Telangana TSBIE TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 2nd Lesson Business Activities Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 2nd Lesson Business Activities
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by industry? Explain various types of industries with suitable examples.
Answer:
Industry is concerned with the making or manufacturing of goods. It is that part of the production which is involved in changing the form of goods at any stage from raw material to the finished product. E.g.: Weaving woollen yam into cloth. Thus industry imparts form utility in goods.
Classification or types of industries: The industries may be classified as follows.
1) Primary industry: Primary industry is concerned with production of goods with the help of nature. It is nature-oriented industry, which requires very little human effort. E.g: Agriculture, Farming, Fishing, Horticulture etc.
2) Genetic industry: Genetic industry is related to the reproducing and multiplying of certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profits from their sale. E.g: Nurseries, cattle breeding poultry, fish hatcheries etc.
3) Extractive industry: It is engaged in raising some form of wealth from the soil, cli-mate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive industries comes in raw farm and they are used by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products. E.g: Mining, coal, mineral, iron ore, oil industry, extraction of timber and rubber from forests.
4) Construction industry: The industry is engaged in the creation of infrastructure for the smooth development of the economy. It is concerned with the construction, erection or fabrication of products. These industries are engaged in the construction of buildings, roads, dams, bridges and canals.
5) Manufacturing industry: This industry is engaged in the conversion of raw material into semifinished or finished goods. This industry creates form utility in goods by making them suitable for human uses. E.g: Cement industry, Sugar industry, Cotton textile industry, Iron and steel industry, Fertiliser industry etc.
6) Service industry: In modern times, service sector plays an important role in the development of the nation and therefore it is named as service industry. These are engaged in the provision of essential services to the community. E.g: Banking, trans-port, insurance etc.
Question 2.
What is commerce? Describe its branches.
Answer:
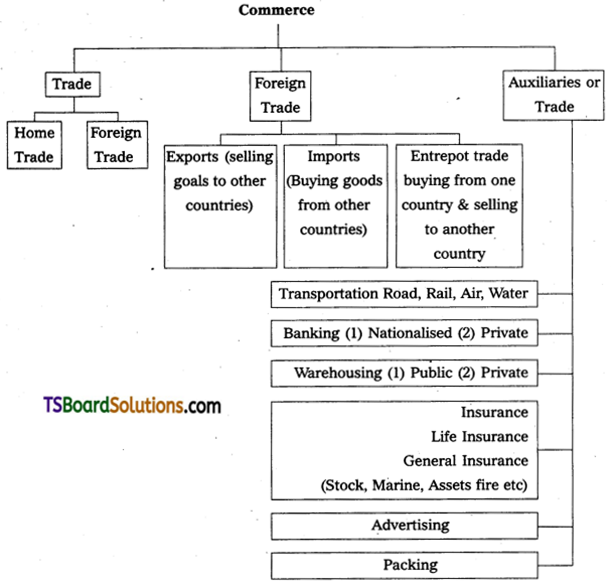
Commerce is concerned with exchange of goods. It includes all those activities which are related to transfer of goods from the places of production to the ultimate consumer. Commerce embraces all those processes which help to break the barriers between producers and consumers. It is the sum total of those processes which are engaged in the removal of hindrances of persons, place, time and exchange.
Branches of commerce:
The activities of commerce may be classified into following two broad categories.
- Trade
- Aids to trade
I) Trade: Trade is a branch of commerce. It connects with buying and selling of goods and services. An individual who does trade is called a trader. Trader transfers the goods from the producer to the consumer.
Trade may be classified into a) Home trade, b) Foreign trade. Home trade may again sub-divided into (i) Wholesale trade and (ii) Retail trade.
a) Home trade: Home trade is also known as ‘domestic trade’ or ‘Internal trade’ Home trade is carried on within the boundaries of a nation. Home trade again is of two types: wholesale trade and retail trade.
- Wholesale trade: It implies buying and selling of goods in large quantities. Traders who engage themselves in whole sale trade are called ‘wholesalers’. Wholesale serves as a connecting link between the producers and the retailers.
- Retail trade: It involves buying and selling of goods in small quantities. Traders engaged in retail trade are called ‘retailers’. They serve as a connecting link between wholesalers and consumers.
b) Foreign trade: It refers to buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries through international air ports and sea ports. Foreign trade is also known as ‘external trade’ or ‘International trade’.
- Export trade: It means the sale of goods to foreign countries. For example India exports tea to the U.K.
