH = EB = 88.2 m be the height of balloon from the line AB.
At the eyes of the girl D, the angle of elevations are ∠FDC = 60° and ∠EDC = 30°
Now, FG = EC = 88.2 – 1.2 = 87 m.
Let the distance travelled by the balloon,
HB = y m and AH = x m.
∴ DG = x m and GC = ym
In right angled ∆FGD
tan 60° = \(\frac{\mathrm{FG}}{\mathrm{DG}}\)
⇒ \(\sqrt{3}\) = \(\frac{87}{\mathrm{x}}\)
⇒ x = \(\frac{87}{\sqrt{3}}\) ………. (1)
Again, in right angled ∆ECD,
tan 30° = \(\frac{\mathrm{EC}}{\mathrm{DC}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{87}{\mathrm{DG}+\mathrm{GC}}\)
⇒ x + y = 87\(\sqrt{3}\) …………. (2)
∴ From equation (1), substituting
x = \(\frac{87}{\sqrt{3}}\) in equation (2), we get
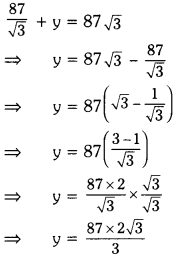
⇒ y = 29 × 2\(\sqrt{3}\) = 58 \(\sqrt{3}\) m.
Hence, the distance travelled by the balloon during the interval is 58 \(\sqrt{3}\) m.
![]()
Question 2.
The angles of elevation of the top of a lighthouse from 3 boats A, B and C in a straight line of same side of the lighthouse are a, 2a, 3a respectively. If the distance between the boats A and B is x meters, find the height of lighthouse.
Solution:
From the figure,
Let PQ be the height of the lighthouse = h m
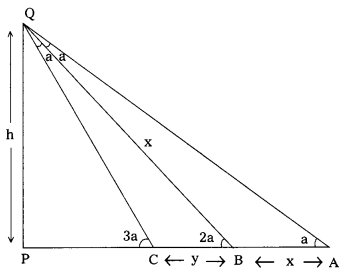
A = First point of observation
B = Second point of observation
C = Third point of observation
Given, AB = x and BC = y (Not given in the text)
Exterior angle = Sum of the opposite interior angles
∠PBQ = ∠BQA + ∠BAQ and
∠PCQ = ∠CBQ + ∠CQB
∴ AB = x = QB
By applying the sine rule,
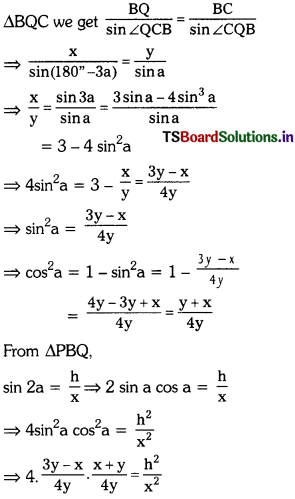
⇒ h2 = \(\frac{x^2}{4 y^2}\) (3y – x)(x + y)
∴ h = \(\frac{x}{2 y} \sqrt{(3 y-x)(x+y)}\)
Height of lighthouse
= \(\frac{x}{2 y} \sqrt{(3 y-x)(x+y)}\) meters.
Question 3.
Inner part of a cupboard is in the cuboidical shape with its length, breadth and height in the ratio 1 : \(\sqrt{2}\) : 1. What is the angle made by the longest stick which can be inserted cupboard with its base inside ?
Solution:

Inner part of a cupboard is in the cuboidical shape.
Ratio of length, breadth and height are
1 : \(\sqrt{2}\) : 1
In the figure,
Let AB be the length and BC be the height of the cupboard.
AC be the length of the stick.
‘θ’ be the angle of elevation of the stick making with base of the cupboard.
In ∆ABC,
tan θ = \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{AB}}\)
⇒ tan θ = \(\frac{1}{1}\)
⇒ tan θ = tan 45°
θ = 45°
∴ The angle of elevation is 45°.
![]()
Question 4.
An iron spherical ball of volume 232848 cm3 has been melted and converted into a cone with the vertical angle of 120°. What are its height and base ?
Solution:
Given :
AC = Slant height = l
AB = Vertical height = h
BC = radius = r
Volume of iron spherical ball
V = 232848 cm3
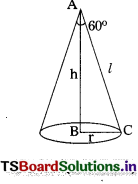
As per the problem,
Volume of spherical ball = Volume of cone
∴ \(\frac{1}{3}\) πr2h = 232848
In ∆ABC,
tan 60° = \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{AB}}\)
\(\sqrt{3}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{r}}{\mathrm{h}}\) ⇒ r = \(\sqrt{3}\) h
\(\frac{1}{3}\) π(\(\sqrt{3}\) h)2 × h = 232848
\(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 3 × h2 × h = 232848
h3 = \(\frac{232848 \times 7}{22}\)
h3 = 10584 × 7 = 74088
h3 = 423
h = 42
But r = h\(\sqrt{3}\)
∴ r = 42\(\sqrt{3}\)
![]()
Question 5.
A right circular cylindrical tower, height ‘h’ and radius ‘r’, stands on the ground. Let ‘P’ be a point in the horizontal plane ground and ABC be the semi-circular edge of the top of the tower such that B is the point in it nearest to P. The angles of elevation of the points A and B are 45° and 60° respectively. Show that \(\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{r}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}(1+\sqrt{5})}{2}\).
Solution:
As shown in the figure
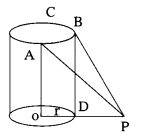
OA = BD = h (height of cylinder)
OD = r (radius of cylinder)
‘O’ is the centre.
ABC is the edge of semi-circle (in the top of cylinder).
B is nearer to the point R So B should be at the outer edge of diameter. That means just above ‘D’.
∠DPB = 60°, ∠OPA = 45° (given)
In ∆BDP, tan P = \(\frac{\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{DP}}\) (P = 60°, BD = h)
tan 60° = BD/DP
⇒ \(\sqrt{3}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{DP}}\)
⇒ h = \(\sqrt{3}\) DP …………… (1)
In ∆OAP, tan P = \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OP}}\) (here P = 45°, OA = h)
⇒ tan 45° = \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OP}}\) = 1 ⇒ OA = OP
So OA = h = OP = OD + DP
So h = r + DP …………. (2)
From the equation (1) & (2)
h = \(\sqrt{3}\) DP, h = r + DP
∴ \(\sqrt{3}\) DP = r + DP
So r = \(\sqrt{3}\) DP – DP
r = DP(\(\sqrt{3}\) – 1) …………. (3)
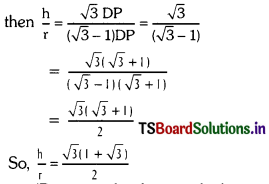
(But in text book, it is asked as \(\frac{\sqrt{3}(1+\sqrt{5})}{2}\) which is wrong).