We are offering TS 10th Class Maths Notes Chapter 10 Mensuration to learn maths more effectively.
TS 10th Class Maths Notes Chapter 10 Mensuration
Cuboid :
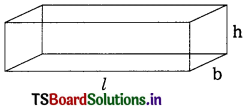
l, b and h denote respectively the length, breadth and height of a cuboid then
- Lateral surface area = 2h(l + b)
- Total surface area = 2(lb + bh + hl)
- Volume = lbh
- Diagonal of the cuboid = \(\sqrt{l^2+b^2+h^2}\)
Cube :
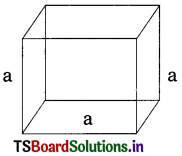
If the length of each edge of cube is “a” units then
- Lateral surface area = 4a2
- Total surface area = 6a2
- Volume = a3
- Diagonal of the cube = √3 × a = a√3
Right Prism :

- Lateral surface area = Perimeter of base × height
- Total Surface area = Lateral Surface area + 2(Area of end Surface)
- Volume = Area of base × height
Right Circular Cylinder:

If r is the radius of the base and ‘h’ is the height, then
- Lateral surface area = 2πrh
- Total surface area = 2πr(h + r)
- Volume = πr2h
![]()
Right Pyramid :
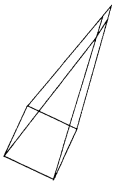
- Lateral surface area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × perimeter of base × slant height
- Total Surface area = Lateral surface area + area of base
- Volume = \(\frac{1}{3}\) × area of base × height
Right Circular Cone :

If ‘r’ is the radius of the base, ‘h’ is the height and is slant height, then
- Lateral surface area = πrl.
- Total Surface area = πr(l + r)
- Volume = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr2h
- l2 = h2 + r2
Sphere :
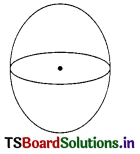
If ‘r’ is radius of sphere, then
- Lateral surface area = 4πr2
- Total surface area = 4πr2
- Volume = \(\frac{4}{3}\) πr3
Hemisphere :
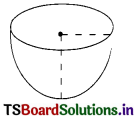
If Y is the radius of hemi-sphere, then
- Lateral surface area = 2πr2
- Total surface area = 3πr2
- Volume = \(\frac{4}{3}\)πr3
Right Circular Hollow Cylinder:
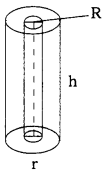
- Area of each end = π(R2 – r2)
- Curved surface area of hollow Cylinder = External area + Internal area
= 2πrh + 2πRh = 2πh(R + r) - Total surface area = 2πRh + 2πrh + 2(πR2 – πr2)
= 2πh(R + r) + 2π(R + r)(R – r)
= 2π(R + r) (R + h – r) - Volume of the material = External volume – Internal volume
= πR2h – πr2h = 7th(R2 – r2)
![]()
Spherical Shell:

If R and r are the outer and inner radii of a spherical shell, then
- Outer surface area = 4πR2
- Volume of material = \(\frac{4}{3}\) π
→ The volume of the solid-formed by joining two basic solids is the sum of the volumes of the constituents.
→ In calculating the S.A of a combination of solids, we cannot add the surface area of the two constituents, because some part of the surface area disappears in the process of joining them.
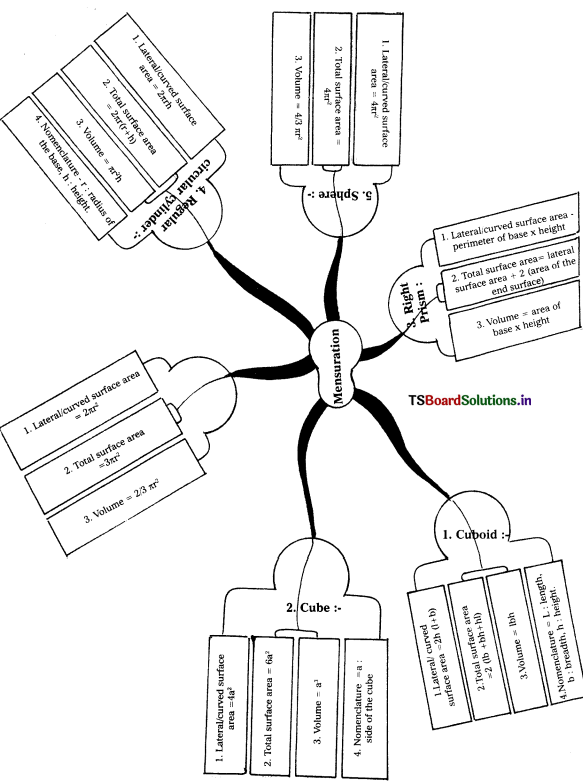
Flow Chat:
Brahmagupta (598 – 668):
- Brahmagupta was born in the state of Rajasthan.
- He worked in the great astronomical centre of ancient India – Ujjain.
- He made significant contributions to Trigonometry.