- Import trade: It refers to the purchase of goods from foreign countries. For instance India buys petrol from Iran.
- Entrepot trade: Importing (buying) goods from one country for the purpose of ex-porting (selling) them to another country is called entrepot trade. This type of trade is also known as re-export trade.
II) Aids to trade: Trade or exchange of goods involves several difficulties, which can be removed by auxiliaries are known as aids to trade. It refers to all those activities, which directly or indirectly facilitate smooth exchange of goods and services.
![]()
Aids to trade includes transport, Communication, Warehousing, Banking, Insurance, Advertising. These ensure smooth flow of goods from producers to the consumers. The various aids to trade in commerce are explained in below:
1) Transport: There will be a vast distance between centers of production and centres of consumption. This difficulty is removed by transport. Transport creates place utility. There are several kinds of transport such as air, water and land transport. The geo-graphical distance between producers and consumers is removed with the help of following means of transport.
2) Communication: Communication means transmitting or exchange of information froth one person to another. It can be oral or in writing. It is necessary to communicate information from one to another. Modern means of communication like telephone, email, video conference etc play an important role in establishing contact between businessmen, producers and consumers.
3) Warehousing: There is a time gap between production and consumption. It becomes necessary to make arrangements for storage or warehousing. The goods such as umbrellas and woolen clothes are produced throughout the year but are demanded only during particular seasons like rainy and winter season. Therefore goods need to be stored in warehouses till they are demanded. So, it creates time utility by supplying the goods at right time to consumer.
4) Insurance: Insurance reduces the problem of risks. Business is subject to risks and uncertainities. Risks may be due to fire, theft, accident or any other natural calamity. Insurance companies who act as risk bearer cover risks. Insurance tries to reduce risks by spreading them out over a larger number of people by encouraging them to take insurance policies.
5) Banking: Banking solves the problem of finance. Banking and financial institutions solves the problem of payment and facilitate exchange between buyer and seller. Banks provide such finance to them. Banks also advance loans in the form of overdraft, cash credit and discounting of bills of exchange.
6) Advertising: Advertising fills the knowledge gap. Exchange of goods and services is possible only if producers can bring the products to the consumers. Advertising and publicity are important medias of mass communication. Advertising helps the consumers to know about the various brands manufactured by several manufacturers. The medias used to advertise products are Radio, Newspapers, Magazines, TV, Internet etc.
Question 3.
Discuss the significance of commerce in the present scenario.
Answer:
Commerce can also be defined as The sum total of those processes. Which are engaged in the removal of hindrances of person, place and time in the exchange of commodities’.
Importance of commerce:
The importance of commerce is explained below:
1) Commerce tries to satisfy increasing human wants: Human wants and desires are never ending. Commerce has made distribution and movement of goods possible from one part of the world to the other. Today we can buy anything produced anywhere in the world. Hence commerce facilitates the people to satisfy their needs, desires and wants by distribution and exchange of the goods and services.
2) Commerce helps us to increase our standard of living: Standard of living refers to quality of life enjoyed by the members of a society. When a man consumes more products his standard of living improves. Commerce helps us to get what we want at the right time, right place and at the right price and thus helps in improving our standard of living.
3) Commerce links producers and consumers: Commerce makes a link between producers and consumers through retailers and wholesalers and also through the aids to trade. Thus it creates and facilitates the contact between the centres of production and consumption.
4) Commerce generates employment opportunities: The growth of commerce and trade cause the growth of agencies of trade such as banking, transport, warehousing, insurance, advertising etc. Thus, development of commerce generates more and more employment opportunities.
5) Commerce increases national income and wealth: When production increases, national income also increases. It also helps to earn foreign exchange by way of exports and duties levied on imports.
6) Commerce helps in expansion of aids-to-trade: With the growth in trade and commerce there is a growing need for expansion and modernization of aids to trade. Aids to trade such as banking communication, advertising and publicity, transport, insurance etc. are expanded and modernised for the smooth conduct of commerce.
7) Commerce encourages international trade: With the help of transport and communication development, countries can exchange their surplus. Commodities and earn foreign exchange. Thus, the commerce ensures faster economic growth of the country.
8) Commerce benefit underdeveloped countries: Underdeveloped countries can import skilled labour and technical knowhow from developed countries, while the advanced countries can import raw materials from underdeveloped countries. This helps in laying down the seeds of industrialisation in the underdeveloped countries.
9) Commerce helps during emergencies: During emergencies like floods, earthquakes and wars, commerce helps in reaching the essential requirements like food stuff, medicines and relief measures to the affected area.
![]()
Question 4.
Define trade and explain various types of aids to trade.
Answer:
Trade: Buying and selling of goods and services to earn profit is called trade. The person who undertakes this job is known as trader. It is a branch of commerce.
Aids to trade:
Trade or exchange / distribution of goods involves several difficulties, which can be removed by auxiliaries are known as aids to trade. It refers to all those activities which directly or indirectly facilitate smooth exchange of goods and services.
Aids to trade includes Transport, Communication, Warehousing, Banking, Insurance, Advertising. These ensure smooth flow of goods from producers to the consumers. The various aids to trade in commerce are explained in following points.
1) Transport: There will be a vast distance between centres of production and centres of consumption. This difficulty is removed by transport. Transport creates place utility. There are several kinds of transport such as air, water and land transport. The geo-graphical distance between producers and consumers is removed with the help of following means of transport, (i) Land (ii) Water (iii) Air.
2) Communication: Communication means transmitting or exchange of information from one person to another. It can be oral or in writing. It is necessary to communicate information from one to another. Modem means of communication like telephone, email, teleconference, video-conference etc. play an important role in establishing contact between businessmen, producers and consumers.
3) Warehousing: There is a time gap between production & consumption. It becomes necessary to make arrangements for storage or warehousing. The goods such as umbrellas and woolen clothes are produced throughout the year but are demanded only during particular seasons like rainy and winter season. Therefore goods need to be stored in warehouses till they are demanded. So it creates time utility by supplying the goods at right time to consumers.
4) Insurance: Insurance reduces the problems of risks. Business is subject to risks and uncertainities. Risks may be due to fire, theft, accident or any other natural calamity. Insurance companies who act as risk bearer cover risks. Insurance tries to reduce risks by spreading them out over a large number of people by encouraging them to take insurance policies.
5) Banking: Banking solves the problem of finance. Banking and financial institutions solves the problem of payment and facilitate exchange between buyer and seller. Banks provide such finance to them. Banks also advance loans in the form of overdraft, cash credit and discounting of bills of exchange.
6) Advertising: Exchange of goods and services is possible only if producers can bring the products to the consumers. Advertising and publicity are important medias of mass communication. Advertising helps the consumers to know about the various brands manufactured by several manufacturers. The medias used to advertise products are Radio, Newspaper, Magazines, TV; Internet etc.
Question 5.
Explain inter-relationship between industry, commerce and trade.
Answer:
Business is divided into two categories: Industry and commerce. Commerce is again sub-divided into trade and aids to trade practically all of them are closely related to each other. They are inseparable. All of them are parts of the whole business system. Industry and commerce are closely related to each other. Industry cannot exist without commerce and commerce cannot exist without industry because every producer has to find his market for his product to sell. But the producer has no direct connection with the buyer or consumers. Hence, industry needs commerce.
BUSINESS = INDUSTRY + COMMERCE
Commerce is concerned with the sale, transfer or exchange of goods and services. Hence commerce needs industry for the production of goods and services. Commerce makes the necessary arrangement for linking between producers and ultimate consumers. It includes all those activities that are involved in buying, selling, transporting, banking, warehousing of goods, and insurance of safeguarding the goods.
COMMERCE = TRADE + AIDS TO TRADE
Thus industry, commerce, and trade are closely related to one another and are inter-dependent as shown in the figure below. In conclusion, we can say that industry, trade and commerce are inter-related with each other. Industry is concered with production of goods and services and commerce arranges its sales; but the actual operation of sales is in the hands of trade. So they cannot work independently.
![]()
Question 6.
Describe the various Hindrances of Commerce.
Answer:
Commerce is concerned with exchange of goods. It includes all those activities which are related to transfer of goods from the place of production to the ultimate consumers. Whereas trade involves buying and selling of goods, commerce has a wider meaning. Commerce include trade and aids to trade. The aids to trade include transport, banking, insurance, warehousing, advertisement and salesmanship.
Hindrances of trade: In the course of exchange of goods various problems are encountered. The hindrances in the way of smooth trade may be place, person, finance, time, knowledge and risk.
1) Hindrances of place: Generally, all the goods are not consumed at the same place where are produced. The goods are to be taken from a place where there is less demand, to the place where there is more demand. The activity of movement of the goods is called transportation. Thus transport eliminates the hindrances of place.
2) Hindrances of persons: In the present day world the consumers are in millions and it is not possible for the producers to know the consumers who are in need of goods produced by them. A chain of middlemen like wholesalers, retailers, dealers etc. Purchase goods from the producers and take them to the customers. Thus, middlemen remove the hindrances of persons.
3) Hindrances of finance: There is always time lag between the production and sale of goods. It takes time to collect money and hence need finance for trade. Commerce makes exchange of goods and services possible by removing these hindrances through the agency of banks.
4) Hindrances of time: As the goods are produced in anticipation of demand, there is a need to store the until they are required for consumption. Warehousing eliminates the hindrances of time and provides time utility to goods.
5) Hindrances of knowledge: The consumers may not be aware of the availability of various goods in the market. The absence of information is another hindrance. This is eliminated through advertising. Advertisement is done through T.V., radio, news papers, magazines, wall posters, hoardings etc.
6) Hindrances of risk: There are risks involved in production, transporting goods from one place to another, warehousing. The businessmen would like to cover these risks. Insurance companies undertake to compensate the loss suffered due to such risks. So, insurances eliminates hindrances of risks.
Question 7.
Distinguish between trade, commerce and industry.
Answer:
Differences between trade, commerce and industry.
| Basis of Difference | Trade | Commerce | Industry |
| 1. Meaning | It is related to the purchase and sale of goods. | It is related to the activities which deals with taking of goods from producers to consumers. | All those activities which deal with conversion of raw material into finished goods. |
| 2. Capital | More capital is required than commerce. | It requires less capital. | Capital needs are high. |
| 3. Scope | It deals with purchase and sale of goods. | It includes trade and aids to trade. | Primary manufacturing, processing etc., industries are covered under industry. |
| 4. Risk | It involves greater risk. | The risk involved is comparatively less. | It involves greater risk compared to any other activity. |
| 5. Utility | Trade creates possession utility. | Commerce creates time and place utility. | Industry creates form utility. |
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Industry.
Answer:
Industry is concerned with the making or manufacturing of goods. It is that part of the production which is involved in changing the form of goods at any stage from raw material to the finished product. E.g.: Weaving woollen yam into cloth. Thus industry imparts form utility in goods.
Question 2.
What is Trade?
Answer:
Trade: Buying and selling of goods and services to earn profit is called trade. The person who undertakes this job is known as trader. It is a branch of commerce.
Trade is a branch of commerce. It connects with buying and selling of goods and services. An individual who does trade is called a trader. Trader transfers the goods from the producer to the consumer.
Trade is classified into two types: (I) Home trade (II) Foreign trade
I) Home trade: Home trade is also known as ‘domestic trade’ or ‘Internal trade’. Home trade is carried on within the boundaries of a nation.
Home trade is again divided into two types:
- Wholesale trade and
- Retail trade
(i) Wholesale trade: It implies buying and selling of goods in large quantities. Traders who engage themselves in wholesale trade are called ‘wholesalers’. Wholesale serves as a connecting link between the producers and the retailers.
(ii) Retail trade: It involves buying and selling of goods in small quantities. Traders en-gaged in retail trade are called ‘retailers’. They serve as a connecting link between wholesalers and consumers.
(II) Foreign trade: It refers to buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries through international air ports and sea ports. Foreign trade is also known as ‘external trade’ or ‘international trade’. Foreign trade is again may be classified into three categories as mentioned below.
- Export trade: It means the sale of goods to foreign countries. For example India exports tea to the united kingdom.
- Import trade: It refers to the purchase of goods from foreign countries. For instance India buys petrol from Iran.
- Entrepot trade: Importing (buying) goods from one country for the purpose of ex-porting (selling) them to another country is called entrepot trade. This type of trade is also known as ‘re-export’ trade.
Question 3.
State the types of foreign trade.
Answer:
When trade takes place between two countries it is called foreign trade or external trade or international trade. Two countries are involved in foreign trade. External trade generally requires permission from the respective countries. The hindrances of place, time, risk, exchange are overcome with the help of various agencies. Foreign trade may be classified into export trade, import trade and entrepot trade.
1) Export trade: This trade refers to sale of goods to foreign countries.
E.g.: India exports tea to U.K.
2) Import trade: The purchase of goods from other countries is known as import trade.
Ex: India buys petrol from Iran.
3) Entrepot trade: When goods are imported (purchased) from one country with a view to exporting (selling) them to other country, it is called entrepot trade or re-export trade.
Ex: India imported petrol from Iran and export the same to Nepal.
Question 4.
Explain the classification of industries.
Answer:
Classification or types of industries: The industries may be classified as follows.
1) Primary industry: Primary industry is concerned with production of goods with the help of nature. It is nature-oriented industry, which requires very little human effort.
E.g: Agriculture, Farming, Fishing, Horticulture etc.
2) Genetic industry: Genetic industry is related to the reproducing and multiplying of certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profits from their sale.
E.g: Nurseries, cattle breeding poultry, fish hatcheries etc.
3) Extractive industry: It is engaged in raising some form of wealth from the soil, cli-mate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive industries comes in raw farm and they are used by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products.
E.g: Mining, coal, mineral, iron ore, oil industry, extraction of timber and rubber from forests.
4) Construction industry: The industry is engaged in the creation of infrastructure for the smooth development of the economy. It is concerned with the construction, erection or fabrication of products. These industries are engaged in the construction of buildings, roads, dams, bridges and canals.
![]()
5) Manufacturing industry: This industry is engaged in the conversion of raw material into semifinished or finished goods. This industry creates form utility in goods by making them suitable for human uses.
E.g: Cement industry, Sugar industry, Cotton textile industry, Iron and Steel industry, Fertiliser industry etc.
6) Service industry: In modern times, service sector plays an important role in the development of the nation and therefore it is named as service industry. These are engaged in the provision of essential services to the community.
E.g: Banking, Trans-port, Insurance etc.
Question 5.
Define ‘Entrepot trade’ with example.
Answer:
When goods are imported from one country and the same are exported to another country, such trade is called entrepot trade.
E.g.:
- India importing wheat from U.S. and exporting the same to Srilanka.
- India imports petrol from Iran and export the same to Nepal.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Industry.
Answer:
Industry is concerned with the making or manufacturing of goods. It is that part of the production which is involved in changing the form of goods from raw material to the finished product.
E.g.: Weaving woollen yam into cloth. Thus industry creates form utility in goods.
Question 2.
Commerce.
Answer:
- Commerce is concerned with exchange of goods. It includes all those activities which are related to transfer of goods from the places of production to the ultimate consumer. Commerce embraces all those processes which help to break the barriers between producers and consumers.
- It is the sum total of those processes which are engaged in the removal of hindrances of persons, place, time and exchange.
Question 3.
Trade.
Answer:
- All the activities engaged in buying and selling of goods and services a re called trade.
- Therefore trade includes sale, transfer or exchange of goods and services with the intention of making profit. The object of trade is to make goods available to those who need them and willing to pay for them.
- Trade is the final stage of business activities and involves transfer of ownership.
Question 4.
Home Trade.
Answer:
- The trade is carried on within the boundaries of the nation is called Home Trade. Home trade is also called as internal trade or domestic trade.
- Home trade refers to a trade where buying and selling of goods takes place between the persons who belong to the same country. So, home For movement of goods internal transport system is used.
![]()
Question 5.
Entrepot trade.
Answer:
- When goods are imported from one country and the same are exported to another country, such trade is called entrepot trade.
- E.g.: India importing wheat from U.S. and exporting the same to Srilanka.
Question 6.
Transportation.
Answer:
There is a vast distance between centres of production and centres of consumption. Goods are to be moved from the places of production to the place where they are demanded.
- The activity which is concerned with movement of goods is called transportation. Trans-port create place utility.
- There are several kinds of transport such as air, water and land transport. The geo-graphical distance between producers and consumers is removed with the help of transport.
Question 7.
Warehousing.
Answer:
- There is time gap between production and consumption. Hence, it became necessary to make arrangements for storage or warehousing.
- It is one of the aid to trade, which facilitates to store the goods until they get demand or consumed.
- Some goods are to be stored in warehouses till they are demanded. Warehousing creates time utility.
Question 8.
Genetic Industries.
Answer:
- Genetic industry is related to the reproducing and multiplying certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profit from their sale.
- E.g.: Nurseries, cattle breeding, poultry farm, fish hatcheries etc.
Question 9.
Extractive industries.
Answer:
- These industries are engaged in raising some form of wealth from the soil, climate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive industry comes in raw form and they are used by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products.
- E.g.: Mining, coal, mineral, iron ore oil, extraction of timber and rubber from forests.
Question 10.
Banking.
Answer:
- Banking solve the problem of finance.
- Producers and traders require money for carrying on production and trade. Banks are the institutions which supply funds for industries and trade.
- They pool savings from the public and make them available to industry. So, banking is an important function of commerce.